GERD
How to submit an article:
- Registered users can submit any published journal article that has a unique DOI (Digital Object Identifier) name or link to Research Hub.
- For example, you can paste the full DOI link:
https://doi.org/10.1109/5.771073or just the DOI name:10.1109/5.771073into the field above and click submit. - The person who is first to submit a valid article to Research Hub will forever be credited for it, and every article submission earns you +6 Research Points.
GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) is a chronic condition where stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing symptoms such as heartburn and regurgitation.
Also known as: Acid Reflux, Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, Heartburn
Published research studies are articles that present the findings of original research that has undergone a peer-review process and has been made publicly available in scholarly journals, books or other media.

Effectiveness of Nutritional Ingredients on Upper Gastrointestinal Conditions and Symptoms: A Narrative Review
2022 Feb 05 Nutrients Schulz RM, Ahuja NK, Slavin JL
Review Article Melatonin Ginger Peppermint Caraway Alginate GERDGinger, peppermint and caraway oil combination showed strong effectiveness in managing upper gastrointestinal complaints, with melatonin and marine alginate demonstrating moderate evidence.

Magnesium alginate versus proton pump inhibitors for the treatment of laryngopharyngeal reflux: a non-inferiority randomized controlled trial
2022 Jan 15 European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology Pizzorni N, Ambrogi F, Eplite A, Rama S, Robotti C, Lechien J, et al.
Randomised Controlled Trial Proton Pump Inhibitor Alginate Magnesium GERDAlginate, as a treatment option for laryngopharyngeal reflux, is equally effective as proton pump inhibitors and may serve as a potential alternative treatment.

Effects and mechanisms of acupuncture and electroacupuncture for functional dyspepsia: A systematic review
2020 May 21 World Journal of Gastroenterology Guo Y, Wei W, Chen JD
Indigestion GERDPositive effects of acupuncture and electroacupuncture were observed in regulating gastric motility, gastric accommodation, mental status, gastrointestinal hormones, and central and autonomic functions while improving dyspeptic symptoms and quality of life.

Efficacy of Chinese Herbal Formula Sini Zuojin Decoction in Treating Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Clinical Evidence and Potential Mechanisms
2020 Feb 27 Frontiers in Pharmacology Li Shaowei, Huang Mengfen, Wu Guojing, Huang Weihan, Huang Zhanhui, Yang Xiaoqian, et al.
Chinese herbal formula Sini Zuojin Decoction (SNZJD) might be useful in the treatment of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD).
Systematic Review GERD Si Ni Zuo Jin DecoctionAlginates: From the ocean to gastroesophageal reflux disease treatment
2019 Sep 16 The Turkish Journal of Gastroenterology , Bor S, Kalkan IH, , Celebi A, , Dincer D, , Akyuz F, , Dettmar P, , Ozen H,
Alginate has a unique mode of action in producing raft formation, making it a fast and effective option for mild GERD symptoms. It can also be used in combination with PPIs for more severe cases, especially in regurgitation-dominant GERD and atypical symptoms. Additionally, alginates are proven to be safe and efficient in treating GERD in children, pregnancy, and lactation.
Review Article Alginate GERDResearch insights are moderated by the Research Hub team and offer an at-a-glance overview of interesting research findings.

2022 Nutrients
Ginger, peppermint and caraway oil combination showed strong effectiveness in managing upper gastrointestinal complaints, with melatonin and marine alginate demonstrating moderate evidence.
Review Article Alginate Caraway Ginger Melatonin Peppermint
Effectiveness of Nutritional Ingredients on Upper Gastrointestinal Conditions and Symptoms: A Narrative Review
Schulz RM, Ahuja NK, Slavin JL

2022 European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology
Alginate, as a treatment option for laryngopharyngeal reflux, is equally effective as proton pump inhibitors and may serve as a potential alternative treatment.
Randomised Controlled Trial Alginate Magnesium Proton Pump Inhibitor
Magnesium alginate versus proton pump inhibitors for the treatment of laryngopharyngeal reflux: a non-inferiority randomized controlled trial
Pizzorni N, Ambrogi F, Eplite A, Rama S, Robotti C, Lechien J, et al.

2020 World Journal of Gastroenterology
Positive effects of acupuncture and electroacupuncture were observed in regulating gastric motility, gastric accommodation, mental status, gastrointestinal hormones, and central and autonomic functions while improving dyspeptic symptoms and quality of life.
Indigestion
Effects and mechanisms of acupuncture and electroacupuncture for functional dyspepsia: A systematic review
Guo Y, Wei W, Chen JD

2017 Acupuncture in Medicine
Patients receiving acupuncture combined with western medicine had a superior global symptom improvement compared with those receiving western medicine alone for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease.
Systematic Review
Acupuncture for the treatment of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Zhu, J., Guo, Y., Liu, S., et al.
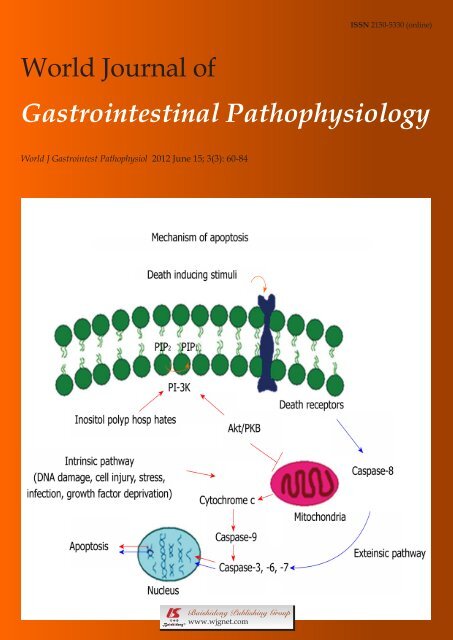
2016 World Journal of Gastrointestinal Pathophysiology
Hydrogen carbonate-rich mineral water significantly reduces heartburn frequency and severity, improving quality of life with excellent tolerability.
Clinical Study Mineral Water
Efficacy and tolerability of hydrogen carbonate-rich water for heartburn
Beer AM
Review Articles
Review articles summarise and critically evaluate the current state of research on a specific topic or field by synthesising multiple primary research studies.

Effectiveness of Nutritional Ingredients on Upper Gastrointestinal Conditions and Symptoms: A Narrative Review
2022 Feb 05 Nutrients Schulz RM, Ahuja NK, Slavin JL
Review Article Melatonin Ginger Peppermint Caraway Alginate GERDGinger, peppermint and caraway oil combination showed strong effectiveness in managing upper gastrointestinal complaints, with melatonin and marine alginate demonstrating moderate evidence.

Efficacy of Chinese Herbal Formula Sini Zuojin Decoction in Treating Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Clinical Evidence and Potential Mechanisms
2020 Feb 27 Frontiers in Pharmacology Li Shaowei, Huang Mengfen, Wu Guojing, Huang Weihan, Huang Zhanhui, Yang Xiaoqian, et al.
Chinese herbal formula Sini Zuojin Decoction (SNZJD) might be useful in the treatment of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD).
Systematic Review GERD Si Ni Zuo Jin DecoctionAlginates: From the ocean to gastroesophageal reflux disease treatment
2019 Sep 16 The Turkish Journal of Gastroenterology , Bor S, Kalkan IH, , Celebi A, , Dincer D, , Akyuz F, , Dettmar P, , Ozen H,
Alginate has a unique mode of action in producing raft formation, making it a fast and effective option for mild GERD symptoms. It can also be used in combination with PPIs for more severe cases, especially in regurgitation-dominant GERD and atypical symptoms. Additionally, alginates are proven to be safe and efficient in treating GERD in children, pregnancy, and lactation.
Review Article Alginate GERD
Acupuncture for the treatment of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
2017 Oct Acupuncture in Medicine Zhu, J., Guo, Y., Liu, S., et al.
Systematic Review Meta-Analysis GERDPatients receiving acupuncture combined with western medicine had a superior global symptom improvement compared with those receiving western medicine alone for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease.

Efficacy and Safety of Modified Banxia Xiexin Decoction (Pinellia Decoction for Draining the Heart) for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
2017 Feb 19 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Yunkai Dai, Yunzhan Zhang, Danyan Li, Jintong Ye, Weijing Chen, Ling Hu
Evidence from this systematic review shows that modified Banxia Xiexin decoction (MBXD) has a positive efficacy in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Systematic Review Meta-AnalysisClinical Trials
Clinical trials are research studies that involve people and are conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of new treatments or interventions, such as drugs, medical devices, or behavioural therapies.

Magnesium alginate versus proton pump inhibitors for the treatment of laryngopharyngeal reflux: a non-inferiority randomized controlled trial
2022 Jan 15 European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology Pizzorni N, Ambrogi F, Eplite A, Rama S, Robotti C, Lechien J, et al.
Randomised Controlled Trial Proton Pump Inhibitor Alginate Magnesium GERDAlginate, as a treatment option for laryngopharyngeal reflux, is equally effective as proton pump inhibitors and may serve as a potential alternative treatment.

Consistent Efficacy of Wendan Decoction for the Treatment of Digestive Reflux Disorders
2015 Jan The American Journal of Chinese Medicine Ling W, Huang Y, Xu JH, Li Y, Huang YM, Ling HB, et al.
The consistent therapeutic efficacy of the single TCM formula on GERD and BRD indirectly indicates reflux as a common pathogenesis in reflux-associated GI disorders.
Randomised Controlled Trial Digestive Reflux Disorders Wen Dan TangStudy Protocols
Published study protocols are detailed plans that outline the objectives, methodology, statistical analyses, and organisation of a research study that have been made publicly available for others to review and use as a reference.
Presentation Slides

Review Article
Ginger, peppermint and caraway oil combination showed strong effectiveness in managing upper gastrointestinal complaints, with melatonin and marine alginate demonstrating moderate evidence.
Schulz RM, Ahuja NK, Slavin JL

Randomised Controlled Trial
Alginate, as a treatment option for laryngopharyngeal reflux, is equally effective as proton pump inhibitors and may serve as a potential alternative treatment.
Pizzorni N, Ambrogi F, Eplite A, Rama S, Robotti C, Lechien J, Schindler A

Positive effects of acupuncture and electroacupuncture were observed in regulating gastric motility, gastric accommodation, mental status, gastrointestinal hormones, and central and autonomic functions while improving dyspeptic symptoms and quality of life.
Guo Y, Wei W, Chen JD

Systematic Review
Patients receiving acupuncture combined with western medicine had a superior global symptom improvement compared with those receiving western medicine alone for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease.
Zhu, J., Guo, Y., Liu, S., Su, X., Li, Y., Yang, Y., Hou, L., Wang, G., Zhang, J., Chen, J. J. D., Wang, Q., Wei, R., & Wei, W.

Clinical Study
Hydrogen carbonate-rich mineral water significantly reduces heartburn frequency and severity, improving quality of life with excellent tolerability.
Beer AM
Clinical Study
Drinking hydrogen carbonate-rich mineral water significantly reduces heartburn episodes and improves quality of life in individuals with dyspeptic symptoms.
Pohl U, Auinger A, Bothe G, Uebelhack R

Cohort Study
High intake of magnesium from foods is linked to a significant decrease in the odds of developing reflux oesophagitis and Barrett's oesophagus.
Dai Q, Cantwell MM, Murray LJ, Zheng W, Anderson LA, Coleman HG
Executive Summary
Write an executive summary in the form of a blog article on the topic of "Research into Chinese medicine treatment for GERD" summarising the research below and using language that can be easily understood by patients and avoiding medical jargon using a professional and caring tone of voice.
Write an executive summary in the form of a blog article on the topic of "Researched Chinese medicine treatments for GERD" summarising the research below in an objective and easy to understand way, and using language that can be easily understood by patients. Group the article into Chinese medicine treatments first, followed by nutrition and other treatments. Avoid using medical jargon and use a professional and caring tone of voice.
Write me a concise but easy to understand executive summary on the topic of "Chinese medicine treatments for GERD" based on the following research that I will give you. Your summary should be 2 paragraphs long in Australian English spelling and include references to the studies.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Nutrients found that Ginger, peppermint and caraway oil combination showed strong effectiveness in managing upper gastrointestinal complaints, with melatonin and marine alginate demonstrating moderate evidence. The methodology consisted of a literature review of the scientific studies pertaining to nutritional ingredients for upper gastrointestinal relief. The selection was based on recurring mentions within the literature and frequent appearance in consumer products. A predefined search for specific nutritional ingredients and terms related to upper GI health was conducted in five databases - Embase, Medline, Derwent drug file, ToXfile, and PubMed. A manual search was also undertaken for each ingredient to ensure comprehensive review. The studies that gained inclusion encompassed 16 human clinical trials assessing nine different ingredients. The products investigated were divided into categories, including botanicals - with sub-categories of fiber and combinations, and non-botanical extracts. Several products demonstrated good potential, others showed promising but moderate results, while some had limited support from the scientific research.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology found that Alginate, as a treatment option for laryngopharyngeal reflux, is equally effective as proton pump inhibitors and may serve as a potential alternative treatment. Researchers employed a non-inferiority randomized controlled trial with fifty participants, all of whom exhibited laryngopharyngeal symptoms. They were divided into two treatment groups; one group received the alginate suspension Gastrotuss in three daily doses, while the other was administered Omeprazole once daily. The Reflux Symptom Index and Reflux Finding Score were used to measure the severity of symptoms both before the treatment and after the two-month treatment period. It was found that both groups had similar Reflux Symptom Index and Reflux Finding Score values initially. After the two-month treatment, both groups demonstrated significant decrease in these indices, suggesting that the symptoms and signs of laryngopharyngeal reflux were significantly reduced, regardless of the treatment given. The difference between the changes in both Reflux Symptom Index and Reflux Finding Score from the two groups was found to be insignificant, thereby indicating that the effectiveness of Alginate is non-inferior to Proton Pump Inhibitors.
A published in 2020 in the journal World Journal of Gastroenterology found that Positive effects of acupuncture and electroacupuncture were observed in regulating gastric motility, gastric accommodation, mental status, gastrointestinal hormones, and central and autonomic functions while improving dyspeptic symptoms and quality of life. In this systematic review, we pooled randomized controlled trials with mechanistic investigations of acupuncture or electroacupuncture in improving dyspeptic symptoms, and illustrated the existing results that may provide potential explanations for the therapeutic effects. The findings of included studies in this review suggest that acupuncture and electroacupuncture can improve gastric motility and accommodation, regulate gastrointestinal hormones and mental status, and alter certain central and autonomic functions in patients with functional dyspepsia. However, due to limitations in the included articles, high-quality studies with well-planned designs and multiregional investigations are necessary to provide more convincing and credible evidence.
A Systematic Review published in 2017 in the journal Acupuncture in Medicine found that Patients receiving acupuncture combined with western medicine had a superior global symptom improvement compared with those receiving western medicine alone for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. A total of 12 trials involving 1235 patients were included. Meta-analyses demonstrated that patients receiving MA/EA combined with WM had a superior global symptom improvement compared with those receiving WM alone with no significant heterogeneity. Recurrence rates of those receiving MA/EA alone were lower than those receiving WM with low heterogeneity, while global symptom improvement (six studies) and symptom scores (three studies) were similar. Descriptive analyses suggested that acupuncture also improves quality of life in patients with GORD.
A Clinical Study published in 2016 in the journal World Journal of Gastrointestinal Pathophysiology found that Hydrogen carbonate-rich mineral water significantly reduces heartburn frequency and severity, improving quality of life with excellent tolerability. This open, single-center, single-arm clinical pilot study involved 50 patients aged 18-64, suffering from heartburn at least twice weekly for over three months. Excluding those with severe diseases or on heartburn medication, participants drank 1.5 liters of hydrogen carbonate-rich mineral water daily for six weeks, with 300 ml consumed at each meal. The study included five visits for monitoring. Efficacy was assessed through patient self-assessments in a heartburn diary, symptom-specific questionnaires (Reflux Disease Questionnaire, Quality of Life in Reflux and Dyspepsia, Gastrointestinal Quality of Life Index), and overall health-related quality of life using the SF-12. Efficacy and safety were evaluated using the Wilcoxon test, χ2 test, and U-test, considering changes in symptoms and vital signs. The study reported significant reductions in heartburn occurrences at week 6 in both the intention-to-treat and per-protocol populations. The average weekly heartburn episodes decreased by 5.1, and the duration of symptoms reduced by 19 minutes. Symptom frequency decreased in 89.6% of patients, and symptom duration in 79.2%. There were improvements in all dimensions of the RDQ and disease-specific quality of life. Both patients and investigators rated the water’s efficacy positively, with no serious adverse events reported. Additionally, a slight but significant decrease in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure was observed. The study concluded that hydrogen carbonate-rich mineral water is effective and well-tolerated in alleviating heartburn, enhancing quality of life.
A Clinical Study published in 2016 in the journal Open Journal of Gastroenterology found that Drinking hydrogen carbonate-rich mineral water significantly reduces heartburn episodes and improves quality of life in individuals with dyspeptic symptoms. This one-arm pilot study involved 56 men and women experiencing frequent heartburn. Participants were instructed to drink 1.5 liters of mineral water high in hydrogen carbonate daily for six weeks. They kept a daily diary to record the number and duration of heartburn episodes. Additionally, several questionnaires were used to assess the effects of the water on their condition and quality of life. These included the Reflux Disease Questionnaire (RDQ), Quality of Life in Reflux and Dyspepsia questionnaire (QOLRAD), Gastrointestinal Quality of Life Index (GILQI), and the Short Form Health Survey (SF-12). The study analyzed changes in symptoms and quality of life before and after the treatment using the Wilcoxon test. The study reported a significant decrease in the number of weekly heartburn episodes and the duration of each episode after the six-week intervention. Participants also experienced a notable reduction in the severity of heartburn, regurgitation, and dyspeptic complaints. There was a significant improvement in disease-specific quality of life as measured by GILQI and QOLRAD, and in general health-related quality of life as assessed by SF-12. These findings suggest that drinking hydrogen carbonate-rich mineral water can be an effective alternative treatment for dyspeptic symptoms and heartburn, leading to an enhanced quality of life.
A Cohort Study published in 2015 in the journal British Journal of Nutrition found that High intake of magnesium from foods is linked to a significant decrease in the odds of developing reflux oesophagitis and Barrett's oesophagus. The study involved participants who were cases of oesophageal adenocarcinoma, Barrett's oesophagus, reflux oesophagitis and population-based controls, all gathered from throughout Ireland between 2002 and 2005. Each participant completed a 101-item Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ). The association between dietary intakes of magnesium, calcium and the ratio of calcium to magnesium on the risk of oesophageal adenocarcinoma, Barrett's oesophagus and reflux oesophagitis was analysed using unconditional logistic regression analysis, adjusting for potential confounders. In terms of results, participants consuming the highest amounts of magnesium from food considerably reduced their odds of reflux oesophagitis and Barrett's oesophagus when compared to those consuming the smallest amounts. This protective effect of magnesium was even more noticeable when the intake of calcium to magnesium was low. However, no significant associations were found between magnesium intake and the risk of oesophageal adenocarcinoma.
Moderation Tools
Topic
Sign In
Users not signed in are limited to viewing the 5 most recent items of content.