Prostatitis
How to submit an article:
- Registered users can submit any published journal article that has a unique DOI (Digital Object Identifier) name or link to Research Hub.
- For example, you can paste the full DOI link:
https://doi.org/10.1109/5.771073or just the DOI name:10.1109/5.771073into the field above and click submit. - The person who is first to submit a valid article to Research Hub will forever be credited for it, and every article submission earns you +6 Research Points.
Also known as: Chronic Prostatitis
Related Topics
Published research studies are articles that present the findings of original research that has undergone a peer-review process and has been made publicly available in scholarly journals, books or other media.

Effectiveness and safety of acupuncture combined with traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of chronic prostatitis
2021 Dec 10 Medicine Li C, Xu L, Lin X, Li Q, Ye P, Wu L, et al.
Acupuncture combined with TCM is safe and effective for alleviating chronic prostatitis (CP). It can be used as an effective treatment for chronic prostatitis in the clinic.
Systematic Review Meta-Analysis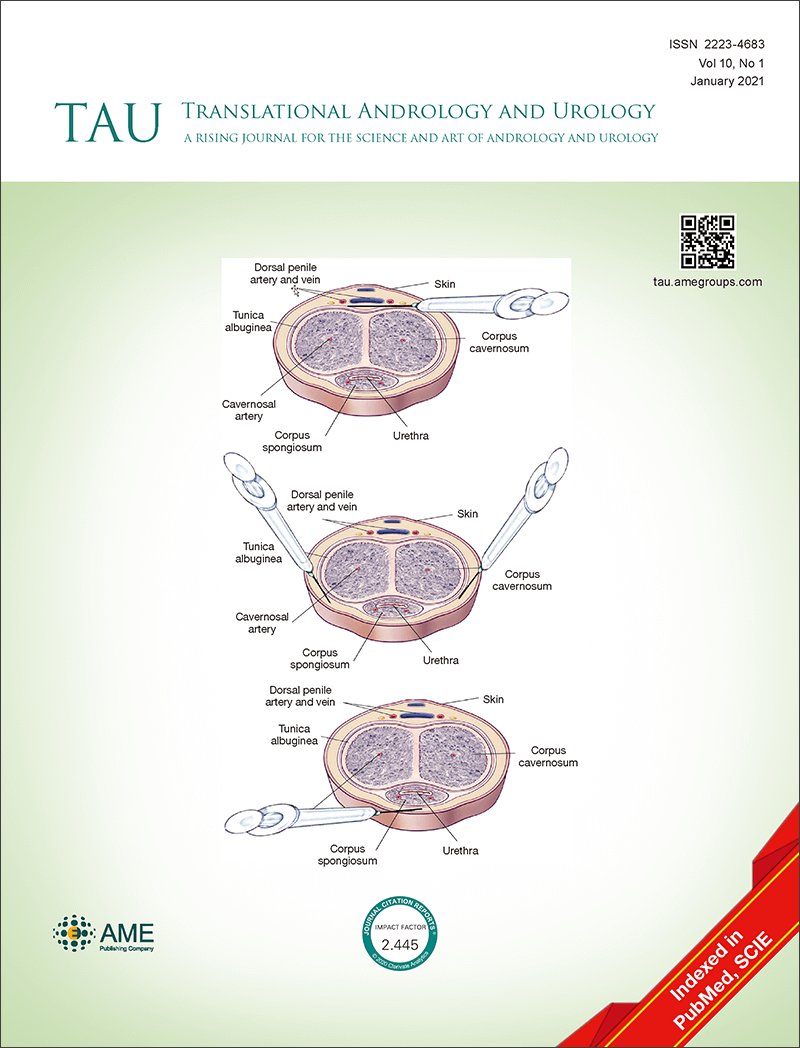
Optimal acupoint and session of acupuncture for patients with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a meta-analysis
2021 Jan Translational Andrology and Urology Zhang W, Fang Y, Shi M, Zhang M, Chen Y, Zhou T
Acupuncture has promising efficacy for patients with CP/CPPS, especially category IIIB, in aspects of relieving pain and urinary symptoms and improving the QOL. Acupuncture may serve as a standard treatment option when available, and a tailored comprehensive treatment strategy for CP/CPPS is the future trend.
Meta-Analysis
Therapeutic efficacy of orally administered pollen for nonallergic diseases: An umbrella review
2019 Aug 21 Phytotherapy Research Antonelli M, Donelli D, Firenzuoli F
The study concludes that flower pollen extracts may be useful as a complementary remedy for the management of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), chronic prostatitis (CP), and vasomotor symptoms.
Review Article
The effect of sensation of transmission along meridian acupuncture for chronic nonbacterial prostatitis
2019 Jun 11 World Journal of Acupuncture-Moxibustion MING, FU, S.-ren, HOU, Y.-lin, & CHEN, et al.
Both the method of transmission sensation along meridian and the method of non-transmission sensation along meridian can effectively relieve the clinical symptoms and anxiety symptoms of patients with chronic nonbacterial prostatitis, improve the quality of life, and the method of transmission sensation along meridian had a more advantageous effect.
Randomised Controlled Trial Bladder Conditions
Acupuncture for Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome: A Randomized, Sham Acupuncture Controlled Trial
2018 Oct Journal of Urology Qin Z, Zang Z, Zhou K, Wu J, Zhou J, Kwong JSW, et al.
Acupuncture demonstrated clinical and long-lasting benefits compared with sham acupuncture for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome, as evidenced by significant reductions in the NIH-CPSI total score at weeks 8, 20, and 32, with improvements in various secondary outcomes. Further randomized controlled trials with larger sample sizes are recommended for future validation.
Randomised Controlled Trial AcupunctureResearch insights are moderated by the Research Hub team and offer an at-a-glance overview of interesting research findings.

2016 Scientific Reports
Acupuncture may be recommended for the treatment of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome with relatively rare incidence of adverse events.
Systematic Review
Network Meta-Analysis of the Efficacy of Acupuncture, Alpha-blockers and Antibiotics on Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome
Qin, Z., Wu, J., Tian, J. et al.

2016 Medicine
Current evidence supports acupuncture as an effective treatment for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome-induced symptoms, particularly in relieving pain.
Systematic Review Bladder Conditions
Systematic Review of Acupuncture for Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome
Qin Z, Wu J, Zhou J, Liu Z.
2016 Neurourology and Urodynamics
Acupuncture has promising efficacy for patients with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
Systematic Review Pelvic Pain
The efficacy of acupuncture in managing patients with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: A systemic review and meta-analysis
Chang SC, Hsu CH, Hsu CK, Yang SSD, Chang SJ

2013 Asian Journal of Andrology
Chinese herbal medicine appears to be more effective than Western medication in improving quality of life and reducing prostate volume in benign prostatic hyperplasia patients.
Systematic Review
Efficacy and safety of Chinese herbal medicine for benign prostatic hyperplasia: systematic review of randomized controlled trials
Ma CH, Lin WL, Lui SL, Cai XY, Wong VT, Ziea E, et al.
Review Articles
Review articles summarise and critically evaluate the current state of research on a specific topic or field by synthesising multiple primary research studies.

Effectiveness and safety of acupuncture combined with traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of chronic prostatitis
2021 Dec 10 Medicine Li C, Xu L, Lin X, Li Q, Ye P, Wu L, et al.
Acupuncture combined with TCM is safe and effective for alleviating chronic prostatitis (CP). It can be used as an effective treatment for chronic prostatitis in the clinic.
Systematic Review Meta-Analysis
Therapeutic efficacy of orally administered pollen for nonallergic diseases: An umbrella review
2019 Aug 21 Phytotherapy Research Antonelli M, Donelli D, Firenzuoli F
The study concludes that flower pollen extracts may be useful as a complementary remedy for the management of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), chronic prostatitis (CP), and vasomotor symptoms.
Review Article
Network Meta-Analysis of the Efficacy of Acupuncture, Alpha-blockers and Antibiotics on Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome
2016 Oct 19 Scientific Reports Qin, Z., Wu, J., Tian, J. et al.
Systematic Review Meta-AnalysisAcupuncture may be recommended for the treatment of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome with relatively rare incidence of adverse events.

Systematic Review of Acupuncture for Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome
2016 Mar Medicine Qin Z, Wu J, Zhou J, Liu Z.
Systematic Review Meta-Analysis Bladder ConditionsCurrent evidence supports acupuncture as an effective treatment for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome-induced symptoms, particularly in relieving pain.

The efficacy of acupuncture in managing patients with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: A systemic review and meta-analysis
2016 Jan 06 Neurourology and Urodynamics Chang SC, Hsu CH, Hsu CK, Yang SSD, Chang SJ
Systematic Review Meta-Analysis Pelvic PainAcupuncture has promising efficacy for patients with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are research studies that involve people and are conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of new treatments or interventions, such as drugs, medical devices, or behavioural therapies.

The effect of sensation of transmission along meridian acupuncture for chronic nonbacterial prostatitis
2019 Jun 11 World Journal of Acupuncture-Moxibustion MING, FU, S.-ren, HOU, Y.-lin, & CHEN, et al.
Both the method of transmission sensation along meridian and the method of non-transmission sensation along meridian can effectively relieve the clinical symptoms and anxiety symptoms of patients with chronic nonbacterial prostatitis, improve the quality of life, and the method of transmission sensation along meridian had a more advantageous effect.
Randomised Controlled Trial Bladder Conditions
Acupuncture for Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome: A Randomized, Sham Acupuncture Controlled Trial
2018 Oct Journal of Urology Qin Z, Zang Z, Zhou K, Wu J, Zhou J, Kwong JSW, et al.
Acupuncture demonstrated clinical and long-lasting benefits compared with sham acupuncture for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome, as evidenced by significant reductions in the NIH-CPSI total score at weeks 8, 20, and 32, with improvements in various secondary outcomes. Further randomized controlled trials with larger sample sizes are recommended for future validation.
Randomised Controlled Trial AcupunctureStudy Protocols
Published study protocols are detailed plans that outline the objectives, methodology, statistical analyses, and organisation of a research study that have been made publicly available for others to review and use as a reference.

Efficacy of acupuncture combined with traditional Chinese medicine on chronic prostatitis
2021 Nov 19 Medicine Zheng X, Yan Z, Wang W, Mao W, Wang Y, Zhao Y, et al.
This study will provide the latest evidence of efficacy for the acupuncture combined with TCM in the treatment of chronic prostatitis, and the effectiveness for chronic prostatitis will be evaluated.
Study Protocol Acupuncture Chinese Medicine Prostatitis
Efficacy of acupuncture combined with traditional Chinese medicine on chronic prostatitis: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis
2021 Nov 19 Medicine Zheng, Xianglong; Yan, Zhangren; Wang, Wanchun; Mao, Wenli; Wang, Yuhan; Zhao, et al.
The effectiveness of acupuncture combined with TCM for chronic prostatitis will be evaluated.
Study Protocol Acupuncture
Acupuncture for chronic prostatitis
2018 Apr Medicine Peng, T., Cheng, Y., Jin, Y., et al.
The study will provide clear evidence to assess the effectiveness and side effects of acupuncture for chronic prostatitis.
Study ProtocolPresentation Slides

Systematic Review
Acupuncture may be recommended for the treatment of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome with relatively rare incidence of adverse events.
Qin, Z., Wu, J., Tian, J. et al.

Systematic Review
Current evidence supports acupuncture as an effective treatment for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome-induced symptoms, particularly in relieving pain.
Qin Z, Wu J, Zhou J, Liu Z.

Systematic Review
Acupuncture has promising efficacy for patients with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
Chang SC, Hsu CH, Hsu CK, Yang SSD, Chang SJ

Systematic Review
Chinese herbal medicine appears to be more effective than Western medication in improving quality of life and reducing prostate volume in benign prostatic hyperplasia patients.
Ma CH, Lin WL, Lui SL, Cai XY, Wong VT, Ziea E, Zhang ZJ
Executive Summary
Write an executive summary in the form of a blog article on the topic of "Research into Chinese medicine treatment for Prostatitis" summarising the research below and using language that can be easily understood by patients and avoiding medical jargon using a professional and caring tone of voice.
Write an executive summary in the form of a blog article on the topic of "Researched Chinese medicine treatments for Prostatitis" summarising the research below in an objective and easy to understand way, and using language that can be easily understood by patients. Group the article into Chinese medicine treatments first, followed by nutrition and other treatments. Avoid using medical jargon and use a professional and caring tone of voice.
Write me a concise but easy to understand executive summary on the topic of "Chinese medicine treatments for Prostatitis" based on the following research that I will give you. Your summary should be 2 paragraphs long in Australian English spelling and include references to the studies.
A Systematic Review published in 2016 in the journal Scientific Reports found that Acupuncture may be recommended for the treatment of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome with relatively rare incidence of adverse events. Based on decreases in the National Institutes of Health Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI) score, a network meta-analysis indicated that electro-acupuncture, acupuncture, alpha-blockers, antibiotics, and dual therapy are superior to placebo in decreasing this score. Additionally, electro-acupuncture and dual therapy were more effective than alpha-blockers in decreasing the total NIH-CPSI total score. Other network meta-analyses did not show significant differences between interventions other placebo. The incidence of adverse events of acupuncture was relatively rare (5.4%) compared with placebo (17.1%), alpha-blockers (24.9%), antibiotics (31%) and dual therapy (48.6%). Overall, rank tests and safety analyses indicate that electro-acupuncture/acupuncture may be recommended for the treatment of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
A Systematic Review published in 2016 in the journal Medicine found that Current evidence supports acupuncture as an effective treatment for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome-induced symptoms, particularly in relieving pain. Real acupuncture was superior to sham acupuncture in improving symptoms (pain, voiding) and quality of life (Qof) domain subscores. Compared to sham acupuncture and medicine, acupuncture appears to be more effective at improving the global assessment. Two trials found that there is no significant difference between acupuncture and sham acupuncture in decreasing the IPSS score. Acupuncture failed to show more favorable effects in improving both symptoms and the Qof domain compared with medicine. Overall, current evidence supports acupuncture as an effective treatment for CP/CPPS-induced symptoms, particularly in relieving pain. Based on the meta-analysis, acupuncture is superior to sham acupuncture in improving symptoms and Qof. Acupuncture might be similar to medicine (Levofloxacinand, Ibuprofen, and Tamsulosin) in its long-term effects, but evidence was limited due to high ROB among included trials as well as potential heterogeneity. Acupuncture is associated with rare and slightly adverse events.
A Systematic Review published in 2016 in the journal Neurourology and Urodynamics found that Acupuncture has promising efficacy for patients with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Three and four randomized controlled trials compared acupuncture with sham acupuncture (n = 101 vs. 103) and medical treatment (n = 156 vs. 138), respectively. The results revealed that acupuncture was superior to sham acupuncture as regards response rate, NIH-CPSI, and IPSS reductions, therefore, excluding the placebo effect. Compared to standard medical treatments, acupuncture had a significantly higher response rate. Acupuncture has promising efficacy for patients with CP/CPPS. Compared to standard medical treatment, it has better efficacy. Thus, it may also serve as a standard treatment option when available.
A Systematic Review published in 2013 in the journal Asian Journal of Andrology found that Chinese herbal medicine appears to be more effective than Western medication in improving quality of life and reducing prostate volume in benign prostatic hyperplasia patients. The method utilized in this research involved the systematic review of randomized controlled trials from diverse electronic databases. These trials were focused on comparing Chinese herbal medicine, in standalone or supplementary use with Western medication, against placebo or solely Western medication. All trials reviewed pertained to benign prostatic hyperplasia. Outcomes measured included changes in patients' urological symptoms, urodynamic measures, prostate volume and the occurrence of adverse events. The analysis revealed that Chinese herbal medicine was superior to Western medicines in terms of improving patients' quality of life as well as reducing the size of the prostate. Furthermore, the occurrence and frequency of adverse events in patients treated with Chinese herbal medicines were found to be similar to those observed in placebo groups and lesser compared to groups treated with Western medication. However, due to the limited number of trials and their methodological quality, the evidence supporting the efficacy of Chinese herbal medicine remains weak.
Moderation Tools
Topic
Sign In
Users not signed in are limited to viewing the 5 most recent items of content.