Mood
How to submit an article:
- Registered users can submit any published journal article that has a unique DOI (Digital Object Identifier) name or link to Research Hub.
- For example, you can paste the full DOI link:
https://doi.org/10.1109/5.771073or just the DOI name:10.1109/5.771073into the field above and click submit. - The person who is first to submit a valid article to Research Hub will forever be credited for it, and every article submission earns you +6 Research Points.
Related Topics
Published research studies are articles that present the findings of original research that has undergone a peer-review process and has been made publicly available in scholarly journals, books or other media.

Anti-Menopausal Effect of Soybean Germ Extract and Lactobacillus gasseri in the Ovariectomized Rat Model
2023 Oct 23 Nutrients Lee SH, Lim TJ, Yun EJ, Kim KH, Lim S
Animal Study Experimental Study SoybeanA combination of soybean germ extract and a probiotic significantly improved menopause-related conditions and mood in an ovariectomized rat model.

Adjuvant pomegranate juice intake improves the inflammatory status of hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A randomized and placebo-controlled trial
2023 Aug Complementary Therapies in Medicine Yousefi M, Sadriirani M, Mahmoodi S, Samimi B, Pourmahmoudi A, Hosseinikia M, et al.
Randomised Controlled Trial CRPPomegranate juice consumption appears to somewhat enhance inflammatory status and complete blood count in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
The Potential Effect of Blueberry on Cognitive Health and Mood State based on Human Intervention Studies: Systematic Review and Mini Meta-Analysis
2023 Aug CNS & Neurological Disorders - Drug Targets Soveid N, Barkhidarian B, Moradi S, Gholami F, Rasaei N, Himmerich H, et al.
Meta-Analysis Systematic Review Blueberry Cognitive FunctionBlueberry consumption significantly improves two-back test accuracy, suggesting potential cognitive benefits.

Acute effects of fresh versus dried Hayward green kiwifruit on sleep quality, mood, and sleep-related urinary metabolites in healthy young men with good and poor sleep quality
2023 Mar 14 Frontiers in Nutrition Kanon AP, Giezenaar C, Roy NC, McNabb WC, Henare SJ
Randomised Controlled Trial Serotonin Sleep KiwifruitConsumption of fresh or dried kiwifruit in the evening improves aspects of sleep quality and mood, potentially mediated through changes in serotonin metabolism.

Acupuncture for comorbid depression and insomnia in perimenopause: A feasibility patient-assessor-blinded, randomized, and sham-controlled clinical trial
2023 Feb 06 Frontiers in Public Health Zhao FY, Zheng Z, Fu QQ, Conduit R, Xu H, Wang HR, et al.
Randomised Controlled Trial Perimenopausal DepressionAcupuncture can improve both perimenopausal depression and insomnia with short-medium term effects while being a safe treatment.
Research insights are moderated by the Research Hub team and offer an at-a-glance overview of interesting research findings.

2023 Nutrients
A combination of soybean germ extract and a probiotic significantly improved menopause-related conditions and mood in an ovariectomized rat model.
Animal Study Soybean
Anti-Menopausal Effect of Soybean Germ Extract and Lactobacillus gasseri in the Ovariectomized Rat Model
Lee SH, Lim TJ, Yun EJ, Kim KH, Lim S
2023 CNS & Neurological Disorders - Drug Targets
Blueberry consumption significantly improves two-back test accuracy, suggesting potential cognitive benefits.
Meta-Analysis Blueberry Cognitive Function
The Potential Effect of Blueberry on Cognitive Health and Mood State
based on Human Intervention Studies: Systematic Review and Mini
Meta-Analysis
Soveid N, Barkhidarian B, Moradi S, Gholami F, Rasaei N, Himmerich H, et al.

2023 Complementary Therapies in Medicine
Pomegranate juice consumption appears to somewhat enhance inflammatory status and complete blood count in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
Randomised Controlled Trial CRP
Adjuvant pomegranate juice intake improves the inflammatory status of hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A randomized and placebo-controlled trial
Yousefi M, Sadriirani M, Mahmoodi S, Samimi B, Pourmahmoudi A, Hosseinikia M, et al.

2023 Frontiers in Nutrition
Consumption of fresh or dried kiwifruit in the evening improves aspects of sleep quality and mood, potentially mediated through changes in serotonin metabolism.
Randomised Controlled Trial Kiwifruit Serotonin Sleep
Acute effects of fresh versus dried Hayward green kiwifruit on sleep quality, mood, and sleep-related urinary metabolites in healthy young men with good and poor sleep quality
Kanon AP, Giezenaar C, Roy NC, McNabb WC, Henare SJ

2023 Frontiers in Public Health
Acupuncture can improve both perimenopausal depression and insomnia with short-medium term effects while being a safe treatment.
Randomised Controlled Trial Perimenopausal Depression
Acupuncture for comorbid depression and insomnia in perimenopause: A feasibility patient-assessor-blinded, randomized, and sham-controlled clinical trial
Zhao FY, Zheng Z, Fu QQ, Conduit R, Xu H, Wang HR, et al.
Review Articles
Review articles summarise and critically evaluate the current state of research on a specific topic or field by synthesising multiple primary research studies.
The Potential Effect of Blueberry on Cognitive Health and Mood State based on Human Intervention Studies: Systematic Review and Mini Meta-Analysis
2023 Aug CNS & Neurological Disorders - Drug Targets Soveid N, Barkhidarian B, Moradi S, Gholami F, Rasaei N, Himmerich H, et al.
Meta-Analysis Systematic Review Blueberry Cognitive FunctionBlueberry consumption significantly improves two-back test accuracy, suggesting potential cognitive benefits.

The Role of Kiwifruit in Supporting Psychological Well-Being: A Rapid Review of the Literature
2022 Nov 03 Nutrients Billows M, Kakoschke N, Zajac IT
Review Article Mental Health Fatigue MoodEating two gold kiwifruit daily can lead to significant improvements in mood and energy, thereby boosting psychological well-being in adults.

The effect of cocoa-rich products on depression, anxiety, and mood: A systematic review and meta-analysis
2021 May 10 Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition Fusar-Poli L, Gabbiadini A, Ciancio A, Vozza L, Signorelli MS, Aguglia E
Systematic Review Meta-Analysis Depression Anxiety CocoaCocoa-rich products consumption can improve mood and affect in the short term.

The effect of almond intake on lipid profile: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
2021 Jan Food & Function Asbaghi O, Moodi V, Hadi A, Eslampour E, Shirinbakhshmasoleh M, Ghaedi E, et al.
Systematic Review Meta-Analysis Triglyceride Cholesterol AlmondAlmond intake significantly changed the concentrations of triglycerides, total cholesterol and low-density lipoproteins

The effect of blueberry interventions on cognitive performance and mood: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials
2020 Mar Brain, Behavior, and Immunity Travica N, D'Cunha NM, Naumovski N, Kent K, Mellor DD, Firth J, et al.
Systematic Review Cognitive FunctionBlueberries and their products may improve certain measures of cognitive performance, particularly memory, and positively affect mood.
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are research studies that involve people and are conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of new treatments or interventions, such as drugs, medical devices, or behavioural therapies.

Adjuvant pomegranate juice intake improves the inflammatory status of hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A randomized and placebo-controlled trial
2023 Aug Complementary Therapies in Medicine Yousefi M, Sadriirani M, Mahmoodi S, Samimi B, Pourmahmoudi A, Hosseinikia M, et al.
Randomised Controlled Trial CRPPomegranate juice consumption appears to somewhat enhance inflammatory status and complete blood count in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.

Acute effects of fresh versus dried Hayward green kiwifruit on sleep quality, mood, and sleep-related urinary metabolites in healthy young men with good and poor sleep quality
2023 Mar 14 Frontiers in Nutrition Kanon AP, Giezenaar C, Roy NC, McNabb WC, Henare SJ
Randomised Controlled Trial Serotonin Sleep KiwifruitConsumption of fresh or dried kiwifruit in the evening improves aspects of sleep quality and mood, potentially mediated through changes in serotonin metabolism.

Acupuncture for comorbid depression and insomnia in perimenopause: A feasibility patient-assessor-blinded, randomized, and sham-controlled clinical trial
2023 Feb 06 Frontiers in Public Health Zhao FY, Zheng Z, Fu QQ, Conduit R, Xu H, Wang HR, et al.
Randomised Controlled Trial Perimenopausal DepressionAcupuncture can improve both perimenopausal depression and insomnia with short-medium term effects while being a safe treatment.

The effects of acupuncture on clinical efficacy and steady-state visual evoked potentials in insomnia patients with emotional disorders: A randomized single-blind sham-controlled trial
2023 Jan 18 Frontiers in Neurology Leixiao Zhang, Yanli Deng, Ruting Hui, Yu Tang, Siyi Yu, Ying Li, et al.
Acupuncture have a good clinical effect on patients with insomnia and emotional disorders and have a significant regulatory effect on abnormally excited brain potentials.
Randomised Controlled Trial Acupuncture
The Effects of Walnuts and Academic Stress on Mental Health, General Well-Being and the Gut Microbiota in a Sample of University Students: A Randomised Clinical Trial
2022 Nov 11 Nutrients Herselman MF, Bailey S, Deo P, Zhou XF, Gunn KM, Bobrovskaya L
Randomised Controlled Trial Students Stress Gut Microbiota WalnutWalnut consumption improves mental health indicators and negates some negative effects of academic stress on students' health and gut microbiota, especially in females.
Study Protocols
Published study protocols are detailed plans that outline the objectives, methodology, statistical analyses, and organisation of a research study that have been made publicly available for others to review and use as a reference.
Presentation Slides

Animal Study
A combination of soybean germ extract and a probiotic significantly improved menopause-related conditions and mood in an ovariectomized rat model.
Lee SH, Lim TJ, Yun EJ, Kim KH, Lim S

Meta-Analysis
Blueberry consumption significantly improves two-back test accuracy, suggesting potential cognitive benefits.
Soveid N, Barkhidarian B, Moradi S, Gholami F, Rasaei N, Himmerich H, Mirzaei K

Randomised Controlled Trial
Pomegranate juice consumption appears to somewhat enhance inflammatory status and complete blood count in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
Yousefi M, Sadriirani M, Mahmoodi S, Samimi B, Pourmahmoudi A, Hosseinikia M, Sadeghi O, Roustaei N, Saeedinezhad Z, Espín JC, Ansari S, Panahande SB

Randomised Controlled Trial
Consumption of fresh or dried kiwifruit in the evening improves aspects of sleep quality and mood, potentially mediated through changes in serotonin metabolism.
Kanon AP, Giezenaar C, Roy NC, McNabb WC, Henare SJ

Randomised Controlled Trial
Acupuncture can improve both perimenopausal depression and insomnia with short-medium term effects while being a safe treatment.
Zhao FY, Zheng Z, Fu QQ, Conduit R, Xu H, Wang HR, Huang YL, Jiang T, Zhang WJ, Kennedy GA

Cohort Study
Acupuncture shows promise in improving psychiatric symptoms, physical symptoms, and quality of life in patients with treatment-resistant mood disorders, highlighting its potential as a complementary therapy for these conditions.
Matsuura Y, Hongo S, Taniguchi H, Yasuno F, Sakai T

Randomised Controlled Trial
Walnut consumption improves mental health indicators and negates some negative effects of academic stress on students' health and gut microbiota, especially in females.
Herselman MF, Bailey S, Deo P, Zhou XF, Gunn KM, Bobrovskaya L

Review Article
Eating two gold kiwifruit daily can lead to significant improvements in mood and energy, thereby boosting psychological well-being in adults.
Billows M, Kakoschke N, Zajac IT

Randomised Controlled Trial
Consuming New Zealand green kiwifruit improves sleep quality, mood, and increases the concentration of serotonin metabolites.
Kanon AP, Giezenaar C, Roy NC, McNabb WC, Henare SJ

Randomised Controlled Trial
Vitamin D supplementation effectively improves depressive symptoms in women with type 2 diabetes and low vitamin D levels, regardless of the dose administered.
Penckofer S, Ridosh M, Adams W, Grzesiak M, Woo J, Byrn M, Kouba J, Sheean P, Kordish C, Durazo-Arvizu R, Wallis D, Emanuele MA, Halaris A

Randomised Controlled Trial
Dark chocolate exerts prebiotic effects and may improve negative emotional states via the gut-brain axis.
Shin JH, Kim CS, Cha L, Kim S, Lee S, Chae S, Chun WY, Shin DM

Randomised Controlled Trial
Chamomile capsules prove effective in reducing emotional symptoms related to menstrual cycles.
Najafi Mollabashi E, Ziaie T, Bostani Khalesi Z

Systematic Review
Cocoa-rich products consumption can improve mood and affect in the short term.
Fusar-Poli L, Gabbiadini A, Ciancio A, Vozza L, Signorelli MS, Aguglia E

Experimental Study
Supplementation with standardized saffron extract improves depressive symptoms and social relationships in healthy individuals experiencing subclinical low mood and stress.
Jackson PA, Forster J, Khan J, Pouchieu C, Dubreuil S, Gaudout D, Moras B, Pourtau L, Joffre F, Vaysse C, Bertrand K, Abrous H, Vauzour D, Brossaud J, Corcuff JB, Capuron L, Kennedy DO

Systematic Review
Almond intake significantly changed the concentrations of triglycerides, total cholesterol and low-density lipoproteins
Asbaghi O, Moodi V, Hadi A, Eslampour E, Shirinbakhshmasoleh M, Ghaedi E, Miraghajani M

Systematic Review
Blueberries and their products may improve certain measures of cognitive performance, particularly memory, and positively affect mood.
Travica N, D'Cunha NM, Naumovski N, Kent K, Mellor DD, Firth J, Georgousopoulou EN, Dean OM, Loughman A, Jacka F, Marx W

Systematic Review
Green tea influences liver enzymes differently based on an individual's health status, reducing levels in patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, but slightly increasing levels in healthy subjects.
Mahmoodi M, Hosseini R, Kazemi A, Ofori‐Asenso R, Mazidi M, Mazloomi SM
Review Article
Avocado and soybean unsaponifiables may effectively reduce inflammation and symptoms related to osteoarthritis, autoimmune diseases, and menopause.
Salehi B, Rescigno A, Dettori T, Calina D, Docea AO, Singh L, Cebeci F, Özçelik B, Bhia M, Dowlati Beirami A, Sharifi-Rad J, Sharopov F, C. Cho W, Martins N

Systematic Review
Almond intake significantly reduces body weight and fat mass in adults, yet it does not impact body mass index, waist circumference, or fat-free mass.
Eslampour E, Moodi V, Asbaghi O, Ghaedi E, Shirinbakhshmasoleh M, Hadi A, Miraghajani M

Systematic Review
Traditional Chinese acupuncture seems to be effective in improving some symptoms of postpartum depression.
Tong P, Dong LP, Yang Y, Shi YH, Sun T, Bo P

Systematic Review
Black pepper, beyond its culinary use, offers medicinal benefits like antimicrobial, antioxidant, anticancer, anti-diabetic, and anti-inflammatory properties mainly attributed to the compound piperine.
Takooree H, Aumeeruddy MZ, Rengasamy KRR, Venugopala KN, Jeewon R, Zengin G, Mahomoodally MF

Systematic Review
Green tea consumption was shown to reduce psychopathological symptoms like anxiety and was also shown to effect cognition, with noted benefits for memory and attention. Green tea was also linked with the activation of working memory as seen in functional MRI.
Mancini E, Beglinger C, Drewe J, Zanchi D, Lang UE, Borgwardt S

Randomised Controlled Trial
Dark chocolate reduces subsequent food intake in postmenopausal women more effectively than milk and white chocolate.
Marsh CE, Green DJ, Naylor LH, Guelfi KJ

Systematic Review
The severity of primary restless legs syndrome symptoms can be significantly ameliorated by acupuncture.
Xu XM, Liu Y, Jia SY, Dong MX, Cao D, Wei YD.

Randomised Controlled Trial
Walnuts appear to enhance mood in non-depressed healthy young males.
Pribis P

Randomised Controlled Trial
Peppermint capsules can effectively reduce the severity of painful menstrual cramps in young women without causing any apparent change in pain duration.
Heshmati A, Dolatian M, Mojab F, shakeri N, Nikkhah S, Mahmoodi Z

Review Article
Date palm pollen (DPP) containing various compounds has been used as an aphrodisiac and fertility enhancer historically and shows promise in treating fertility disorders.
Tahvilzadeh M, Hajimahmoodi M, Rahimi R

Review Article
Among the bioactive compounds present in jujube fruit, triterpenic acids and polysaccharides have antiproliferative and anticancer effects on various cancer cell lines.
Zoya Tahergorabi, Mohammad Reza Abedini, Moodi Mitra, Mohammad Hassanpour Fard, and Hossein Beydokhti

Review Article
Cocoa and chocolate, rich in antioxidant molecules like epicatechin, enhance brain health, stimulate brain perfusion, and reduce the risk of Alzheimer's disease and stroke.
Nehlig A

Experimental Study
Pomegranate juice can enhance memory function and brain activity in tasks related to verbal and visual memory in older adults experiencing memory problems.
Bookheimer SY, Renner BA, Ekstrom A, Li Z, Henning SM, Brown JA, Jones M, Moody T, Small GW

Clinical Study
Consuming two kiwifruits daily can improve overall mood, particularly for individuals starting with moderate mood disturbance.
Carr AC, Bozonet SM, Pullar JM, Vissers MCM
Executive Summary
Write an executive summary in the form of a blog article on the topic of "Research into Chinese medicine treatment for Mood" summarising the research below and using language that can be easily understood by patients and avoiding medical jargon using a professional and caring tone of voice.
Write an executive summary in the form of a blog article on the topic of "Researched Chinese medicine treatments for Mood" summarising the research below in an objective and easy to understand way, and using language that can be easily understood by patients. Group the article into Chinese medicine treatments first, followed by nutrition and other treatments. Avoid using medical jargon and use a professional and caring tone of voice.
Write me a concise but easy to understand executive summary on the topic of "Chinese medicine treatments for Mood" based on the following research that I will give you. Your summary should be 2 paragraphs long in Australian English spelling and include references to the studies.
A Animal Study published in 2023 in the journal Nutrients found that A combination of soybean germ extract and a probiotic significantly improved menopause-related conditions and mood in an ovariectomized rat model. The study employed an ovariectomized rat model to understand the effects of a combination of soybean germ extract containing 30% isoflavone and a probiotic. The methodology included assessing the effects of this combination on several health markers including body weight, estrogen markers, uterine and bone health, vascular markers, and neurotransmitter levels in these rats. Once implemented, the combination of soybean germ extract and the probiotic showcased significant improvement in body weight and uterine and bone health of the rats. There were also noticeable effects on the lipid profile, liver function, and vascular markers. Most interestingly, the combination had a positive impact on the levels of serotonin and norepinephrine, indicating potential mood-enhancing effects, which are crucial in managing symptoms post-menopause. This essentially shows the potential of a dietary approach towards menopausal management, especially given the observed benefits without the side effects typically associated with hormone replacement therapy.
A Meta-Analysis published in 2023 in the journal CNS & Neurological Disorders - Drug Targets found that Blueberry consumption significantly improves two-back test accuracy, suggesting potential cognitive benefits. Methodology: A comprehensive search was conducted in April 2021 for relevant clinical trials on blueberry supplementation and its effects on cognitive performance and mood. The search was conducted through PubMed/Medline, Scopus, Embase, and Google Scholar, and the random effect size was used to estimate the pooled effect size. Cochrane Q test and I-squared tests were used to evaluate heterogeneity between studies, and a subgroup analysis was done to detect potential sources of such heterogeneity. Fourteen randomized trials were included in the quantitative analysis, and six were pooled for statistical analysis. Results: Blueberry intervention did not produce any significant impact on mood state score, attention task reaction time, or on the percentages of attention task accuracy. Similarly, it had no significant effect on one-back test accuracy. However, a noticeable positive effect was detected in two-back test accuracy, indicating possible cognitive benefits associated with blueberry consumption.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2023 in the journal Complementary Therapies in Medicine found that Pomegranate juice consumption appears to somewhat enhance inflammatory status and complete blood count in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. The study was a randomized, double-blinded placebo-controlled trial involving 48 patients and had two parallel arms. As part of their standard hospital care, patients were either given 500 mL of whole pomegranate juice daily or a placebo for a period of 14 days. The researchers focused on measuring inflammatory indicators and complete blood counts both at the start of the study and at the end of the 14-day intervention period. Following the 14-day intervention, there was a distinguishable decrease in primary outcomes including inflammatory markers such as C reactive protein, interleukin-6, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate in the group that consumed pomegranate juice as compared to the readings before the intervention. In addition, considerable changes were also observed in secondary outcomes such as neutrophils, lymphocytes, platelets, platelets-to-lymphocyte and neutrophils-to-lymphocyte ratios in the pomegranate juice group compared to the parameters before the intervention. Finally, the mean changes in levels of interleukin-6, white blood cells, neutrophils, lymphocyte, platelets, platelets-to-lymphocyte ratio, blood oxygen saturation and MCV were significantly different between the two groups by the end of intervention, while no significant difference was noted in other blood indices.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2023 in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition found that Consumption of fresh or dried kiwifruit in the evening improves aspects of sleep quality and mood, potentially mediated through changes in serotonin metabolism. A randomized, single-blind crossover study involving 24 men with varying sleep quality levels was conducted. Participants were provided with one of three treatments during their standard evening meal at home: the flesh of two fresh green kiwifruits, dried green kiwifruit powder (with skin and equivalent to the dry matter of two fresh kiwifruits) mixed with water, or a water control. Various factors were evaluated including subjective and objective sleep quality, mood, and urine concentration of several compounds including the serotonin metabolite 5-HIAA, vitamin C, and B-vitamins. Findings indicated that regardless of sleep quality group, dried kiwifruit consumption was associated with an improvement in morning sleepiness, alertness upon waking, and vigor as compared to the control. Both fresh and dried kiwifruit treatments suggested an improvement in self-esteem and overall mood disturbance. Increase in the urinary concentration of serotonin metabolite was observed with both kiwifruit treatments. Amongst poor sleepers, ease of awakening was notably improved after the intake of dried kiwifruit and showed signs of improvement with fresh kiwifruit. For good sleepers, there seemed to be an improvement in getting to sleep with fresh kiwifruit. Poor sleepers were found to have lower quantities of certain B-vitamins compared to good sleepers. Thus, both dried and fresh kiwifruit consumption with a standard evening meal showed a positive impact on sleep quality and mood.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2023 in the journal Frontiers in Public Health found that Acupuncture can improve both perimenopausal depression and insomnia with short-medium term effects while being a safe treatment. The experiment involved seventy eligible participants who were randomly assigned to either a real-acupuncture (RA) or a sham-acupuncture (SA) group. They were given 17 sessions of either RA or SA treatments over an 8-week timeframe. The primary outcomes for mood and sleep were evaluated using the 17-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale and the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index scores. Secondary outcomes included an evaluation of anxiety symptoms, perimenopausal symptoms, and quality of life. Also, participants' experiences and overall satisfaction with treatment were assessed. Blood samples were collected as well to measure reproductive hormone levels. Reports indicate that 65 participants completed all treatment sessions while 54 and 41 participants completed the 8-week and 16-week follow-ups respectively. The results showed the RA group to have a bigger reduction of Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index scores at post-treatment and 8-week follow-up compared to the sham-acupuncture group. Although, the change in the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale scores for the RA group wasn’t significantly different from the sham group. There were no significant mean differences for the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale or the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index between the two groups from the beginning to the 16th-week follow-up, nor were any differences noted in serum reproductive hormone levels among the groups. No major adverse events were reported.
A Cohort Study published in 2022 in the journal Journal of Acupuncture and Meridian Studies found that Acupuncture shows promise in improving psychiatric symptoms, physical symptoms, and quality of life in patients with treatment-resistant mood disorders, highlighting its potential as a complementary therapy for these conditions. This prospective study explored the effects of acupuncture on physical symptoms and quality of life (QoL) in patients with treatment-resistant major depressive disorder (MDD) and bipolar disorder (BD). After 12 weeks of acupuncture treatment, significant improvements were observed in psychiatric symptoms, physical symptoms, and various aspects of QoL. These findings suggest that acupuncture may be beneficial for both the physical and mental well-being of patients with treatment-resistant mood disorders, although further research is needed to validate these preliminary results.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal Nutrients found that Walnut consumption improves mental health indicators and negates some negative effects of academic stress on students' health and gut microbiota, especially in females. In the study, the researchers launched a randomized clinical trial to study the effects of academic stress and daily walnut consumption on undergraduate students' mental health, general health biomarkers, and the gut microbiota. The specific aim was to examine the implications of stress and diet interplay, focusing specifically on the consumption of walnuts due to their previously demonstrated positive impact on mental wellbeing. In analyzing the results, they found that academic stress negatively affected the self-reported mood and overall mental health of the students. However, a daily intake of walnuts appeared to improve the mental health indicators. Notably, it provided a buffer against the adverse effects of academic stress on metabolic and stress biomarkers. Particularly in female students, academic stress was linked to reduced gut microbial diversity, a negative effect which walnut consumption seemed to counteract. The effects on male participants could not be definitively ascertained due to the smaller participant size.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Nutrients found that Eating two gold kiwifruit daily can lead to significant improvements in mood and energy, thereby boosting psychological well-being in adults. The study conducted a literature review through databases like CINAHL, Embase, and PubMed, searching for English language articles published from 2005 to July 2022. These articles had to be randomized trials involving kiwifruit interventions targeting adults and assessing psychological well-being. The researchers used the Joanna Briggs Institute's critical appraisal tool to evaluate potential bias in these trials. After the search, they selected two suitable trials involving 202 participants. In discussing the results, the evidence found shows that regularly consuming two gold kiwifruits daily was linked with a significant decrease in mood disturbance and fatigue, and a significant increase in vigor and overall well-being. These effects were more pronounced in participants who had more significant initial mood disturbances. The study concluded by underlining the potential utility of consuming gold kiwifruit daily to promote improved psychological health.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal NSNZ 2021 found that Consuming New Zealand green kiwifruit improves sleep quality, mood, and increases the concentration of serotonin metabolites. A total of 24 men, ranging in age and with varying sleep quality were selected for the study, in a single-blind crossover design, which was randomized. Participants were provided three treatments on separate occasions, each differing by 6-8 days: consumption of two fresh kiwifruits, ingesting green kiwifruit powder mixed with water equivalent to two fresh kiwifruits, or a simple water control. Poor sleepers noted that they woke up more easily after consuming dried kiwifruit, with a similar but less pronounced trend observed when they consumed fresh kiwifruit. Conversely, good sleepers showed a trend towards better sleep initiation with fresh kiwifruit, but not with the dried kiwifruit. Independent of the participants' sleep quality, both fresh and dried kiwifruit largely improved mood and self-esteem. Consumption of dried kiwifruit significantly elevated morning alertness, post-wakening behaviour, and vigour. Both forms of kiwifruit ingestion led to higher urinary concentrations of the serotonin metabolite known as 5-HIAA.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal Journal of Diabetes Research found that Vitamin D supplementation effectively improves depressive symptoms in women with type 2 diabetes and low vitamin D levels, regardless of the dose administered. In the study, a double-blind randomized active comparator-controlled trial was performed. Female participants with significant depressive symptoms, as indicated by the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression scale, received weekly oral vitamin D supplements: a group received a higher dose (50,000 IU), while the control group received a lower dose (5,000 IU). These doses were taken over the course of 6 months, and participants' vitamin D and depression levels were evaluated at baseline, at the 3-month point, and at the end of the study. The improvement in depressive symptoms over the course of the study was significant, irrespective of the supplement dose given. There was no discernible difference between the depression scores of those who received the higher dose compared to those who received the lower dose. This remained true when considering women with moderate baseline depressive symptoms. However, among women with severe depressive symptoms at the outset, both groups showed similar improvements in their follow-up depression scores. The dose administered did not affect the significant time-related decrease in depressive symptoms.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry found that Dark chocolate exerts prebiotic effects and may improve negative emotional states via the gut-brain axis. To assess the association between the mood-altering effects of dark chocolate and the gut microbiota, we performed fecal 16S rRNA sequencing analysis for the DC85 and CON groups. Gut microbial diversity was significantly higher in DC85 than CON (P<.05). Blautia obeum levels were significantly elevated and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii levels were reduced in DC85 compared to CON (P<.05). Furthermore, we found that the observed changes in negative affect scores were negatively correlated with diversity and relative abundance of Blautia obeum (P<.05).
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2021 in the journal European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology: X found that Chamomile capsules prove effective in reducing emotional symptoms related to menstrual cycles. In the methodology of this clinical trial, 118 Guilan University students were split into two groups – one receiving chamomile capsules, the other a placebo – with each participant taking one capsule every eight hours for seven days before menstruation. The Premenstrual Symptoms Screening Tool was used to gather data. The assessment of the results reveals that the group of students who consumed the chamomile capsules observed a more noteworthy decrease in menstrual-related mood disorders when compared to the placebo group. Moreover, even after controlling for other variables, there was a significant difference between the two groups in terms of changes in mood symptom severity.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition found that Cocoa-rich products consumption can improve mood and affect in the short term. The study carried out a systematic review and meta-analysis in line with PRISMA guidelines to ascertain the effects of cocoa-derived food on depressive and anxiety symptoms, as well as positive and negative affect. Potential sources were found on Web of Knowledge and PsycINFO until April 3, 2020. Out of 761 documents screened, nine studies were picked. Two trials were involved in examining the long-term impact (>1 week) of cocoa consumption, two reviewed the short-term effects (3 days), and five studies were conducted in acute conditions (single administration). The results indicate that cocoa-rich products had a significant overall effect on reducing depressive and anxiety symptoms. There was also significant improvement in both positive and negative affect. The effect size in all meta-analyses was medium, while the heterogeneity was low. Despite these promising outcomes, the conclusions must be cautiously interpreted due to the short duration of the trials and the limited number of participants and studies included in the meta-analyses.
A Experimental Study published in 2021 in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition found that Supplementation with standardized saffron extract improves depressive symptoms and social relationships in healthy individuals experiencing subclinical low mood and stress. The study employed a double-blind, randomized, parallel groups design involving 56 healthy male and female participants aged between 18 and 54. They received either 30 mg standardized saffron extract or a placebo daily for 8 weeks. The saffron's chronic effects on subjective feelings of anxiety, stress, and depression were evaluated using a series of questionnaires. The acute effects of saffron following exposure to a lab-based psychosocial stressor were determined through assessing psychological and physiological parameters. As part of the process, the level of crocetin, a compound found in saffron, was quantified in the participants' urine. The results indicated that individuals who received the saffron extract reported lower depression scores and improved social relationships after the 8-week period. A significant increase in urinary crocetin levels was observed with saffron supplementation, and these changes were found to be correlated with a decrease in depression scores. Additionally, the usual decrease in heart rate variability, a reaction commonly seen during the exposure to stressors, was found to be diminished after acute intake of saffron. The findings suggest that saffron extract can help improve subclinical depressive symptoms in healthy individuals and may increase resilience against the development of stress-related psychiatric disorders.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Food & Function found that Almond intake significantly changed the concentrations of triglycerides, total cholesterol and low-density lipoproteins To estimate the overall effect of almond intake, we employed the random-effect model. In total, 27 studies with 36 effect sizes were included in our analysis (1154 cases and 904 control subjects). The meta-analysis revealed that almond intake significantly changed the concentrations of triglycerides, total cholesterol, and low-density lipoproteins; however it did not have a significant effect on high-density lipoprotein levels. Meta-regression analysis indicated a linear relationship between the dose of almond and change in TG. This meta-analysis concludes that almond intake can significantly reduce lipid parameters.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Brain, Behavior, and Immunity found that Blueberries and their products may improve certain measures of cognitive performance, particularly memory, and positively affect mood. The systematic review process involved evaluating the results from randomized controlled trials that investigated the effects of blueberries and blueberry products on cognitive performance and mood. A total of eleven articles, encompassing twelve studies, were examined. The studies employed various forms of blueberries - freeze-dried, whole, and concentrate. Different demographic groups were considered across the studies: children, young adults, and older people with or without known cognitive impairment. The studies considered the impact of consumed or supplemented blueberries, varied in dosage and duration, on cognitive performance, specifically in relation to both short-term and long-term memory, as well as spatial memory. Also, the studies investigated the effects on mood, particularly the potential enhancement of positive feelings. The findings revealed that eight out of twelve studies reported an improvement in cognitive performance following the ingestion of blueberries, although variations in each specific study's design, dosage, and anthocyanin content made cross-study comparisons challenging. Regarding mood, out of five studies, only one study reported a significant improvement in mood upon consumption of blueberry products, while the others reported no significant change. Despite differences, all studies featured a low risk of bias overall, underscoring the perceived validity of these findings.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Phytotherapy Research found that Green tea influences liver enzymes differently based on an individual's health status, reducing levels in patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, but slightly increasing levels in healthy subjects. The researchers initiated a comprehensive review and analysis of randomized clinical trials relating to green tea supplementation's effects on liver enzymes. This analysis included forms of green tea supplementation, such as catechin. The information to support this examination was sourced from four medical and health databases and included all trials examining the influence of green tea or its derivatives on specific liver enzymes, including Alanine Transaminase, Aspartate Aminotransferase, Alkaline Phosphatase, and Bilirubin. Altogether, fifteen trials were considered for inclusion in this research. The study found that while the overall effect of green tea on liver enzymes was nonsignificant, further analysis showed that the impact of green tea on liver enzymes varies depending on an individual's health status. Notably, the use of green tea reduced liver enzyme levels in participants diagnosed with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. However, in contrast, a small but statistically significant increase in liver enzyme levels was observed in healthy subjects. These findings suggest that the therapeutic potential of green tea may differ significantly based on an individual's health condition.
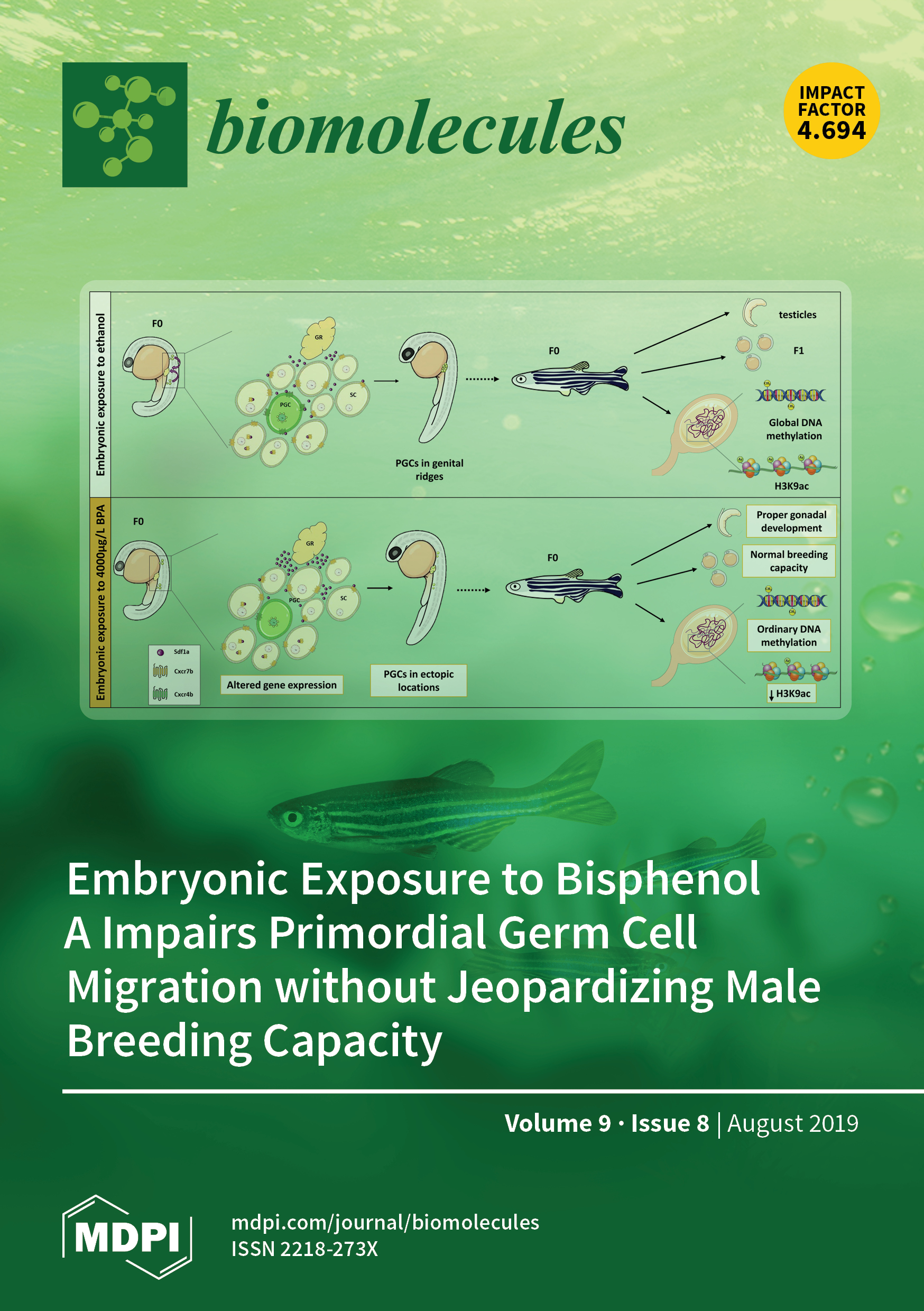
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Biomolecules found that Avocado and soybean unsaponifiables may effectively reduce inflammation and symptoms related to osteoarthritis, autoimmune diseases, and menopause. The research involves summarizing various studies on the biological effects of the avocado-soybean unsaponifiables (ASU), highlighting its potent anti-inflammatory properties. The extracted ASU are a combination of elements derived from the fruits and seeds of avocados and soybeans. To understand its impact, the researchers categorized the applications of ASU in treating different conditions such as osteoarthritic pain, hip and knee osteoarthritis, autoimmune diseases, and menopause-related symptoms amongst postmenopausal women. The discussion revealed significant links between avocado and soybean unsaponifiables and symptom improvement in areas of osteoarthritic pain, autoimmune conditions, and postmenopause. Particularly notable is the ASU mixture's potential role as an adjunct treatment, meaning it’s meant to supplement primary treatments for such conditions. Its benefits were not only limited to physical reduction of inflammation and associated pain, but also improved mood and quality of life for postmenopausal women by significantly reducing menopause-related symptoms. The study also delves into the safety, toxicological considerations, and regulatory practices related to the use of ASU.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Food & Function found that Almond intake significantly reduces body weight and fat mass in adults, yet it does not impact body mass index, waist circumference, or fat-free mass. The methodology used in this study started with a comprehensive search of online databases including PubMed, Scopus, ISI Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and Google Scholar until January 2020. The goal was to identify relevant randomized controlled trials for inclusion, which led to the discovery of 28 trials among 2983 reports, that were deemed suitable for analysis. The data were reported as weighted mean differences and standard deviations to signify the impact of almond consumption on different bodily measures including body weight, body mass index, waist circumference, fat mass, and fat-free mass. As for the results, pooling of data was done utilizing a random-effects model, the outcome of which indicated a significant reduction in body weight and fat mass following almond intake. However, no meaningful change was found in measures of body mass index, waist circumference, or fat-free mass as a result of almond consumption. Interestingly, such intake showed a significant influence on weight and fat mass reduction, with no observable effect on the other parameters examined.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal Journal of the Chinese Medical Association found that Traditional Chinese acupuncture seems to be effective in improving some symptoms of postpartum depression. A total of 887 PPD patients from 12 randomised controlled trials were included in the quantitative meta-analysis, with 443 patients in the treatment group and 444 patients in the control group. Patients in the acupuncture group had significantly better performances assessed by the Hamilton Depression Scale than those in the control group, and the pooled MD was −1.27 (95% CI: −2.55 to 0.01; p = 0.05, I2 = 83%) in the random-effect model. In addition, significantly better performance in the effective rate was observed in the acupuncture group than in the control group, and the pooled RR was 1.20 (95% CI: 1.09 to 1.33; p < 0.0001, I2 = 46%). However, in subgroup analysis for the acupuncture therapy alone, only effective rate showed a significantly better performance.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition found that Black pepper, beyond its culinary use, offers medicinal benefits like antimicrobial, antioxidant, anticancer, anti-diabetic, and anti-inflammatory properties mainly attributed to the compound piperine. The study was a systematic review of existing scientific data on the traditional uses, composition, and pharmacological attributes of black pepper. Information was gathered from recognized databases such as Science Direct and Google Scholar, as well as books and other online resources. The study primarily focused on literature in English and evaluated traditional medicinal uses of black pepper in various regions, the common ailments it was used to address, and the preferred modes of preparation. The results of the study affirm the significant medicinal qualities of black pepper. Its antimicrobial activity was demonstrated against various pathogens, and it showed strong antioxidant effects against several reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. The research also highlighted the anticancer effects of black pepper on cell lines from various sites including breast, colon, cervix, and prostate. Furthermore, the benefits of black pepper in managing diabetes and lipid levels in the body were also confirmed. It was also noted for its anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anticonvulsant, and neuroprotective effects. Piperine was identified as the major bioactive compound in black pepper which is responsible for these beneficial effects along with other compounds such as piperic acid, piperlonguminine, and more.
A Systematic Review published in 2017 in the journal Phytomedicine found that Green tea consumption was shown to reduce psychopathological symptoms like anxiety and was also shown to effect cognition, with noted benefits for memory and attention. Green tea was also linked with the activation of working memory as seen in functional MRI. The effects of green tea cannot be attributed to a single constituent of the beverage. This is exemplified in the finding that beneficial green tea effects on cognition are observed under the combined influence of both caffeine and l-theanine, whereas separate administration of either substance was found to have a lesser impact.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2017 in the journal Appetite found that Dark chocolate reduces subsequent food intake in postmenopausal women more effectively than milk and white chocolate. In the study, 14 healthy postmenopausal women participated in three separate experimental trials done in a counterbalanced order. Each trial was conducted at a specific time and was spaced one week apart. The women's food intake, appetite perceptions, mood, and levels of certain appetite-related peptides were measured and analyzed following their consumption of an isocaloric amount of dark chocolate (80% cocoa), milk chocolate (35% cocoa), and white chocolate (cocoa butter). The results indicated a significant decrease in food intake after consuming dark chocolate compared to milk and white chocolate. Furthermore, blood glucose and insulin levels were found to temporarily increase after consuming milk and white chocolate, unlike in the case of dark chocolate. In addition, the consumption of high cocoa content chocolate, like dark and milk chocolate, elevated the pancreatic polypeptide, which differed from the response to white chocolate. The conditions had no significant effect on active ghrelin or leptin hormones, and the mood of the participants remained largely unaffected.
A Systematic Review published in 2017 in the journal Sleep Medicine Reviews found that The severity of primary restless legs syndrome symptoms can be significantly ameliorated by acupuncture. Complementary and alternative therapies have been found to be effective in both primary and secondary restless legs syndrome (RLS). The severity of primary RLS symptoms can be significantly ameliorated by exercise training, transcutaneous spinal direct current stimulation, pneumatic compression devices, light therapy, repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, and acupuncture. Pneumatic compression devices and yoga also improve RLS-related disorders. Exercise training is highly efficacious in the reduction of symptom severity in uremic RLS and related effects such as poor quality of life. Endovenous laser ablation may be a good choice for patients with concurrent RLS and superficial venous insufficiency.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2016 in the journal Nutrients found that Walnuts appear to enhance mood in non-depressed healthy young males. The study's methodology involved an evaluation process using 64 volunteer college students. These individuals were randomly assigned into two different treatment sequences - one involving a walnut intake followed by a placebo, and the other vice versa. Both of these sequences began with an evaluation of the volunteers' base mood, measured using Profiles of Mood States (POMS). After an eight-week interval of sticking to the prescribed plan, their mood was assessed again. This was followed by a 'washout' period of six weeks, during which the volunteer groups reversed their dietary routines - those on walnuts moved to placebo and the ones on placebo switched to walnuts. After another eight-week interval, a final mood assessment occurred. The results displayed a lack of significant mood changes in females or when setting aside gender distinctions in the analysis. The exciting element of this study was found in assessing specifically healthy, non-depressed male subjects. There was a pertinent improvement in their Total Mood Disturbance score, implying an enhancement in mood when consuming walnuts.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2016 in the journal Journal of Herbal Medicine found that Peppermint capsules can effectively reduce the severity of painful menstrual cramps in young women without causing any apparent change in pain duration. This research was a double-blind clinical trial with 102 female students, who reported experiencing primary dysmenorrhea. Participants were evenly divided into two groups: one receiving three 330mg peppermint capsules per day and the other receiving identical placebo capsules filled with starch. The participants used their respective capsules from the first to the third day of their menstrual cycle. The assessment of pain level was done before the test run and over two successive menstrual cycles using a visual analog scale. In the results, no substantial differences were seen between the two experimental groups in terms of pain duration and severity before the intervention. However, after the intervention, a significant reduction was found in the severity of pain among the group treated with peppermint capsules, while the placebo group showed no such change. The duration of pain did not present any significant differences between the two groups after the trial.
A Review Article published in 2016 in the journal Journal of Evidence-Based Complementary & Alternative Medicine found that Date palm pollen (DPP) containing various compounds has been used as an aphrodisiac and fertility enhancer historically and shows promise in treating fertility disorders. The study focused on the analysis of date palm pollen (DPP), the male reproductive dust of palm flowers, traditionally used as a dietary supplement, especially as a fertility enhancer. The research underlined the investigation of the various compounds isolated from DPP, which include amino acids, fatty acids, flavonoids, saponins, and estroles. The discussion of the results reveals that while there are a limited number of clinical trials evaluating the benefits of DPP in humans, a number of experimental studies have been conducted on the reproductive effects of DPP. These compounds and their effects potentially contribute to DPP's application in treating fertility disorders. It was concluded that DPP holds considerable promise in the context of fertility therapy, demonstrating key pharmacological activities that could be harnessed for treatment.
A Review Article published in 2015 in the journal Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics found that Among the bioactive compounds present in jujube fruit, triterpenic acids and polysaccharides have antiproliferative and anticancer effects on various cancer cell lines. Phytochemical data combined with information about biological activity confirm that jujube fruits are rich in bioactive compounds that can benefit human health. This review article shows that among the bioactive compounds present in jujube fruit, triterpenic acids and polysaccharides have antiproliferative and anticancer effects on various cancer cell lines. It seems that the induction of apoptosis is one of the main mechanisms for the anticancer activities of the jujube fruit, due to the presence of the bioactive compounds. However, the biological effects of other identified and unidentified compounds in these fruits should be also investigated in areas where there are suitable climatic conditions for the cultivation of these plants.
A Review Article published in 2013 in the journal British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology found that Cocoa and chocolate, rich in antioxidant molecules like epicatechin, enhance brain health, stimulate brain perfusion, and reduce the risk of Alzheimer's disease and stroke. The study involved taking a comprehensive look at the substances contained in cocoa powder and chocolate, their absorption into the brain, and their resulting stimulatory effects on multiple areas of the brain, particularly those connected to comprehension and memory. It also delved into the beneficial effects of epicatechin, a flavonoid found abundantly in cocoa and chocolate, which showed improvements in cognition in both animals and humans. Interestingly, the research showed that the consumption of chocolate could induce mood enhancement, elaborating on its common consumption during times of emotional stress. The study further investigated flavonoids' preservation of cognitive abilities in rats during aging, noting the reduced risk of developing Alzheimer's disease and the decreased likelihood of stroke in humans, demonstrating their wider effects beyond just mood enhancement. The research then looked into flavonoids' interactions within the various signaling pathways related to proteins and lipids in the brain, shedding light on how they inhibit neuron death from neurotoxic elements like oxygen radicals, all while promoting neuron survival and synaptic plasticity. The overall intent of the research was to gather and examine the available data regarding the effects of cocoa and chocolate on brain health and cognitive capacities.
A Experimental Study published in 2013 in the journal Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine found that Pomegranate juice can enhance memory function and brain activity in tasks related to verbal and visual memory in older adults experiencing memory problems. The study was a preliminary, placebo-controlled, randomized trial involving 32 older participants with memory complaints. They were randomly tasked to consume 8 ounces of either pomegranate juice or a placebo drink that had a similar flavor daily for a duration of 4 weeks. Before and after the study duration, the subjects underwent memory tests and functional MRI scans while involved in cognitive tasks. Additionally, blood samples were extracted to ascertain peripheral biomarkers. The test subjects and investigators were oblivious to the groupings to ensure objectivity. The results from the study pointed out that the group that had pomegranate juice had notable improvements in their verbal memory as determined by the Buschke selective reminding test and also a rise in their antioxidant capacity. This group also recorded increased fMRI activity during tasks related to verbal and visual memory in comparison to the placebo group. This may suggest that consumption of pomegranate juice may boost memory function by elevating functional brain activity during tasks.
A Clinical Study published in 2013 in the journal Journal of Nutritional Science found that Consuming two kiwifruits daily can improve overall mood, particularly for individuals starting with moderate mood disturbance. The research study investigated the potential mood-enhancing effects of kiwifruit, involving a sample group of 35 young adult males who were supplemented with either half or two kiwifruits a day for 6 weeks. Through this observational period, their moods were evaluated with the use of Profile of Mood States questionnaires that were administered at the start and end of the intervention. In the results discussion, it was noted that there was no observable effect on overall mood for the group that consumed half a kiwifruit daily. However, interestingly, for those who consumed two kiwifruits daily, there was a trend towards a decrease in total mood disturbance as well as depression. This was especially significant among participants with higher initial mood disturbance, showing decrease in mood disturbance and fatigue, and increase in vigour. This research also observed a significant increase in dietary vitamin C intake and corresponding plasma levels among the participants. There was no apparent effect of consuming two kiwifruits daily on the mood scores of participants with low initial mood disturbance.
Moderation Tools
Topic
Sign In
Users not signed in are limited to viewing the 5 most recent items of content.