Food As Medicine
How to submit an article:
- Registered users can submit any published journal article that has a unique DOI (Digital Object Identifier) name or link to Research Hub.
- For example, you can paste the full DOI link:
https://doi.org/10.1109/5.771073or just the DOI name:10.1109/5.771073into the field above and click submit. - The person who is first to submit a valid article to Research Hub will forever be credited for it, and every article submission earns you +6 Research Points.
Sub-Topics:
- Adzuki Bean
- Almond
- Apple
- Avocado
- Banana
- Bee Pollen
- Bitter Melon
- Black Pepper
- Blueberry
- Caraway
- Carrot
- Ceylon Cinnamon
- Chamomile
- Cherry
- Chilli
- Chinese Cinnamon
- Chrysanthemum
- Citrus Peel
- Cocoa
- Coffee
- Coix Seed
- Common Bean
- Cucumber
- Cumin
- Daikon
- Date Fruit
- Eggplant
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil
- Fennel Seed
- Fenugreek
- Food Nutrients
- Ginger
- Goji Berry
- Grapes
- Green Tea
- Honey
- Jujube
- Kiwifruit
- Lavender
- Lemon
- Lemongrass
- Lotus Seed
- Mediterranean Diet
- Mineral Water
- Mung Bean
- Mushroom
- Oats
- Peanut
- Pear
- Pecan
- Peppermint
- Plum
- Pomegranate
- Pu-Erh Tea
- Pumpkin
- Raspberry
- Raspberry Leaf
- Raw Milk
- Rice Congee
- Saffron
- Sardine
- Sesame
- Snow Fungus
- Soybean
- Spirulina
- Spring Onion
- Star Anise
- Strawberry
- Tomato
- Turmeric
- Walnut
- Watermelon
- Wheatgrass
- Yoghurt
Related Topics
Published research studies are articles that present the findings of original research that has undergone a peer-review process and has been made publicly available in scholarly journals, books or other media.

A systematic review of the therapeutic properties of lemon essential oil
2025 Sep Advances in Integrative Medicine Gonçalves S, Castro J, Almeida A, Monteiro M, Rodrigues T, Fernandes R, et al.
The results of the systematic review consistently demonstrated the efficacy of lemon essential oil in reducing anxiety among students, Acute myocardial infarction patients, and pre-surgical patients, as well as improving physiological benefits such as blood pressure and heart rate in Acute myocardial infarction patients and cognitive performance among students, and measures related to halitosis in oral health.
Systematic Review Halitosis Cognitive Function Myocardial Infarction Anxiety Lemon
Comparison of Ziziphus jujube Mill. Syrup versus polyethylene glycol in children with functional constipation: a randomized clinical trial
2025 Jan 11 Scientific Reports Keihanian F, Maleknejad S, Saeidinia A, Soltanipour S, Pirooz A
Clinical Study Randomised Controlled Trial Children's Health Constipation JujubeJujube syrup presented improved results in treating pediatric functional constipation compared to polyethylene glycol, demonstrating a potentially effective and safe alternative treatment.

Ziziphus jujube promotes fertility and pregnancy outcomes in Rat model of uterine adhesions
2025 Jan 27 Frontiers in Pharmacology Asgharzadeh F, Attarian M, Khazaei M, Al-Asady AM, Mansoori S, Naimi H, et al.
Treatment with resulted in a significant reduction in uterine tissue fibrosis, positive outcomes in embryonic development, pregnancy rates, and pregnancy outcomes, as well as inhibition of formation of extra-uterine adhesion bands to internal organs.
Animal Study Pregnancy Uterine Adhesion Endometriosis Jujube
Lactobacillus acidophilus 6074 Fermented Jujube Juice Ameliorated DSS‐induced Colitis via Repairing Intestinal Barrier, Modulating Inflammatory Factors, and Gut Microbiota
2024 Dec 15 Molecular Nutrition & Food Research Li H, Fan L, Yang S, Tan P, Lei W, Yang H, et al.
Animal Study Lactobacillus Gut Microbiota Colitis JujubeOral administration of Lactobacillus acidophilus 6074 fermented jujube juice can improve gut microbiota, alleviate intestinal inflammation, and reduce colon damage in mice.

Immunomodulatory Acidic Polysaccharide from Jujube Fruit (Zizyphus jujuba Mill.): Insight into Their Chemical Characteristics and Modes of Action
2024 Dec 20 Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry Feng L, Ju M, Ma C, Li K, Cai S
Experimental Study Animal Study JujubeThe ZJMP-2 polysaccharide fraction from jujube, consisting of various sugars and acid, significantly enhances immune cell activity and stimulates lymphocyte proliferation.
Research insights are moderated by the Research Hub team and offer an at-a-glance overview of interesting research findings.

2025 Scientific Reports
Jujube syrup presented improved results in treating pediatric functional constipation compared to polyethylene glycol, demonstrating a potentially effective and safe alternative treatment.
Clinical Study Children's Health Constipation Jujube
Comparison of Ziziphus jujube Mill. Syrup versus polyethylene glycol in children with functional constipation: a randomized clinical trial
Keihanian F, Maleknejad S, Saeidinia A, Soltanipour S, Pirooz A

2024 Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
The ZJMP-2 polysaccharide fraction from jujube, consisting of various sugars and acid, significantly enhances immune cell activity and stimulates lymphocyte proliferation.
Experimental Study Jujube
Immunomodulatory Acidic Polysaccharide from Jujube Fruit (Zizyphus jujuba Mill.): Insight into Their Chemical Characteristics and Modes of Action
Feng L, Ju M, Ma C, Li K, Cai S

2024 Molecular Nutrition & Food Research
Oral administration of Lactobacillus acidophilus 6074 fermented jujube juice can improve gut microbiota, alleviate intestinal inflammation, and reduce colon damage in mice.
Animal Study Colitis Gut Microbiota Jujube Lactobacillus
Lactobacillus acidophilus 6074 Fermented Jujube Juice Ameliorated DSS‐induced Colitis via Repairing Intestinal Barrier, Modulating Inflammatory Factors, and Gut Microbiota
Li H, Fan L, Yang S, Tan P, Lei W, Yang H, et al.

2024 International Journal of Biological Macromolecules
A polysaccharide from Tremella aurantialba improves ulcerative colitis symptoms by targeting epithelial cell ferroptosis and modulating the gut microbiota.
Experimental Study Gut Microbiota Intestinal Barrier Snow Fungus Ulcerative Colitis
Tremella aurantialba polysaccharides alleviate ulcerative colitis in mice by improving intestinal barrier via modulating gut microbiota and inhibiting ferroptosis
Peng G, Wang S, Zhang H, Xie F, Jiao L, Yuan Y, et al.

2024 Life
Pomegranate extract could potentially benefit women's reproductive health, enhance fertility, regulate menstrual cycles, support pregnancy, and help treat polycystic ovary syndrome.
Review Article Breast Cancer PCOS Pomegranate
Therapeutic Potential of Pomegranate Extract for Women’s Reproductive Health and Breast Cancer
Jang JY, Kim D, Im E, Kim ND
Review Articles
Review articles summarise and critically evaluate the current state of research on a specific topic or field by synthesising multiple primary research studies.

A systematic review of the therapeutic properties of lemon essential oil
2025 Sep Advances in Integrative Medicine Gonçalves S, Castro J, Almeida A, Monteiro M, Rodrigues T, Fernandes R, et al.
The results of the systematic review consistently demonstrated the efficacy of lemon essential oil in reducing anxiety among students, Acute myocardial infarction patients, and pre-surgical patients, as well as improving physiological benefits such as blood pressure and heart rate in Acute myocardial infarction patients and cognitive performance among students, and measures related to halitosis in oral health.
Systematic Review Halitosis Cognitive Function Myocardial Infarction Anxiety Lemon
Therapeutic Potential of Pomegranate Extract for Women’s Reproductive Health and Breast Cancer
2024 Oct 03 Life Jang JY, Kim D, Im E, Kim ND
Review Article PCOS Breast Cancer PomegranatePomegranate extract could potentially benefit women's reproductive health, enhance fertility, regulate menstrual cycles, support pregnancy, and help treat polycystic ovary syndrome.

Ziziphus jujuba (Jujube) in Metabolic Syndrome: From Traditional Medicine to Scientific Validation
2024 Oct 01 Current Nutrition Reports Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar M, Fazeli Kakhki H, Hosseinzadeh H
Review Article Obesity Type 2 Diabetes Metabolic Syndrome High Blood Pressure JujubeZiziphus jujuba and its main components, lupeol and betulinic acid, show promise in treating complications of metabolic syndrome, including diabetes, obesity, and hypertension.

The effect of consumption Ziziphus jujuba on metabolic factors: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
2024 Jun Clinical Nutrition Open Science Heydarian A, Tahvilian N, Shahinfar H, Abbas-Hashemi SA, Bahari H, Cheshmeh S, et al.
Meta-Analysis Systematic Review Metabolic Syndrome JujubeDaily intake of Ziziphus jujuba can control weight and improve lipid profile indicators.
The Potential Role of Ziziphus Jujube in the Management of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy
2024 Jun 30 Journal of Tumor Science Research , Talabaki H, Salehifar E,
The review highlights the promising experimental data on Ziziphus extracts and pure active compounds in the treatment of neuropathy.
Review Article Peripheral Neuropathy Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Chemotherapy JujubeClinical Trials
Clinical trials are research studies that involve people and are conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of new treatments or interventions, such as drugs, medical devices, or behavioural therapies.

Comparison of Ziziphus jujube Mill. Syrup versus polyethylene glycol in children with functional constipation: a randomized clinical trial
2025 Jan 11 Scientific Reports Keihanian F, Maleknejad S, Saeidinia A, Soltanipour S, Pirooz A
Clinical Study Randomised Controlled Trial Children's Health Constipation JujubeJujube syrup presented improved results in treating pediatric functional constipation compared to polyethylene glycol, demonstrating a potentially effective and safe alternative treatment.

The effects of jujube (Ziziphus jujube) on metabolic and mental health outcomes in patients with metabolic syndrome: A randomized controlled trial
2024 Jun Complementary Therapies in Medicine Parastouei K, Nashtar SB, Al-Attar Z, Shekarchizadeh-Esfahani P, Askari G
Randomised Controlled Trial Stress Triglyceride Cholesterol JujubeConsuming jujube notably reduces waist circumference, triglycerides, and stress, while increasing high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in subjects with metabolic syndrome.

Walnut Consumption Improves Sleep Quality: A Randomized-Controlled Trial
2024 Feb 28 The 14th European Nutrition Conference FENS 2023 Izquierdo-Pulido M, Zerón-Rugerio MF, Ibarra-Picón A, Diez-Hernández M, Pérez-Cano F, Cambras T
Randomised Controlled Trial Sleep WalnutDaily consumption of walnuts improves sleep quality and reduces daytime sleepiness in healthy young adults.

Concurrent training associated with moderate walnut consumption improved isokinetic strength, subjective sleep quality, cognitive performance and postural balance in elderly active men: a randomized controlled trial
2024 Feb 29 Aging Clinical and Experimental Research Kamoun A, Yahia A, Farjallah MA, Maaloul R, Marzougui H, Bouaziz M, et al.
Randomised Controlled Trial Postural Balance Cognitive Function Sleep WalnutWalnut consumption while doing concurrent training improves strength, sleep quality, standing support, cognitive performance and postural balance in elderly men.

A dietary intervention for postmenopausal hot flashes: A potential role of gut microbiome. An exploratory analysis
2023 Dec Complementary Therapies in Medicine Kahleova H, Holtz DN, Strom N, La Reau A, Kolipaka S, Schmidt N, et al.
Randomised Controlled Trial Plant-Based Diet Low Fat Diet Gut Microbiota SoybeanChanges in gut microbiome associated with a low-fat, vegan diet and cooked soybeans may reduce the frequency and severity of postmenopausal hot flashes.
Study Protocols
Published study protocols are detailed plans that outline the objectives, methodology, statistical analyses, and organisation of a research study that have been made publicly available for others to review and use as a reference.
Presentation Slides

Clinical Study
Jujube syrup presented improved results in treating pediatric functional constipation compared to polyethylene glycol, demonstrating a potentially effective and safe alternative treatment.
Keihanian F, Maleknejad S, Saeidinia A, Soltanipour S, Pirooz A

Experimental Study
The ZJMP-2 polysaccharide fraction from jujube, consisting of various sugars and acid, significantly enhances immune cell activity and stimulates lymphocyte proliferation.
Feng L, Ju M, Ma C, Li K, Cai S

Animal Study
Oral administration of Lactobacillus acidophilus 6074 fermented jujube juice can improve gut microbiota, alleviate intestinal inflammation, and reduce colon damage in mice.
Li H, Fan L, Yang S, Tan P, Lei W, Yang H, Gao Z

Experimental Study
A polysaccharide from Tremella aurantialba improves ulcerative colitis symptoms by targeting epithelial cell ferroptosis and modulating the gut microbiota.
Peng G, Wang S, Zhang H, Xie F, Jiao L, Yuan Y, Ma C, Wu H, Meng Z

Review Article
Pomegranate extract could potentially benefit women's reproductive health, enhance fertility, regulate menstrual cycles, support pregnancy, and help treat polycystic ovary syndrome.
Jang JY, Kim D, Im E, Kim ND

Review Article
Ziziphus jujuba and its main components, lupeol and betulinic acid, show promise in treating complications of metabolic syndrome, including diabetes, obesity, and hypertension.
Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar M, Fazeli Kakhki H, Hosseinzadeh H

Animal Study
Manuka honey has demonstrated the potential to inhibit the proliferation of human breast cancer cells and stimulate apoptosis in these cells.
Márquez-Garbán DC, Yanes CD, Llarena G, Elashoff D, Hamilton N, Hardy M, Wadehra M, McCloskey SA, Pietras RJ

Meta-Analysis
Daily intake of Ziziphus jujuba can control weight and improve lipid profile indicators.
Heydarian A, Tahvilian N, Shahinfar H, Abbas-Hashemi SA, Bahari H, Cheshmeh S, Aryaeian N

Randomised Controlled Trial
Consuming jujube notably reduces waist circumference, triglycerides, and stress, while increasing high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in subjects with metabolic syndrome.
Parastouei K, Nashtar SB, Al-Attar Z, Shekarchizadeh-Esfahani P, Askari G

Animal Study
Jujube fruit extracts significantly alleviate oxidative stress in rodent models, potentially offering a valuable dietary supplement against diseases linked to oxidative stress.
Zhu D, Zhu Y, Tan H, Ding R, Dai Q, Du X, Liu Y, Yue R

Cohort Study
Greater intake of blueberries considerably decreases the risk of age-related macular degeneration, while a remarkable dietary intake of anthocyanins inversely correlates with cataract incidents.
Sesso HD, Rautiainen S, Park SJ, Kim E, Lee IM, Glynn RJ, Buring JE, Christen WG

Randomised Controlled Trial
Walnut consumption while doing concurrent training improves strength, sleep quality, standing support, cognitive performance and postural balance in elderly men.
Kamoun A, Yahia A, Farjallah MA, Maaloul R, Marzougui H, Bouaziz M, Souissi N, Elleuch MH, Hammouda O

Randomised Controlled Trial
Daily consumption of walnuts improves sleep quality and reduces daytime sleepiness in healthy young adults.
Izquierdo-Pulido M, Zerón-Rugerio MF, Ibarra-Picón A, Diez-Hernández M, Pérez-Cano F, Cambras T

Systematic Review
Eating plums, especially dried plums, significantly lowers LDL levels and total cholesterol levels, particularly in adults with existing health issues.
Heydarian A, Tahvilian N, Asbaghi O, Cheshmeh S, Nadery M, Aryaeian N

Review Article
Lemongrass essential oil can effectively treat periodontitis, gingivitis, oral malodour, skin aging, and dandruff, and it is comparable to certain established treatments.
Kusuma IY, Perdana MI, Vágvölgyi C, Csupor D, Takó M

Review Article
Jujube, a Chinese native plant with numerous active components, exhibits calming effects, nourishes blood, and strengthens the spleen and stomach, alongside promising neuroprotective and cardiovascular benefits.
Zhu D, Jiang N, Wang N, Zhao Y, Liu X

Data Mining
The traditional Chinese medicine prescription combination of Chrysanthemi Flos, Cassiae Semen, Lycii Fructus, Angelicae Sinensis Radix and Salviae Miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizoma presents potential for treating retinal diseases.
Zhang JX, Zhang KL, Chang XW, Gu JF, Wei SB, Zhu BY, Wang Q, Wu DL, Gui SY, Yan H, Duan JA

Meta-Analysis
Consuming carrots can significantly decrease the risk of cancer.
Ojobor CC, O’Brien GM, Siervo M, Ogbonnaya C, Brandt K

Systematic Review
Pomegranate fruit and its phytochemicals may offer a novel, natural alternative for the treatment of pathological anxiety, with fewer adverse effects than traditional medications.
Flores-Bazán T, Betanzos-Cabrera G, Guerrero-Solano JA, Negrete-Díaz JV, German-Ponciano LJ, Olivo-Ramírez D

Randomised Controlled Trial
Changes in gut microbiome associated with a low-fat, vegan diet and cooked soybeans may reduce the frequency and severity of postmenopausal hot flashes.
Kahleova H, Holtz DN, Strom N, La Reau A, Kolipaka S, Schmidt N, Hata E, Znayenko-Miller T, Holubkov R, Barnard ND

Experimental Study
The compound (Z)-5’-Hydroxyjasmone 5’-O-β-D-Glucopyranoside from chrysanthemum flowers demonstrated superior antioxidant and anti-osteoporosis effects.
Le The Hoai, Nguyen Thi Huong, Bui Thi Thu Trang

Systematic Review
Pomegranate can significantly enhance women's health during and after menopause by reducing hot flashes severity and other menopause symptoms.
Moeini R, Shirafkan H, Gorji N

Review Article
Almond consumption has beneficial impacts on cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, obesity, and it can improve cognitive performance and protect against skin aging.
Ouzir M

Experimental Study
Fructus Lycii and Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge extract (FSE) shows potential as a clinical treatment for retinitis pigmentosa by inhibiting photoreceptor cell death following oxidative stress.
Yang Y, Wang Y, Deng Y, Lu J, Xiao L, Li J, Zhou Y, Nie F, Chen X, Peng J, Tan H, Qin Y, Peng Q

Review Article
Fruits, especially kiwifruits, and rye bread can enhance bowel movements and help manage chronic constipation better than conventional dietary methods.
Van Der Schoot A, Katsirma Z, Whelan K, Dimidi E

Cohort Study
Long-term consumption of green tea can potentially lessen the risk of depression in postmenopausal women by decreasing inflammation and boosting estradiol levels.
Wan Z, Qin X, Tian Y, Ouyang F, Wang G, Wan Q

Clinical Study
Consuming bicarbonate-calcium mineral water, low in sodium, can help manage calcium imbalance and support bone health in perimenopausal women.
Marino C, Pagano I, Castaldo G, Grimaldi M, D’Elia M, Santoro A, Conte A, Molettieri P, Parisella C, Buonocore M, D’Ursi AM, Rastrelli L

Animal Study
A combination of soybean germ extract and a probiotic significantly improved menopause-related conditions and mood in an ovariectomized rat model.
Lee SH, Lim TJ, Yun EJ, Kim KH, Lim S

Experimental Study
A combination of Walnut Peptide and Casein Peptide substantially alleviates anxiety disorder symptoms and enhances memory by improving neurotransmitter function in mice.
Li Q, Jia X, Zhong Q, Zhong Z, Wang Y, Tang C, Zhao B, Feng H, Hao J, Zhao Z, He J, Zhang Y

Experimental Study
Phenolic extracts from turmeric and ginger have significant anti-inflammatory effects and enhance wound healing in Wistar rats.
Bouchama C, Zinedine A, Rocha JM, Chadli N, El Ghadraoui L, Chabir R, Raoui SM, Errachidi F

Network Pharmacology
The research unveils luteolin, quercetin, and kaempferol in RALRG as promising complementary components for RP treatment, with a key role in managing oxidative stress and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways.
Wu J, Sun Z, Zhang D, Liu H, Wu J, Zhang S

Review Article
Pomegranate and its by-products, particularly the peel, contain bioactive compounds with potential antimicrobial, anticancer and antiviral properties.
Valero-Mendoza AG, Meléndez-Rentería NP, Chávez-González ML, Flores-Gallegos AC, Wong-Paz JE, Govea-Salas M, Zugasti-Cruz A, Ascacio-Valdés JA

Randomised Controlled Trial
A beverage formula containing fish roe, snow fungus, and yeast enhances cognitive function by improving memory, response times, and emotional recognition, while reducing anxiety and fatigue.
Lin YK, Lin YH, Chiang CF, Jingling L

Review Article
The bioactive peptides found in walnuts have potential neuroprotective effects, including reducing oxidative stress and neuroinflammation, and promoting autophagy and balance in the cholinergic system.
Zhang L, Bai YY, Hong ZS, Xie J, Tian Y

Randomised Controlled Trial
Daily consumption of pecans for a month can help protect against post-meal oxidative stress in aging adults.
Cogan B, Pearson RC, Jenkins NT, Paton CM, Cooper JA

Experimental Study
Lycium barbarum polysaccharide may decrease apoptosis in retinal photoreceptor cells of retinitis pigmentosa mice by suppressing nuclear factor-kappa B/NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain-associated protein 3 pathway.
Wang Y, Deng Y, Lu J, Peng J, Zhou Y, Yang Y, Peng Q

Review Article
Soy protein, bioactive peptides, and isoflavones are generally safe for consumption and may help reduce the risk of several significant health conditions.
Tan ST, Tan SS, Tan CX

Systematic Review
Pomegranate consumption positively affects triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels.
Bahari H, Rezaiian F, Goudarzi K, Nooshan Mirmohammadali S, Asbaghi O, sadat Hosseini kolbadi K, Naderian M, Hosseini A

Review Article
Plums, which are rich in bioactive compounds, antioxidants, and vitamins, can help maintain blood glucose level, bone health, heart health and even treat certain cancers.
Ayub H, Nadeem M, Mohsin M, Ambreen S, Khan F, Oranab S, Rahim M, Zubair khalid M, Zongo E, Zarlasht M, Ullah S

Network Pharmacology
The compounds apocarotenoids and carotenoids found in saffron extract could potentially interact with multiple targets, helping to manage the symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome.
Tiwari A, Modi SJ, Girme A, Hingorani L

Experimental Study
Moderate consumption of blueberries may effectively reduce bone loss in healthy postmenopausal women.
Hodges JK, Maiz M, Cao S, Lachcik PJ, Peacock M, McCabe GP, McCabe LD, Cladis DP, Jackson GS, Ferruzzi MG, Lila MA, Bailey RL, Martin BR, Weaver CM

Meta-Analysis
Blueberry consumption significantly improves two-back test accuracy, suggesting potential cognitive benefits.
Soveid N, Barkhidarian B, Moradi S, Gholami F, Rasaei N, Himmerich H, Mirzaei K

Network Pharmacology
Gold kiwifruit extracts contained different bioactive materials which showed selective cytotoxic activity against human oral tumor cells and displayed anti-HIV, antioxidant, and antibacterial activities.
Motohashi N, Shirataki Y, Kawase M, Tani S, Sakagami H, Satoh K, Kurihara T, Nakashima H, Mucsi I, Varga A, Molnár J

Experimental Study
The fermented jujube seeds extract significantly enhances sleep by binding to the GABA receptors, thus offers a promising natural alternative for sleep disorders treatment.
Bae GY, Ahn Y, Hong KB, Jung EJ, Suh HJ, Jo K

Review Article
The Mediterranean diet and reduced intake of trans fatty acids, saturated fatty acids, and discretionary foods like fast food and sugar-sweetened beverages may improve fertility rates.
Alesi S, Habibi N, Silva TR, Cheung N, Torkel S, Tay CT, Quinteros A, Winter H, Teede H, Mousa A, Grieger JA, Moran LJ

Systematic Review
Natural calcium-rich mineral waters offer a bioavailable calcium source, beneficial for bone health, cardiovascular function, weight management, and overall well-being.
Pop MS, Cheregi DC, Onose G, Munteanu C, Popescu C, Rotariu M, Turnea MA, Dograru G, Ionescu EV, Oprea D, Iliescu MG, Minea M, Stanciu LE, Silișteanu SC, Oprea C

Systematic Review
There is evidence to support significant improvements to total sleep time and sleep efficiency with the ingestion of tart cherries.
Stretton B, Eranki A, Kovoor J, Bacchi S, Gupta A, Maddern G, Boyd M

Review Article
Honey intake has observed beneficial effects on various health aspects like cardiovascular, metabolic risk factors, and wound healing, primarily replacing other sweeteners.
Palma-Morales M, Huertas JR, Rodríguez-Pérez C

Animal Study
Jin Si Huang Ju tea, a traditional Chinese beverage, contains compounds that potentially reduce lipids, mitigate insulin resistance and reduce liver inflammation in vitro.
Li X, Li R, Wang X, Zhang X, Xiao Z, Wang H, Sun W, Yang H, Yu P, Hu Q, Guo Q, Sun H

Systematic Review
Oat consumption can significantly improve lipid profiles, particularly reducing total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol, with potential positive effects on triglycerides and HDL cholesterol under certain conditions.
Amerizadeh A, Ghaheh HS, Vaseghi G, Farajzadegan Z, Asgary S

Review Article
Nutrition, particularly an anti-inflammatory Mediterranean diet supplemented with oily fish and omega-3 supplements, can potentially reduce inflammation and improve symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
Nikiphorou E, Philippou E

Review Article
Crocin, a compound derived from saffron, has shown considerable potential in hindering tumor growth and improving immune status, across various malignant tumors.
Bao X, Hu J, Zhao Y, Jia R, Zhang H, Xia L

Cohort Study
Young coconut water has been found to be more effective than carrot juice in reducing the severity of dysmenorrhea in teenage girls.
Candra Wahyuni

Systematic Review
Vitamin D supplementation significantly reduces pain levels in people suffering from primary dysmenorrhea.
Chen YC, Chiang YF, Lin YJ, Huang KC, Chen HY, Hamdy NM, Huang TC, Chang HY, Shieh TM, Huang YJ, Hsia SM

Review Article
Eating apples and apple products can enhance health by protecting the cardiovascular system, combating cancer and cognitive impairment, and improving hair growth, among other beneficial effects.
Zhang Y, Zeng M, Zhang X, Yu Q, Zeng W, Yu B, Gan J, Zhang S, Jiang X

Experimental Study
Zhangyanming Tablets show potential as a protective agent for retinal function in early-stage, genetically-caused blindness in mice, possibly due to their antioxidant and anti-/pro-apoptotic properties.
Huang Z, Huang Q, Xu K, Liang L, Li Y, Zhou W, Ning N, Zhou J, Hu J, Liu S, Dang L

Randomised Controlled Trial
Consumption of blueberry powder daily improves vascular function, cognitive abilities, and reduces blood pressure in healthy older individuals.
Wood E, Hein S, Mesnage R, Fernandes F, Abhayaratne N, Xu Y, Zhang Z, Bell L, Williams C, Rodriguez-Mateos A

Experimental Study
Bee-collected pollen and bee bread, particularly when artificially fermented, demonstrate significant antiviral activity against the H1N1 strain of the influenza A virus.
Dimitriou T, Asoutis Didaras N, Barda C, Skopeliti D, Kontogianni K, Karatasou K, Skaltsa H, Mossialos D

Clinical Study
Consuming two medium-sized green kiwifruits an hour before bed can improve sleep quality and recovery stress balance among elite athletes.
Doherty R, Madigan S, Nevill A, Warrington G, Ellis JG

Review Article
Berry fruits such as blueberries, cranberries, raspberries, and strawberries could potentially improve gut microbiota and reverse dysbiosis in chronic kidney disease patients.
Coutinho-Wolino KS, Melo MFS, Mota JC, Mafra D, Guimarães JT, Stockler-Pinto MB

Systematic Review
Saffron shows promising improvements in dealing with women's health issues related to labor, childbirth, premenstrual syndrome and menopause.
Irani M, Rahmanian A, Soltani N

Randomised Controlled Trial
Walnut consumption may improve attention, fluid intelligence, and reduce ADHD symptoms in adolescents who consistently incorporated them into their diet.
Pinar-Martí A, Gignac F, Fernández-Barrés S, Romaguera D, Sala-Vila A, Lázaro I, Ranzani OT, Persavento C, Delgado A, Carol A, Torrent J, Gonzalez J, Roso E, Barrera-Gómez J, López-Vicente M, Boucher O, Nieuwenhuijsen M, Turner MC, Burgaleta M, Cana

Systematic Review
Honey dressing significantly promotes healing and reduces recovery time in managing diabetic foot ulcers.
Yildiz Karadeniz E, Kaplan Serin E

Systematic Review
Consumption of natural mineral water increases diuresis in both humans and animals, evident sometimes after just one intake.
Vitali M, Fontana M, De Giorgi A, Marotta D, Crucianelli S, Antonucci A, Protano C

Review Article
Sardines, being an affordable source of Omega-3 and other cardioprotective nutrients, can potentially reduce the need for Omega-3 supplementation and manage cardiometabolic diseases.
Santos HO, May TL, Bueno AA

Experimental Study
The anthocyanins from the Gardenblue variety of blueberries exhibit strong antiproliferative effects on various cancer cells, especially liver cancer cells.
Zhao F, Wang J, Wang W, Lyu L, Wu W, Li W
Case Report
The combination of epigallocatechin gallate, vitamin B12, folic acid, and hyaluronic acid could effectively counter precancerous lesions of the uterine cervix caused by HPV infections.
Grandi G, Botticelli L, Fraia PD, Babalini C, Masini M, Unfer V

Clinical Study
Consuming a honey-based gel, such as 'Bear Strength honey gel,' led to a notable reduction in diastolic and mean arterial blood pressure, with gender-specific improvements in redox status among healthy adults.
Patouna A, Sevdalis P, Papanikolaou K, Kourti M, Skaperda Z, Jamurtas A, Kouretas D

Review Article
Green tea helps alleviate symptoms in multiple benign gynecological disorders, primarily due to a compound called Epigallocatechin-3-gallate.
Hazimeh D, Massoud G, Parish M, Singh B, Segars J, Islam MS

Randomised Controlled Trial
Consumption of fresh or dried kiwifruit in the evening improves aspects of sleep quality and mood, potentially mediated through changes in serotonin metabolism.
Kanon AP, Giezenaar C, Roy NC, McNabb WC, Henare SJ

Randomised Controlled Trial
A combination of epigallocatechin gallate, folic acid, vitamin B12, and hyaluronic acid may effectively clear HPV infections and cervical lesions in women.
Aragona C, Bezerra Espinola MS, Bilotta G, Porcaro G, Calcagno M

Randomised Controlled Trial
Korean pear extracts appear to alleviate air pollution-related respiratory hypersensitivity by modulating beneficial gut microflora and suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Yang M, Lee U, Cho HR, Lee KB, Shin YJ, Bae MJ, Park KY

Randomised Controlled Trial
Cinnamon, ginger, and mint enhanced chocolates effectively reduce menstrual pain and improve blood iron levels without increasing body weight or negatively affecting cholesterol.
Shalaby, A, Moawad O, Mostafa M

Systematic Review
Our dose-response analysis indicated that moderate green tea consumption (500–1000 mL/d) was associated with a 21% to 24% lower risk of stroke.
Wang ZM, Chen B, Zhou B, Zhao D, Wang LS

Systematic Review
Almond consumption can significantly reduce the serum concentration of the inflammatory mediator, Interleukin-6, in adults but no significant effect is found on C-reactive protein.
Hariri M, Amirkalali B, Baradaran HR, Gholami A

Cohort Study
Ginger consumption could counteract the negative influence of disgust, induced by sexual body fluids, on sexual arousal in individuals.
Wen G, Zhang Y, Nyman TJ, Jern P, Santtila P

Experimental Study
Chrysanthemum morifolium contains natural bioactive compounds, including 29 types of phenolics, which display significant antioxidant activity.
Youssef H, Ali S, Sanad M, Dawood D

Review Article
Oats, in various edible forms, can regulate appetite hormones, aid weight management, strengthen the immune system, and contribute to gut health, making them effective for obesity management.
Shehzad A, Rabail R, Munir S, Jan H, Fernández-Lázaro D, Aadil RM

Review Article
Australian native plums contain phytochemicals that exhibit health benefits such as cardiovascular and liver protection.
Li J, Liu H, Mazhar MS, Quddus S, Agar OT, Suleria HAR

Systematic Review
Saffron supplementation significantly decreased oxidative stress markers and has beneficial effects in reducing oxidative stress.
Abedi A, Ghobadi H, Sharghi A, Iranpour S, Fazlzadeh M, Aslani MR
Randomised Controlled Trial
Bicarbonate-rich mineral water “Staatl. Fachingen STILL” significantly reduces heartburn more effectively than placebo, improving patients’ quality of life.
Labenz J, Anschütz M, Walstab J, Wedemeyer RS, Wolters H, Schug B

Cohort Study
Regular consumption of raw carrots is associated with a significant, dose-dependent reduction in lung cancer incidence, suggesting a potential cancer-protective effect attributed to polyacetylenic compounds, particularly falcarinol and falcarindiol, present in raw carrots.
Deding U, Baatrup G, Kaalby L, Kobaek-Larsen M

Clinical Study
Avocado consumption correlates with a wider variety of healthier food choices, offering potential benefits for weight control strategies.
Guan VX, Neale EP, Probst YC

Randomised Controlled Trial
Pomegranate extract supplements can help improve clinical symptoms and lower blood cell counts associated with inflammation in patients with allergic asthma.
Hosseini SA, Shateri Z, Abolnezhadian F, Maraghi E, Haddadzadeh Shoushtari M, Zilaee M

Randomised Controlled Trial
Pomegranate juice supplementation has been found to effectively decrease testosterone levels in overweight and obese women diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome.
Abedini M, Ramezani‐Jolfaie N, Ghasemi‐Tehrani H, Tarrahi MJ, Amani R

Review Article
Carrot and carotene consumption could diminish the risk of a wide range of negative health consequences, including multiple types of cancer.
Yi X, Li J, Liao D, Peng G, Zheng X, Xu H, Zhang T, Ai J
Review Article
Honey exhibits multifaceted benefits for brain health, acting as a memory booster, neuroprotective agent, anti-stress, and anti-nociceptive substance, fostering potential therapeutic applications to enhance overall cognitive well-being.
Zamri NA, Ghani N, Ismail CAN, Zakaria R, Shafin N

Randomised Controlled Trial
The combination of dark chocolate with herbs could be one of the therapies for period pain.
Azizah RNP, Anggreini P, Prasetya F

Cohort Study
Heavy coffee consumption increases the risk of cardiovascular disease mortality in individuals with severe hypertension, while green tea consumption does not.
Teramoto M, Yamagishi K, Muraki I, Tamakoshi A, Iso H

Animal Study
Specific fractions of Lycium barbarum, commonly known as Goji berry, reduce heart and kidney damage caused by anthracyclines while possibly enhancing their therapeutic effects.
Hvarchanova N, Stoeva S, Radeva-Ilieva M, Zhelev I, Georgieva M, Dzhenkov D, Georgiev KD

Cohort Study
Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a green tea component, showed potential in treating uterine fibroids and associated infertility without causing liver toxicity or folate deficiency.
Siblini H, Al-Hendy A, Segars J, González F, Taylor HS, Singh B, Flaminia A, Flores VA, Christman GM, Huang H, Johnson JJ, Zhang H

Clinical Study
Chrysanthemum extract can be utilised as a natural ingredient to lessen post-meal cholesterol levels and enhance antioxidant status, after eating a high-fat meal.
Chen L, Sun J, Pan Z, Lu Y, Wang Z, Yang L, Sun G

Network Pharmacology
Chrysanthemum has several active ingredients that can potentially treat dry eye by inhibiting inflammation-related factors and pathways, thus reducing inflammation of lacrimal gland tissue.
Cao LY, Long Q, Jiang PF, Peng J, Peng QH

Experimental Study
A novel compound in walnuts, defined as 3-hydroxy-4-iminobutyric acid, can enhance sleep duration by disturbing motor activity and adjusting certain neurotransmitters in the brain of mice.
Ji J, Ye Y, Sheng L, Sun J, Hong Q, Liu C, Ding J, Geng S, Xu D, Zhang Y, Sun X

Review Article
Pomegranate and its active components can protect against natural and chemical toxic agents, impacting mechanisms such as oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, and liver or cardiac function regulation.
Hosseini A, Razavi BM, Hosseinzadeh H

Review Article
Through innovative refinement, nanocurcumin, evolved from turmeric's primary component curcumin, has improved characteristics and pharmaceutical potential, particularly in drug delivery systems.
Jyotirmayee B, Nayak SS, Mohapatra N, Sahoo S, Mishra M, Mahalik G

Experimental Study
Pu-erh tea can potentially prevent depression-like behaviors induced by nighttime blue light from electronic devices by reshaping gut microbiota and increasing short-chain fatty acids generation.
Zhao S, Hu S, Sun K, Luo L, Zeng L

Review Article
Consumption of tea and coffee may possibly provide anti-inflammatory effects, contributing to reduced cardiovascular risk and mortality.
Surma S, Sahebkar A, Banach M

Network Pharmacology
Compound Chrysanthemum extract may alleviate visual fatigue through its interaction with several components, targets, and pathways.
Qiu J, Zheng B, Zhou H, Ye C, Shi M, Shi S, Wu S

Experimental Study
Vincentka natural mineral water reduces gastric damage and improves antioxidant capacity in an animal model of acute gastric ulcers.
BUDINSKAYA K, NÁDENÍČEK J, STRAČINA T, HENDRYCH M, PÍREK O, BARTÁKOVÁ A, ŠUDÁKOVÁ M, SVÍZELA V, NOVÁKOVÁ Z, NOVÁKOVÁ M, BABULA P

Randomised Controlled Trial
Consuming green kiwifruits is associated with a clinically relevant increase of ≥ 1.5 complete spontaneous bowel movements per week in those experiencing constipation.
Gearry R, Fukudo S, Barbara G, Kuhn-Sherlock B, Ansell J, Blatchford P, Eady S, Wallace A, Butts C, Cremon C, Barbaro MR, Pagano I, Okawa Y, Muratubaki T, Okamoto T, Fuda M, Endo Y, Kano M, Kanazawa M, Nakaya N, Nakaya K, Drummond L

Systematic Review
Menthacarin, derived from peppermint and caraway oil, effectively reduces symptoms, offers a safe alternative to risky drugs like cisapride, and shows promise for managing stomach problems in primary care.
Madisch A, Frieling T, Zimmermann A, Hollenz M, Labenz J, Stracke B, Miehlke S

Systematic Review
Avocado consumption may lead to a reduction in total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in people with high cholesterol without impacting body weight.
James-Martin G, Brooker PG, Hendrie GA, Stonehouse W

Review Article
Carrot's bioactive compounds can regulate immune response, reduce oxidative stress, and prevent damaging oxidative destruction, making it a potential preventive tool for various diseases.
Anjani G, Ayustaningwarno F, Eviana R

Systematic Review
Tart cherry juice shows promise in aiding blood sugar control and supporting heart health, highlighting its potential as a natural dietary addition.
Moosavian SP, Maharat M, Chambari M, Moradi F, Rahimlou M

Animal Study
Pu-erh tea and its ingredient theabrownin improve liver, jejunum, and adipose tissue functions in metabolic syndrome mice, modulating circadian rhythm, glycerophospholipid, and linoleic acid metabolism.
Hou Y, Zhang Z, Cui Y, Peng C, Fan Y, Tan C, Wang Q, Liu Z, Gong J

Randomised Controlled Trial
Drinking pomegranate juice and sumac can help reduce symptoms in outpatients diagnosed with COVID-19, alongside standard treatment.
Forouzanfar F, Ahmadpoor M, Farahi MM, Hadianfar A, Sahebkar A, Esmaily H, Nematy M, Rakhshandeh H

Randomised Controlled Trial
In women with polycystic ovary syndrome, cinnamon reduced insulin resistance and testosterone levels similar to metformin, and ginger decreased follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones.
Dastgheib M, Barati-Boldaji R, Bahrampour N, Taheri R, Borghei M, Amooee S, Mohammadi-Sartang M, Wong A, Babajafari S, Mazloomi SM

Experimental Study
The type of dairy production system can influence the overall and specific levels of microRNAs, potentially affecting the functional potential of dairy products.
Abou el qassim L, Alonso J, Zhao K, Le Guillou S, Diez J, Vicente F, Fernández-Sanjurjo M, Iglesias-Gutiérrez E, Guan L, Royo LJ

Cohort Study
Frequent consumption of sugar-sweetened coffee can adversely affect blood sugar control in patients with diabetes mellitus in Korea.
Yoo H, Park K

Randomised Controlled Trial
Walnut consumption improves mental health indicators and negates some negative effects of academic stress on students' health and gut microbiota, especially in females.
Herselman MF, Bailey S, Deo P, Zhou XF, Gunn KM, Bobrovskaya L

Experimental Study
The ethanol extract from green kiwifruit peel enhances sleep duration and onset, proving to be a potential natural aid for treating sleep disorders.
Kim D, Yoon M, Kim S, Um MY, Cho S

Review Article
Green tea's catechins demonstrate therapeutic effects against neurodegenerative diseases via anti-inflammatory, antioxidant actions, and activating diverse brain cellular pathways.
Afzal O, Dalhat MH, Altamimi ASA, Rasool R, Alzarea SI, Almalki WH, Murtaza BN, Iftikhar S, Nadeem S, Nadeem MS, Kazmi I

Network Pharmacology
Manuka honey exhibits a dual role in immune modulation, triggering a pro-inflammatory response by elevating cytokine expression and neutrophil recruitment via TLR signaling, while also influencing the phenotypic and functional maturation of macrophages.
Masad RJ, Nasser RA, Bashir G, Mohamed YA, Al-Sbiei A, Al-Saafeen BH, Fernandez-Cabezudo MJ, Al-Ramadi BK

Review Article
Chinese jujube contains cAMP, a compound usually absent in plant cells, which may accelerate our understanding of plant cAMP metabolism.
Yuan Y, Liu ZG, Feng C, Liu MJ

Experimental Study
Pu-erh tea, through the increase of Cinnabarinic acid, can improve obesity induced by circadian rhythm disorders by enhancing fat metabolism and altering gut microbes.
Hu S, Hu C, Luo L, Zhang H, Zhao S, Liu Z, Zeng L

Randomised Controlled Trial
Pomegranate extract consumption improves antioxidant levels, reduces oxidative stress and cardiovascular risk factors including blood pressure and body fat, and increases lean body mass.
Al-Dujaili EAS, Casey C, Stockton A

Review Article
Walnuts, rich in anti-inflammatory ingredients, potentially regulate neuroinflammation, improve cognitive function, reduce oxidative stress, and maintain gut health, thereby suggesting their use against neurodegenerative diseases.
Tan B, Wang Y, Zhang X, Sun X

Randomised Controlled Trial
A diet low in fat, vegan, and inclusive of daily cooked soybeans significantly reduces the frequency and severity of hot flashes in postmenopausal women.
Barnard ND, Kahleova H, Holtz DN, Znayenko-Miller T, Sutton M, Holubkov R, Zhao X, Galandi S, Setchell KDR

Randomised Controlled Trial
Two gold kiwifruit daily are as effective as fiber-matched psyllium in treating constipation in adults and should be considered as a treatment option.
Bayer SB, Heenan P, Frampton C, Wall CL, Drummond LN, Roy NC, Gearry RB

Systematic Review
Kiwifruit and kiwifruit extracts may have a positive impact on constipation in adults by increasing weekly bowel movements, reducing abdominal pain, and minimizing straining.
Eltorki M, Leong R, Ratcliffe EM

Systematic Review
Meta-analysis indicates that fruit consumption, particularly kiwifruits, effectively alleviates constipation symptoms, offering valuable insights into improving gut health.
Huo J, Wu L, Lv J, Cao H, Gao Q

Randomised Controlled Trial
A daily intake of 50 grams of prunes can maintain hip bone density in postmenopausal women, potentially reducing hip fracture risks.
De Souza MJ, Strock NCA, Williams NI, Lee H, Koltun KJ, Rogers C, Ferruzzi MG, Nakatsu CH, Weaver C

Randomised Controlled Trial
The combined use of chamomile and saffron with usual medication enhances the efficacy against depression and ensures long term improvement.
Ahmad S, Azhar A, Tikmani P, Rafique H, Khan A, Mesiya H, Saeed H

Review Article
Consuming 2-3 cups of coffee daily can help prevent cardiovascular disease and drinking at least 3 cups of green tea has similar benefits.
Chieng D, Kistler PM
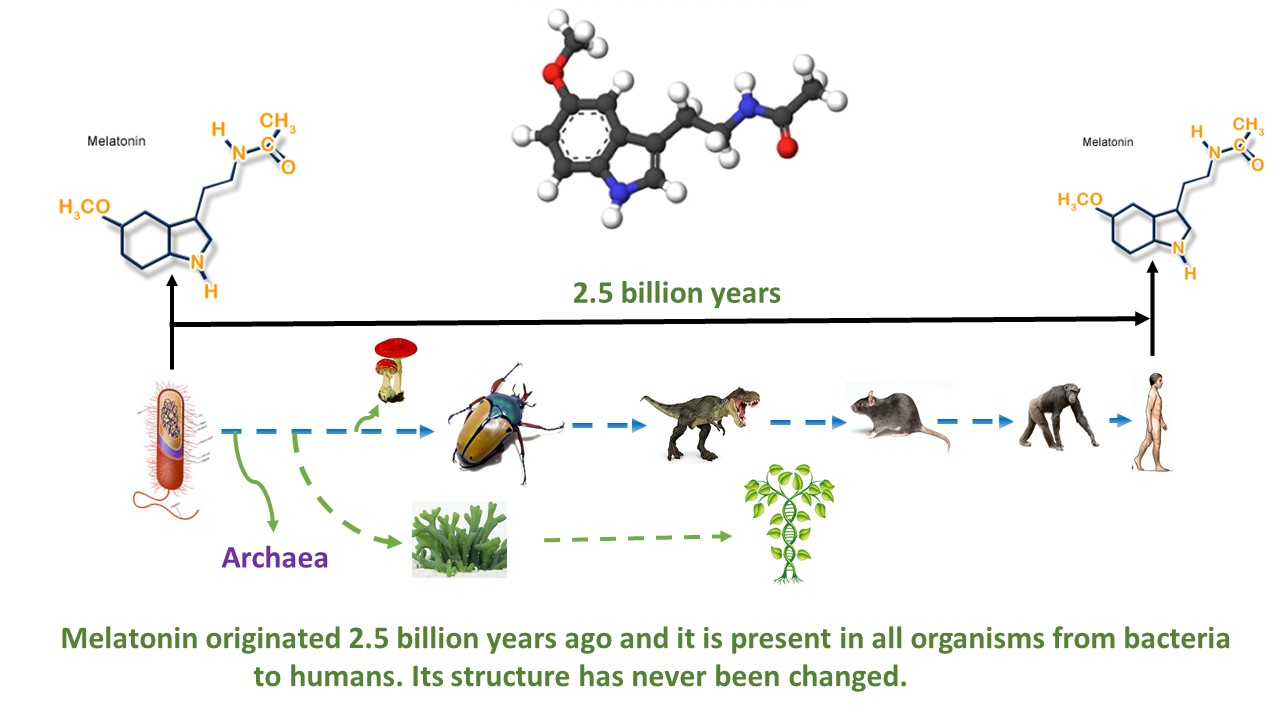
Review Article
Recent revelations of L-DOPA, dopamine, 5-hydroxytryptophan, tryptamine, serotonin, N-acetylserotonin, melatonin, 2-hydroxymelatonin, AFMK, AMK, and vitamin D3 derivatives in honey expand its health benefits.
Kim TK, Fabisiak A, Brzeminski P, Reiter RJ, Slominski AT

Experimental Study
Carotenoid-rich foods like orange carrots were more effective in mitigating Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease than those with low carotenoid levels.
Balbuena E, Cheng J, Eroglu A

Network Pharmacology
Kelulut honey, either alone or in combination with metformin or clomiphene, can alleviate oxidative stress and reproductive and metabolic abnormalities in rats with polycystic ovary syndrome.
Kamal DAM, Ibrahim SF, Ugusman A, Mokhtar MH

Systematic Review
Honey is effective in treating coughs in children above 12 months.
Mashat GD, Hazique M, Khan KI, Ramesh P, Kanagalingam S, Ul Haq Z, Victory Srinivasan N, Khan AI, Khan S

Randomised Controlled Trial
Consumption of wild blueberries over six months can improve cognitive performance and speed of processing information amongst older adults.
Cheatham CL, Canipe LG, Millsap G, Stegall JM, Chai SC, Sheppard KW, Lila MA

Systematic Review
Meta-analysis revealed that lavender, particularly L. angustifolia, significantly reduces stress, making it a potentially valuable component in stress management programs.
Ghavami T, Kazeminia M, Rajati F

Systematic Review
Prunes demonstrate potential as a dietary intervention to protect against, prevent and even reverse bone loss in osteoporosis, particularly in postmenopausal women.
Damani JJ, De Souza MJ, VanEvery HL, Strock NCA, Rogers CJ

Review Article
Pomegranate extract and its phytochemicals can potentially inhibit severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-COV-2) and improve gut microbiota, preventing obesity and diabetes.
Maphetu N, Unuofin JO, Masuku NP, Olisah C, Lebelo SL

Experimental Study
Pomegranate juice extract may reduce the damage to the endometrium in Polycystic ovary syndrome through its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and anti-proliferative effects.
Ibrahim MAA, Sadek MT, Sharaf Eldin HEM

Experimental Study
Using grape seed oil in the sardine canning process enhances the lipid nutritional quality and increases the fat, protein, and ash contents.
Bouriga N, Rjiba Bahri W, Mili S, Massoudi S, Quignard JP, Trabelsi M

Experimental Study
Chrysanthemum extract has protective effects on light-damaged retinas, reducing oxidative stress and improving cellular viability.
Gong Y, Wang X, Wang Y, Hao P, Wang H, Guo Y, Zhang W

Experimental Study
Oral administration of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharides may constitute a new, effective therapy for Atopic dermatitis, improving both immune response and intestinal microbiota.
Xie L, Yang K, Liang Y, Zhu Z, Yuan Z, Du Z

Systematic Review
Aromatherapy, specifically lavender, appears to be an effective, affordable, and holistic approach to reducing the length of labour in expectant women.
Ghiasi A, Bagheri L, Sharaflari F

Review Article
Depression, a prevalent and debilitating disorder, necessitates novel treatments beyond conventional drugs. Stingless bee honey, rich in antioxidants, emerges as a potential antidepressant candidate, explored comprehensively through monoamine, inflammatory, and neurotrophin hypotheses.
Zakaria FH, Samhani I, Mustafa MZ, Shafin N

Randomised Controlled Trial
Honey, combined with Iron (Fe), effectively enhances hemoglobin levels and reduces oxidative stress markers in anemic expectant mothers.
A A, Astuti A, Leli L, Saad R

Review Article
Honey, owing to its bioactive compounds, demonstrates potential in treating COVID-19 symptoms by reducing oxidative damage and enhancing the immune system.
Soares S, Bornet M, Grosso C, Ramalhosa MJ, Gouvinhas I, Garcia J, Rodrigues F, Delerue-Matos C

Meta-Analysis
Green tea supplementation can significantly reduce body weight in women with polycystic ovary syndrome, hence potentially beneficial in its clinical management.
Colonetti L, Grande AJ, Toreti IR, Ceretta LB, da Rosa MI, Colonetti T

Randomised Controlled Trial
Inhalation and massage therapy with lavender essential oil significantly mitigates perceived labour pain in women.
Karatopuk S, Yarıcı F

Bananas and plantains contain compounds with anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, and antioxidative properties that hold promise for potentially reversing neurological disorders.
Oyeyinka BO, Afolayan AJ

Randomised Controlled Trial
Despite previous suggestions, daily avocado consumption for six months did not decrease visceral adipose tissue volume in individuals with elevated waist circumference.
Lichtenstein AH, Kris‐Etherton PM, Petersen KS, Matthan NR, Barnes S, Vitolins MZ, Li Z, Sabaté J, Rajaram S, Chowdhury S, Davis KM, Galluccio J, Gilhooly CH, Legro RS, Li J, Lovato L, Perdue LH, Petty G, Rasmussen AM, Segovia‐Siapco G, Sirirat R, Su

Randomised Controlled Trial
Soybean lettuce extract effectively reduces symptoms of menopause syndrome without notable side effects.
Han AL, Lee HK, Chon HS, Pae HO, Kim MS, Shin YI, Kim S

Experimental Study
Goji berry supplementation can potentially improve gut microbiota and prevent liver injury caused by acute alcohol consumption.
Guo L, Guan Q, Duan W, Ren Y, Zhang XJ, Xu HY, Shi JS, Wang FZ, Lu R, Zhang HL, Xu ZH, Li H, Geng Y

Randomised Controlled Trial
Both whole blueberries and freeze-dried blueberry powder significantly enhanced plasma nitrite levels, a marker of cardiovascular health, but did not significantly affect other cardiovascular risk factors.
Wang Y, Gallegos JL, Haskell-Ramsay C, Lodge JK

Cohort Study
Moderate consumption of carrots is associated with a lower incidence of colorectal cancer, implying a potential cancer prevention effect in a certain dose-range.
Jiang Z, Chen H, Li M, Wang W, Fan C, Long F

Randomised Controlled Trial
Avocado honey, rich in bioactive compounds, can serve as a natural sweetener without negatively impacting anthropometric and biochemical parameters.
Hernández Salazar M, Flores A, Ramírez E, Llaca Díaz J, Rodríguez B, Castro H

Animal Study
Cooked adzuki beans contribute notably to preventing obesity and regulating gut microbiota composition, while also alleviating systemic inflammation and metabolic disorders.
Zhao Q, Liu Z, Zhu Y, Wang H, Dai Z, Yang X, Ren X, Xue Y, Shen Q

Randomised Controlled Trial
Cocoa extract supplementation in older adults reduced cardiovascular disease related death rates, but did not significantly lessen total cardiovascular events.
Sesso HD, Manson JAE, Aragaki AK, Rist PM, Johnson LG, Friedenberg G, Copeland T, Clar A, Mora S, Moorthy MV, Sarkissian A, Carrick WR, Anderson GL

Review Article
Saffron plant's various parts contain bioactive compounds that, when extracted using innovative techniques, show significant potential for use in food, nutraceutical and drug formulations.
Bakshi RA, Sodhi NS, Wani IA, Khan ZS, Dhillon B, Gani A

Systematic Review
Dietary strategies, such as caloric restriction and ketogenic diets, can alleviate chronic pain and enhance quality of life.
Cuevas-Cervera M, Perez-Montilla J, Gonzalez-Muñoz A, Garcia-Rios M, Navarro-Ledesma S

Systematic Review
Higher daily tea consumption, especially green tea, is linked to a lower risk of cerebral hemorrhage in adults.
Cheng P, Zhang J, Liu W, Sun Q, Fu Z, Lin H, Bi S, Zhu J

Animal Study
Certain natural mineral waters, when combined with a low-calorie diet, effectively reduce cholesterol and glucose levels in mice with metabolic syndrome.
Narciso L, Martinelli A, Torriani F, Frassanito P, Bernardini R, Chiarotti F, Marianelli C

Animal Study
Fermented gold kiwi extract exhibits antioxidant properties, providing protection to the stomach lining and reducing inflammation, making it promising for treating gastritis and gastric ulcers.
Jeon EJ, Choi JH, Lee NY, Oh HJ, Kwon HS, Kwon J

Experimental Study
Berries, largely due to their phenolic compounds, enhance internal antioxidant status and positively influence gut microbiota composition, promoting beneficial bacteria and suppressing harmful types.
Chen J, Shu Y, Chen Y, Ge Z, Zhang C, Cao J, Li X, Wang Y, Sun C

Review Article
Cherries and blueberries, rich in phenolic compounds, can be effectively used in pharmaceutical products, smart foods, functional beverages, and nutraceuticals to prevent or treat diseases.
Gonçalves AC, Nunes AR, Flores-Félix JD, Alves G, Silva LR

Randomised Controlled Trial
Consuming New Zealand green kiwifruit improves sleep quality, mood, and increases the concentration of serotonin metabolites.
Kanon AP, Giezenaar C, Roy NC, McNabb WC, Henare SJ

Systematic Review
Ginger, native to Southeast Asia, possesses antioxidant and antiviral properties, contributing to healthy ageing and potential prevention of age-related disorders.
Ozkur M, Benlier N, Takan I, Vasileiou C, Georgakilas AG, Pavlopoulou A, Cetin Z, Saygili EI

Animal Study
Pu-erh tea has been validated to have significant anti-oxidative effects, reducing serum MDA levels and increasing serum SOD and GSH-Px levels.
Yang CY, Hung KC, Yen YY, Liao HE, Lan SJ, Lin HC

Animal Study
Walnut seed skin extract demonstrates potential hepato-renal protective effects, inhibiting inflammatory responses, oxidative stress and apoptosis, in kidney-damaged Sprague-Dawley rats.
Askin S, Askin H, Dursun E, Palabiyik E, Uguz H, Cakmak , Koc K

Review Article
Ellagic acid, commonly found in various plant foods, can enhance cancer treatment by boosting the effects of chemotherapy and radiotherapy while reducing their side effects.
Xue P, Zhang G, Zhang J, Ren L

Review Article
Consuming kiwifruit, particularly the green variety, can effectively alleviate upper gastrointestinal symptoms like abdominal discomfort, pain, and indigestion.
Bayer SB, Frampton CM, Gearry RB, Barbara G

Experimental Study
Pu-erh tea may prevent circadian rhythm disorders by promoting tryptophan metabolism and signaling interactions in the gut-liver-brain axis.
Hu S, Luo L, Bian X, Liu RH, Zhao S, Chen Y, Sun K, Jiang J, Liu Z, Zeng L

Randomised Controlled Trial
Chamomile vaginal gel effectively improved the sexual function of postmenopausal women, and can be a potential treatment option for those unable to undergo hormone therapy.
Bosak Z, Iravani M, Moghimipour E, Haghighizadeh M, Jelodarian P

Cohort Study
Eating more avocados, specifically two servings a week, is associated with a significantly lesser risk of cardiovascular disease and coronary heart disease.
Pacheco LS, Li Y, Rimm EB, Manson JAE, Sun Q, Rexrode K, Hu FB, Guasch‐Ferré M

Randomised Controlled Trial
Green tea extract, specifically epigallocatechin gallate, can inhibit tumor growth and enhance the quality of life in women suffering from uterine fibroids.
Badawy A, Shady NW, Maklad SMA, Ait-Allah AS

Meta-Analysis
Regular peanut consumption appears to positively influence lipid metabolism, reducing levels of triglycerides in the blood.
Parilli-Moser I, Hurtado-Barroso S, Guasch-Ferré M, Lamuela-Raventós RM
Review Article
Pu-erh tea possesses therapeutic mechanisms potentially beneficial for metabolic diseases due to its interaction with liver and gut microbiome.
Jia W, Rajani C, Lv A, Fan TP, Zheng X

Experimental Study
Ethanol and n-hexane extracts of Chrysanthemum indicum reveal potent anticancer activity against HepG2 cancer cells by promoting apoptosis and reducing cell proliferation.
Mehboob Z, Sharif S, Lodhi MS, Zaigham K

Experimental Study
Saffron and its bioactive molecules, notably crocins, have been found to be as effective as common antidepressants in treating depression disorders.
Siddiqui SA, Ali Redha A, Snoeck ER, Singh S, Simal-Gandara J, Ibrahim SA, Jafari SM

Review Article
Purple carrot roots, rich in bioactive compounds like anthocyanin, may be effective in preventing metabolic syndrome and cancer by reducing inflammation and metabolic changes.
Rasheed H, Shehzad M, Rabail R, Kowalczewski P, Kidoń M, Jeżowski P, Ranjha MMAN, Rakha A, Din A, Aadil RM

Systematic Review
Among the mentioned plants, castor oil and date fruit have more evidence in cervical ripening and onset of labor.
Ghasemi M, Ebrahimzadeh-Zagami S, Ghavami V.

Review Article
Pomegranate juice, due to its unique bioactive compounds, could potentially alleviate complications related to SARS-CoV-2 infections, especially in patients with pre-existing chronic diseases.
Banihani SA

Review Article
The Jing Si Herbal Drink, composed of various antiviral, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory herbs, has been confirmed as potentially effective in treating COVID-19 symptoms.
Lu PH, Tseng CW, Lee JL, Lee EY, Lin YP, Lin IH, Yu MC, Lu KC, Kuo KL

Systematic Review
Edible medicinal plants like saffron, chamomile, dill seeds, and castor oil have demonstrated positive effects on various aspects of labor, indicating potential natural alternatives for aiding childbirth.
Ivari FR, Vatanchi AM, Yousefi M, Badaksh F, Salari R

Randomised Controlled Trial
Walnut oligopeptide improves cognitive performance and sleep quality among teenagers and elderly people.
Yeh AL, Chao CL, Huang WF, Lin HC, Wang CJ

Clinical Study
Lavender aromatherapy is more effective in reducing pain intensity during active Phase I labor than lemon aromatherapy.
Lestari CI, Amilia R, Rospia ED

Randomised Controlled Trial
The intake of date palm enhances the sexual function in infertile couples.
Jahromi AR, Mosallanezhad Z, Hosini FS, Jamali S, Sharifi N

Meta-Analysis
Certain species of citrus extracts effectively control dyslipidemia, reducing total cholesterol, LDL, and triglycerides while increasing HDL, primarily due to their rich antioxidant composition.
Carvalho BMR, Nascimento LC, Nascimento JC, Gonçalves VSS, Ziegelmann PK, Tavares DS, Guimarães AG

Review Article
Cherry juice, when consumed several days before exercise, hastens muscle function recovery post-exercise, making it a valuable 'precovery' intervention.
McHugh MP

Systematic Review
Higher consumption of coffee and specifically decaffeinated coffee raises the risk of rheumatoid arthritis, while caffeinated coffee, tea and caffeine intake doesn't.
Asoudeh F, Dashti F, Jayedi A, Hemmati A, Fadel A, Mohammadi H

Randomised Controlled Trial
Chamomile was found to be less effective than mefenamic acid for relieving cyclic menstrual pain.
Alcaraz EM, Laumbach SG, Amico J

Randomised Controlled Trial
The proprietary herbal blend LN18178 significantly boosts testosterone levels, muscle strength and mid-upper arm circumference in young, healthy males.
Sreeramaneni PGA, Yalamanchi A, Konda MR, Cherukuri SHV, Maroon JC

Review Article
Ginger, peppermint and caraway oil combination showed strong effectiveness in managing upper gastrointestinal complaints, with melatonin and marine alginate demonstrating moderate evidence.
Schulz RM, Ahuja NK, Slavin JL

Systematic Review
Raspberry consumption can help to reduce blood glucose levels and stabilize the blood lipid profile due to its bioactive compounds.
Piña-Contreras N, Martínez-Moreno AG, Ramírez-Anaya JDP, Espinoza-Gallardo AC, Valdés EHM

Systematic Review
Plums, specifically European and Japanese species, exhibit anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that may be used for the treatment and prevention of cancer.
Bahrin AA, Moshawih S, Dhaliwal JS, Kanakal MM, Khan A, Lee KS, Goh BH, Goh HP, Kifli N, Ming LC

Randomised Controlled Trial
Four weeks' treatment with pomegranate supplement greatly helps in alleviating menopausal symptoms and enhancing the quality of life in menopausal women.
Adel-Mehraban MS, Tansaz M, Mohammadi M, Yavari M

Review Article
Equol, a powerful estrogen-like compound derived from soy, could be key to better health in postmenopausal women if gut microbiome could be altered to facilitate its production.
Leonard LM, Choi MS, Cross TWL

Systematic Review
Consumption of sesame seeds and its products positively influences human glucose metabolism, potentially making it a beneficial addition to glucose-lowering diets.
Sohouli MH, Haghshenas N, Hernández‐Ruiz , Shidfar F

Meta-Analysis
Cinnamon is a safe therapeutic agent without significant adverse effects based on systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
Gu DT, Tung TH, Jiesisibieke ZL, Chien CW, Liu WY

Clinical Study
Daily oral consumption of one avocado enhances the elasticity and firmness of the facial skin in healthy women.
Henning SM, Guzman JB, Thames G, Yang J, Tseng CH, Heber D, Kim J, Li Z

Randomised Controlled Trial
Lemon juice boosts gastric secretions and emptying rate, and reduces blood sugar response to starchy food, potentially due to acid-inhibition of digestion enzyme in saliva.
Freitas D, Boué F, Benallaoua M, Airinei G, Benamouzig R, Lutton E, Jourdain L, Dubuisson RM, Maître X, Darrasse L, Le Feunteun S

Review Article
Curcumin, a spice used in Indian cooking, shows potential therapeutic effects in various retinal diseases, including during the COVID era.
Chandrasekaran PR, Madanagopalan VG

Randomised Controlled Trial
A daily dose of Chrysanthemum flower extract was found to significantly reduce serum uric acid levels, potentially improving hyperuricemia.
Takara T, Yamamoto K, Suzuki N, Yamashita S, Iio S, Kakinuma T, Baba A, Takeda S, Yamada W, Nagata M, Shimoda H

Review Article
Goji berries, notably their polysaccharides, exhibit protective effects against inflammatory bowel disease through the preservation of healthy gut microbiota.
Sun Q, Du M, Kang Y, Zhu MJ

Meta-Analysis
Oat supplementation interventions can improve cardiovascular health markers among adults, regardless of their diet or metabolic conditions.
Llanaj E, Dejanovic GM, Valido E, Bano A, Gamba M, Kastrati L, Minder B, Stojic S, Voortman T, Marques-Vidal P, Stoyanov J, Metzger B, Glisic M, Kern H, Muka T

Experimental Study
Ellagic acid, found naturally in pomegranates, significantly inhibits growth and migration of gastric cancer cells without causing notable side effects.
Cheshomi H, Bahrami AR, Rafatpanah H, Matin MM

Meta-Analysis
Saffron intake might aid in reducing depressive symptoms but it should not be regarded as an exclusive solution for treating depression.
Musazadeh V, Zarezadeh M, Faghfouri AH, Keramati M, Ghoreishi Z, Farnam A

Experimental Study
Saffron petal extract and anthocyanins can alleviate symptoms of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome by rectifying hormonal imbalances and reducing inflammation in PCOS mice.
Moshfegh F, Balanejad SZ, Shahrokhabady K, Attaranzadeh A

Review Article
The flower of Chrysanthemum morifolium, widespread in Asia, has been discovered as a treatment for diverse diseases, including obesity, heart disease, and cancer, due to its beneficial phytoconstituents.
Pandey J, Bastola T, Dhakal B, Poudel A, Devkota HP

Review Article
Chrysanthemums, popular floricultural crops, not only hold significant ornamental value but also exhibit various therapeutic potentials including antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anticancer activities.
Hadizadeh H, Samiei L, Shakeri A

Review Article
Adzuki and Mung beans have great potential as functional foods for health promotion and disease prevention, offering an excellent source of essential nutrients and biodiversity for sustainable agriculture.
Shahrajabian MH, Sun W, Cheng Q

Meta-Analysis
Isoflavone supplementation noticeably impacts menopausal symptoms and hormonal changes in postmenopausal women.
Kang I, Rim CH, Yang HS, Choe JS, Kim JY, Lee M

Review Article
High doses of vitamin C, vitamin D supplementation and natural honey can potentially decrease fatalities and support the management of COVID-19.
Rabby MII, Hossain F, Islam MA, Islam AKMS, Akhi IJ, Akter F

Theoretical Article
The jujube tree bears fruit endowed with substantial nutritional value and contains numerous phytochemical components with reported antioxidant, anti-cancer and neuroprotective properties.
Aafi E, Reza M, Mirabzadeh M

Systematic Review
Fresh and dried ginger displays key botanical, phytochemical and ethnopharmacological differences, which are fundamental for their specific clinical uses in treating gastrointestinal issues.
Lai W, Yang S, Lin X, Zhang X, Huang Y, Zhou J, Fu C, Li R, Zhang Z

Meta-Analysis
Tea supplements, especially green tea, significantly decrease fasting blood glucose and fasting insulin levels and reduce body weight in women with polycystic ovary syndrome.
Shen W, Pan Y, Jin B, Zhang Z, You T, Qu Y, Han M, Yuan X, Zhang Y

Experimental Study
Consuming oats significantly lessens total and LDL cholesterol levels and mediates a prebiotic effect on the gut microbiome, contributing to its cholesterol-lowering ability.
Xu D, Feng M, Chu YF, Wang S, Shete V, Tuohy KM, Liu F, Zhou X, Kamil A, Pan D, Liu H, Yang X, Yang C, Zhu B, Lv N, Xiong Q, Wang X, Sun J, Sun G, Yang Y

Randomised Controlled Trial
Regular intake of goji berries can increase Macular Pigment Optical Density, potentially helping to prevent or delay the development of age-related macular degeneration.
Li X, Holt RR, Keen CL, Morse LS, Yiu G, Hackman RM

Review Article
Fresh Hass avocados have been found to reduce cardiovascular disease risk, assist weight loss, improve cognitive function, and promote colonic microbiota health.
Dreher ML, Cheng FW, Ford NA

Systematic Review
Turmeric curcuminoids are associated with better pain relief than NSAIDs in knee osteoarthritis.
An-Fang Hsiao, Yi-Chieh Lien, I-Shiang Tzeng, Chien-Ting Liu, Sheng-Hsun Chou, Yi-Shiung Horng

Review Article
Pomegranate juice and its bioactive components may serve as cost-effective, next-generation non-pharmacologic anticancer therapies, particularly against colorectal and prostate cancer.
Hussein L, Gouda M, Buttar HS

Review Article
Cinnamomum cassia, or cinnamon, exhibits promising therapeutic benefits in combating gastritis by targeting inflammation pathways, according to preclinical studies.
Lee JH, Park DH, Lee S, Seo HJ, Park SJ, Jung K, Kim SY, Kang KS

Experimental Study
Cocoa bean husk, a by-product of cocoa processing, exhibits potent antioxidant and anticancer effects on prostate cancer cells due to its high phenolic compound content.
Choi J, Yang C, Lim W, Song G, Choi H

Review Article
The pomegranate plant has a rich inventory of phytochemical constituents showing pharmacological efficiency in treating cardiovascular and endocrine diseases.
Eghbali S, Askari SF, Avan R, Sahebkar A

Randomised Controlled Trial
High avocado intake significantly reduces the intake of energy and various macro and micronutrients in Hispanic/Latino families.
Pacheco LS, Bradley RD, Denenberg JO, Anderson CAM, Allison MA
Systematic Review
Eating kiwifruits improves bowel movements and decreases stool consistency, also providing anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits to the gut barrier.
Antonelli M, Donelli D

Cohort Study
Consumption of sardines can effectively prevent type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension, particularly in senior citizens, due to their high omega 3, EPA, and DHA content.
Nurdiana Febriyanti V

Cohort Study
Sardines are highly proven to be able to effectively prevent type 2 diabetes, prevent hypertension, and lower blood pressure, especially for senior citizens.
Nurdiana Febriyanti V

Randomised Controlled Trial
Date fruit consumption appears to be useful for promoting and increasing breast milk quantity in breastfeeding mothers. Date fruits may be an alternative galactagogue.
Modepeng T, Pavadhgul P, Bumrungpert A, Kitipichai W

Randomised Controlled Trial
A combined treatment of soy and hop extract is a safe and effective alternative to traditional hormone replacement therapy for improving postmenopausal symptoms.
Kim HI, Kim MK, Lee I, Yun J, Kim EH, Seo SK

Systematic Review
Date fruit consumption several weeks prior to delivery can decrease the need for labor induction and/or augmentation and might have a beneficial effect on labor duration.
Sagi-Dain L, Sagi S

Randomised Controlled Trial
Consumption of one avocado per day can potentially reduce visceral adiposity and subsequently decrease the risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Reboussin DM, Kris-Etherton PM, Lichtenstein AH, Li Z, Sabate J, Matthan NR, Petersen K, Rajaram S, Vitolins M, Ford N

Systematic Review
Green tea treatment has shown potential in improving oral hygiene and gingival health, and reducing periodontitis and caries.
Mazur M, Ndokaj A, Jedlinski M, Ardan R, Bietolini S, Ottolenghi L

Systematic Review
Green tea supplementation improves total antioxidant capacity and impacts oxidative stress based on dose levels in adults.
Rasaei N, Asbaghi O, Samadi M, Setayesh L, Bagheri R, Gholami F, Soveid N, Casazza K, Wong A, Suzuki K, Mirzaei K

Cohort Study
The consumption of avocado is associated with better cognitive function in older adults.
Cheng FW, Ford NA, Taylor MK

Clinical Study
Consuming soymilk-honey fermented with a specific type of probiotic significantly reduces osteocalcin levels, which may impact bone health in postmenopausal women.
Desfita S, Sari W, Yusmarini Y, Pato U, Zakłos-Szyda M, Budryn G

Experimental Study
Tiger nut and walnut supplementation in diets can improve testosterone levels and help control vasoconstriction, potentially benefiting hypertensive individuals.
Olabiyi AA, Morsch VM, Oboh G, Schetinger MRC

Review Article
Green tea and its component EGCG, demonstrate potential as a treatment for endometriosis by inhibiting growth, invasion, adhesion and angiogenesis.
Chen X, Man GCW, Hung SW, Zhang T, Fung LWY, Cheung CW, Chung JPW, Li TC, Wang CC

Randomised Controlled Trial
Chamomile capsules prove effective in reducing emotional symptoms related to menstrual cycles.
Najafi Mollabashi E, Ziaie T, Bostani Khalesi Z

Review Article
Lavender aromatherapy, whether administered through massage or inhalation, appears effective in reducing active phase labor pain.
Hatami Rad R

Systematic Review
Almond-based diets may be effective in promoting short-chain fatty acid-producing bacteria and lowering glycated haemoglobin and body mass index in patients with type 2 diabetes compared with control.
Ojo O, Wang XH, Ojo OO, Adegboye ARA

Clinical Study
Consumption of green tea enriched with a citrus polyphenol, α-glucosyl hesperidin, can prevent weight gain and reduce body mass index, especially in individuals under 50 years.
Yoshitomi R, Yamamoto M, Kumazoe M, Fujimura Y, Yonekura M, Shimamoto Y, Nakasone A, Kondo S, Hattori H, Haseda A, Nishihira J, Tachibana H

Systematic Review
Green tea extract could be considered a potential agent to attenuate PCOS complications mainly due to its effect on weight loss and glycemic levels.
Maleki V, Taheri E, Varshosaz P, Tabrizi FPF, Moludi J, Jafari-Vayghan H, Shadnoush M, Jabbari SHY, Seifoleslami M, Alizadeh M

Systematic Review
Soy food intake, particularly fermented soy products, appear to have a protective effect on fracture risk among Asian women, especially in early menopause.
Akhavan Zanjani M, Rahmani S, Mehranfar S, Zarrin M, Bazyar H, Moradi Poodeh B, Zare Javid A, Hosseini SA, Sadeghian M

Animal Study
Adzuki beans, when added to a high-fat diet, lessen obesity, improve liver function, enhance insulin sensitivity, and balance gut microbiota.
Zhao Q, Hou D, Fu Y, Xue Y, Guan X, Shen Q

Experimental Study
Co-fermentation of Ganpu tea with Chachi peel alters its chemical profile, reducing certain compounds while increasing others, thus enhancing its unique flavor.
Xu Y, Liang PL, Chen XL, Gong MJ, Zhang L, Qiu XH, Zhang J, Huang ZH, Xu W

Systematic Review
Coffee extract supplementation significantly improves parameters of metabolic syndrome, with the effects varying according to the types and doses of coffee administered.
Ramli NNS, Alkhaldy AA, Mhd Jalil AM

Randomised Controlled Trial
Pomegranate extract supplement shows potential in improving glycemic indicators, serum lipids, anthropometrics, and blood pressure in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Goodarzi R, Jafarirad S, Mohammadtaghvaei N, Dastoorpoor M, Alavinejad P

Randomised Controlled Trial
A new method for assessing the effects of therapies on atherosclerosis shows that pomegranate juice/extract has a significant influence on carotid vessel-wall-plus-plaque thickness.
Zhao Y, Spence JD, Chiu B
Randomised Controlled Trial
Small-intestinal release peppermint oil is a cost-effective treatment for Irritable Bowel Syndrome, yielding modest quality of life gains and relieving abdominal pain.
Weerts ZZRM, Essers BAB, Jonkers DMAE, Willems JIA, Janssen DJPA, Witteman BJM, Clemens CHM, Westendorp A, Masclee AAM, Keszthelyi D

Systematic Review
Chocolate and cocoa product consumption significantly improved lipid profiles, but had no significant effect on other heath aspects such as cognitive function and blood pressure.
Tan TYC, Lim XY, Yeo JHH, Lee SWH, Lai NM
Network Pharmacology
A combination of extracts from chrysanthemum were found to be more effective in treating hyperuricemia and potentially developing anti-hyperuricemic functional foods.
Kim OK, Yun JM, Lee M, Kim D, Lee J

Systematic Review
D-Limonene, a bioactive compound found in citrus peels, shows potential anticancer activity and is better tolerated in breast cancer patients compared to its derivative perillyl alcohol.
Chebet JJ, Ehiri JE, McClelland DJ, Taren D, Hakim IA

Experimental Study
The Licorice and Jujube formula is seen as commonly used and potentially effective for treating menopausal symptoms as per classical Chinese medicine.
Coyle ME, Liu J, Yang H, Wang K, Zhang AL, Guo X, Lu C, Xue CC

Systematic Review
Drinking coffee may be linked to lower mortality risk in type 2 diabetes patients.
Shahinfar H, Jayedi A, Khan TA, Shab-Bidar S

Review Article
Pu-erh tea, with its complex components, interacts greatly with gut microbiomes and holds significant potential for healthcare applications.
Liu JY, He D, Xing YF, Zeng W, Ren K, Zhang C, Lu Y, Yang S, Ou SJ, Wang Y, Xing XH

Experimental Study
Zeaxanthin dipalmitate, a wolfberry-derived carotenoid, can delay retinal degeneration in mice modelling Retinitis Pigmentosa mainly through its anti-inflammatory and oxidative stress effects.
Liu F, Liu X, Zhou Y, Yu Y, Wang K, Zhou Z, Gao H, So KF, Vardi N, Xu Y

Systematic Review
A variety of Chinese herbal medicines have been reported to effectively prevent or treat nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by regulation of the gut microbiota and the gut-liver axis.
Yang XF, Lu M, You L, Gen H, Yuan L, Tian T, Li CY, Xu K, Hou J, Lei M

Animal Study
Adzuki bean extracts have shown more potential than black soybean extracts in lowering blood pressure in hypertensive rats, acting on the renin-angiotensin system.
Jeong EW, Park SY, Yang YS, Baek YJ, Yun DM, Kim HJ, Go GW, Lee HG

Animal Study
Omega-3 fatty acids found in selected fish oils, particularly smoked eel, effectively managed dyslipidemia and reduced cardiovascular disease risk factors.
Kontostathi M, Isou S, Mostratos D, Vasdekis V, Demertzis N, Kourounakis A, Vitsos A, Kyriazi M, Melissos D, Tsitouris C, Karalis E, Klamarias L, Dania F, Papaioannou GT, Roussis V, Polychronopoulos E, Anastassopoulou J, Theophanides T, Rallis MC, Black H

Experimental Study
Chrysanthemum, a traditional Chinese medicine, shows significant antioxidant activity and hepatoprotective effects, making it a potential resource for functional foods and medicinal materials.
Chen L, Liu Y, Huang X, Zhu Y, Li J, Miao Y, Du H, Liu D

Systematic Review
Green tea consumption has been found to be effective in preventing the contraction of influenza infections.
Rawangkan A, Kengkla K, Kanchanasurakit S, Duangjai A, Saokaew S

Systematic Review
Ginger significantly improves sperm health, enhancing quality parameters like count, viability, motility, morphology and DNA integrity, thereby boosting fertility.
Gholami‐Ahangaran M, Karimi‐Dehkordi M, Akbari Javar A, Haj Salehi M, Ostadpoor M

Review Article
The date palm enhances both male and female fertility parameters through its nutritional attributes and antioxidant functionality.
Shehzad M, Rasheed H, Naqvi SA, Al-Khayri JM, Lorenzo JM, Alaghbari MA, Manzoor MF, Aadil RM

Experimental Study
Boron-rich mineral and medicinal waters can significantly increase boron accumulation in fruit flies and humans, largely elevating their boron status.
Seidel U, Haegele FA, Baumhof E, Jans K, Seidler Y, Kremer D, Bakker SJL, Birringer M, Lüersen K, Bosy‐Westphal A, Rimbach G

Systematic Review
Tremella fuciformis polysaccharides effectively reduce inflammation in ulcerative colitis, promoting healing by restoring intestinal and mucus barrier functions.
Xu Y, Xie L, Zhang Z, et al

Review Article
Date palm tree products and by-products are exceptionally rich in bioactive compounds offering potential health benefits, therefore suitable to be used as natural ingredients in food manufacturing.
Echegaray N, Gullón B, Pateiro M, Amarowicz R, Misihairabgwi JM, Lorenzo JM

Review Article
Almonds can support colonic microbiota health by promoting microflora richness and diversity, increasing the ratio of symbiotic to pathogenic microflora, and concentrations of health-promoting colonic bioactives.
Dreher ML

Review Article
Recent systematic reviews and meta-analyses of nut RCTs showed that almonds were the only nut that had a small but significant decrease in both mean body mass and fat mass, compared to control diets.
Dreher ML

Systematic Review
The consumption of cocoa or dark chocolate can reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and fasting blood sugar levels in diabetic patients.
Darand M, Hajizadeh Oghaz M, Hadi A, Atefi M, Amani R

Animal Study
Goji berry supplementation in does' diet positively influences both their reproductive and productive performance, likely through adjustment of hormonal patterns and milk production.
Andoni E, Curone G, Agradi S, Barbato O, Menchetti L, Vigo D, Zelli R, Cotozzolo E, Ceccarini MR, Faustini M, Quattrone A, Castrica M, Brecchia G

Review Article
In reproductive health, honey can improve infertility, protect the postmenopausal reproductive tract, prevent toxic effects, maintain sperm quality by restoring testosterone levels and treat vulvovaginal candidiasis infections.
Zaid SSM, Ruslee SS, Mokhtar MH
Review Article
Curcumin, with its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial and antimutagenic properties, is a potential therapeutic agent for retinal diseases.
Nebbioso M, Franzone F, Greco A, Gharbiya M, Bonfiglio V, Polimeni A

Experimental Study
Fructus Lycii and Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge extract improve retinal morphology and function by regulating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway to curb oxidative reactions.
Ou C, Jiang P, Tian Y, Yao Z, Yang Y, Peng J, Zeng M, Song H, Peng Q

Randomised Controlled Trial
Lavandula angustifolia essential oil inhalation seemed to enhance overall sleep patterns, quality, and efficiency in postmenopausal women with insomnia.
dos Reis Lucena L, dos Santos-Junior JG, Tufik S, Hachul H

Systematic Review
Phytoestrogens, used in various forms, have shown improvement in urogenital menopause symptoms and improved women's sexual function, promoting overall quality of life.
Abdi F, Rahnemaei FA, Roozbeh N, Pakzad R

Clinical Study
Green tea therapy can significantly improve rheumatoid arthritis symptoms, correlating with changes in specific circulating serum molecules, miR-125b and miR-146a.
Al-Rawaf HA, Alghadir AH, Gabr SA

Review Article
There is a notable gap in scientific research on the potential health benefits and antioxidant activity of matcha tea compared to green tea.
Sivanesan I, Gopal J, Muthu M, Chun S, Oh JW

Randomised Controlled Trial
Consumption of blueberry supplement did not show significant improvement in metabolic health markers, however, it induced changes in gene expression, indicating a potential longer-term effect.
Rousseau M, Horne J, Guénard F, de Toro-Martín J, Garneau V, Guay V, Kearney M, Pilon G, Roy D, Couture P, Couillard C, Marette A, Vohl MC

Systematic Review
Cocoa-rich products consumption can improve mood and affect in the short term.
Fusar-Poli L, Gabbiadini A, Ciancio A, Vozza L, Signorelli MS, Aguglia E

Review Article
Tea polyphenols can help rebalance gut microbiota, alleviating imbalances caused by obesity, diabetes, and UV damage, with effects varying by tea type.
Khairudin MAS, Mhd Jalil AM, Hussin N

Review Article
Green tea and its chief bioactive component have the potential to improve certain female reproductive disorders such as endometriosis, polycystic ovary syndrome, and dysmenorrhea.
Kamal DAM, Salamt N, Zaid SSM, Mokhtar MH

Systematic Review
Cocoa flavanols exhibit health and aging benefits and may act as powerful agents in preventing chronic diseases such as cardiovascular and metabolic disorders, and cancer.
Martin M, Ramos S

Randomised Controlled Trial
Eating sardines twice a week for a year significantly reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in prediabetic individuals aged 65 and above.
Díaz-Rizzolo DA, Serra A, Colungo C, Sala-Vila A, Sisó-Almirall A, Gomis R

Randomised Controlled Trial
A one-year, sardine-enriched diet in an elderly population with pre-diabetes exerts a greater protective effect against developing type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular events.
Díaz-Rizzolo DA, Serra A, Colungo C, Sala-Vila A, Sisó-Almirall A, Gomis R

Experimental Study
Black pepper and its major component, piperine, can effectively regulate anemia of inflammation by reducing the overexpression of hepcidin, a hormone that controls iron levels.
Banerjee S, Katiyar P, Kumar L, Kumar V, Saini SS, Krishnan V, Sircar D, Roy P

Systematic Review
Coffee consumption, particularly boiled coffee, may increase levels of certain cardiovascular risk markers, but no strong link was found to anti-inflammatory effects.
Daneschvar HL, Smetana GW, Brindamour L, Bain PA, Mukamal KJ

Randomised Controlled Trial
Combining resistance training with saffron supplementation enhances happiness levels and increases dopamine and serotonin concentrations more than resistance training alone.
Moghadam BH, Bagheri R, Roozbeh B, Ashtary-Larky D, Gaeini AA, Dutheil F, Wong A

Systematic Review
Consumption of certain foods like rapeseed/canola oil, avocados, and turmeric can lead to moderate to large reductions in LDL cholesterol levels.
Schoeneck M, Iggman D

Review Article
Pomegranate has a variety of phytochemicals which possess wide-ranging activities including antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-oncogenic properties, and resistance to cerebrovascular disease.
Ge S, Duo L, Wang J, GegenZhula , Yang J, Li Z, Tu Y

Experimental Study
Two French natural mineral waters (NMW1 and NMW2) show anti-inflammatory effects and can reduce intestinal inflammation in mice with induced colitis.
Barnich N, Rodrigues M, Sauvanet P, Chevarin C, Denis S, Le Goff O, Faure-Imbert D, Hanh T, Roques CF, Chassaing B, Alric M

Systematic Review
Tremella polysaccharide is a safe natural active ingredient, which can be used in the prevention, treatment and rehabilitation of diseases.
Ma, X., Yang, M., He, Y., Zhai, C., & Li, C.

Randomised Controlled Trial
Adding oat bran to the diet of pregnant women with gestational diabetes can help significantly reduce their fasting and postprandial blood glucose levels.
Barati Z, Iravani M, Karandish M, Haghighizadeh MH, Masihi S

Randomised Controlled Trial
Avocado/soy unsaponifiables effectively treat osteoarthritis by controlling the balance between oxidant and antioxidant molecular markers.
Jangravi Z, Basereh S, Zaree Mahmoudabadi A, Saberi M, Alishiri GH, Korani M

Systematic Review
These results indicate that a certain concentration of snow fungus polysaccharides can effectively alleviate skin damage caused by UVA, and they may be used as an effective component of cosmetics.
Fu H, You S, Zhao D, An Q, Zhang J, Wang C, Wang D, Li M.

Systematic Review
Epidemiological studies suggest that the consumption of spicy chilli food is associated with reduced risk of all-cause as well as heart disease–related mortality.
Ofori-Asenso R, Mohsenpour MA, Nouri M, Faghih S, Liew D, Mazidi M.

Systematic Review
Isoflavones found in soybeans can reduce risks of certain cancers and alleviate menopause-related symptoms among women, such as vasomotor syndromes, spinal bone loss, and hypertension.
Chen LR, Chen KH

Cohort Study
Moderate coffee consumption may potentially reduce the risk of low HDL-C and high fasting blood glucose amongst Korean male adults.
Tan LJ, Jeon HJ, Park SH, Kim SA, Lim K, Chung S, Chang PS, Lee J, Kang D, Shin S

Review Article
Pomegranate demonstrates anti-proliferative, anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory properties that can effectively control the progression of various respiratory diseases.
Shaikh SB, Bhandary YP

Systematic Review
A systematic analysis indicates that ginger has a higher safety profile than NSAIDs for pain relief, with a smaller number of gastric side effects and fewer kidney risks.
Negi R, Sharma DS, Gaur DR, Bahadur A, Jelly P

Systematic Review
Based on beneficial effects and minimal side effects, ginger may be a potential adjunct treatment for primary dysmenorrhea.
Negi R, Sharma DS, Gaur DR, Bahadur A, Jelly P

Review Article
The fresh rhizoma of Roscoe, a traditional Chinese medicine, has proven effects on the nervous and cardiovascular systems and has antibacterial, antitumor, and antioxidant properties.
Li X, Ao M, Zhang C, Fan S, Chen Z, Yu L
Review Article
Saffron and its components, crocin and crocetin, show potential in treating various eye disorders, including inflammation, macular edema, and glaucoma.
Sepahi S, Ghorani-Azam A, Hossieni SM, Mohajeri SA, Khodaverdi E

Review Article
Bee honey and propolis could have potential beneficial effects as supporting treatments for COVID-19, enhancing immunity and inhibiting viral activity.
Ali AM, Kunugi H

Systematic Review
Raspberry leaf for childbirth, highlighting the lack of robust evidence on its effects, safety, and efficacy during pregnancy, emphasizing the need for more comprehensive research.
Bowman R, Taylor J, Muggleton S, Davis D

Experimental Study
Supplementation with standardized saffron extract improves depressive symptoms and social relationships in healthy individuals experiencing subclinical low mood and stress.
Jackson PA, Forster J, Khan J, Pouchieu C, Dubreuil S, Gaudout D, Moras B, Pourtau L, Joffre F, Vaysse C, Bertrand K, Abrous H, Vauzour D, Brossaud J, Corcuff JB, Capuron L, Kennedy DO

Animal Study
Traditional fermented products made from soybeans and rice, commonly consumed in the Japanese diet, show significant potential in preventing the progression of fatty liver disease.
Kanno R, Koshizuka T, Miyazaki N, Kobayashi T, Ishioka K, Ozaki C, Chiba H, Suzutani T

Randomised Controlled Trial
Enriching a regular diet with oat β-glucan can improve glycemic control, augment feelings of fullness, and positively modulate gut microbiota in individuals with type-2 diabetes.
Pino JL, Mujica V, Arredondo M

Experimental Study
Pomegranate juice extract (PPJE) appears to reduce chemotherapy-induced skin side effects by inhibiting inflammation and promoting wound repair on the skin.
Rapa SF, Magliocca G, Pepe G, Amodio G, Autore G, Campiglia P, Marzocco S

Systematic Review
Current evidence shows that short-term honey supplementation following surgical or physiological menopause exerts an oestrogenic, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effect on the female reproductive system.
Ismail NH, Ibrahim SF, Jaffar FHF, Mokhtar MH, Chin KY, Osman K

Review Article
Green tea, coffee, wine, and curry have beneficial health effects due to the polyphenols they contain, which possess both antioxidant and pro-oxidant properties.
Ohishi T, Fukutomi R, Shoji Y, Goto S, Isemura M

Systematic Review
The existing evidence, although with low level of confidence, suggests that walnut intake may have a beneficial effect on cognition-related outcomes, including cognitive function, mood, and stroke.
Cahoon, D., Shertukde, S. P., Avendano, E. E., Tanprasertsuk, J., Scott, T. M., Johnson, E. J., Chung, M., & Nirmala, N.

Review Article
Oily fish, particularly sardines, due to their high omega-3 and taurine content, may play a protective role in slowing the progression towards type 2 diabetes.
Díaz-Rizzolo DA, Miro A, Gomis R

Clinical Study
Consumption of blueberries can alter levels of certain beneficial compounds in the blood, potentially contributing to improved cognitive function in older adults.
Rutledge GA, Sandhu AK, Miller MG, Edirisinghe I, Burton-Freeman BB, Shukitt-Hale B

Review Article
Phytochemicals in carrots, particularly carotenoids, are effective at reducing eyesight degeneration and treating chronic eye defects due to their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Taiwo EA, Abdulkareem TT, Fajemisin E

Systematic Review
Almond intake significantly changed the concentrations of triglycerides, total cholesterol and low-density lipoproteins
Asbaghi O, Moodi V, Hadi A, Eslampour E, Shirinbakhshmasoleh M, Ghaedi E, Miraghajani M

Experimental Study
Pomegranate seed oil, rich in conjugated linolenic acid, potentially acts as a cytotoxic agent on tissue tumor cells, reducing polycystic ovary syndrome manifestations.
Bahmani M, Shokri S, Akhtar ZN, Abbaszadeh S, Manouchehri A

Experimental Study
Ginger honey supplementation does not reduce cortisol levels, however, it significantly increases glutathione and estrogen levels in test mice.
Usman AN, Raya I, Yasmin R, Aliyah , Dirpan A, Arsyad A, Permatasari AE, Sumidarti A, Umami N, Emmasitah

Meta-Analysis
The study reveals that pomegranate juice does not significantly affect vascular adhesion factors, but can effectively reduce the inflammatory marker, interleukin-6.
Asgary S, Karimi R, Joshi T, Kilpatrick KL, Moradi S, Samimi Z, Mohammadi E, Farzaei MH, Bishayee A

Systematic Review
Higher coffee consumption, specifically 3-4 cups daily, is associated with a 21% lower risk of stroke, with no further reductions with increased intake.
Shao C, Tang H, Wang X, He J

Review Article
Tea and coffee possess health promoting properties and can effectively prevent and treat metabolic disorders, including obesity, through the suppression of fat storage.
Sirotkin AV, Kolesarova A

Experimental Study
Ginger supplementation can prevent ethanol-induced reproductive dysfunction by improving hormone levels, reducing oxidative damage, inflammation, and regulating genes involved in testosterone synthesis.
Li N, Xing Y, Sultan AH, Raeeszadeh M, Akbari A, Liu H

Experimental Study
The Lycium ruthenicum Murr variety of goji berry exhibits a stronger antioxidant activity and antiproliferative effect on cancer cells compared to Lycium barbarum L.
Xiong L, Deng N, Zheng B, Li T, Liu RH

Systematic Review
The supplementary intake of green tea does not significantly affect blood glucose, fasting insulin, hemoglobin A1c, and insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Asbaghi O, Fouladvand F, Gonzalez MJ, Ashtary-Larky D, Choghakhori R, Abbasnezhad A

Randomised Controlled Trial
Walnut consumption coupled with concurrent training improves lipid profile, steroid hormone levels, and systematic inflammation in elderly men.
Kamoun A, Hammouda O, Turki M, Maaloul R, Chtourou M, Bouaziz M, Driss T, Souissi N, Chamari K, Ayadi F

Review Article
Coffee's bioactive compounds may exhibit various health benefits such as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties on the digestive tract and stimulating effects on motor function.
Iriondo-DeHond A, Uranga JA, del Castillo MD, Abalo R

Review Article
Regular coffee consumption, due to its bioactive compounds, may have protective effects against chronic disorders and certain neurodegenerative conditions.
Socała K, Szopa A, Serefko A, Poleszak E, Wlaź P

Review Article
Isoflavones, mainly found in soy-derived products, show beneficial effects on bone health, potential cancer risk reduction, and alleviation of menopausal symptoms, but not on cardiovascular risk.
Gómez-Zorita S, González-Arceo M, Fernández-Quintela A, Eseberri I, Trepiana J, Portillo MP

Systematic Review
Regular walnut consumption is consistently linked to improved cognitive performance in adults, particularly those at higher risk of cognitive decline.
Lauren E Theodore, Nicole J Kellow, Emily A McNeil, Evangeline O Close, Eliza G Coad, Barbara R Cardoso,

Randomised Controlled Trial
DKB114, a mixture of Linn flower extract, effectively reduces serum uric acid level, suggesting its potential as a dietary supplement for hyperuricemia treatment.
Park YH, Kim DH, Lee JS, Jeong HI, Lee KW, Kang TH

Randomised Controlled Trial
Consumption of jujube seed had a positive impact on improving the sleep quality of postmenopausal women and could be recommended as a useful herbal medication.
Mahmoudi R, Ansari S, Haghighizadeh MH, Maram NS, Montazeri S.

Randomised Controlled Trial
Daily consumption of tart cherry juice may reduce processes involved in accelerated atherogenesis, potentially decreasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Johnson SA, Navaei N, Pourafshar S, Jaime SJ, Akhavan NS, Alvarez-Alvarado S, Proaño GV, Litwin NS, Clark EA, Foley EM, George KS, Elam ML, Payton ME, Arjmandi BH, Figueroa A

Review Article
Jujube fruits contain a high amount of various bioactive compounds exerting antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antiobesity, anti-cardiovascular disease, hepatoprotective, antidiabetic, anti-microbial, anticancer, and gastrointestinal-protective effects.
Rashwan, A. K, Karim, N., Shishir, M. Rezaul Islam, Bao, T., Lu, Y., & Chen, W.

Systematic Review
Consuming walnuts does not significantly alter blood glucose levels, indicating cardiovascular protective effects of walnuts are not due to improved glycaemic control.
Neale, E., Guan, V., Tapsell, L., & Probst, Y.

Experimental Study
Green tea polyphenolic compounds, (-)-epigallocatechin (EGC) and (-)-epicatechin-3-gallate (ECG), can diminish harmful Alzheimer's disease linked Aβ aggregates and ameliorate symptoms.
Chen T, Yang Y, Zhu S, Lu Y, Zhu L, Wang Y, Wang X

Review Article
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids supplementation during the prenatal and perinatal period could have a protective effect on neurodevelopmental disorders including ADHD, ASD, and MDD in youth.
Chang JPC, Su KP

Experimental Study
Mineral water increases the diversity of gut microbiota by aiding the growth of Bacteroidetes taxa.
Zhou K, Liu W, Chen Z, Yang D, Qiu Z, Feng H, Li C, Jin M, Li J, Xu Q, Shen Z

Review Article
Flavonoids from jujube have been found to stimulate the expression of erythropoietin (EPO), a hormone stimulating blood production.
Chen J, Tsim KWK

Review Article
Recent studies have indicated that jujube possesses a wide range of pharmacological activities in nervous system, cardiovascular system, as well as anti-oxidation and anti-cancer properties.
Chen J, Tsim KWK

Systematic Review
Green tea supplementation raises adiponectin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Asbaghi O, Fouladvand F, Ashtary-Larky D, Bagheri R, Choghakhori R, Wong A, Baker JS, Abbasnezhad A

Experimental Study
Chrysanthemum coronarium L. extract can both stimulate bone building cells and inhibit bone breaking cells, so has potential as a natural treatment for osteoporosis.
Kim SA, Lee AS, Hur HJ, Lee SH, Sung MJ

Systematic Review
Green tea consumption notably reduces body weight, body mass index, and body fat, especially in long-term use, at lower dosages, and among overweight individuals with type-2 diabetes.
Asbaghi O, Fouladvand F, Gonzalez MJ, Aghamohammadi V, Choghakhori R, Abbasnezhad A

Review Article
Catechins in green tea potentially counteract osteoporosis by negatively affecting bone loss processes and enhancing bone formation processes.
Huang HT, Cheng TL, Lin SY, Ho CJ, Chyu JY, Yang RS, Chen CH, Shen CL

Systematic Review
Lavender can decrease the severity of labor pain, which could influence health policy makers and gynecologists.
Kazeminia M, Abdi A, Vaisi-Raygani A, Jalali R, Shohaimi S, Daneshkhah A, Salari N, Mohammadi M

Clinical Study
High phenolic early harvest extra virgin olive oil shows notable improvement in cognitive function compared to a moderate phenolic version and the Mediterranean diet alone.
Tsolaki M, Lazarou E, Kozori M, Petridou N, Tabakis I, Lazarou I, Karakota M, Saoulidis I, Melliou E, Magiatis P

Cohort Study
Habitual and high-frequency tea consumption, particularly green tea, is associated with a reduced prevalence of cognitive impairment in middle-aged and older individuals.
Zhang J, Wang A, Zhang X, Chen S, Wu S, Zhao X, Zhang Q

Randomised Controlled Trial
Incorporating tree nuts into a Western-style diet subtly modifies specific DNA methylation regions within sperm, thereby showing parts of the sperm epigenome can respond to dietary changes.
Salas‐Huetos A, James ER, Salas‐Salvadó J, Bulló M, Aston KI, Carrell DT, Jenkins TG

Review Article
Catechin-rich green tea extract (GTE) exercised anti-inflammatory activities can be beneficial in managing Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) by reducing liver injury and gut-derived endotoxins.
Hodges JK, Sasaki GY, Bruno RS

Review Article
Honey's phytochemical components and bioactive compounds have potential antiviral effects, potentially making it an effective natural product against COVID-19.
Al-Hatamleh MAI, Hatmal MM, Sattar K, Ahmad S, Mustafa MZ, Bittencourt MDC, Mohamud R

Review Article
Juhua, the flower head of Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat, possesses multiple medicinal properties and has a significant role in dietary herbal medicine in China.
Yuan H, Jiang S, Liu Y, Daniyal M, Jian Y, Peng C, Shen J, Liu S, Wang W

Experimental Study
Pomegranate juice increases the effectiveness of lung cancer treatment with the low dose chemotherapy drug Cisplatin, while simultaneously reducing its toxicity on normal cells.
Nasser M, Damaj Z, Hijazi A, Merah O, Al-Khatib B, Hijazi N, Trabolsi C, Damaj R, Nasser M

Review Article
Beverages, through their diverse nutritional contents, have notable effects on rheumatoid arthritis progression by interacting with immune signaling pathways and altering the microbiome.
Dey M, Cutolo M, Nikiphorou E

Experimental Study
The major components of green tea and coffee, EGCG and CGA respectively, may have anti-cancer effects, though these effects seem to vary for different types of cancer.
Hayakawa S, Ohishi T, Miyoshi N, Oishi Y, Nakamura Y, Isemura M

Randomised Controlled Trial
Daily consumption of decaffeinated green tea catechins may enhance working memory.
Baba Y, Inagaki S, Nakagawa S, Kaneko T, Kobayashi M, Takihara T

Systematic Review
The consumption of green tea significantly lowers low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and total cholesterol, but it does not affect high-density lipoprotein cholesterol or triglycerides.
Xu R, Yang K, Li S, Dai M, Chen G

Randomised Controlled Trial
The use of ginger, chamomile, and honey significantly diminished the intensity of dysmenorrhea pain as compared to the use of mefenamic acid.
Shabani F, Chabra A, Vakilian K, Bioos S, Bozorgi M, Ayati MH, Nejatbakhsh F

Randomised Controlled Trial
Inhalation aromatherapy using Damask rose and lavender essential oils can reduce anxiety and pain in women after they have had a cesarean section.
Abbasijahromi A, Hojati H, Nikooei S, Jahromi HK, Dowlatkhah HR, Zarean V, Farzaneh M, Kalavani A

Systematic Review
Lavender demonstrates significant benefits for pain relief and episiotomy wound healing in postpartum.
Abedian S, Abedi P, Jahanfar S, Iravani M, Zahedian M

Systematic Review
The most important tremella mushroom benefits are anti-aging, anti-inflammatory, lower cholesterol, combat obesity, protect nerves and may fight cancer.
Mohamad Hesam Shahrajabian, Wenli Sun, Hong Shen and Qi Cheng

Randomised Controlled Trial
Fenugreek improves breast milk production in mothers and increases the weight gain of newborns during their first week of life.
Ravi R, Joseph J

Systematic Review
Cinnamon supplementation significantly decreases inflammation and oxidative stress levels, serving as a potential additive for cardiometabolic health improvement.
Zhu, Changyou; Yan, Hongmei; Yin, Zheng; Santos, Heitor O; Melahat Sedanur Macit; et al

Meta-Analysis
Supplementation with blueberry shows a potential for beneficial impact on reducing body weight, which might indirectly influence cardiovascular disease risk factors.
Miraghajani M, Momenyan S, Arab A, Hasanpour Dehkordi A, Symonds ME

Review Article
Green tea and its compounds, especially catechins, may potentially prevent and treat osteoarthritis due to their potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Barbalho SM, Goulart RA, Buglio DS, Araujo AC, Guiguer EL

Review Article
Green tea polyphenols can potentially protect against neurodegenerative disorders like Parkinson's Disease through antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective actions.
Malar DS, Prasanth MI, Brimson JM, Sharika R, Sivamaruthi BS, Chaiyasut C, Tencomnao T

Systematic Review
The literature overall supports an inverse association between green tea and cardiovascular disease-related health outcomes, while the included meta-analyses generally suggested an inverse association between green tea and BMI-related and blood pressure outcomes.
Abe SK, Inoue M

Systematic Review
Higher consumption of coffee correlates with a significant decrease in the risk of liver cancer or hepatocellular carcinoma.
Bhurwal A, Ratta P, Yoshitake S, Pioppo L, Reja D, Dellatore P, Rustgi V

Systematic Review
Honey can be used as an alternative to antibiotics by clinicians who wish to offer treatment for upper respiratory tract infections, which may help to combat antimicrobial resistance.
Abuelgasim H, Albury C, Lee J

Systematic Review
Honey is more effective than usual care alternatives for improving upper respiratory tract infection symptoms, particularly cough frequency and cough severity.
Abuelgasim H, Albury C, Lee J

Clinical Study
Montmorency tart cherry juice can significantly improve blood pressure, fasting glucose, cholesterol rates and respiratory exchange ratio in those with metabolic syndrome.
Desai T, Roberts M, Bottoms L
Review Article
In jujube fruit, the contents of sugar, vitamin C, and cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) are around 2, 100, and 1000 times those of apple, respectively.
Liu, M., Wang, J., Wang, L. et al.

Randomised Controlled Trial
Concentrated pomegranate juice consumption can potentially lower cardiovascular disease risk factors in women with polycystic ovary syndrome.
Abedini M, Ghasemi‐Tehrani H, Tarrahi MJ, Amani R

Randomised Controlled Trial
A botanical formula of lutein ester, zeaxanthin, and extracts from blackcurrant, chrysanthemum, and goji berry can effectively lessen eye fatigue and improve macular function.
Kan J, Wang M, Liu Y, Liu H, Chen L, Zhang X, Huang C, Liu BY, Gu Z, Du J

Review Article
Honey, with its variable composition based on botanical origin, exhibits antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, suggesting its potential efficacy in managing obesity-related dysfunctions, including neurodegeneration, through improved glycemic control and lipid profile.
Terzo S, Mulè F, Amato A

Clinical Study
Magnesium-rich mineral water effectively treats and prevents constipation in children, leading to regular, painless bowel movements.
Kulikov AG, Zakharova IN, Tvorogova TM, Stepurina LL, Elezova LI

Systematic Review
Eggplant may possibly be used in the treatment of anemia, atherosclerosis, and fatty degeneration.
Meenakshi Sharma and Prashant Kaushik

Network Pharmacology
Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat. ethanol extract (CEE) presents a potential protective effect on lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung injury in mice.
Liu G, Zheng Q, Pan K, Xu X

Review Article
Magnesium sulfate-rich natural mineral waters are effective and safe as a natural treatment for functional constipation.
Dupont C, Hébert G

Systematic Review
Green tea supplementation significantly lowers fasting glucose levels but does not significantly affect fasting insulin and haemoglobin A1c values.
Xu R, Bai Y, Yang K, Chen G

Network Pharmacology
Seasonal variations influence the nutrient composition of European sardines, with lipid levels peaking from July to September and amino acid content highest during winter.
Šimat V, Hamed I, Petričević S, Bogdanović T

Systematic Review
For primary dysmenorrhoea, cinnamon/fennel/ginger effectively reduced pain intensity, and cinnamon shortened the duration of pain.
Xu Y, Yang Q, Wang X

Experimental Study
Probiotic-enriched mung and adzuki bean sprouts demonstrate increased antioxidant potential and exhibit cytostatic and cytotoxic effects on human stomach cancer cells.
Świeca M, Herok A, Piwowarczyk K, Sikora M, Ostanek P, Gawlik-Dziki U, Kapusta I, Czyż J

Cocoa polyphenols promote gut health by favorably altering gut microbiota composition and producing secondary bioactive metabolites with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Sorrenti V, Ali S, Mancin L, Davinelli S, Paoli A, Scapagnini G

Review Article
Black pepper, particularly the piperine it contains, enhances the absorption of iron, potentially improving athletic performance in endurance sports.
Fernández-Lázaro D, Mielgo-Ayuso J, Córdova Martínez A, Seco-Calvo J

Theoretical Article
Coffee, like many fruits and vegetables, activates a cellular response that boosts antioxidants and repair enzymes, which contributes to a lower risk of several diseases.
Kolb H, Kempf K, Martin S

Randomised Controlled Trial
The use of standardized saffron extract appears to show significant improvement in sleep quality in healthy adults with self-reported sleep issues.
Lopresti AL, Smith SJ, Metse AP, Drummond PD

Meta-Analysis
Chronic consumption of cranberry or cherry juice might considerably improve blood pressure levels.
Wang Y, Gallegos JL, Haskell-Ramsay C, Lodge JK

Experimental Study
Honey contains 20(S)-Hydroxyvitamin D3 (20(OH)D3) and its derivatives, including 20(OH)-7DHC, 25(OH)D3, and 1,25(OH)2D3, indicating their production in bees and suggesting potential health implications.
Kim TK, Atigadda V, Brzeminski P, Fabisiak A, Tang EKY, Tuckey RC, Slominski AT

Experimental Study
We determined the concentration of 20(OH)D3 in honey to be 0.26 µg/g, corresponding to approximately 10 IU/g.
Kim TK, Atigadda V, Brzeminski P, Fabisiak A, Tang EKY, Tuckey RC, Slominski AT

Systematic Review
Green tea catechins-containing mouthwash may potentially be a practical alternative to chlorhexidine due to its efficacy in plaque reduction and minimal side effects.
Gartenmann SJ, Steppacher SL, von Weydlich Y, Heumann C, Attin T, Schmidlin PR

Review Article
Incorporating avocados into the Mediterranean diet may enhance its benefits, offering greater health flexibility and adaptability for non-Mediterranean residents.
Ford NA, Liu AG

Experimental Study
Unpasteurised milk and dairy products intake could potentially alter gut microbiome composition which may influence psychological functioning.
Butler MI, Bastiaanssen TFS, Long-Smith C, Berding K, Morkl S, Cusack AM, Strain C, Busca K, Porteous-Allen P, Claesson MJ, Stanton C, Cryan JF, Allen D, Dinan TG

Randomised Controlled Trial
Eating whole SunGold kiwifruits, both with and without skin, can significantly decrease gut inflammation and alleviate constipation for both healthy people and those with irritable bowel syndrome.
Eady SL, Wallace AJ, Hedderley DI, Bentley-Hewitt KL, Butts CA

Systematic Review
Green coffee supplementation significantly decreases fasting blood sugar, insulin, and triglycerides while boosting high-density lipoprotein levels.
Morvaridi M, Rayyani E, Jaafari M, Khiabani A, Rahimlou M

Daily consumption of coffee and green tea is linked with decreased body mass index, body fat percentage, and cardiovascular risks in middle-aged Japanese women.
Yonekura Y, Terauchi M, Hirose A, Odai T, Kato K, Miyasaka N

Systematic Review
Coffee intake may have a variable effect on inflammation markers, with different responses noted between men and women and across various geographical regions.
Moua ED, Hu C, Day N, Hord NG, Takata Y

Systematic Review
Green tea intake can significantly reduce body weight, body mass index and waist circumference, with the greatest effect seen with lower dosages and shorter treatment durations.
Lin Y, Shi D, Su B, Wei J, Găman MA, Sedanur Macit M, Borges do Nascimento IJ, Guimaraes NS

Systematic Review
Aromatherapy, specifically with lavender essential oil, can effectively alleviate maternal anxiety and labor pain.
Mahbubeh Tabatabaeichehr , Hamed Mortazavi

Systematic Review
Almond intake significantly decreased diastolic blood pressure, and inconsistently, almonds decreased systolic blood pressure.
Eslampour E, Asbaghi O, Hadi A, Abedi S, Ghaedi E, Lazaridi AV, Miraghajani M

Systematic Review
Cinnamon supplementation may help manage metabolic parameters in polycystic ovary syndrome patients by reducing fasting blood sugar, insulin, LDL-C, total cholesterol, and triacylglycerol levels.
Heydarpour F, Hemati N, Hadi A, Moradi S, Mohammadi E, Farzaei MH

Experimental Study
Pomegranate juice has potential beyond ascorbic acid alone in enhancing iron absorption and assimilation, supporting Ayurveda's proposition of managing iron deficiency anemia with pomegranate.
Balasubramani SP, Varghese RK, Vishnuprasad CN, Venkatasubramanian P

Systematic Review
Meta-analysis showed that date fruit consumption can significantly reduce the active phase of labor, and also significantly improve the bishop score.
Bagherzadeh Karimi A, Elmi A, Mirghafourvand M, Baghervand Navid R

Systematic Review
Cinnamon supplementation can improve blood pressure by a modest degree.
Hadi A, Campbell MS, Hassani B, Pourmasoumi M, Salehi-sahlabadi A, Hosseini SA

Review Article
Different varieties of dates pose impressive nutritional profiles and exhibit multiple health benefits, including anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and cholesterol lowering potential.
Hussain MI, Farooq M, Syed QA

Randomised Controlled Trial
Chamomile capsules can decrease the amount of menstrual bleeding and thus, can offer remedy for women suffering from heavy periods.
Mollabashi EN, Ziaie T, Bekhradi R, Khalesi ZB

Review Article
Pomegranate, due to its polyphenols, flavonoids and fatty acids, exhibits significant pain-relieving effects and could potentially be used as a treatment for various types of pain.
Guerrero-Solano JA, Jaramillo-Morales OA, Velázquez-González C, De la O-Arciniega M, Castañeda-Ovando A, Betanzos-Cabrera G, Bautista M

Randomised Controlled Trial
Lemon juice, but not black tea, can lower and delay the blood glucose concentration peak after consuming bread.
Freitas D, Boué F, Benallaoua M, Airinei G, Benamouzig R, Le Feunteun S

Randomised Controlled Trial
Daily intake of 3 grams of oat beta-glucans significantly reduces LDL-Cholesterol, Total Cholesterol, and non-HDL-Cholesterol levels without impacting intestinal well-being or glucose levels.
Cicero AFG, Fogacci F, Veronesi M, Strocchi E, Grandi E, Rizzoli E, Poli A, Marangoni F, Borghi C

Systematic Review
Green tea, containing antioxidative catechins, may possess some beneficial effects in reducing the risk of specific types of cancer.
Filippini T, Malavolti M, Borrelli F, Izzo AA, Fairweather-Tait SJ, Horneber M, Vinceti M

Randomised Controlled Trial
Certain essential oils such as lavender, neroli, jasmine, roman chamomile, clary sage, and Indian sandalwood can potentially increase oxytocin concentrations in postmenopausal women.
Tarumi W, Shinohara K

Systematic Review
Almond consumption was found to significantly reduce systolic blood pressure.
Li Z, Bhagavathula AS, Batavia M, Clark C, Abdulazeem HM, Rahmani J, Yin F

Meta-Analysis
Consumption of raw milk early in life appears to provide protection against asthma and allergies, regardless of whether children live on farms or in rural, non-farm areas.
Brick T, Hettinga K, Kirchner B, Pfaffl MW, Ege MJ

Meta-Analysis
Pomegranate juice supplementation notably diminishes inflammation and vascular dysfunction markers in adults, offering potential cardiovascular health benefits.
Wang P, Zhang Q, Hou H, Liu Z, Wang L, Rasekhmagham R, Kord-Varkaneh H, Santos HO, Yao G

Systematic Review
Cinnamon supplementation in type 2 diabetes patients significantly reduces systolic and diastolic blood pressure, but doesn't significantly affect body weight and waist circumference.
Jamali N, Jalali M, Saffari-Chaleshtori J, Samare-Najaf M, Samareh A

Systematic Review
Honey exhibits significant anti-Helicobacter pylori activity, with at least 10% concentration proving effective in inhibiting gastric and duodenal ulcers, highlighting its therapeutic potential.
Adam Q, Annuar F, Alfizah H, Mohd Fahami NA

Systematic Review
These reports suggest the benefits of a walnut-enriched diet in brain disorders and in other chronic diseases, due to the additive or synergistic effects of walnut components for protection against oxidative stress and inflammation in these diseases.
Chauhan A, Chauhan V.

Systematic Review
Green tea influences liver enzymes differently based on an individual's health status, reducing levels in patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, but slightly increasing levels in healthy subjects.
Mahmoodi M, Hosseini R, Kazemi A, Ofori‐Asenso R, Mazidi M, Mazloomi SM

Meta-Analysis
Coffee consumption shows a strong association with decreased risk of liver and endometrial cancer.
Zhao LG, Li ZY, Feng GS, Ji XW, Tan YT, Li HL, Gunter MJ, Xiang YB

Experimental Study
Lactic acid bacteria strains isolated from indigenous Bangladeshi raw milk demonstrate strong probiotic potential and antimicrobial activity against various pathogens.
Reuben RC, Roy PC, Sarkar SL, Rubayet Ul Alam ASM, Jahid IK

Clinical Study
Green tea intake can significantly reduce both systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Xu R, Yang K, Ding J, Chen G

Randomised Controlled Trial
Daily avocado consumption improves attentional inhibition and increases serum lutein concentrations, irrespective of changes in lutein status, in adults with obesity.
Edwards CG, Walk AM, Thompson SV, Reeser GE, Erdman JW, Burd NA, Holscher HD, Khan NA

Randomised Controlled Trial
Intranasal application of essential oils such as lavender and fennel (Pinetonina™) significantly lowers cortisol levels and improves sleep quality.
Polonini H, Mesquita D, Lanine J, Dijkers E, Gkinis S, Raposo NRB, Brandão MAF, Ferreira AO

Systematic Review
Ginger has been effective in a majority of studies, including those that examined the alleviation of nausea and vomiting of pregnancy, digestive function, improvement in the expression level of markers for colorectal cancer risk, and anti-inflammatory functions.
Anh NH, Kim SJ, Long NP, Min JE, Yoon YC, Lee EG, Kim M, Kim TJ, Yang YY, Son EY, Yoon SJ, Diem NC, Kim HM, Kwon SW.

Review Article
Bioactive compounds found in avocado waste products exhibit various biological properties, with potential applications in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
Jimenez P, Garcia P, Quitral V, Vasquez K, Parra-Ruiz C, Reyes-Farias M, Garcia-Diaz DF, Robert P, Encina C, Soto-Covasich J

Clinical Study
Children with asthma, aged between 2 and 18, were found to be significantly shorter than their healthy counterparts.
Mohamadi Sorme F, Tabarra M, Alimadady H, Rahimi R, Sepidarkish M, Karimi M

Randomised Controlled Trial
The combination of ginger and chamomile was as effective as mefenamic acid in managing dysmenorrhea pain and more efficient in reducing related symptoms.
Shabani F, Zareian MA

Cohort Study
Regular consumption of raw carrots, specifically 2-4 or more per week, is associated with a decreased risk of colorectal cancer.
Deding U, Baatrup G, Christensen LP, Kobaek-Larsen M

Systematic Review
Honey showed a significant antimicrobial activity against all targeted periopathogen and could be effective in the treatment of periodontal disease.
Hbibi A, Sikkou K, Khedid K, El Hamzaoui S, Bouziane A, Benazza D

Network Pharmacology
Ganpu tea, derived from Pu-erh tea and the pericarp of Chachi, enhances antioxidant capacities and modulates gut microbiota beneficially more than Pu-erh tea alone.
Zheng Y, Zeng X, Chen T, Peng W, Su W

Experimental Study
Chrysanthemum morifolium, Naringenin and Apigenin can alleviate depression-like behavior by interfering with specific metabolic pathways.
Liu T, Zhou N, Xu R, Cao Y, Zhang Y, Liu Z, Zheng X, Feng W

Network Pharmacology
Pomegranate fruit extract significantly enhances cartilage gene expression and chondrogenesis in human adipose-derived stem cells compared to Avocado/Soybean Unsaponifiable.
Bahramian H, Teimourinejad A, Hashemibeni B, Salehi H, Mostafavi FS, Kazemi M

Systematic Review
Cocoa consumption significantly reduces markers of oxidative stress in the adult population, affirming its important role in the human metabolic pathway.
Mehrabani S, Arab A, Mohammadi H, Amani R

Systematic Review
Almond intake significantly reduces body weight and fat mass in adults, yet it does not impact body mass index, waist circumference, or fat-free mass.
Eslampour E, Moodi V, Asbaghi O, Ghaedi E, Shirinbakhshmasoleh M, Hadi A, Miraghajani M

Review Article
The Chrysanthemum indicum L. plant has been discovered to have multiple pharmacological capabilities including anti-inflammatory, antioxidation, antipathogenic, anticancer, immune regulation, and hepatoprotective effects.
Shao Y, Sun Y, Li D, Chen Y

Review Article
Prunus mume fruit extracts display hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, antibacterial effects, and show promise for treating cancer and alleviating chemotherapy side-effects.
Bailly C

Review Article
Saffron shows potential as a promising therapeutic agent in treating neurodegenerative ocular diseases.
Ramírez JM, Salazar JJ, Fernández-Albarral JA, de Hoz R, Ramírez AI, López-Cuenca I, Salobrar-García E, Pinazo-Durán MD

Systematic Review
Cinnamon intake significantly reduces body weight, body mass index, waist circumference, and fat mass in adults, and can be recommended as a supplement for obesity management.
Mousavi SM, Rahmani J, Kord-Varkaneh H, Sheikhi A, Larijani B, Esmaillzadeh A

Review Article
The date fruit contains compounds such as flavonoids that can protect tissues from harm and reduce risks of illnesses like cardiovascular disease and cancer.
Bentrad N, Hamida-Ferhat A

Review Article
Coffee and decaffeinated coffee appear to provide long-term protection against developing type 2 diabetes, potentially due to the influence of chlorogenic acids.
Williamson G

Review Article
Avocado, particularly the Hass variety, has substantial health benefits due to its rich contents of nutrients, fiber, and bioactive constituents including antioxidants.
Majid D, Dar BN, Parveen S, Jabeen A, Allai FM, Sofi SA, Ganaie TA

Systematic Review
Chamomile shows promise in alleviating premenstrual syndrome (PMS) symptoms.
Khalesi ZB, Beiranvand SP, Bokaie M

Randomised Controlled Trial
Consuming walnuts daily can reduce cardiovascular risk factors in chronic kidney disease patients without altering significant physiological levels.
Sanchis P, Molina M, Berga F, Muñoz E, Fortuny R, Costa-Bauzá A, Grases F, Buades JM

Randomised Controlled Trial
Pomegranate juice can reduce melatonin, increase insulin levels, and improve insulin resistance in individuals with impaired fasting glucose.
Banihani SA, Fashtaky RA, Makahleh SM, El‐Akawi ZJ, Khabour OF, Saadeh NA

Systematic Review
Gout patients regularly ingesting cherry extract/juice reported fewer gout flare ups than those patients who did not supplement their diets with cherry products.
Chen PE, Liu CY, Chien WH, Chien CW, Tung TH

Review Article
Traditional Chinese medicine, especially Zuo Gui Wan, red raspberry leaves, and Orthosiphon stamineus, seems to control gestational diabetes effectively without reported toxicity.
Xu YXZ, Xi S, Qian X

Clinical Study
Drinking at least 1.5 to 2 litres of bicarbonate-rich mineral water daily significantly reduces dietary acid load in healthy adults.
Wasserfurth P, Schneider I, Ströhle A, Nebl J, Bitterlich N, Hahn A

Review Article
The Mediterranean diet, especially the high consumption of extra-virgin olive oil, significantly reduces the risks of vascular diseases and Alzheimer's.
Román GC, Jackson RE, Reis J, Román AN, Toledo JB, Toledo E

Systematic Review
Cinnamon supplementation can significantly reduce body weight, body mass index, and waist-hip ratio.
Zeinab Yazdanpanah,Maryam Azadi-Yazdi,Hadis Hooshmandi,Nahid Ramezani-Jolfaie,Amin Salehi-Abargouei,

Experimental Study
Pu-erh tea's ability to lower blood pressure is primarily due to theabrownins and caffeine, which cause vasodilation irrespective of the endothelium.
Luo Dan, Chen Xuejiao, Zhu Xu, Liu Shuang, Li Jie, Xu Jianping, Zhao Jinhua, Ji Xu

Theoretical Article
Consumption of oat β-glucan may lower cholesterol and risk of cardiovascular disease by altering gut bacteria and their effects on bile acid and cholesterol metabolism.
Joyce SA, Kamil A, Fleige L, Gahan CGM

Coix lacryma-jobi sprout extract effectively inhibits cervical cancer cell growth by triggering cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
Son, E.S., Kim, SH., Kim, Y.O. et al

Systematic Review
A combination of peppermint oil and caraway oil is an effective and safe short-term treatment for functional dyspepsia.
Juanjuan Li, Lin Lv, Jiaqi Zhang, Lin Xu, Enjin Zeng, Zedan Zhang, Fengyun Wang, Xudong Tang

Experimental Study
Pu-erh tea was found to lower triglyceride and total cholesterol levels more significantly than green, oolong, or black teas.
Huang, F., Zheng, X., Ma, X. et al.

Coix seed extract could augment the efficacy of gemcitabine therapy in pancreatic cancer cells at least partly due to the alteration of ABC transporter-mediated drug efflux function.
Qian, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Feng, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Gu, M.

Review Article
Oats improve gastrointestinal health, reduce cholesterol, and regulate satiety, with effects on the gut microbiome constituting an appealing new research area.
Korczak R, Kocher M, Swanson KS

Cohort Study
Caramanico Terme’s mineral water treatment significantly improves health and reduces the risk of major diseases like cardiovascular, cancer, and neurological conditions.
Di Marco M, De Novellis AMP, Carluccio V, Bozzelli R, Orlando M, Lanuti P

Systematic Review
Cinnamon supplementation leads to a significant reduction in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure in adults.
Seyed Mohammad Mousavi, Ahmad Jayedi, Yahya Jalilpiran, Maryam Hajishafiee, Azadeh Aminianfar, Ahmad Esmaillzadeh.

Systematic Review
Peppermint oil significantly reduces colonic spasm during colonoscopy, but does not affect the adenoma detection rate or cecal intubation time.
Nehme, Fredy; Al Momani, Laith; Alomari, Mohammad ; Zafar, Yousaf

Review Article
Avocado's nutritional and therapeutic properties show potential for novel drug discovery in prevention and treatment of prevalent diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and cardiovascular issues.
Bhuyan , Alsherbiny , Perera , Low , Basu , Devi , Barooah , Li , Papoutsis

Systematic Review
Higher carrot consumption is associated with a lower risk of developing lung cancer, particularly adenocarcinoma.
Xu H, Jiang H, Yang W, Song F, Yan S, Wang C, Fu W, Li H, Lyu C, Gan Y, Lu Z

Clinical Study
Hépar mineral water, rich in sulphates and magnesium, effectively treats functional constipation, showing significant results within 7 days.
Dupont C, Constant F, Imbert A, Hébert G, Zourabichvili O, Kapel N

Cohort Study
Pregnant women's stature, BMI, sedentary lifestyle, as well as the regular consumption of certain foods, influence the formation and severity of striae gravidarum.
Ren P, Zhao W, Dai X, Wang X, Yu J, Yuan Y, Wu Y

Systematic Review
Pu-erh tea has considerable inhibitory effects on alpha-amylase and alpha-glucosidase, indicating potential anti-hyperglycemic benefits.
Yang, CY., Yen, YY., Hung, KC. et al.

Review Article
Kiwifruit supplementation may be associated with direct and indirect anticancer effects, the former likely due to ascorbic acid-mediated reduction of DNA oxidative injury and cytotoxic effect on cancer cell lines.
Lippi G, Mattiuzzi C

Review Article
Chrysanthemum, rich in unique chemical compounds, offers significant health benefits such as stress relief, cardio protection, immunity boost, improved eye health, and osteoporosis risk reduction.
SHAHRAJABIAN, M. H., SUN, W., ZANDI, P., CHENG, Q.

Systematic Review
Eating date fruits seems to reduce gestation duration and duration of the first stage of labor, and also increase cervical dilation on admission.
Nasiri M, Gheibi Z, Miri A, Rahmani J, Asadi M, Sadeghi O, Maleki V, Khodadost M

Systematic Review
Our study found ginger is a promising herbal medicine for health care, which is beneficial for nausea and vomiting, metabolic syndrome and pain.
Li H, Liu Y, Luo D, Ma Y, Zhang J, Li M, Yao L, Shi X, Liu X, Yang K.

Systematic Review
Avocado-soybean unsaponifiables treatment is effective in reducing knee osteoarthritis symptoms without increasing adverse events, contrary to those with hip osteoarthritis.
Simental‐Mendía M, Sánchez‐García A, Acosta‐Olivo CA, Vilchez‐Cavazos F, Osuna‐Garate J, Peña‐Martínez VM, Simental‐Mendía LE

Review Article
Honey, comprising mainly carbohydrates, particularly fructose and glucose, demonstrates potential performance benefits and immunological advantages when consumed around exercise, suggesting a role in exercise nutrition.
Hills , Mitchell , Wells , Russell

Systematic Review
Oral administration of honey is associated with increased serum testosterone levels in males, supported by in vivo studies suggesting mechanisms involving luteinizing hormone production, Leydig cell viability, oxidative damage reduction, enhanced StAR gene expression, and aromatase activity inhibition.
Banihani SA

Systematic Review
The collective evidence, which is mainly based on in vivo system studies, reveals that oral administration of honey increases serum testosterone level in males.
Banihani SA

Systematic Review
Aromatherapy enhances physio-psychological well-being in postpartum women.
TSAI SS, WANG HH, CHOU FH

Animal Study
Pomegranate rind extract has been found to decrease pain and inflammation, suggesting it could contribute to treating rheumatoid arthritis.
Karwasra R, Singh S, Sharma D, Sharma S, Sharma N, Khanna K

Results demonstrate that 100% watermelon juice is a palatable, effective means of increasing serum lycopene in older adult women, a group at risk for low carotenoid intake.
Ellis, A.C., Dudenbostel, T. & Crowe-White, K

Randomised Controlled Trial
Our study offers the first evidence of the positive contribution of tea drinking to brain structure and suggests a protective effect on age-related decline in brain organisation.
Li J, Romero-Garcia R, Suckling J, Feng L.

Randomised Controlled Trial
Consuming walnuts can enhance sperm motility and morphology, potentially improving fertility in males with infertility issues.
Robbins W, Kim H, Houman J, Lee GW

Systematic Review
The mung bean has been documented to ameliorate hyperglycemia, hyperlipemia, and hypertension, and prevent cancer and melanogenesis, as well as possess hepatoprotective and immunomodulatory activities.
Hou, D., Yousaf, L., Xue, Y., Hu, J., Wu, J., Hu, X., Feng, N., & Shen, Q. (2019).

Systematic Review
Saffron shows promising effectiveness in alleviating symptoms of depression and anxiety and augmenting the effects of antidepressants.
Marx W, Lane M, Rocks T, Ruusunen A, Loughman A, Lopresti A, Marshall S, Berk M, Jacka F, Dean OM

Systematic Review
Drinking certain types of mineral water can positively influence metabolic syndrome factors like blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels.
Costa-Vieira D, Monteiro R, Martins MJ

Randomised Controlled Trial
Adzuki bean extract administered once a day can result in increased HDL-C concentration.
Kitano-Okada T, Nagata R, Han KH, Mikami N, Satoh K, Nishihira J, Sasaki K, Ohba K, Fukusima M

Randomised Controlled Trial
Peppermint oil capsules may significantly reduce the severity of premenstrual syndrome symptoms in reproductive-age women.
Agajani Delavar M, Ebrahimi S, Esmaeilzadeh S, Khamse A

Systematic Review
Ginger enhances semen quality and improves sperm parameters, an impact linked to increased levels of gonadal hormones, decreased cell damage, and valued nutrients in ginger.
Banihani SA

Meta-Analysis
Chamomile has demonstrative positive effects on generalized anxiety disorders and sleep quality, but exhibits minimal impact on state anxiety and insomnia.
Hieu TH, Dibas M, Surya Dila KA, Sherif NA, Hashmi MU, Mahmoud M, Trang NTT, Abdullah L, Nghia TLB, Y MN, Hirayama K, Huy NT

Network Pharmacology
Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide, a major bioactive component in the edible medicinal mushroom, exhibits substantial health benefits, including enhancing the immune system, combatting tumors, and delaying aging.
Yang D, Liu Y, Zhang L.

Experimental Study
Pomegranate extracts and a probiotic strain have shown a combined effect in reducing fat content and the development of fat cells, potentially useful in preventing and treating obesity.
Sorrenti V, Randazzo CL, Caggia C, Ballistreri G, Romeo FV, Fabroni S, Timpanaro N, Raffaele M, Vanella L

Systematic Review
Coffee consumption shows a protective effect against colorectal and colon cancers, particularly among US subjects and European men.
Sartini M, Bragazzi N, Spagnolo A, Schinca E, Ottria G, Dupont C, Cristina M

Experimental Study
The pectin-free fraction of Lycium barbarum, or goji berry, strongly inhibits growth in breast cancer cells, and this effect is enhanced by adding polysaccharides.
Georgiev KD, Slavov IJ, Iliev IA.

Experimental Study
The pectin-free fraction from Lycium barbarum fruit exhibits significant antioxidant activity and inhibits the growth of breast cancer cells.
Georgiev KD, Slavov IJ, Iliev IA

There is low quality evidence that bitter melon adjunct preparations improved glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.
Peter EL, Kasali FM, Deyno S, Mtewa A, Nagendrappa PB, Tolo CU, Ogwang PE, Sesaazi D

Systematic Review
Bioactive compounds present in different parts of radishes, such as leaves, sprouts, stem and roots, act on a variety of potential drug targets associated with ailments, such as cancer, inflammation, liver injury and diabetes.
Abinaya ManivannanOrcID,Jin-Hee Kim,Do-Sun Kim,Eun-Su Lee andHye-Eun Lee

Systematic Review
Black pepper, beyond its culinary use, offers medicinal benefits like antimicrobial, antioxidant, anticancer, anti-diabetic, and anti-inflammatory properties mainly attributed to the compound piperine.
Takooree H, Aumeeruddy MZ, Rengasamy KRR, Venugopala KN, Jeewon R, Zengin G, Mahomoodally MF

Randomised Controlled Trial
Synbiotic pomegranate juice (containing inulin and lactobacillus) can improve insulin resistance, reduce testosterone level, and aid weight loss in women suffering from Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome.
Esmaeilinezhad Z, Babajafari S, Sohrabi Z, Eskandari MH, Amooee S, Barati-Boldaji R

Systematic Review
The health benefits of goji berries include enhancing hemopoiesis, antiradiation, antiaging, anticancer, improvement of immunity, and antioxidation.
Zheng Feei Ma, Hongxia Zhang, Sue Siang Teh, Chee Woon Wang, Yutong Zhang, Frank Hayford, Liuyi Wang, Tong Ma, Zihan Dong, Yan Zhang, Yifan Zhu,

Systematic Review
Goji berries, rich in antioxidants, confer health benefits including protection against aging, cancer, and radiation, as well as enhancing immunity and blood production.
Zheng Feei Ma, Hongxia Zhang, Sue Siang Teh, Chee Woon Wang, Yutong Zhang, Frank Hayford, Liuyi Wang, Tong Ma, Zihan Dong, Yan Zhang, Yifan Zhu,

Randomised Controlled Trial
Kiwifruit increases water retention in the small bowel and ascending colon and increases total colonic volume. It could be used as a dietary alternative to laxatives in mild constipation.
Wilkinson‐Smith V, Dellschaft N, Ansell J, Hoad C, Marciani L, Gowland P, Spiller R

Network Pharmacology
Raw pu-erh tea extract has superior antioxidant capacity due to higher polyphenol content, but ripe pu-erh offers a cheaper, yet effective alternative for antioxidant or antimicrobial properties.
Roda G, Marinello C, Grassi A, et al.

Randomised Controlled Trial
Dark chocolate with high cocoa content can affect colonic functionality and stimulate certain brain regions in healthy adults.
Fox M, Meyer-Gerspach AC, Wendebourg MJ, Gruber M, Heinrich H, Sauter M, Woelnerhanssen B, Koeberle D, Juengling F

Animal Study
Ripened Pu-erh tea extract demonstrates a stronger anti-diabetic impact than raw Pu-erh tea extract, potentially due to the fermentation process and its probiotic benefits to certain gut bacteria.
Qianzhi Ding, Wei Zheng, Bowei Zhang, Xiaojuan Chen, Jie Zhang, Xu Pang, Yong Zhang, Dexian Jia, Surui Pei Yuesheng Dong Baiping Ma

Randomised Controlled Trial
Daily consumption of tart cherry juice for 12 weeks showed anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory properties which may reduce blood pressure and lower LDL cholesterol in older adults.
Chai S, Davis K, Zhang Z, Zha L, Kirschner K

Randomised Controlled Trial
Daily consumption of tart cherry juice may enhance cognitive abilities in older adults, likely due to reduction of hypertension, inflammation, and oxidative stress.
Chai SC, Jerusik J, Davis K, Wright RS, Zhang Z

Network Pharmacology
The purple chrysanthemum tea, imbued with unique antioxidants and affected by infusion time, showed comparatively higher antioxidant activity than the yellow chrysanthemum.
Han AR, Nam B, Kim BR, Lee KC, Song BS, Kim SH, Kim JB, Jin CH.
Review Article
Cherries and their products have antioxidant properties, the capacity to inhibit the acute inflammatory response to urate crystals, and the ability to decrease bone resorption that is characteristic of gouty bone erosions.
Collins MW, Saag KG, Singh JA

Randomised Controlled Trial
Daily consumption of three gold-fleshed kiwifruit is associated with a significant increase of two complete spontaneous bowel movements per week and reduction in gastrointestinal discomfort in mildly constipated adults.
Eady SL, Wallace AJ, Butts CA, Hedderley D, Drummond L, Ansell J, Gearry RB

Experimental Study
Lemongrass extract has potential as a supplement to chemotherapy, reducing colon cancer growth, enhancing treatment effectiveness, and mitigating side effects like weight loss.
Ruvinov I, Nguyen C, Scaria B, Vegh C, Zaitoon O, Baskaran K, Mehaidli A, Nunes M, Pandey S

Theoretical Article
Chrysanthemum, a plant primarily grown in China and Japan, offers significant health benefits including stress reduction, cardiovascular improvement, and lowering osteoporosis risk.
SHAHRAJABIAN MH

Review Article
Blueberry anthocyanins have a potential role in preventing osteoporosis and demonstrate positive antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity.
, Jones DR

Review Article
Honey exhibits efficacy in otolaryngology, supported by high-quality evidence, particularly in preventing oral mucositis in cancer patients, alleviating pediatric cough, and managing post-tonsillectomy pain.
Tharakan T, Bent J, Tavaluc R

Randomised Controlled Trial
Consumption of date fruits has a positive impact on the onset and progression of labour, whilst improving infant outcome.
Ahmed IE, Mirghani HO, Mesaik MA, Ibrahim YM, Amin TQ

Systematic Review
Most bioactive walnut micronutrients synergize to affect multiple metabolic pathways leading to protection from chronic noncommunicable diseases.
Ros, Emilioa,b; Izquierdo-Pulido, Maríab,c; Sala-Vila, Aleix
Systematic Review
Ginger supplementation enhances the production of testosterone in males by reducing oxidative stress and increasing luteinizing hormone production, cholesterol in testes, and blood flow to the testes.
Banihani SA

Experimental Study
Dietary supplementation with Goji berries enhances Bifidobacteria and butyrate-producing bacteria growth, resulting in potential preventative effects against colitis.
Kang Y, Yang G, Zhang S, Ross CF, Zhu MJ

Review Article
(-)-Epigallocatechingallate (EGCG), a natural product, has potent anti-proliferation, anti-metastasis, and pro-apoptosis effects on cervical cancer cells, enhancing the effects of conventional drugs.
Wang YQ, Lu JL, Liang YR, Li QS

Meta-Analysis
Dietary carrot intake is associated with a decreased risk of breast cancer.
Chen H, Shao F, Zhang F, Miao Q

The consumption of epicatechin, plentiful in foods like cocoa, positively influences memory, executive function, and processing speed, particularly in older adults.
Haskell-Ramsay C, Schmitt J, Actis-Goretta L

Review Article
Tea catechins, found in green tea, may reduce the rates of influenza infection and diminish certain cold symptoms.
Furushima D, Ide K, Yamada H

Randomised Controlled Trial
Consuming two SunGold kiwifruits daily over 12 weeks improved vitamin C status, reduced blood pressure, waist measurements and altered faecal microbiota composition in prediabetic individuals.
Wilson R, Willis J, Gearry R, Hughes A, Lawley B, Skidmore P, Frampton C, Fleming E, Anderson A, Jones L, Tannock G, Carr A

Systematic Review
Incorporating walnuts into the diet improved blood lipid profile without adversely affecting body weight or blood pressure.
Marta Guasch-Ferré, Jun Li, Frank B Hu, Jordi Salas-Salvadó, Deirdre K Tobias

Animal Study
The herbal formula B210 can alleviate snoring in aged rats by modifying the activities and breathing time of relevant nerves.
Chung KT, Hsu CH, Lin CL, Wang SE, Wu CH

Systematic Review
Subgroup analysis suggests consuming at least 30 grams of dark chocolate per day for a trial period between four to eight weeks may lead to reductions in weight and body mass index.
Kord-Varkaneh H, Ghaedi E, Nazary-Vanani A, Mohammadi H, Shab-Bidar S

Randomised Controlled Trial
Tremella fuciformis, as a nutritional supplement, safely improved subjective memory complaints and cognitive functions in individuals suffering from subjective cognitive impairment.
Ban S, Lee SL, Jeong HS, Lim SM, Park S, Hong YS, Kim JE

Systematic Review
Ginger supplementation has a favorable effect on levels of triacylglycerol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, especially in doses of 2 grams or less per day.
Pourmasoumi M, Hadi A, Rafie N, Najafgholizadeh A, Mohammadi H, Rouhani MH

Systematic Review
Fennel caused a significant increase in mean menstrual bleeding in the first cycle after treatment in the intervention group compared to the control.
Nafiseh Ghassab Abdollahi, Mojgan Mirghafourvand and Sanaz Mollazadeh

Systematic Review
The consumption of mung beans and sprouts in regular basis are not only providing nutrients, but also maintains the microbial flora in the gut, reduces the absorption of toxic compounds, decreases the menace of obesity, hypercholesterolemia, and cardiovascular diseases, and also prevents cancer and diabetes.
Kumar Ganesan, Bao junXu

Systematic Review
Aromatherapy with lavender demonstrated effectiveness in reducing labor pain during childbirth.
Mirzaiinajmabadi K, Makvandi S, Mirteimoori M, Sadeghi R, , , ,

Randomised Controlled Trial
Green tea extract can potentially control pain and improve knee joint physical function in adults suffering from osteoarthritis.
Hashempur MH, Sadrneshin S, Mosavat SH, Ashraf A

Citrus limon extracts could be a promising antioxidant source for the prevention and/or treatment of oxidative stress-related diseases.
Makni M, Jemai R, Kriaa W, Chtourou Y, Fetoui H.

Review Article
Honey, a natural food supplement, emerges as a potent therapeutic antioxidant with diverse medicinal effects, including wound healing, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antifungal, antiviral, and antidiabetic properties, suggesting its potential as a novel antioxidant in managing oxidative stress-related diseases.
Ahmed S, Sulaiman SA, Baig AA, Ibrahim M, Liaqat S, Fatima S, Jabeen S, Shamim N, Othman NH

Review Article
Honey may be used as a potential antidiabetic agent that has the potential to reduce the complications of diabetes.
Bobiş O, Dezmirean DS, Moise AR

Randomised Controlled Trial
Chamomile extract significantly improved sleep quality among the elderly, suggesting its potential as a safe sleep-promotion tool for this population.
Adib-Hajbaghery M, Mousavi SN
Clinical Study
Adding fresh herbs like parsley and chives to air-fried sardines reduces the levels of harmful cholesterol oxidation products formed during cooking.
Ferreira FS, Sampaio GR, Keller LM, Sawaya ACHF, Chávez DWH, Torres EAFS, Saldanha T

Systematic Review
Date palm components (pollen, pit powder, and gemmule extract) significantly improve male fertility directly through hormonal changes and indirectly via antioxidant abilities.
Tatar T, Akdevelioğlu Y

Systematic Review
Green tea consumption was shown to reduce psychopathological symptoms like anxiety and was also shown to effect cognition, with noted benefits for memory and attention. Green tea was also linked with the activation of working memory as seen in functional MRI.
Mancini E, Beglinger C, Drewe J, Zanchi D, Lang UE, Borgwardt S

Network Pharmacology
Adzuki beans, rich in flavonoids and saponins, can potentially prevent obesity by inhibiting enzymes related to fat accumulation and enhancing lipid breakdown.
Liu R, Zheng Y, Cai Z, Xu B

Randomised Controlled Trial
The extract from Hovenia Dulcis fruit (HDE) appears to decrease hangover symptoms effectively by regulating the body's inflammatory response to alcohol.
Kim H, Kim YJ, Jeong HY, Kim JY, Choi EK, Chae SW, Kwon O

Practice Guideline
Long-chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids have various health benefits for postmenopausal women including reducing triglycerides and improving depression and psychotic symptoms.
Sánchez-Borrego R, von Schacky C, Osorio MJA, Llaneza P, Pinto X, Losa F, Navarro MC, Lubián D, Mendoza N

Review Article
Kiwifruits can relieve constipation and irritable bowel syndrome, potentially through protease-activated signaling, modulation of microflora, changes in colonic methane, bile flux, or mediation of inflammatory processes.
Bayer SB, Gearry RB, Drummond LN
Systematic Review
High consumption of carrots is associated with a reduced risk of urothelial cancer.
Luo X, Lu H, Li Y, Wang S

Systematic Review
Cocoa consumption has strong beneficial impacts on cardiovascular health, reducing blood pressure, improving vascular function, and modulating lipid and glucose metabolism.
Ludovici V, Barthelmes J, Nägele MP, Enseleit F, Ferri C, Flammer AJ, Ruschitzka F, Sudano I

Systematic Review
Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide alleviated hydrogen peroxide‑induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in skin fibroblasts via upregulation of SIRT1 expression, indicating that TFPS may act as a potential therapeutic agent for oxidative‑stress‑associated skin diseases and aging.
Shen T, Duan C, Chen B, Li M, Ruan Y, Xu D, Shi D, Yu D, Li J, Wang C.

Experimental Study
Lavender essential oil, particularly its primary constituents linalool and linalyl acetate, may offer a beneficial anxiolytic effect through its interaction with certain neurological mechanisms.
Malcolm BJ, Tallian K

Review Article
Jujube possesses neuroprotective activities, including protecting neuronal cells against neurotoxin stress, stimulating neuronal differentiation, increasing expression of neurotrophic factors, and promoting memory and learning.
Chen J, Liu X, Li Z, et al.

Randomised Controlled Trial
Pomegranate juice consumption over a short period promotes red blood cell production without significantly changing metabolic health and inflammation markers in healthy individuals.
Manthou E, Georgakouli K, Deli CK, Sotiropoulos A, Fatouros IG, Kouretas D, Haroutounian S, Matthaiou C, Koutedakis Y, Jamurtas AZ

Randomised Controlled Trial
Honey has been shown to provide similar pain relief to traditional medication mefenamic acid for women with primary dysmenorrhea, with fewer side effects.
Amiri Farahani L, Hasanpoor-Azghdy SB, Kasraei H, Heidari T

Randomised Controlled Trial
Green tea consumption leads to weight loss and decreased levels of fasting insulin and free testosterone in overweight women with polycystic ovarian syndrome.
Tehrani HG, Allahdadian M, Zarre F, Ranjbar H, Allahdadian F

Animal Study
Dried plums potentially prevent and reverse bone loss in postmenopausal women facing osteoporosis, offering a promising functional food therapy solution with long-lasting effects.
Arjmandi BH, Johnson SA, Pourafshar S, Navaei N, George KS, Hooshmand S, Chai SC, Akhavan NS

Animal Study
Curcumin's potential anxiolytic and antidepressant impacts do not significantly alter behavior or interact with the benzodiazepine site of the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor A.
Ceremuga TE, Helmrick K, Kufahl Z, Kelley J, Keller B, Philippe F, Golder J, Padrón G

Animal Study
Blueberries can reduce the proliferation of ovarian cancer cells by downregulating the levels of specific biomarkers, exhibiting potential for non-pharmaceutical therapy.
Lin W, Li Z

Review Article
Dried plums, or prunes, have potential to exert beneficial effects on bone health and may help in combating osteoporosis in postmenopausal women, if consumed as part of their recommended fruit intake.
Wallace T

Case Report
Chamomile consumption may stimulate abundant milk production and increase lactogenesis in lactating women.
Silva FV, Dias F, Costa G, Campos MG

Systematic Review
Avocado, with its lipid-lowering, antihypertensive, antidiabetic, anti-obesity, and cardioprotective effects, can potentially manage metabolic syndrome more efficaciously than synthetic treatment options.
Tabeshpour J, Razavi BM, Hosseinzadeh H

Randomised Controlled Trial
Pomegranate juice intake can reduce systolic and diastolic blood pressure and inflammation markers, but may increase triglyceride and very low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels.
Moazzen H, Alizadeh M

Experimental Study
Pumpkin seeds have a higher total phenolic compound content, but phenolic compounds from amaranth grains show stronger antiradical properties.
Peiretti PG, Meineri G, Gai F, Longato E, Amarowicz R

Experimental Study
When combined, Silibinin and Pu-erh tea extract prove more effective in preventing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease than when used individually.
Wen-Yi Hu, Xiao-Hui Ma, Wang-Yi Zhou, Xin-Xin Li, Ting-Ting Sun, He Sun

Network Pharmacology
A mixture of Chrysanthemum indicum Linne flower and Cinnamomum cassia significantly mitigates hyperuricemia in rats by inhibiting xanthine oxidase activity and enhancing uric acid excretion.
Lee YS, Son E, Kim SH, Lee YM, Kim OS, Kim DS

Randomised Controlled Trial
Luteolin, found in chrysanthemum flower extract, can potentially reduce serum uric acid levels, suggesting it may help prevent gout.
Hirano M, Takeda S, Hitoe S, Shimoda H

Clinical Study
Blueberry intake for four weeks decreased levels of a biomarker for oxidative DNA damage in postmenopausal women with pre and early stage hypertension.
Johnson SA, Feresin RG, Navaei N, Figueroa A, Elam ML, Akhavan NS, Hooshmand S, Pourafshar S, Payton ME, Arjmandi BH

Meta-Analysis
Consuming pomegranate juice consistently can lead to significant reductions in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure, suggesting its potential cardioprotective benefits.
Sahebkar A, Ferri C, Giorgini P, Bo S, Nachtigal P, Grassi D

Review Article
Honeybee products like honey, propolis, and royal jelly have demonstrated potential benefits in treating metabolic diseases, cancers, and other illness types.
Pasupuleti VR, Sammugam L, Ramesh N, Gan SH

Randomised Controlled Trial
Gold kiwifruit supplementation increases the abundance of the beneficial gut bacterium Faecalibacterium, which could potentially enhance gut microbiota composition and reduce inflammation.
Blatchford P, Stoklosinski H, Eady S, Wallace A, Butts C, Gearry R, Gibson G, Ansell J

Cohort Study
Regular consumption of honey and yogurt may lower the prevalence of H. pylori infection and reduce the virulence of strains.
Yordanov D, Boyanova L, Markovska R, Ilieva J, Andreev N, Gergova G, Mitov I

Case Report
Raspberry leaf consumption may decrease insulin requirements in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus.
Cheang KI, Nguyen TT, Karjane NW, Salley KES

Significant amounts of small pelagic fish, a nutrient-rich food source, are unnecessarily processed into animal and pet food rather than being directed for human consumption in South Africa and Tanzania.
Isaacs M

Review Article
Fennel exhibits antifungal, antibacterial, antioxidant, antithrombotic and hepatoprotective activities.
Manzoor A.Rather, Bilal A.Dar, Shahnawaz N.Sofia, Bilal A.Bhat, Mushtaq A.Qurishi

Network Pharmacology
Purified polysaccharides extracted from Tremella aurantialba mycelium have improved antioxidant properties and stimulate immune response in macrophage cells.
Deng C, Sun Y, Fu H, Zhang S, Chen J, Xu X.

Randomised Controlled Trial
Walnuts appear to enhance mood in non-depressed healthy young males.
Pribis P

Clinical Study
Saffron has shown potential as an effective and tolerable treatment for major depressive disorder with anxious distress.
Ghajar A, Neishabouri S, Velayati N, Jahangard L, Matinnia N, Haghighi M, Ghaleiha A, Afarideh M, Salimi S, Meysamie A, Akhondzadeh S

Review Article
Previous records suggest pleiotropic pharmacological activities of capsaicin such as an analgesic, anti-obesity, anti-pruritic, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, anti-cancer, anti-oxidant, and neuro-protective functions. Emerging data indicate its clinical significance in treating vascular-related diseases, metabolic syndrome, and gastro-protective effects.
Basith S, Cui M, Hong S, Choi S

Experimental Study
Jujube-containing decoctions, used in Traditional Chinese Medicine, show neuro-protective and differentiating properties and enhance the function of multi-herbal concoctions.
Lam CTW, Gong AGW, Lam KYC, Zhang LM, Chen JP, Dong TTX, Lin HQ, Tsim KWK

Review Article
Goji berries, classified as superfruits, possess potential beneficial implications in the dietary prevention of diseases like diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer.
Kulczyński B, Gramza-Michałowska A

Clinical Study
Drinking 1litre of mineral water daily with meals can reduce risk factors for heart and metabolic diseases, particularly when replacing sugary drinks.
Toxqui L, Vaquero M

Experimental Study
Pu-erh tea's fermentation process alters its microbial community, with aging significantly impacting raw but not ripened Pu-erh, and toxic metabolites present support brewing customs.
Zhang Y, Skaar I, Sulyok M, Liu X, Rao M, et al.

Experimental Study
In 2004, polyphenols were isolated from mung bean sprouts, which exert antibacterial activity against Helicobacter pylori, one of the most common causative organisms in gastrointestinal disorders.
Jiaqiang Luo, Weixi Cai, Tong Wu, Baojun Xu

Randomised Controlled Trial
Montmorency tart cherry juice intake can significantly lower systolic blood pressure in men with early hypertension, with improvements linked to phenolic acids.
Keane KM, George TW, Constantinou CL, Brown MA, Clifford T, Howatson G

Strong bactericidal activity was exhibited by sulforaphene against all strains of Helicobacter pylori.
Sooyeon Li, Sang-Wook Han, Jongkee Kim

Systematic Review
Oral ginger could be an effective treatment for menstrual pain in dysmenorrhea.
Chen X. Chen, Bruce Barrett, Kristine L. Kwekkeboom,

Randomised Controlled Trial
A sardine-enriched diet may have beneficial effects on cardiovascular risk and alters gut microbiota composition in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Balfegó M, Canivell S, Hanzu FA, Sala-Vila A, Martínez-Medina M, Murillo S, Mur T, Ruano EG, Linares F, Porras N, Valladares S, Fontalba M, Roura E, Novials A, Hernández C, Aranda G, Sisó-Almirall A, Rojo-Martínez G, Simó R, Gomis R

Systematic Review
The studies assessed showed that sesame could have a significant effect on oxidative stress and the antioxidant defense system, being considered a food with an important antioxidant function in the different populations studied.
Gouveia Lde A, Cardoso CA, de Oliveira GM, Rosa G, Moreira AS.
Randomised Controlled Trial
Daily consumption of Puer tea extract results in significant weight loss, reduced body fat, and improved lipid profile in a non-Asian overweight population.
Jensen GS, Beaman JL, He Y, Guo Z, Sun H.

Systematic Review
Eating apples appears to be linked to a reduced risk of cancer in various parts of the body.
Fabiani R, Minelli L, Rosignoli P

Systematic Review
Plums display anti-inflammatory, antioxidant properties and can enhance memory, and their consumption shows potential health benefits for cognitive function, bones, and cardiovascular elements.
Igwe EO, Charlton KE

Coix extracts have anti-colorectal cancer potential.
Manosroi, A., Sainakham, M., Chankhampan, C., Manosroi, W., & Manosroi, J.

Clinical Study
Pomegranate juice improves physical function and stiffness, decreases cartilage breakdown enzymes and enhances antioxidant status in patients with knee osteoarthritis.
Ghoochani N, Karandish M, Mowla K, Haghighizadeh MH, Jalali MT

Animal Study
Dried plum was found to be most effective in reducing bone resorption and preventing bone loss caused by ionizing radiation exposure.
Schreurs AS, Shirazi-Fard Y, Shahnazari M, Alwood JS, Truong TA, Tahimic CGT, Limoli CL, Turner ND, Halloran B, Globus RK

Experimental Study
Adzuki beans present anti-atherogenic, anti-thrombogenic and hypocholesterolemic effects, and the ratios PUFA: SFA and n-6:n-3 were considered appropriate for biological system maintenance of a healthy organism.
Hou D, Yousaf L, Xue Y, et al.

Experimental Study
The component pterostilbene, found naturally in blueberries, shows potential in preventing inflammation and oxidative stress on the human cornea, suggesting protection against dry eyes.
Li J, Ruzhi Deng , Hua X, Zhang L, Lu F, Coursey TG, Pflugfelder SC, Li DQ

Clinical Study
Powdered tart cherry supplementation surrounding endurance exercise can decrease muscle damage markers, inflammation, oxidative stress and muscle soreness, while improving performance.
Levers K, Dalton R, Galvan E, O’Connor A, Goodenough C, Simbo S, Mertens-Talcott SU, Rasmussen C, Greenwood M, Riechman S, Crouse S, Kreider RB

Systematic Review
Almond consumption effectively reduces blood lipid levels, thus reducing risk of heart disease.
Musa-Veloso K, Paulionis L, Poon T, Lee HY
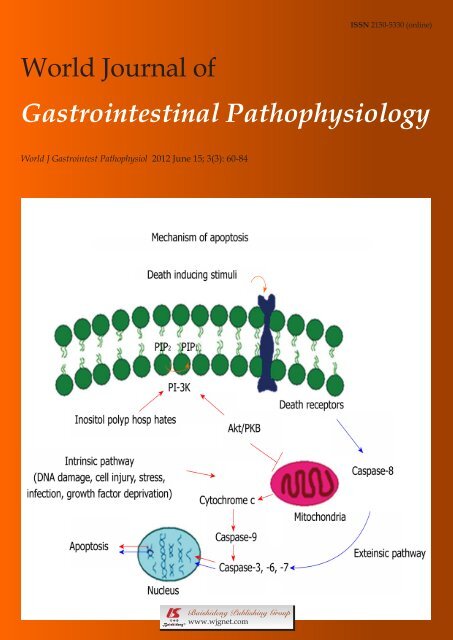
Clinical Study
Hydrogen carbonate-rich mineral water significantly reduces heartburn frequency and severity, improving quality of life with excellent tolerability.
Beer AM

Experimental Study
The ethanol extract of FCI potentially counters bone loss in mice by enhancing osteoblast proliferation and differentiation, facilitated by multiple bioactive compounds.
Li J, Lin X, Zhang Y, Liu W, Mi X, Zhang J, Su J

Experimental Study
Pomegranate juice extract significantly improves hormonal changes in female rats with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
HOSSEIN KARGAR, LEILA KARGAR, EBRAHIM TAVAKOL, NAZANIN SHAFIEI, FARZAD POORGHOLAMI, ELHAM RAHMANIAN, MOHAMMAD POURAHMADI, ZAHRA HASANPOUR

Randomised Controlled Trial
Drinking natural mineral water rich in magnesium sulphate and sodium sulphate daily improves bowel movement frequency and stool consistency in people with functional constipation.
Bothe G, Coh A, Auinger A

Review Article
Adzuki beans possessed strong ABTS free-radical-scavenging capacity and α-glucosidase inhibition activity.
Zhenxing Shi, Yang Yao, Yingying Zhu & Guixing Ren

Clinical Study
Pomegranate juice consumption slightly decreases estrone and testosterone levels in normal weight postmenopausal women.
Kapoor R, Ronnenberg A, Puleo E, Chatterton Jr. RT, Dorgan JF, Seeram NP, Sturgeon SR

Review Article
Milk and honey mixture seems to be at least as effective as dextromethorphan and levodropropizine, the most prescribed over-the-counter antitussives in Italy, in non-specific acute cough in children.
Miceli Sopo S, Greco M, Monaco S, Varrasi G, Di Lorenzo G, Simeone G

Systematic Review
Goji berry was identified as a rich source of antioxidant compounds, with health-promoting properties comparable with other common fruit species.
D. Donno, G.L. Beccaro, M.G. Mellano, A.K. Cerutti, G. Bounous

Systematic Review
The antioxidants present in goji berries have comparable health-promoting properties to those found in other common fruits.
D. Donno, G.L. Beccaro, M.G. Mellano, A.K. Cerutti, G. Bounous

Review Article
Among the bioactive compounds present in jujube fruit, triterpenic acids and polysaccharides have antiproliferative and anticancer effects on various cancer cell lines.
Zoya Tahergorabi, Mohammad Reza Abedini, Moodi Mitra, Mohammad Hassanpour Fard, and Hossein Beydokhti

Randomised Controlled Trial
Chrysanthemum flower oil significantly reduces diet-induced elevation of serum uric acid in Japanese males with high baseline levels.
Ueda T, Honda S, Morikawa H, Kitamura S, Iwama Y, Nakagawa K

Systematic Review
The alleged benefits of raw milk, including improved nutrition, prevention of lactose intolerance, or provision of "good" bacteria, lack scientific basis and are considered myths.
Lucey JA

Mung bean sprout extract has potent antiviral and to a lesser extent, prophylactic activities against both RSV and HSV-1, and in case of HSV-1, these activities were comparable to Acyclovir.
Hafidh, R.R., Abdulamir, A.S., Abu Bakar, F. et al.

Randomised Controlled Trial
Bee pollen and honey may alleviate menopausal symptoms in breast cancer patients undergoing antihormonal treatment.
MÜNSTEDT KARSTEN, VOSS BENJAMIN, KULLMER UWE, SCHNEIDER URSULA, HÜBNER JUTTA

Clinical Study
Daily consumption of blueberries may decrease blood pressure and arterial stiffness in postmenopausal women due to increased nitric oxide production.
Johnson SA, Figueroa A, Navaei N, Wong A, Kalfon R, Ormsbee LT, Feresin RG, Elam ML, Hooshmand S, Payton ME, Arjmandi BH

Experimental Study
Pomegranate Fruit Extract (PFE) can potentially mitigate testosterone-induced Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in rats due to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and pro-apoptotic properties.
Ammar AE, Esmat A, Hassona MDH, Tadros MG, Abdel‐Naim AB, Guns EST

Experimental Study
Two new compounds found in Chrysanthemum indicum flowers have strong antioxidant qualities and are potent in anti-osteoporosis activity.
Luyen BTT, Tai BH, Thao NP, Lee YM, Lee SH, Jang HD, Kim YH

Systematic Review
Consuming carrots reduces the risk of gastric cancer by an indicated 26%.
Fallahzadeh H, Jalali A, Momayyezi M, Bazm S

Systematic Review
Administering honey postoperatively can significantly lessen pain and foster improved wound healing following tonsillectomy.
Hwang SH, Song JN, Jeong YM, Lee YJ, Kang JM

Experimental Study
Epigallocatechin 3-gallate (EGCG), found in green tea, can significantly slow down osteoarthritis progression and reduce associated pain in a post-traumatic osteoarthritis mouse model.
Leong DJ, Choudhury M, Hanstein R, Hirsh DM, Kim SJ, Majeska RJ, Schaffler MB, Hardin JA, Spray DC, Goldring MB, Cobelli NJ, Sun HB
Review Article
A dietary supplement Avocado/Soybean Unsaponifiables aids in treating Osteoarthritis by preventing cartilage degradation and promoting cartilage repair, thereby reducing pain and enhancing joint functionality.
Christiansen BA, Bhatti S, Goudarzi R, Emami S

Systematic Review
Saffron, derived from Crocus sativus flower, shows similar efficacy to antidepressant medications in treating major depression, potentially due to its variety of biochemical effects.
Lopresti AL, Drummond PD

Experimental Study
Jujube fruit promotes the growth of nerve cells and boosts anti-oxidant enzyme production in brain cells.
Chen J, Yan AL, Lam KYC, Lam CTW, Li N, Yao P, Xiong A, Dong TTX, Tsim KWK

Network Pharmacology
Manuka honey exhibits significant anti-influenza viral activity, inhibiting replication with virucidal effects. Combining manuka honey with existing drugs enhances their efficacy, suggesting its medicinal potential.
Watanabe K, Rahmasari R, Matsunaga A, Haruyama T, Kobayashi N

Network Pharmacology
Honey, in general, and particularly manuka honey, has potent inhibitory activity against the influenza virus, demonstrating a potential medicinal value.
Watanabe K, Rahmasari R, Matsunaga A, Haruyama T, Kobayashi N

Systematic Review
Goji (Lycium spp.) has a consolidated safety and efficacy profile, based on scientific literature, clinical trials, expert opinions, history, pharmacology, interactions, adverse effects, toxicology, and dosing.
Ulbricht C, Bryan JK, Costa D, Culwell S, Giese N, Isaac R, Nummy K, Pham T, Rapp C, Rusie E, Weissner W, Windsor RC, Woods J, Zhou S

Network Pharmacology
The consumption of kiwifruit with a meal can increase the rate and extent of the hydrolysis of protein.
Donaldson B, Rush E, Young O, Winger R

Network Pharmacology
Chrysanthemum flower oil can effectively decrease uric acid levels in rats, by reducing production in the liver and enhancing excretion from the kidney.
Honda S, Kawamoto S, Tanaka H, Kishida H, Kitagawa M, Nakai Y, Abe K, Hirata D

Systematic Review
Polyphenolic compounds found in walnuts not only reduce the oxidant and inflammatory load on brain cells but also improve interneuronal signaling, increase neurogenesis, and enhance sequestration of insoluble toxic protein aggregates.
Poulose SM, Miller MG, Shukitt-Hale B

Systematic Review
Ginger could be considered a harmless and possibly effective alternative option for women suffering from nausea and vomiting during pregnancy.
Viljoen, E., Visser, J., Koen, N. et al.

Experimental Study
Consumption of Pu-erh tea can effectively alleviate symptoms of constipation, with effects comparable to the medicinal drug bisacodyl.
LI GUIJIE, WANG QIANG, QIAN YU, ZHOU YALIN, WANG RUI, ZHAO XIN

Randomised Controlled Trial
Pomegranate extract intake, rich in biophenols, lessens salivary cortisol levels, hence potentially improving health-related quality of life, particularly in stress-suffering individuals.
Stockton A, Al-Dujaili E

Review Article
Honey has shown to be a safe and occasionally superior treatment for various wounds compared to current treatments, even in wilderness environments.
Stewart JA, McGrane OL, Wedmore IS

Systematic Review
Regular carrot consumption could potentially reduce the risk of prostate cancer.
Xu X, Cheng Y, Li S, Zhu Y, Xu X, Zheng X, Mao Q, Xie L

Systematic Review
Germination is thought to improve the nutritional and medicinal qualities of mung beans.
Tang, D., Dong, Y., Ren, H. et al.

Systematic Review
A study demonstrated that all pro-inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-12β, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and inducible NO synthase (iNOS), were dramatically down regulated in cells treated with 3.7 mg/mL polyphenols.
Tang, D., Dong, Y., Ren, H. et al.

Systematic Review
Mung bean protein, tannin, and other polyphenols are thought to combine with organophosphorus pesticides, mercury, arsenic, and other heavy metals, promoting the excretion of sediments from the body.
Tang, D., Dong, Y., Ren, H. et al.

Randomised Controlled Trial
Consumption of fenugreek herbal tea and palm dates appears useful in enhancing breast milk production during the initial postpartum period.
El Sakka A, Salama M, Salama K

Randomised Controlled Trial
Tualang honey demonstrates efficacy comparable to Tribestan in enhancing sperm parameters among oligospermic males, including concentration, motility, and morphology, with a favorable safety profile.
Ismail SB, Bakar MB, Nik Hussain NH, Norhayati MN, Sulaiman SA, Jaafar H, Draman S, Ramli R, Wan Yusoff WZ

Animal Study
Regular intake of mineral-rich water, high in sodium bicarbonate, potassium, calcium, and magnesium, potentially reduces risk of Metabolic Syndrome and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
Pereira CD, Severo M, Araújo JR, Guimarães JT, Pestana D, Santos A, Ferreira R, Ascensão A, Magalhães J, Azevedo I, Monteiro R, Martins MJ

Systematic Review
Green tea polyphenols may enhance effectiveness of specific breast cancer endocrine treatments through both estrogen-dependent and -independent mechanisms.
Yiannakopoulou EC

Experimental Study
Honey, specifically its polyphenols, show promising signs of enhancing memory and counteracting neurodegenerative diseases by reducing oxidative stress and neuroinflammation.
Mijanur Rahman M, Gan SH, Khalil MI

Review Article
Blueberries, due to their phenolic compounds, show potential as both dietary and supplemental anti-cancer agents by inhibiting cancer cell growth and promoting apoptosis.
Johnson S, Arjmandi B

Randomised Controlled Trial
Honey plus coffee, presented as a jamlike paste, emerges as a more effective alternative medicine for persistent post-infectious cough (PPC) compared to systemic steroids, demonstrating significant reduction in cough frequency in a randomized controlled trial.
Raeessi MA, Aslani J, Raeessi N, Gharaie H, Zarchi AAK, Raeessi F

Randomised Controlled Trial
Tart cherry juice potentially helps alleviate symptoms of mild to moderate knee osteoarthritis and decreases the levels of high sensitivity C-reactive protein.
Schumacher HR, Pullman-Mooar S, Gupta SR, Dinnella JE, Kim R, McHugh MP

Randomised Controlled Trial
Tart cherry juice shows promise in easing knee osteoarthritis symptoms.
Schumacher HR, Pullman-Mooar S, Gupta SR, Dinnella JE, Kim R, McHugh MP

Randomised Controlled Trial
Korean pear juice can alleviate symptoms of alcohol hangover and aid in alcohol detoxification, with effectiveness influenced by certain genetic variations.
Lee HS, Isse T, Kawamoto T, Baik HW, Park JY, Yang M

Animal Study
Dried plum intake uniquely improves bone density, promotes growth of vertebral trabecular bone, prevents bone loss in tibia, and positively adjusts bone metabolism.
Rendina E, Hembree KD, Davis MKR, Marlow D, Clarke SL, Halloran BP, Lucas EA, Smith BJ

Clinical Study
Pomegranate juice intake for two weeks significantly reduces blood pressure and may improve heart health by lowering vascular endothelial adhesion molecule-1 levels.
Asgary S, Sahebkar A, Afshani MR, Keshvari M, Haghjooyjavanmard S, Rafieian‐Kopaei M

Review Article
Recent phytochemical studies of jujube fruits have shed some light on their biological effects, such as the anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antiobesity, immunostimulating, antioxidant, hepatoprotective, and gastrointestinal protective activities and inhibition of foam cell formation in macrophages.
Gao QH, Wu CS, Wang M.

Review Article
Cocoa and chocolate, rich in antioxidant molecules like epicatechin, enhance brain health, stimulate brain perfusion, and reduce the risk of Alzheimer's disease and stroke.
Nehlig A

Experimental Study
Pomegranate juice can enhance memory function and brain activity in tasks related to verbal and visual memory in older adults experiencing memory problems.
Bookheimer SY, Renner BA, Ekstrom A, Li Z, Henning SM, Brown JA, Jones M, Moody T, Small GW

Review Article
Pomegranates and their extracts may provide natural alternatives to conventional drugs due to their potent activity against various bacterial and viral pathogens.
Howell AB, D'Souza DH

Review Article
Curcumin, a component of Indian spice turmeric, presents a potential natural treatment for depression, influencing neurotransmitters and protecting against several biological systems compromised in depression.
Lopresti AL, Hood SD, Drummond PD

Experimental Study
Adzuki bean exhibited the strongest antiproliferative properties in a dose-dependent manner against all digestive system cancer cell lines, ovary cancer cell SK-OV-3 and breast cancer cell MCF-7 among all legumes tested.
Xu B, Chang SKC

Randomised Controlled Trial
Tart cherry juice may lessen inflammation, thus reducing pain in women with osteoarthritis, according to changes noted in specific inflammatory serum biomarkers.
Kuehl KS, Elliot DL, Sleigh AE, Smith JL

Systematic Review
Soybean isoflavones, whether extracted or synthesized, prove significantly effective in reducing the frequency and severity of hot flashes in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women.
Taku K, Melby MK, Kronenberg F, Kurzer MS, Messina M

Experimental Study
Blueberry consumption prior to puberty can significantly prevent bone cell senescence and bone loss induced due to the removal of ovaries in rats.
Zhang J, Lazarenko OP, Blackburn ML, Badger TM, Ronis MJJ, Chen JR

Experimental Study
Korean pears potentially boost key alcohol-metabolizing enzymes, aiding alcohol detoxification, with effects that may vary due to human ALDH2 polymorphisms.
Lee HS, Isse T, Kawamoto T, Woo HS, Kim AK, Park JY, Yang M

Randomised Controlled Trial
Blended essential oils, including lavender, sage, and marjoram, show potential in relieving menstrual cramps and reducing pain duration in women with primary dysmenorrhea.
Ou MC, Hsu TF, Lai AC, Lin YT, Lin CC

Systematic Review
Regular chocolate or cocoa consumption, rich in flavan-3-ols, has been associated with improved insulin resistance and blood vessel function, suggesting potential cardiovascular benefits.
Hooper L, Kay C, Abdelhamid A, Kroon PA, Cohn JS, Rimm EB, Cassidy A

Experimental Study
Pomegranate polyphenols have notable antioxidant and antiatherogenic effects that lessen cholesterol, oxidized lipids accumulation, and atherosclerosis development in arterial macrophages.
Aviram M, Rosenblat M

Systematic Review
The consumption of green tea catechins is associated with a statistically significant reduction in total and LDL cholesterol levels.
Kim A, Chiu A, Barone MK, Avino D, Wang F, Coleman CI, Phung OJ

Randomised Controlled Trial
Consumption of tart cherry juice can increase exogenous melatonin that is beneficial in improving sleep duration and quality and might be of benefit in managing disturbed sleep.
Howatson G, Bell PG, Tallent J, Middleton B, McHugh MP, Ellis J

Animal Study
Pomegranate extracts enhance bone formation and increase bone calcium content in mice.
Monsefi M, Parvin F, Talaei-Khozani T

Randomised Controlled Trial
Dried plum consumption enhances bone mineral density in postmenopausal women, primarily by reducing the rate of bone turnover.
Hooshmand S, Chai SC, Saadat RL, Payton ME, Brummel-Smith K, Arjmandi BH

Meta-Analysis
Consumption of dark chocolate and cocoa products has been shown to significantly reduce serum levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and total cholesterol (TC), indicating potential cardiovascular benefits.
Tokede OA, Gaziano JM, Djoussé L

Randomised Controlled Trial
Daily goji berry supplementation increases antioxidant levels and protects visual health in the elderly, though the exact mechanism remains unclear.
Bucheli P, Vidal K, Shen L, Gu Z, Zhang C, Miller LE, Wang J

Review Article
Cumin and caraway seeds have shown diverse medicinal applications, thanks to their rich essential oils, as revealed by recent experimental studies.
Johri RK

Experimental Study
Pomegranate extract can inhibit key cellular pathways and activities involved in the progression of osteoarthritis.
Rasheed Z, Akhtar N, Haqqi TM

Theoretical Article
Chamomile, with its numerous terpenoids and flavonoids, has a vast range of medicinal uses and is being developed as a human health promoting therapeutic agent.
Gupta

Punicalagin, extracted from the fruit peel of Punica granatum, displays strong antifungal activity against Candida species, especially when combined with fluconazole.
Endo EH, Garcia Cortez DA, Ueda-Nakamura T, Nakamura CV, Dias Filho BP

Systematic Review
Long-term consumption of tea catechins could be beneficial against high-fat diet-induced obesity and type II diabetes and could reduce the risk of coronary disease.
Chacko, S.M., Thambi, P.T., Kuttan, R. et al.

Randomised Controlled Trial
Pomegranate juice consumption doesn't significantly affect overall progress of carotid intima-media thickness, but may slow its progression in subjects with high oxidative stress and lipid issues.
Davidson MH, Maki KC, Dicklin MR, Feinstein SB, Witchger MS, Bell M, McGuire DK, Provost JC, Liker H, Aviram M

Experimental Study
The extract from Chrysanthemum Indicum Linné effectively reduces inflammation in mouse skin when induced, hinting at potential therapeutic applications for immune-related skin diseases.
Lee DY, Choi G, Yoon T, Cheon MS, Choo BK, Kim HK

Experimental Study
Blueberry consumption can prevent bone loss and positively impact bone metabolism in ovariectomized rats.
Devareddy L, Hooshmand S, Collins JK, Lucas EA, Chai SC, Arjmandi BH

Experimental Study
Tremella fuciformis, a mushroom, shows potential as a protective agent against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's by promoting cell growth and reducing toxicity.
Park KJ, Lee SY, Kim HS, Yamazaki M, Chiba K, Ha HC

Randomised Controlled Trial
Drinking mineral water, especially those high in magnesium, helps lower blood pressure among individuals with borderline hypertension and low calcium or magnesium excretion.
Rylander R, Arnaud MJ

Clinical Study
Migraine patients exhibit lower intracellular magnesium levels, which can be increased by consuming magnesium-rich mineral water, demonstrating its bioavailability.
Thomas J, Millot JM, Sebille S, Delabroise AM, Thomas E, Manfait M, Arnaud MJ
Executive Summary
Write an executive summary in the form of a blog article on the topic of "Research into Chinese medicine treatment for Food As Medicine" summarising the research below and using language that can be easily understood by patients and avoiding medical jargon using a professional and caring tone of voice.
Write an executive summary in the form of a blog article on the topic of "Researched Chinese medicine treatments for Food As Medicine" summarising the research below in an objective and easy to understand way, and using language that can be easily understood by patients. Group the article into Chinese medicine treatments first, followed by nutrition and other treatments. Avoid using medical jargon and use a professional and caring tone of voice.
Write me a concise but easy to understand executive summary on the topic of "Chinese medicine treatments for Food As Medicine" based on the following research that I will give you. Your summary should be 2 paragraphs long in Australian English spelling and include references to the studies.
A Clinical Study published in 2025 in the journal Scientific Reports found that Jujube syrup presented improved results in treating pediatric functional constipation compared to polyethylene glycol, demonstrating a potentially effective and safe alternative treatment. The researchers conducted a double-blind, randomized clinical trial involving children aged 2-10 years old diagnosed with functional constipation. These children were selected from patients referred to the gastroenterology clinic of 17-Shahrivar Hospital in Rasht, Iran. The eligible candidates were divided into two groups, each receiving either polyethylene glycol (PEG) or Ziziphus jujuba syrup (ZS) in a dosing range of 1-5 cc/kg/day. The patients were monitored over a three-month period, with bi-weekly check-ups in the first month, followed by monthly check-ups for the next two months. Additionally, liver and kidney function tests, as well as blood sugar levels, were verified at the start and end of the study. Out of 90 qualified children, 32 patients in the PEG group and 30 in the ZS group finished the follow-ups. The therapeutic response score in the group administered ZS showed a distinct improvement compared to those given PEG. Similarly, the average number of encopresis and pain scores, as measured by a visual analog scale, showed a significant reduction in the ZS group compared to the PEG group. Other indices, such as frequency of defecation and medication adherence, also showed a noticeable improvement in the ZS group. With only a few self-limiting side effects reported in the PEG group, it was determined that ZS provides a potential choice for functional constipation treatment without any adverse events or liver and kidney injury.
A Experimental Study published in 2024 in the journal Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry found that The ZJMP-2 polysaccharide fraction from jujube, consisting of various sugars and acid, significantly enhances immune cell activity and stimulates lymphocyte proliferation. The researchers isolated and purified a new water-soluble polysaccharide fraction, ZJMP-2, from the Jujube plant. Various scientific methods including Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, high-performance gel permeation chromatography-laser light scattering, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, scanning electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy, and nuclear magnetic resonance analyses were employed to characterize ZJMP-2. This polysaccharide is composed of glucose, galactose, arabinose, rhamnose, and galacturonic acid. The study determined its molecular structure and variations that may contribute to its immunoregulatory effect. In terms of the results, ZJMP-2 substantially increased the expression levels of proteins that are important in the immune response, resulting in the activation of macrophages - immune cells that destroy harmful organisms - and promoting the proliferation of lymphocytes - another type of immune cell. This resulted in observable activity in RAW264.7 cells and spleen lymphocytes. ZJMP-2 was also found to boost the heart, spleen, and bone marrow indices, along with spleen cell counts and peripheral blood cell counts. In addition, the number of heart and bone marrow cells in mice increased through the use of ZJMP-2.
A Animal Study published in 2024 in the journal Molecular Nutrition & Food Research found that Oral administration of Lactobacillus acidophilus 6074 fermented jujube juice can improve gut microbiota, alleviate intestinal inflammation, and reduce colon damage in mice. The study used jujube juice as the substrate fermented by L. acidophilus 6074 to observe its effects on gut microbiota, intestinal barrier function, oxidative stress, and inflammatory factors in mice with colitis. The process of fermentation caused significant changes in the compounds of the juice, particularly in organic acids and free amino acids. A high dose of the juice demonstrated significant improvements in overall colitis markers, including the physical condition of the colon and disease activity. Upon administering the fermented jujube juice, it was observed that the treatment promoted the reinforcement of the colonic mucosal barrier, boosting the expression of various tight junction proteins. Moreover, it inhibited the production of proinflammatory factors and reduced oxidative stress, thereby mitigating colon damage. The gut microbiota composition shifted as a result, demonstrating an increase in beneficial bacteria, a boost in short-chain fatty acids, and a reduction in harmful microorganisms. These findings indicate that the fermented juice can restore the balance in gut microbiota altered by intestinal inflammation and lessen the impact of colitis.
A Experimental Study published in 2024 in the journal International Journal of Biological Macromolecules found that A polysaccharide from Tremella aurantialba improves ulcerative colitis symptoms by targeting epithelial cell ferroptosis and modulating the gut microbiota. The methodology used in this research involved isolating TA 2-1, a specific polysaccharide from Tremella Aurantialba, and studying its effects on ulcerative colitis. This was done by introducing it to Caco-2 cells that were undergoing ferroptosis and assessing its impact on cell viability. The influence of TA 2-1 was also examined in mice with artificially induced ulcerative colitis, verifying its ameliorating effects in an in-vivo context. The structure of TA 2-1 and its components were analysed and the polysaccharide's interaction with gut microbiota was explored to understand how it might modulate symptoms or prevent cell death. The results of this study showed that TA 2-1 does not only decrease the rate of cell death in epithelial cells undergoing ferroptosis, but it also repairs the intestinal barrier by upregulating specific proteins such as claudin-1 and zonula occludens-1. TA 2-1 was also found to suppress lipid peroxidation, thus inhibiting ferroptosis. Further investigation revealed that TA 2-1 may alleviate ulcerative colitis by influencing the composition or metabolites of gut microbiota. This research offers promising insight into the potential of TA 2-1 in treating ulcerative colitis.
A Review Article published in 2024 in the journal Life found that Pomegranate extract could potentially benefit women's reproductive health, enhance fertility, regulate menstrual cycles, support pregnancy, and help treat polycystic ovary syndrome. In establishing the potential benefits of pomegranate extract in women's reproductive health, a wide array of methods was employed. Primarily, these included in vitro studies, animal modeling and certain clinical trials. Analyses of the antioxidant properties of the extract were done to ascertain its effectiveness in reducing oxidative stress and consequently, improving fertility. The influence of pomegranate extract on hormonal imbalances and menstrual regulation was also studied. Discussions on the results emphasized the potential of pomegranate extract in supporting women's reproductive health. The extract was found beneficial in enhancing fertility, regulating menstruation and supporting pregnancy. Further, it could help in polycystic ovary syndrome therapy by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing oxidative damage. Its rich nutrient composition was appreciated for potentially fostering placental development and fetal growth, thus possibly mitigating the risk of early birth. Apart from reproductive health, some studies pointed towards pomegranate extract's potential anticancer properties, primarily against breast cancer.
A Review Article published in 2024 in the journal Current Nutrition Reports found that Ziziphus jujuba and its main components, lupeol and betulinic acid, show promise in treating complications of metabolic syndrome, including diabetes, obesity, and hypertension. The research assessed the properties of Ziziphus jujuba and its main bioactive agents, lupeol and betulinic acid, in relation to metabolic syndrome. Investigations focussed on their potential roles in glucose uptake enhancement, hepatic glucose synthesis reduction, insulin sensitivity improvement, and lipid profile modulation. Studies involved identifying the influence of these substances on key signaling pathways and insulin signaling proteins, as well as evaluating their anti-adipogenic effects and capacity to improve endothelial function. Ziziphus jujuba and its constituents exhibited potential therapeutic benefits for metabolic syndrome by facilitating glucose uptake, reducing glucose synthesis, and improving insulin sensitivity. They also showed potential in moderating lipid synthesis and fat accumulation, demonstrating anti-fatty effects and a capacity to influence adipogenic enzymes and transcription factors. Moreover, these substances demonstrated enhanced endothelial function, reflecting positively on vascular health. These accumulative findings suggest promising potential for Z. jujuba, lupeol, and betulinic acid as natural treatments for metabolic syndrome complications.
A Animal Study published in 2024 in the journal Nutrients found that Manuka honey has demonstrated the potential to inhibit the proliferation of human breast cancer cells and stimulate apoptosis in these cells. In the experiment, Manuka honey was applied to three different types of cells: MCF-7 human breast cancer cells, MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells, and non-malignant human mammary epithelial cells. The concentrations applied ranged from 0.3 to 5.0% to observe different effects. In addition to inhibiting cancer cell proliferation, the honey was tested for its ability to cause apoptosis (cell death) among the MCF-7 cells. It was also compared to the effects of tamoxifen, an antiestrogen medication used in breast cancer treatment. The results showed that Manuka honey was able to significantly inhibit the proliferation of MCF-7 cells, though its effects were less pronounced in the MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. The non-malignant cells were not affected. The honey's antitumor activity was comparable to that of tamoxifen. Moreover, Manuka honey stimulated apoptosis in the MCF-7 cells. It was also observed that the honey activated AMPK, which inhibits specific cellular growth signals, and reduced STAT3 levels, a protein often elevated in tumors.
A Meta-Analysis published in 2024 in the journal Clinical Nutrition Open Science found that Daily intake of Ziziphus jujuba can control weight and improve lipid profile indicators. In the methodology, randomized clinical trials were sourced from online resources like PubMed, Scopus, and ISI Web of Science till October 2022. From these resources, four suitable articles were picked for this research. The results section suggests that a notable decrease in body mass index (BMI), triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is observed in individuals consuming Ziziphus jujuba. However, there were no significant changes observed in fasting blood glucose (FBG) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). These findings underscore the potential beneficial impact of Ziziphus jujuba consumption on certain metabolic indicators.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2024 in the journal Complementary Therapies in Medicine found that Consuming jujube notably reduces waist circumference, triglycerides, and stress, while increasing high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in subjects with metabolic syndrome. In this parallel-group, randomized controlled trial, sixty participants diagnosed with metabolic syndrome were randomly assigned to either receive 30g of dried jujube powder or a placebo for an eight-week period. They were instructed to consume half of their given powder at two different points in the day. Four measurements were taken as primary outcomes: lipid profile, fasting blood glucose, waist circumference, and blood pressure. Additionally, mental health measures, such as depression, anxiety, and stress, were evaluated as secondary outcomes. The data analysis showed that consuming jujube didn't lead to significant reductions in fasting blood glucose, total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, blood pressure, or depression and anxiety scores. However, compared to the placebo group, the group consuming jujube showed a key reduction in waist circumference and triglycerides, and an increase in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Moreover, an improvement in stress scores was observed in the jujube group. The study, however, had methodological shortcomings regarding effective blinding and testing for herb purity and potency.
A Animal Study published in 2024 in the journal Food Science & Nutrition found that Jujube fruit extracts significantly alleviate oxidative stress in rodent models, potentially offering a valuable dietary supplement against diseases linked to oxidative stress. In this study, relevant animal studies were sourced from various data platforms including PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Wanfang Data Knowledge Service Platform, and VIP Periodical Service Platform. Risk of bias in the included studies was evaluated using the Systematic Review Center for Laboratory Animal Experimentation risk-of-bias tool. Conducting a meta-analysis followed the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions guidelines and utilized Stata 17.0 software. Nineteen studies were ultimately incorporated into the meta-analysis. The meta-analysis indicated that jujube fruit extracts notably reduced the level of malonaldehyde, a marker of oxidative stress, and raised the levels of superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase, both of which are antioxidant enzymes. However, the levels of another antioxidant enzyme, catalase, didn't exhibit significant improvement. The meta-analysis results uncovered considerable heterogeneity. Subsequent subgroup analysis suggested that the source of the target parameters, animal models used, and types of extract could be contributing to the observed heterogeneity. Despite questionable overall methodological quality in the included studies, the study underscores the potential of jujube fruit extracts as effective antioxidant dietary supplements, particularly useful in conditions where oxidative stress is a key pathogenic factor.
A Cohort Study published in 2024 in the journal The Journal of Nutrition found that Greater intake of blueberries considerably decreases the risk of age-related macular degeneration, while a remarkable dietary intake of anthocyanins inversely correlates with cataract incidents. Middle-aged and older women, numbering 36,653 and 35,402 originally without cataract and AMD, provided data for the study via semiquantitative food frequency questionnaires. Insights were derived on the consumption of blueberries by these women, with frequency varied from none to over two servings weekly. Additionally, total anthocyanin consumption was analysed, with major subclasses adjusted for energy and then into quintiles. Self-reported risk factors for eye diseases were adjusted in the multivariable hazard ratios. On analysis, it was found that a significant portion of participants consumed a minimum of one serving of blueberries weekly. Thus, compared to no blueberry intake, it was observed that those consuming the fruit exhibited a decrease in the total instances of AMD, while visually significant AMD remained unaffected. Furthermore, dietary anthocyanin showed a modest yet significant inverse association with cataract occurrences, but no notable correlation with AMD.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2024 in the journal Aging Clinical and Experimental Research found that Walnut consumption while doing concurrent training improves strength, sleep quality, standing support, cognitive performance and postural balance in elderly men. In the study, twenty healthy elderly men were grouped into two randomly controlled cohorts. There were three training sessions per week featuring a concurrent combination of strength and endurance training. One group received a diet supplemented with 15 grams per day of walnuts (CTW) over six weeks while the other didn't (CT). Their strength, sleep quality, cognitive performance and postural balance were evaluated using an isokinetic strength test, Spiegel questionnaire, Montreal cognitive assessment and balance measurements respectively, 48 hours before and after the intervention period. The results pointed that both groups experienced significant improvements in strength and sleep quality with CTW showing a greater increase in sleep quality. CTW group showed improvements in cognitive performance and postural balance while CT group did not see these benefits. Hence it's observed that combination of concurrent training and walnut consumption was found to be effective in improving strength, sleep quality, cognitive performance and postural balance in elderly men.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2024 in the journal The 14th European Nutrition Conference FENS 2023 found that Daily consumption of walnuts improves sleep quality and reduces daytime sleepiness in healthy young adults. In the above-mentioned experimental trial, 80 young adults were randomly selected to either consume 40 grams of walnuts daily or abstain from eating walnuts and any other nuts for 8 weeks, followed by a two-week break. Actigraphy was used to measure sleep quality, from various dimensions such as duration, latency, awakenings, and sleep efficiency, while daytime sleepiness was measured using the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Furthermore, the concentration of 6-sulfatoxymelatonin, a melatonin metabolite, was assessed in urine samples collected at two intervals throughout the day and night. This research observed a notable improvement in the subjects' sleep quality after an 8-week period of walnut consumption. The participants experienced shorter sleep latency, greater sleep efficiency, and reduced daytime sleepiness. Additionally, there was a heightened concentration of 6-sulfatoxymelatonin in urine samples collected between 20:00 to 23:00. These results suggest that a daily intake of 40 grams of walnuts may augment the secretion of melatonin, thereby improving sleep quality and reducing daytime sleepiness in healthy young adults.
A Systematic Review published in 2024 in the journal Food Science & Nutrition found that Eating plums, especially dried plums, significantly lowers LDL levels and total cholesterol levels, particularly in adults with existing health issues. The researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis using keyword searches on databases such as PubMed, Scopus, and ISI Web of Science up to a specified date. They were on a mission to find eligible trials that would help ascertain the benefits of plum consumption on adult lipid profiles. In their observation of the collected data, they concluded that plum, specifically dried plum consumption, had a noteworthy impact on LDL levels, mainly when the subjects were in an unhealthy state. This consumption led to a significant decrease in total cholesterol levels in the unhealthy subjects. Nevertheless, the study couldn't establish major changes in triglycerides and HDL concentrations as a result of the plum consumption.
A Review Article published in 2024 in the journal Pharmaceuticals found that Lemongrass essential oil can effectively treat periodontitis, gingivitis, oral malodour, skin aging, and dandruff, and it is comparable to certain established treatments. The methodology used in the research followed a scoping review design, which was aimed at identifying, summarizing, and synthesizing existing literature related to the clinical applications of lemongrass essential oil. Three databases, namely PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus, were utilized, following the PRISMA-ScR guidelines, to find articles published within approximately a 10-year timeframe. The results of the review suggest that patients have received noticeable therapeutic benefits from treatments that were primarily administered oromucosally and topically. It can be deduced that the efficacy of lemongrass essential oil in treating periodontitis, gingivitis, and oral malodour is similar to that of chlorhexidine and doxycycline. Moreover, the oil has demonstrated potential in treating skin conditions such as pityriasis versicolor, preventing skin aging, and having anti-dandruff effects. The diverse range of applications of the oil and its efficacy when compared to established treatments highlight its potential for clinical applications.
A Review Article published in 2024 in the journal Foods found that Jujube, a Chinese native plant with numerous active components, exhibits calming effects, nourishes blood, and strengthens the spleen and stomach, alongside promising neuroprotective and cardiovascular benefits. This study statistically evaluated and tracked the research status of Jujube over the past two decades. The research observed, among other things, the plant's traditional use in calming nerves, nourishing blood, and strengthening the spleen and stomach in traditional Chinese medicine. The study found that the Jujube has numerous effective components, including polysaccharides, phenols, and triterpene acids. The study delved into understanding how these components can provide a variety of pharmacological activities. Such activities include neuroprotection, as well as the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. The study also expounded comprehensively the molecular mechanisms and efficacies of Jujube. The research, therefore, provides an exhaustive appraisal of the pharmacological potentials of the Jujube plant and its prospective industrial relevance in food and pharmaceutical industries.
A Data Mining published in 2024 in the journal Traditional Medicine Research found that The traditional Chinese medicine prescription combination of Chrysanthemi Flos, Cassiae Semen, Lycii Fructus, Angelicae Sinensis Radix and Salviae Miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizoma presents potential for treating retinal diseases. Methodology: The researchers employed data mining to discern a new traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) prescription against retinal diseases and explore its medication rule. This was followed by constructing a network of TCMs, core ingredients, core targets, and core pathways using network pharmacology. The binding ability between core active ingredients and core targets was then verified through molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation techniques. Discussion: The novel TCM prescription screened in this study bears great potential in retinal diseases treatment through a unique mechanism of action. This mechanism involves TCM prescriptions that possess clearing heat and supplementing activities, associated with liver and lung meridians. The mechanism was found to act by modulating several core targets implicated in multiple core pathways such as the AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications, and the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, among others. This potentially inhibits the inflammatory response, oxidative stress, and retinal neovascularization and apoptosis of retinal ganglion cells and retinal pigment epithelial cells. This improves retinal structural impairment and can have a significant impact on the treatment of retinal diseases.
A Meta-Analysis published in 2023 in the journal Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition found that Consuming carrots can significantly decrease the risk of cancer. The methodology used in this research involved examining the links between carrot intake and the incidence of cancer. The scope was broad, examining all studies published before June 2022 that offered risk estimates connecting cancer incidence with either carrot consumption, α-carotene intake, or α-carotene plasma levels. Possible sources of such studies included those found via digital searches, manually identified within other studies, or garnered from existing reviews. Analysis was carried out comparing the highest and lowest reported intakes from prospective studies, estimating summary relative risks using a random-effects model. The study's results indicated a strong correlation between carrot consumption and a notable reduction in cancer risk. This conclusion was derived from the analysis of 198 observational studies, 50 of which were prospective studies involving a total of 52,000 cases that specifically recorded carrot intake. Comparatively, on the correlation between α-carotene plasma levels and cancer risk, analysis from 30 prospective studies with 9,331 cases indicated that a higher presence of α-carotene also resulted in decreased cancer risk. Despite a moderate variance between studies, these findings serve as significant evidence in support of the anticancer benefits of carrots.
A Systematic Review published in 2023 in the journal Brain Research found that Pomegranate fruit and its phytochemicals may offer a novel, natural alternative for the treatment of pathological anxiety, with fewer adverse effects than traditional medications. Using a systematic review methodology, the researchers explored the potential anxiolytic (or anxiety-reducing) effects of pomegranate (PG) fruit and its natural compounds. Searches were conducted across numerous databases such as PubMed, ScienceDirect, Google Scholar, WorldWide Science, and Web of Science using specific predetermined terms. Only original articles meeting established inclusion criteria were chosen for review. The data collected from these articles provided information on the part and variety of pomegranates used, the species studied, sample size, anxiety model, dose, route and time of administration, reference drug, main results, and associated mechanisms of action. The review of 59 such studies revealed PG as well as compounds it contains - specifically anthocyanins, flavonoids, tannins, organic acids, and xanthonoids - as having potential anxiolytic effects. According to the existing literature, these effects appear to be driven by several molecular mechanisms. These include the inhibition of specific anxiety-linked receptors, activation of certain cellular pathways associated with anxiety reduction and resilience, modulation of inflammatory proteins, and reduction of oxidative stress. The results position pomegranate and its phytochemicals as a potentially new natural option for the treatment of anxiety disorders. This is the first review to focus on the anxiolytic impact of pomegranates.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2023 in the journal Complementary Therapies in Medicine found that Changes in gut microbiome associated with a low-fat, vegan diet and cooked soybeans may reduce the frequency and severity of postmenopausal hot flashes. In this study, 84 postmenopausal women experiencing two or more moderate-to-severe hot flashes daily were randomly assigned to a low-fat, vegan diet with daily cooked soybeans or allowed to maintain their usual diet. Over a 12-week period, the frequency and severity of hot flashes were tracked using a mobile application. In 11 women from the group, gut microbiome was analyzed at the start and after 12 weeks of the dietary intervention, using deep shotgun metagenomic sequencing. The women who underwent gut microbiome testing experienced a substantial decrease in total hot flashes during the dietary intervention, and severe hot flashes disappeared entirely in this group. Alpha and beta diversity within the microbiome showed no significant difference in the intervention group between baseline and the end of the 12 weeks. Interestingly, adjustments in the relative abundance of certain bacterial strains, notably Porphyromonas and Prevotella corporis, were linked with the reduction in severe day hot flashes, while changes in the relative abundance of Clostridium asparagiforme were associated with a reduction in total severe hot flashes and severe night hot flashes.
A Experimental Study published in 2023 in the journal Journal of Science and Technology - HaUI found that The compound (Z)-5’-Hydroxyjasmone 5’-O-β-D-Glucopyranoside from chrysanthemum flowers demonstrated superior antioxidant and anti-osteoporosis effects. The research involved isolating five compounds from Chrysanthemum indicum L flowers: Syringin, Dihydrosyringin, Benzyl-O-β-D- glucopyranoside, -Phenylethoxy-O--D-glucopyranoside, and (Z)-5’-Hydroxyjasmone 5’-O-β-D-Glucopyranoside. The identification and structure determination of these compounds were performed via the interpretation of their 1D - NMR spectra and comparison to established literature. The collected compounds were then assessed for their antioxidative and anti-osteoporosis activities. During the analysis of results, it was observed that the compound (Z)-5’-Hydroxyjasmone 5’-O-β-D-Glucopyranoside exhibited significantly higher antioxidant activity and anti-osteoporosis effects compared to the others. It showed a strong capacity for peroxyl radical scavenging, surpassing the protection offered by the standard Trolox. Dihydrosyringin also demonstrated a good reducing capacity, as indicated by its CUPRAC values. Furthermore, (Z)-5’-Hydroxyjasmone 5’-O-β-D-Glucopyranoside displayed strong inhibitory effects on osteoclast differentiation, indicating its potential as an anti-osteoporosis agent.
A Systematic Review published in 2023 in the journal Phytotherapy Research found that Pomegranate can significantly enhance women's health during and after menopause by reducing hot flashes severity and other menopause symptoms. The study aimed at understanding the impacts of pomegranate on women's health through and following menopause. To gather data, a rigorous search was conducted on various academic platforms, including PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane, Scopus, and Google Scholar, up to the end of 2022. All forms of clinical research studies, from randomized clinical trials to case series, were considered for review. The material was evaluated using the Cochrane RoB 2.0 tool specifically for quality assessment of randomized clinical trials. To quantify the effects of the pomegranate intervention, standardized mean differences were calculated using a random effect model. It was found that pomegranate significantly reduces the severity of hot flashes in menopausal women, improves their high-density lipoprotein levels, and reduces the Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH). However, no significant improvement was noticed in the low-density lipoprotein, body mass index, and body weight. Despite these findings, the study recognized that the results' conclusiveness was hampered due to small sample sizes and the lack of study design elements such as blinding and randomization.
A Review Article published in 2023 in the journal Nutrire found that Almond consumption has beneficial impacts on cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, obesity, and it can improve cognitive performance and protect against skin aging. The methodology employed in this study included analyzing a range of clinical studies centered on the health benefits linked to the consumption of sweet almond nuts. Various health outcomes correlated with almond consumption were investigated such as body weight, food intake, blood pressure, blood lipid composition, glucose and insulin levels, oxidative status, liver enzymes, and some inflammation biomarkers. The discussion of the results reveals that almond consumption has been found to create favorable alteration in aspects like body weight, food intake, blood pressure, blood lipid composition, glucose, and insulin levels, as well as oxidative status, liver enzymes, and inflammation biomarkers. These findings highlight the beneficial impact of almonds on multiple health issues including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and obesity. Additionally, the consumption of almonds has been associated with improved cognitive performance and protection against skin photodamage and aging.
A Experimental Study published in 2023 in the journal Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy found that Fructus Lycii and Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge extract (FSE) shows potential as a clinical treatment for retinitis pigmentosa by inhibiting photoreceptor cell death following oxidative stress. The study utilized hydrogen peroxide to induce oxidative stress in 661 W cells, which were examined with flow cytometry and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The impact of this oxidative stress on the cells’ mitochondria was observed using an electron microscope to understand the nature of cell death. The study also analyzed the compensatory effect of the Fructus Lycii and Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge extract on the retinal structure and function of rd10 mice using histopathological examination, fundus photographs, and electroretinography. Protein levels were evaluated using Western blot assays, specifically targeting proteins including Tumor Protein p53, Solute Carrier Family 7 Member 11, Glutathione peroxidase 4, Arachidonate-12-Lipoxygenase, and Dipeptidyl peptidase 4. The results showed that hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in 661 W cells increased oxidative stress products and certain protein expressions, while decreasing others. Notably, the activation of Glutathione peroxidase 4 did not lessen reactive oxygen species generation and had little impact on cell death. The research discovered that both Ferrostatin-1 and the extract could lessen reactive oxygen species generation and inhibit cell death of photoreceptors in retinitis pigmentosa, achieving this by inhibiting the expression of one protein and increasing the expression of two others.
A Review Article published in 2023 in the journal Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics found that Fruits, especially kiwifruits, and rye bread can enhance bowel movements and help manage chronic constipation better than conventional dietary methods. An exhaustive analysis was conducted incorporating a multitude of studies, including randomized controlled trials and uncontrolled trials, identified through electronic databases till 12th July 2023. The effect of various foods, drinks, and diets on characteristics such as stool output, gut transit time, symptoms, quality of life, adverse events, and compliance in adults with chronic constipation was inspected. The study also examined the response to different treatments and included a variety of foods such as kiwifruit, high-mineral water, prunes, rye bread, mango, fig, cereal, oat bran, yoghurt, water supplementation, prune juice, and high-fibre or no-fibre diets. The synthesized data revealed that the consumption of fruits, particularly kiwifruits, and rye bread led to a higher stool frequency when compared to standard treatments like psyllium or white bread. High-mineral water also proved more effective regarding response to treatment than low-mineral water. On the other hand, no distinctive difference was identified for prunes when set against psyllium as a treatment option. Overall, the study insightfully suggests dietary modifications as a means to manage chronic constipation, emphasizing the potential of fruits such as kiwifruits and rye bread.
A Cohort Study published in 2023 in the journal Nutrients found that Long-term consumption of green tea can potentially lessen the risk of depression in postmenopausal women by decreasing inflammation and boosting estradiol levels. In the study, researchers performed an analysis on a tea-producing village, incorporating 386 postmenopausal women in the investigation, who participated either as green tea consumers or non-drinkers (control group). The level of estradiol, inflammation markers, sleep quality, and depression symptoms were measured to uncover any correlations. The results reflected significant disparities between the tea-drinking and control groups in terms of depression and insomnia levels, BMI, inflammation levels, and estradiol quantities. By appraising these outcomes, it was found that green tea intake could quell the likelihood of depression via its impact on sleep, inflammation, and estradiol levels. The risk of depression was consequently seen as reduced among postmenopausal women engaging in regular consumption of green tea.
A Clinical Study published in 2023 in the journal Metabolites found that Consuming bicarbonate-calcium mineral water, low in sodium, can help manage calcium imbalance and support bone health in perimenopausal women. The study involved 120 perimenopausal women who consumed 2 liters of a specific bicarbonate-calcium mineral water (Lete) daily for six months. This water was chosen because it is rich in calcium and bicarbonate but low in sodium. The study aimed to determine the impact of this water on bone health and overall metabolism. The participants’ urine and blood serum were analyzed using NMR-based metabolomic procedures. These analyses were conducted to assess the effects of the water not only on calcium metabolism but also on the broader systemic metabolism. The findings indicated that the Lete water effectively compensated for calcium dysmetabolism and supported bone health and integrity in perimenopausal women. While the study primarily focused on bone metabolism, it also provided insights into the potential system-wide metabolic effects of this specific type of mineral water. This suggests that such water could be a valuable dietary supplement for addressing calcium-related metabolic issues, particularly in perimenopausal women.
A Animal Study published in 2023 in the journal Nutrients found that A combination of soybean germ extract and a probiotic significantly improved menopause-related conditions and mood in an ovariectomized rat model. The study employed an ovariectomized rat model to understand the effects of a combination of soybean germ extract containing 30% isoflavone and a probiotic. The methodology included assessing the effects of this combination on several health markers including body weight, estrogen markers, uterine and bone health, vascular markers, and neurotransmitter levels in these rats. Once implemented, the combination of soybean germ extract and the probiotic showcased significant improvement in body weight and uterine and bone health of the rats. There were also noticeable effects on the lipid profile, liver function, and vascular markers. Most interestingly, the combination had a positive impact on the levels of serotonin and norepinephrine, indicating potential mood-enhancing effects, which are crucial in managing symptoms post-menopause. This essentially shows the potential of a dietary approach towards menopausal management, especially given the observed benefits without the side effects typically associated with hormone replacement therapy.
A Experimental Study published in 2023 in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition found that A combination of Walnut Peptide and Casein Peptide substantially alleviates anxiety disorder symptoms and enhances memory by improving neurotransmitter function in mice. The study investigated the effects of the combination of Walnut Peptide (WP) and Casein Peptide (CP) in mice exhibiting elevated anxiety levels by giving them these peptides through oral gavage administration. The researchers designed assessments to carefully examine changes in the subjects' anxiety and memory-related behaviors following this treatment. Besides monitoring behavior, they also scrutinized the levels of several neurotransmitters, such as Serotonin, gamma-aminobutyric acid, dopamine, and acetylcholine, to identify the biological mechanisms underlying the observed effects. The mice treated with the WP + CP combination demonstrated significant improvement in behavioral tests related to anxiety and memory. The analysis also showed that the peptide combination resulted in restoring neurotransmitter dysfunction observed while examining neurotransmitter levels. The peptides had the additional effect of increasing the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA, suggesting a protective role against the neurological effects of anxiety. The research revealed strong correlations between the improvement in behavioral indicators, increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and neurotransmitter levels. The study concluded that the WP+CP combination might serve as an effective alternative therapy for anxiety disorders, implying potential usefulness as dietary supplements or inclusions in common foods.
A Experimental Study published in 2023 in the journal Cosmetics found that Phenolic extracts from turmeric and ginger have significant anti-inflammatory effects and enhance wound healing in Wistar rats. The study utilised the solid-liquid extraction method to obtain phenolic extracts from turmeric and ginger rhizomes. Using Wistar rats as a biological model, the researchers examined the anti-inflammatory effects of the extracts by observing the decrease in edema volume in the rat's hind paw following treatment. Moreover, the healing process of purposefully induced burns on the rat's dorsal region was monitored to evaluate the healing activity. In the discussion of the results, it was observed that the application of creams containing the mentioned extracts resulted in complete healing after 19 days, a marked improvement compared to the control group, which only achieved 60% healing. The extracts demonstrated different levels regarding tissue repair at day 14, showing their respective potency. The study also identified diverse molecular weight distribution of phenolic compounds within the extracts, suggesting potential influence on how they affect anti-inflammatory and wound healing activities.
A Network Pharmacology published in 2023 in the journal Annals of Translational Medicine found that The research unveils luteolin, quercetin, and kaempferol in RALRG as promising complementary components for RP treatment, with a key role in managing oxidative stress and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. The research used various databases such as Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform, GeneCards, and the Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man database to gather the ingredients of RALRG and potential targets of RP and RALRG. A protein-protein interaction network was constructed to visualize these interactions. The R program was utilized to perform functional enrichment. The researchers constructed a visual RALRG-RP-pathway pharmacology network using Cytoscape 3.9.1 and applied molecular docking to compute binding affinity. The research revealed a total of 132 effective active elements in RALRG correlating to 248 target genes. Ninety-two intersection target genes were discovered from the overlap of RP- and RALRG-related genes. These intersection targets were discovered to be primarily involved in oxidative stress, responding to metal ions, and handling chemical stress. Several molecular pathways such as PI3K-AKT and MAPK were identified as closely connected to RP therapy. A potential pharmacology network was designed for the RALRG-RP-pathway with AKT1 and JUN being considered the main targets. The active ingredients luteolin, quercetin, and kaempferol were highlighted as crucial for this mechanism. RALRG overall was established as a main regulator for oxidative stress and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways in the treatment of RP.
A Review Article published in 2023 in the journal Food Chemistry Advances found that Pomegranate and its by-products, particularly the peel, contain bioactive compounds with potential antimicrobial, anticancer and antiviral properties. In the methodological approach of the study, a comprehensive review was undertaken to collate information on the bioactive components found within pomegranates and their by-products (aril, seed, and peel). The study emphasized the pomegranate peel's properties owing to its high content of the bioactive compounds. The aim was to elucidate the nutritional and functional aspects of pomegranates, particularly as a functional food. The results outlined that pomegranates, especially their peel, contain bioactive compounds, including punicalagin, punicalin, ellagic acid, punicic acid, and anthocyanins. Therefore, they have potential functional properties such as antimicrobial, anticancer, and antiviral characteristics. These results suggest that pomegranates could be explored to develop nutraceutical or functional food products due to their profound properties. The peel of the pomegranate, specifically, showcases significant potential for development due to its higher bioactive compound content compared to other parts of the fruit.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2023 in the journal Nutrients found that A beverage formula containing fish roe, snow fungus, and yeast enhances cognitive function by improving memory, response times, and emotional recognition, while reducing anxiety and fatigue. In the study, 64 volunteers were divided into two equal groups, with one group consuming a placebo and the other consuming the formula beverage for a duration of 8 weeks. Cognitive testing was performed initially and at two follow-up points, weeks 4 and 8. Variables tested included memory recall, identification of objects over time, response times, emotional recognition from facial expressions and self-reported anxiety and fatigue levels. The results demonstrated that by weeks 4 and 8, those who consumed the formula beverage showed notable advancements in cognitive functions. These individuals were able to remember objects better and had quicker response times. Notably, they also registered a significant improvement in recognizing happy faces and displayed reduced anxiety and fatigue. Overall, the beverage holds promise as an intervention tool for cognitive improvement in individuals reporting subjective cognitive issues.
A Review Article published in 2023 in the journal Nutrients found that The bioactive peptides found in walnuts have potential neuroprotective effects, including reducing oxidative stress and neuroinflammation, and promoting autophagy and balance in the cholinergic system. The research method used includes the development of various procedures to prepare, isolate, purify, and identify the neuroprotective peptides found in walnuts. Different evaluation approaches were then used to gauge the activity of these peptides within experimental setups, placing emphasis on potential oxidative stress reduction, neuroinflammation mitigation, autophagy promotion, gut microflora regulation, and cholinergic system balance enhancement. The discussion of the results suggests the confirmed neuroprotective benefits of walnut-derived peptides. These peptides showcased their ability to reduce oxidative stress, combat neuroinflammation, stimulate autophagy, and regulate gut microflora and the cholinergic system. Consequently, these findings highlight the value of walnuts in diet, and the potential for these peptides to be utilized as functional food ingredients promoting neurohealth.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2023 in the journal Journal of Medicinal Food found that Daily consumption of pecans for a month can help protect against post-meal oxidative stress in aging adults. The abstract outlines a randomized, parallel, controlled trial where 41 healthy adults aged between 50 and 75 were split into two groups. One group consumed 68 grams of pecans every day for four weeks, while the other group avoided all nuts. Blood samples were obtained from all participants before and after the intervention during fasting and at intervals of 30, 60, and 120 minutes after a meal high in saturated fats. Changes were observed in various parameters, including malondialdehyde - a marker for lipid peroxidation, total antioxidant capacity (TAC), glucose, and insulin levels. The study revealed no significant variances in fasting or post-meal TAC, glucose, or insulin for the pecan consumers compared to the control group. However, there was a noticeable tendency towards a change in fasting lipid peroxidation driven by a minor reduction for the pecan group compared to the control group. Moreover, post-meal lipid peroxidation was suppressed in the pecan group, distinctly different from the control group's results. These outcomes propose that a diet enriched in pecans for one month can provide protection against post-meal oxidative stress in older adults.
A Experimental Study published in 2023 in the journal Digital Chinese Medicine found that Lycium barbarum polysaccharide may decrease apoptosis in retinal photoreceptor cells of retinitis pigmentosa mice by suppressing nuclear factor-kappa B/NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain-associated protein 3 pathway. The team carried out both in vivo and in vitro studies. Initially, mouse retinal ganglion cells were categorized into groups based on the doses of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide they were given and a positive drug control group. These cells were then subject to different H2O2 concentrations to induce apoptosis. Techniques such as flow cytometry, immunofluorescence, and western blot were used to evaluate cell viability, apoptosis rate, and expression of various markers. For in vivo research, the team used C57/BL6 and Rd10 mice divided into similar groups as the in vitro experiment. The mice underwent drug treatment for four weeks, after which their retina's response to light and general health were evaluated using an electroretinogram and histopathological examination. The in vitro experiments showed that the apoptosis rate of ganglion cells significantly increased in the model group, along with up-regulation of certain proteins. However, a high dose of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide decreased the cell apoptosis rate and the levels of certain proteins. Similarly, in vivo testing showed that a high dose of the substance significantly aided in morphological alterations in a retina layer of Rd10 mice, and down-regulated the expression levels of a number of apoptosis-related proteins.
A Review Article published in 2023 in the journal PharmaNutrition found that Soy protein, bioactive peptides, and isoflavones are generally safe for consumption and may help reduce the risk of several significant health conditions. Methodology: This review followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines. It began with a sophisticated multi-database search, featuring resources like Google Scholar, Scopus, and others. This search targeted articles published from 2017 to March 2023 and used specific keywords for accuracy. Forty-three articles were handpicked from this process after excluding reviews, conference reports, duplicates, inaccessible texts, and any non-English publications. Discussion of Results: A thorough examination of the chosen articles resulted in the conclusion that soy proteins, soy bioactive peptides, and soy isoflavones are typically safe for human consumption. Furthermore, it was found that the consumption of these compounds may have beneficial effects, potentially lowering risk factors for ailments such as osteoporosis, various cancers, hypertension, atherosclerosis, and more.
A Systematic Review published in 2023 in the journal Journal of Functional Foods found that Pomegranate consumption positively affects triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. To investigate the impact of pomegranate on lipid profiles, a comprehensive database search was completed up until June 2023, aiming to identify related trials. Statistically, the researchers employed the estimated 95% confidence and the weighted mean difference to measure the variables, including triglycerides, total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. They employed a random-effects model for their analysis. The meta-analysis revealed that pomegranate intake significantly reduces triglyceride levels. Still, it doesn't notably alter the total cholesterol concentrations. Additionally, consuming pomegranate seemed to have a diminishing impact on low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and an enhancing effect on high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels.
A Review Article published in 2023 in the journal International Journal of Food Properties found that Plums, which are rich in bioactive compounds, antioxidants, and vitamins, can help maintain blood glucose level, bone health, heart health and even treat certain cancers. The research explored the health benefits and medicinal effects of plums, a common fruit belonging to the Prunus genus. The study focused not only on their consumption as a food source but also their uses in beverages. Special attention was given to the polyphenolic compounds, bioactive compounds, and antioxidants inherent in plums, such as phenolic acids, anthocyanins, carotenoids, and various organic acids, alongside an array of necessary minerals and vitamins. Apart from detailing traditional nutritional components, the study analyzed the unique constituents of plums like caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid and other phenolic compounds which contribute to its antioxidant property. The broader health benefits provided by these compounds spanning bone health, cardiovascular health, blood glucose stabilization, and potential impacts on gastrointestinal diseases were studied, with a particular emphasis on their possible role in the prevention and treatment of heart disease and specific kinds of cancer: lung and oral. The role of plums' low fat and high dietary fibre content in heart disease prevention was of special focus.
A Network Pharmacology published in 2023 in the journal Medicine found that The compounds apocarotenoids and carotenoids found in saffron extract could potentially interact with multiple targets, helping to manage the symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome. The study utilized a network pharmacology-based approach to identify the possible therapeutic pathways for apocarotenoids and carotenoids in Crocus sativus on polycystic ovary syndrome. The Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Photodiode Array detector (UHPLC-PDA) standardized stigma-based Crocus sativus extract (CSE) was analyzed for these phytochemicals. Information about polycystic ovary syndrome related genes was collected from a knowledge database and networks were established between these targets and Crocus sativus extract phytochemicals to understand its mechanism of action. Through network analysis and screening conditions, the study found four significant targets, including serine/threonine kinase 1, signal transducer and activator of transcription, and two types of mitogen-activated protein kinases. Gene ontology and Kyoto Encyclopaedia of genes and genomes analysis showed that MAP kinase and serine-threonine pathways were crucial targets in polycystic ovary syndrome. Further molecular docking studies were conducted, and carotenoids apocarotenoids were assessed for absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity predictions. Elements like crocetin, picrocrocin, and safranal showed strong binding affinity for the identified targets. This analysis also revealed that these compounds had excellent bioavailability and could cross the blood-brain barrier without demonstrating toxicity. In summary, the study demonstrated that these phytochemicals could act on the identified targets, thus pointing towards the potentiality of Crocus sativus extract in managing polycystic ovary syndrome.
A Experimental Study published in 2023 in the journal The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that Moderate consumption of blueberries may effectively reduce bone loss in healthy postmenopausal women. The research began with a blueberry dose-response study with ovariectomized rats, used as an experimental model simulating postmenopausal conditions. These rats were fed with various doses of blueberry powder, with the aim to identify an optimal dosage for bone calcium retention. The experiment then translated to a human study where fourteen healthy women, all more than four years past menopause, were examined. A baseline was established, and then each participant was provided with varying dosages of freeze-dried blueberry powder equivalent to defined portions of fresh blueberries, to be consumed daily for a series of six weeks at a time. Tracing calcium in the urine was employed as a method to monitor bone calcium balances in both the rat and human trials. The collected data indicated that both the rat and human subjects benefited from blueberry interventions at lower doses. Higher doses, however, showed no such beneficial impact on bone calcium balance. In human subjects, net bone calcium retention increased with low and medium doses of blueberry consumption. Increased urinary excretion of hippuric acid, a metabolite of the antioxidants present in blueberries, was observed with an increase in blueberry consumption. No significant associations were found between bone resorption biomarkers and the interventions implemented in the study.
A Meta-Analysis published in 2023 in the journal CNS & Neurological Disorders - Drug Targets found that Blueberry consumption significantly improves two-back test accuracy, suggesting potential cognitive benefits. Methodology: A comprehensive search was conducted in April 2021 for relevant clinical trials on blueberry supplementation and its effects on cognitive performance and mood. The search was conducted through PubMed/Medline, Scopus, Embase, and Google Scholar, and the random effect size was used to estimate the pooled effect size. Cochrane Q test and I-squared tests were used to evaluate heterogeneity between studies, and a subgroup analysis was done to detect potential sources of such heterogeneity. Fourteen randomized trials were included in the quantitative analysis, and six were pooled for statistical analysis. Results: Blueberry intervention did not produce any significant impact on mood state score, attention task reaction time, or on the percentages of attention task accuracy. Similarly, it had no significant effect on one-back test accuracy. However, a noticeable positive effect was detected in two-back test accuracy, indicating possible cognitive benefits associated with blueberry consumption.
A Network Pharmacology published in 2023 in the journal Journal of Ethnopharmacology found that Gold kiwifruit extracts contained different bioactive materials which showed selective cytotoxic activity against human oral tumor cells and displayed anti-HIV, antioxidant, and antibacterial activities. The methodology involved stepwise extraction of gold kiwifruit with hexane, acetone, methanol, and 70% methanol; the extracts were then fractionated using silica gel and ODS column chromatographies to examine their biological activities. Different fractions like H1, H2 (from the hexane extract), A1, A2 (from the acetone extract), and M2 (from the methanol extract) were tested, as well as more hydrophilic fractions from the 70% methanol extract. In the discussion of the results, fractions H1, H2, A1, A2 and M2 displayed notable cytotoxic activity against human oral tumor cell lines, with these showing more sensitivity compared to human gingival fibroblasts. The hydrophilic fractions from the 70% methanol extract demonstrated higher anti-HIV activity, radical generation, and oxygen scavenging activity. However, the antibacterial activity of these fractions was generally lower than that of the more lipophilic (hexane, acetone, methanol) extracts, indicating no distinct antimicrobial action. Interestingly, all fractions were inactive against Helicobacter pylori.
A Experimental Study published in 2023 in the journal Foods found that The fermented jujube seeds extract significantly enhances sleep by binding to the GABA receptors, thus offers a promising natural alternative for sleep disorders treatment. Methodology: An aqueous extract of jujube seeds (ZW) was fermented, following a starch-removing enzymatic degradation process, to increase its γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) content, resulting in a fermented product (ZW-FM). The sleep-promoting effect of ZW-FM was evaluated using rodent models; specifically, sleep tests were performed on ICR mice with pentobarbital-induced sleep, while the electroencephalography analysis was undertaken in Sprague Dawley rats. Awakening relief effects of ZW-FM were assessed using a caffeine-induced insomnia model. To understand the mechanism, GABA receptor type A (GABA) antagonists were used. Results: The groups given ZW-FM treatment displayed a longer sleep duration, particularly increased δ-wave time during non-rapid eye movement sleep, and reduced sleep latency. Particularly, the model treated with ZW-FM showed an increase in non-rapid-eye-movement sleep and a reduction in the REM sleep duration, brought about by caffeine treatment. The enhanced sleep induction caused by ZW-FM was hindered by GABA receptor antagonists, thereby validating the involvement of a GABAergic mechanism in promoting sleep.
A Review Article published in 2023 in the journal Human Reproduction Update found that The Mediterranean diet and reduced intake of trans fatty acids, saturated fatty acids, and discretionary foods like fast food and sugar-sweetened beverages may improve fertility rates. This title represents a systematic scoping review of four electronic databases, namely Medline and EMBASE via Ovid Processing, CAB Direct, and CINAHL via EBSCO. The researchers included observational works, consisting of prospective and retrospective cohort, cross-sectional, and case-control studies, up to September 27, 2021. The criteria for study inclusion were women of reproductive age in the preconception stage who were examined for the connection between preconception diet and fertility outcomes. From the total of 36 studies that were found eligible for review, the one diet that stood out with the most significant and consistent association with increased clinical pregnancy rates was the Mediterranean diet. Dietary factors such as reducing trans fatty acids, saturated fatty acids, and discretionary food intake, which includes fast food and sugar-rich drinks, were found to lead to an improvement in live birth, clinical pregnancy rates, and associated ART outcomes. However, this study also found that elements like seafood, dairy, and soy showed varying findings across a few studies. Despite the mixed results, it was noted that following some of these dietary regulations, notably Mediterranean diet, shows consistency with healthy eating guidelines, implying potential benefits in fertility.
A Systematic Review published in 2023 in the journal Nutrients found that Natural calcium-rich mineral waters offer a bioavailable calcium source, beneficial for bone health, cardiovascular function, weight management, and overall well-being. This systematic review analyzed peer-reviewed articles, clinical trials, and experimental studies from the past decade. It focused on the health benefits of calcium-rich mineral waters, especially for individuals with lactose intolerance or on plant-based diets. The review process assessed the contribution of these waters to daily calcium intake and their bioavailability compared to other calcium sources. The review found that natural mineral waters high in calcium can significantly enhance calcium intake, with improved absorption rates. These waters show promise in promoting bone health and cardiovascular function, including potential reductions in blood pressure and cardiovascular disease risk. Some evidence suggests benefits in weight management. However, the review highlighted the need for further research on interactions with other dietary components, effects on specific health conditions, and long-term consumption impacts. Despite these gaps, calcium-rich mineral waters are recognized as a valuable dietary calcium source for a diverse population.
A Systematic Review published in 2023 in the journal Current Sleep Medicine Reports found that There is evidence to support significant improvements to total sleep time and sleep efficiency with the ingestion of tart cherries. We identified a total of 277 unique records, from which 8 studies of low-moderate methodological quality were included in the systematic review. Meta-analysis of subjectively recalled sleep efficiency (SE) and total sleep time (TST) were not significant. Objective SE, however, was significantly higher in the cherry cohort when compared to placebo with an effect size of 0.63 (95% CI 0.29–0.97, P < 0.01). There was low associated heterogeneity (I2 = 0%). Objective TST was significantly higher in the cherry cohorts, with a pooled effect size of 1.21 (95% CI 0.83–1.58, P < 0.01). There was high associated heterogeneity (I2 = 81.5%).
A Review Article published in 2023 in the journal Nutrients found that Honey intake has observed beneficial effects on various health aspects like cardiovascular, metabolic risk factors, and wound healing, primarily replacing other sweeteners. In this comprehensive review study, the researchers went beyond just looking at one or two aspects of health; instead, they embarked on an ambitious task of reviewing forty-eight clinical trials that were published between 1985 and 2022, involving a total of 3655 subjects. The researchers aimed to critically analyze the effect of honey on multiple health indices, including, but not limited to, cardiovascular and metabolic risk factors, glucose tolerance, mucositis inflicted by chemo-radiotherapy, cough in children, and wound healing. The evaluation and analysis of the data involved a thorough examination of the results of each of the clinical trials, consideration of several potential variables, and detailed cross-study comparisons. This broad and deep investigation allowed the researchers to draw correlations and pinpoint the beneficial influences of honey, considered a nutritious and natural food. The results from these clinical trials saw more beneficial effects on health from honey intake when compared to neutral or negative outcomes. It was most notably effective, particularly when used as a substitute for other sweeteners. The review also pointed out the potential use of honey as a safe adjuvant to be used in combination with drugs for specific illnesses. Confidently stating that honey has clear benefits in the clinical trials analyzed, the researchers fostered a promising narrative for the further exploration and acceptance of honey as a health booster.
A Animal Study published in 2023 in the journal European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry found that Jin Si Huang Ju tea, a traditional Chinese beverage, contains compounds that potentially reduce lipids, mitigate insulin resistance and reduce liver inflammation in vitro. The researchers identified 14 compounds in the Jinsi Huangju tea using different spectroscopic techniques, 11 of which had not been previously identified in this plant. Two of these compounds, apigenin-7-O-6″-malonylglucoside and luteolin-7-O-6″-malonylglucoside, were synthesized for the first time with a yield of 1.2% over 5 steps. In the findings, the natural compound apigenin-7-O-6″-malonylglucoside was found to inhibit the function of pancreatic lipase, reduce cellular lipid contents, and attenuate insulin resistance when tested in vitro. It was also observed to restore lipid and inflammatory profiles in plasma and the liver, as well as reduce hepatic steatosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) mouse models. Thus, Jinsi Huangju and its active components are strong candidates for the development of drugs or functional foods that could provide a therapeutic strategy for hyperlipidaemia and NAFLD.
A Systematic Review published in 2023 in the journal Current Problems in Cardiology found that Oat consumption can significantly improve lipid profiles, particularly reducing total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol, with potential positive effects on triglycerides and HDL cholesterol under certain conditions. In the methodology of this review study, information was gathered from various databases, including PubMed, Web of Science, and Google Scholar. The gathered data consisted of a total of 17 studies that explored the direct effects of oat consumption on lipid profiles. The focus of the studies included were the impacts of oat on levels of total cholesterol, VLDL, LDL-C, TG, and HDL-C. The review was meticulous, with a detailed examination of each study, particularly those showing positive effects of oat/beta-glucan consumption on triglycerides. The review's results revealed that oat intake significantly reduces the levels of total cholesterol, VLDL, and LDL-C. The effect of oat ingestion on triglyceride levels was varied; of the 17 studies, 6 reported a decrease in triglycerides. Interestingly, one study showed an improvement in HDL-C levels following oat consumption. It was also observed that oat intake might effectively reduce triglycerides in healthy individuals and overweight people or those with diabetes or metabolic syndrome, especially when larger amounts of oat were consumed over a longer duration or in conjunction with a calorie-reducing diet. The use of oat together with certain dietary programs was suggested to potentially enhance its positive effects on lipid profiles.
A Review Article published in 2023 in the journal Autoimmunity Reviews found that Nutrition, particularly an anti-inflammatory Mediterranean diet supplemented with oily fish and omega-3 supplements, can potentially reduce inflammation and improve symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. The review examines evidence indicating a possible connection between nutrition and the risk and management of rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disease having an immune-inflammatory response. The impact of different food types was considered, including pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory foods. Specifically, the research highlights the effectiveness of a Mediterranean diet, rich in fish and supplemented with omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, in reducing inflammation and oxidation. Other factors such as herbs and spices, beverages, vitamin D, and probiotics were also taken into account. The research emphasizes the direct and indirect role of nutrition through the management of co-morbidity. The disease activity was observed to improve with dietary changes, particularly a propensity to reduce inflammation, oxidation, and beneficial effects on gut microbiota. An anti-inflammatory Mediterranean diet, supplemented with consumption of oily fish at least twice a week, and daily intake of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplements of 2 g, has been recommended. The study also highlights the importance of rheumatologists working closely with registered dietitians to support patients in managing a well-balanced diet according to their individual needs.
A Review Article published in 2023 in the journal PeerJ found that Crocin, a compound derived from saffron, has shown considerable potential in hindering tumor growth and improving immune status, across various malignant tumors. The methodology for the study involved an in-depth review of modern pharmacological studies that have analyzed the therapeutic effects of crocin, a natural compound that can be extracted from saffron. Various anti-tumor effects were assessed including the induction of tumor cell death (apoptosis), restrictions on tumor cell proliferation, and potential barriers to invasion and metastasis of these cells. The potential for enhancement of sensitivity to chemotherapy and improvement of immune status were also examined. Following the review, the study revealed that crocin has significant anti-tumor properties. It showed that this natural compound can induce apoptosis in tumor cells, inhibit their expansion and progression, and even prevent their invasiveness and metastasis. Furthermore, crocin demonstrated the potential to enhance the body’s responsiveness to chemotherapy and help boost the immune system. These effects were observed across a range of different malignant tumors, including stomach, liver, cervical, breast, and colorectal cancers.
A Cohort Study published in 2023 in the journal Journal of Global Research in Public Health found that Young coconut water has been found to be more effective than carrot juice in reducing the severity of dysmenorrhea in teenage girls. In this experimental study, research was conducted using a pre-experimental research design with a two group comparison pre-test and post-test. The research population was compiled of teenage girls from a school in the City of Kediri. The investigators selected a sample of 32 respondents using purposive sampling methods, and utilized observation sheets and pain scale measurements from the Femoralis Rectus Sheath as their primary data collection tools. The results of the study highlighted a significant difference in the effectiveness of the two tested interventions, young coconut water and carrot juice, for the alleviation of dysmenorrhea symptoms. In this comparison, it was found that young coconut water showed higher effectiveness in reducing the pain severity in teenage girls than carrot juice.
A Systematic Review published in 2023 in the journal Nutrients found that Vitamin D supplementation significantly reduces pain levels in people suffering from primary dysmenorrhea. In the methodology of this study, a systematic database search was conducted for randomized controlled trials assessing the effects of oral vitamin D supplementation on relieving the symptoms of primary dysmenorrhea. The trials included comparisons of vitamin D treatment with placebo or standard care. Pain levels due to dysmenorrhea were gauged using a visual analogue or numerical rating scale. Analyses were conducted using a standardized mean difference in a meta-analysis. The results indicated that pain levels were considerably lower in participants who took vitamin D compared to the placebo, showcasing vitamin D's effectiveness in managing dysmenorhea-related pain. Notably, these relief effects were recorded regardless of the vitamin D administration duration (more or less than 70 days) and frequency, provided that the average weekly dosage was above 50,000 IU. This suggests that the significant pain relief provided by vitamin D supplementation could make it a potent alternative treatment for primary dysmenorrhea.
A Review Article published in 2023 in the journal Food Science & Nutrition found that Eating apples and apple products can enhance health by protecting the cardiovascular system, combating cancer and cognitive impairment, and improving hair growth, among other beneficial effects. The study took a comprehensive approach to evaluate the health benefits of apples and apple products by conducting a literature review of relevant clinical, epidemiological, in vitro, and in vivo studies. It involved an exhaustive search of the PubMed database for a ten-year period, sourcing studies that reported on the effects of different apple products: juices, purees, pomaces, dried apples, and extracts rich in apple bioactives. The findings indicate that the consumption of apples and their derivations contributes to multiple aspects of human health. These products exhibited a range of protective effects against diseases such as cardiovascular conditions and cancer. Moreover, they were associated with enhanced cognitive function, facilitated hair growth, the healing of burn wounds, and improved oral health. The use of apples and apple-based products also helped to reduce UV-induced skin pigmentation, alleviated the symptoms of atopic dermatitis and cedar hay fever, and even prevented skin flushing caused by niacin. The beneficial impacts of apple consumption can be attributed to a variety of mechanisms including, but not limited to, vascular endothelial protection, blood lipid regulation, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, as well as anti-invasion and antimetastatic tendencies. These results provide a significant reference point for various fields, including medicine and nutrition, contributing to their development and application.
A Experimental Study published in 2023 in the journal Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy found that Zhangyanming Tablets show potential as a protective agent for retinal function in early-stage, genetically-caused blindness in mice, possibly due to their antioxidant and anti-/pro-apoptotic properties. Eighty mice with Retinitis Pigmentosa (RP) were divided into two groups, with one group receiving Zhangyanming Tablets (ZYMT) and a control group getting distilled water. After a period of 7 and 14 days, the researchers conducted tests through electroretinogram, fundus photography, and histological examination to assess the retinal function and structure of the subjects. They furthered the study using TUNEL, immunofluorescence and qPCR to evaluate cell apoptosis and the expressions of particular genes. The ZYMT-treated mice displayed a notable enhancement in retinal reactions and overall preservation of retinal structure when compared to the control group. Particularly noticeable were increases in retinal thickness and cell count, alongside a significantly lowered rate of cell death. A comprehensive follow-up shows the altered expressions of several genes in the retina following the application of ZYMT. These results, combined, suggest a key role of ZYMT in mitigating the effects of RP especially in early stages.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2023 in the journal The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that Consumption of blueberry powder daily improves vascular function, cognitive abilities, and reduces blood pressure in healthy older individuals. This double-blind, parallel randomized controlled trial engaged 61 healthy older individuals aged between 65 to 80 years old. Participants were given either 26g of freeze-dried wild blueberry (WBB) powder, comprising 302 mg anthocyanins, or a similar placebo with zero mg anthocyanins. Measurements were made for endothelial function, cognitive function, arterial stiffness, blood pressure, cerebral blood flow, gut microbiome, and blood parameters, both at the start of the trial and again following 12 weeks of daily consumption. In addition, plasma and urinary polyphenol metabolites were analyzed through the use of microelution solid-phase extraction combined with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. In the WBB group, there was a notable increase in endothelial function and a decrease in 24-hour ambulatory systolic blood pressure, when compared to the placebo group. Enhanced immediate recall on the auditory verbal learning task was also observed, along with better accuracy on a task-switch task following administering of WBB. Notably, the total 24-hour urinary excretion of polyphenols also significantly increased in the WBB group comparative to the control group. In contrast, there were no discernible changes in cerebral blood flow or gut microbiota composition. These findings imply that WBB polyphenols could contribute to reducing future cardiovascular disease risk in older populations, and might enhance memory processes and executive functioning in older adults at risk of cognitive decline.
A Experimental Study published in 2023 in the journal Foods found that Bee-collected pollen and bee bread, particularly when artificially fermented, demonstrate significant antiviral activity against the H1N1 strain of the influenza A virus. The research investigated the antiviral properties of bee-collected pollen (BCP) and bee bread (BB), including versions that had undergone artificial fermentation. The experiment also assessed separate proteins, water content, and -butanol portions of these substances. The analysis evaluated their effectiveness against the H1N1 strain of the influenza A virus (IAV). The antiviral behavior of these materials was taken in lab conditions via a comparative real-time PCR analysis working on their inhibitory concentration and selectivity index. The outcomes revealed artificial fermentation improved the antiviral effectiveness of BCP. The protein fractions within the BCP and BB presented the greatest antiviral activity. Observations also highlighted that the chemical composition, prominent in proteins, and potentially microbiome metabolism determined the antiviral properties of BCP and BB. The chemical profile analysis emphasized the existence of some specialized metabolites that might be contributing towards this antiviral action.
A Clinical Study published in 2023 in the journal Nutrients found that Consuming two medium-sized green kiwifruits an hour before bed can improve sleep quality and recovery stress balance among elite athletes. The study began with an initial assessment, after which all participants were instructed to consume two medium-sized green kiwifruits an hour before bedtime over a 4-week span. Data was collected through baseline and post-intervention questionnaires, as well as daily sleep diary entries throughout the study duration. There was a notable positive effect of kiwifruit consumption on essential aspects of sleep and recovery in professional athletes. After the intervention period, improvements were observed in sleep quality and recovery stress balances. Additionally, there was an increase in total sleep time, sleep efficiency, and a decrease in the number of times participants woke after falling asleep. The study concludes that kiwifruits positively influence sleep and recovery in high-performing athletes.
A Review Article published in 2023 in the journal Nutrition Reviews found that Berry fruits such as blueberries, cranberries, raspberries, and strawberries could potentially improve gut microbiota and reverse dysbiosis in chronic kidney disease patients. Methodology: This research explores the therapeutic potential of berry fruits, including blueberries, cranberries, raspberries, and strawberries, in relation to modulating gut microbiota in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients. The fruit’s rich polyphenol and nutrient content are assumed to promote the selective growth of beneficial bacteria, thus improving the clinical status of these patients. The study scrutinizes the impact on the abundance of mucus-producing bacteria and short-chain fatty acids specifically. Discussion of Results: The gathered evidence illustrates that berry fruits, particularly with a daily intake of 5 mg, can promote diversity in the gut microbiota and possibly reverse dysbiosis, a common issue in chronic kidney disease patients. These fruits are found to increase the expression of mRNA involved in gut tight junctions such as occludin, TJP1, and mucin, and they may reduce uremic toxins by controlling the gut microbiota, improving the uremic condition. As such, long-term use of berry fruits could be an effective strategy for CKD patients.
A Systematic Review published in 2023 in the journal Modern Care Journal found that Saffron shows promising improvements in dealing with women's health issues related to labor, childbirth, premenstrual syndrome and menopause. For the methodology, the investigators implemented a systematic review by utilizing the PICO process to explore various databases like PubMed, Scopus, Cochrane, among others, until February 2023. A strategically designed search was conducted using a set of keywords related to saffron and women's health conditions. From a pool of 164 articles, 20 randomized controlled trials that met the minimum score based on the Jadad scale were included in the study. In terms of results, the investigation revealed that saffron holds positive impacts on labor and childbirth, such as enhancing Bishop's score, fostering labor progression, and reducing labor pain intensity and fatigue. Moreover, it helps with episiotomy healing and ameliorates mood swings and psychological symptoms associated with menopause and premenstrual syndrome. The study also acknowledges some influence of saffron on postpartum depression.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2023 in the journal EClinicalMedicine found that Walnut consumption may improve attention, fluid intelligence, and reduce ADHD symptoms in adolescents who consistently incorporated them into their diet. For their methods, the investigators utilized a 6-month randomised controlled nutrition intervention across multiple schools, enrolling 771 healthy teenagers. These participants, aged between 11-16 years, were split into two groups - one that was given a daily amount of 30 grams of raw walnut kernels to incorporate into their diet and a control group. Neuropsychological aspects like working memory, attention, fluid intelligence, and executive function were assessed, along with behavioral aspects such as socio-emotional and ADHD symptoms. Alpha-linolenic acid status was determined at the start and end of the trial as a measure of compliance. In regard to the results, general improvements in sustained attention, fluid intelligence, and a reduction in ADHD symptoms were recorded in participants who were more compliant in integrating walnuts into their diet. However, there was no significant improvement observed in the neuropsychological function of healthy adolescents overall.
A Systematic Review published in 2023 in the journal Journal of Tissue Viability found that Honey dressing significantly promotes healing and reduces recovery time in managing diabetic foot ulcers. For the research methodology, the study used a combination of randomized controlled trials, quasi-experimental, and cross-sectional studies. Only the randomized controlled trials and quasi-experimental studies were chosen for the meta-analysis, while observational studies were subject to a descriptive analysis. In terms of the results discussion, the meta-analysis indicated that using honey as a dressing for diabetic foot ulcers resulted in a reduction in wound recovery time, pain experienced, duration of hospital stay, and an acceleration in wound granulation. Therefore, it was concluded that honey dressing is an effective intervention for accelerating healing in diabetic foot ulcers.
A Systematic Review published in 2023 in the journal International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health found that Consumption of natural mineral water increases diuresis in both humans and animals, evident sometimes after just one intake. This systematic review, adhering to PRISMA guidelines, evaluated the diuretic effects of natural mineral water on healthy individuals. Comprehensive searches were conducted in PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library up to November 2022, including both human and animal studies. A total of 12 studies were identified, predominantly from Italy and one from Bulgaria, covering publications from 1962 to 2019 for human studies and 1967 to 2001 for animal studies. All included studies consistently reported an increase in diuresis following the consumption of natural mineral water, with some studies observing this effect after a single administration. However, the quality of these studies, especially the older ones, was noted to be suboptimal. The review underscores the need for newer clinical studies with improved methodological approaches and advanced statistical data processing to validate these findings more robustly.
A Review Article published in 2023 in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition found that Sardines, being an affordable source of Omega-3 and other cardioprotective nutrients, can potentially reduce the need for Omega-3 supplementation and manage cardiometabolic diseases. The abstract primarily acknowledges the importance of Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids with respect to managing diseases related to heart health and metabolism, for instance, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, hypertriglyceridaemia, and fatty liver disease. However, these fatty acids are not the sole beneficial component of sardines. Minerals including but not limited to calcium, potassium, and magnesium as well as substances like taurine and arginine found in sardines have a significant role in controlling mild inflammation and oxidative stress which are usually present in cardiovascular diseases and hemodynamic dysfunction. The results discussed in the abstract suggest a positive correlation between consumption of sardines and potential cardiometabolic benefits. By considering the dose-response relationship effects, a pragmatic approach towards consumption of nutrients was suggested. The intake of sardines was seen not only as a means of Omega-3 supplementation but also as a comprehensive approach to enhancing cardiovascular health. The abstract concludes with an emphasis on the many beneficial nutrients found in sardines besides Omega-3, underlining the need to shift the focus from synthetic supplementation to natural dietary improvement.
A Experimental Study published in 2023 in the journal Molecules found that The anthocyanins from the Gardenblue variety of blueberries exhibit strong antiproliferative effects on various cancer cells, especially liver cancer cells. 65 varieties of blueberries were collected, focusing on their nutritional and functional values. Among these, the Gardenblue variety showed the highest anthocyanin content in fresh fruit. This content was further increased through the process of ultrasound-assisted solvent extraction and macroporous resin absorption, transforming it into a dried powder. Biological experiments were then conducted to determine the antiproliferative effects of Gardenblue anthocyanins on various cancer cell strains, such as cervical, liver, breast, and lung cells. Furthermore, these anthocyanins were combined with the chemotherapy drugs, cisplatin and doxorubicin, to assess any potential enhanced antiproliferative effects. The research results confirmed that Gardenblue anthocyanins exert a substantial antiproliferative effect on multiple cancer cell types, particularly hepatoma or liver cancer cells. These anthocyanins displayed no evident toxic effects, as measured by the MTT assay, a laboratory colorimetric technique. Notably, the antiproliferative benefits were amplified when the anthocyanins were combined with doxorubicin, a treatment for liver cancer. Analysis suggests that the anthocyanins might induce cell apoptosis (cell death) by bonding with DNA in a manner that modifies or damages the DNA, thus preventing cell proliferation. This suggests potential application of Gardenblue anthocyanin extract as a functional agent against liver cancer cells.
A Case Report published in 2023 in the journal Journal of Personalized Medicine found that The combination of epigallocatechin gallate, vitamin B12, folic acid, and hyaluronic acid could effectively counter precancerous lesions of the uterine cervix caused by HPV infections. The methodology used in this research centred around treating a 39-year-old patient who had a history of HPV, cervix lesions, and multiple failed surgical attempts to treat the condition. The treatment plan applied was unique, utilizing a blend of epigallocatechin gallate, vitamin B12, folic acid, and hyaluronic acid, administered over an eight week period. The results showed promising effects, with the patient's histological and cytological analyses revealing only a chronic cervicitis instead of any malignant lesions or cellular dysplasia. Therefore, the necessity for invasive total hysterectomy was minimized, demonstrating the potential for the selected treatment plan to manage precancerous lesions of the uterine cervix.
A Clinical Study published in 2023 in the journal Biomedical Reports found that Consuming a honey-based gel, such as 'Bear Strength honey gel,' led to a notable reduction in diastolic and mean arterial blood pressure, with gender-specific improvements in redox status among healthy adults. The study included 20 healthy participants (10 men, 10 women) who incorporated 70g of 'Bear Strength honey gel' into their daily diet for 14 days. Physiological parameters (weight, height, BMI, body fat, waist-to-hip ratio, resting heart rate, and blood pressure) and hematological data were evaluated before and after consumption. Redox biomarkers, including Glutathione (GSH), catalase (CAT), total antioxidant capacity (TAC), protein carbonyls (PCARBS), and thiobarbituric reactive substances (TBARS), were measured. Post-consumption, the honey-based gel showed a significant decrease in diastolic and mean arterial blood pressure, particularly in women. However, no significant changes were observed in other physiological or hematological variables. Notably, GSH levels increased in both genders, TAC increased universally, and TBARS levels decreased in the total group and women. PCARBS levels decreased exclusively in the women's group. These findings highlight the honey-based gel's potential positive impact on blood pressure and redox status, emphasizing gender-specific effects in healthy adults.
A Review Article published in 2023 in the journal Nutrients found that Green tea helps alleviate symptoms in multiple benign gynecological disorders, primarily due to a compound called Epigallocatechin-3-gallate. The paper reviews the role of the compound Epigallocatechin-3-gallate found in green tea, and its effects on various benign gynecological conditions. The compound is noted for its antioxidant and prooxidant qualities, allowing it to interact with multiple cellular pathways that are crucial for disease pathogenesis. The studied conditions include uterine fibroids, endometriosis, dysmenorrhea, adenomyosis, menopause, and polycystic ovary syndrome. The research accounts for the specific mechanisms through which the compound might affect each condition, such as anti-fibrotic, anti-angiogenic, and pro-apoptotic mechanisms. The results suggest that green tea consumption can lead to improved symptom management in these disorders. It was found to lessen the intensity of symptoms associated with uterine fibroids and endometriosis, by invoking anti-fibrotic, anti-angiogenic, and pro-apoptotic mechanisms. It also helped manage pain linked with dysmenorrhea and adenomyosis through reducing uterine contractility and widely felt pain. Additionally, it showed efficacy in weight and osteoporosis control during menopause, and showed potential benefits in managing polycystic ovary syndrome. However, claims regarding its influence on fertility were deemed controversial.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2023 in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition found that Consumption of fresh or dried kiwifruit in the evening improves aspects of sleep quality and mood, potentially mediated through changes in serotonin metabolism. A randomized, single-blind crossover study involving 24 men with varying sleep quality levels was conducted. Participants were provided with one of three treatments during their standard evening meal at home: the flesh of two fresh green kiwifruits, dried green kiwifruit powder (with skin and equivalent to the dry matter of two fresh kiwifruits) mixed with water, or a water control. Various factors were evaluated including subjective and objective sleep quality, mood, and urine concentration of several compounds including the serotonin metabolite 5-HIAA, vitamin C, and B-vitamins. Findings indicated that regardless of sleep quality group, dried kiwifruit consumption was associated with an improvement in morning sleepiness, alertness upon waking, and vigor as compared to the control. Both fresh and dried kiwifruit treatments suggested an improvement in self-esteem and overall mood disturbance. Increase in the urinary concentration of serotonin metabolite was observed with both kiwifruit treatments. Amongst poor sleepers, ease of awakening was notably improved after the intake of dried kiwifruit and showed signs of improvement with fresh kiwifruit. For good sleepers, there seemed to be an improvement in getting to sleep with fresh kiwifruit. Poor sleepers were found to have lower quantities of certain B-vitamins compared to good sleepers. Thus, both dried and fresh kiwifruit consumption with a standard evening meal showed a positive impact on sleep quality and mood.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2023 in the journal Journal of Clinical Medicine found that A combination of epigallocatechin gallate, folic acid, vitamin B12, and hyaluronic acid may effectively clear HPV infections and cervical lesions in women. Forty women with persistent HPV infections and cervical lesions were enrolled in this study and were then divided into two groups. Women in the treatment group were given a 12-week treatment comprising of 200mg epigallocatechin gallate, 400µg folic acid, 1mg vitamin B12, and 50mg hyaluronic acid. In contrast, the control group received no treatment. A significant difference was noted between the two groups post-treatment. In the control group, the majority of women still had a Low-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion (LSIL) at the close of the study, with varying changes in viral DNA content. However, in the case of the treated group, most women had achieved full viral clearance, showing no signs of lesions post-treatment, thus highlighting the potential effectiveness of the treatment combination.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2023 in the journal Journal of Medicinal Food found that Korean pear extracts appear to alleviate air pollution-related respiratory hypersensitivity by modulating beneficial gut microflora and suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines. In the preclinical and randomized double-blind clinical studies, mild-asthma subjects living in Seoul, Korea were divided into two groups: one receiving a daily treatment of pear extracts for four weeks, and a placebo group. The pear extract was tested for its ability to mitigate respiratory hypersensitivity connected to air pollution. The treatment's effects were evaluated based on the toxicokinetic study of exposure biomarkers for airborne polyaromatic hydrocarbons and levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in human subjects. In terms of results, it was found that those individuals receiving daily pear extract exhibited decreased levels of exposure biomarkers related to airborne polyaromatic hydrocarbons. Furthermore, the pear extract treatment was associated with a significant increase in populations of fiber-degrading bacteria that boost beneficial gut microflora crucial for immune defense. Additionally, the extracts significantly suppressed the production of various pro-inflammatory cytokines, as per the preclinical tests conducted on asthma-induced mice. Overall, these outcomes suggest a beneficial role of Korean pear extracts in mitigating air pollution-related respiratory hypersensitivity.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2023 in the journal Journal of Food and Dairy Sciences found that Cinnamon, ginger, and mint enhanced chocolates effectively reduce menstrual pain and improve blood iron levels without increasing body weight or negatively affecting cholesterol. The methodology of the study involved a sample of 48 female student volunteers, aged 18-25, from Mansoura University who were experiencing dysmenorrhea. These volunteers were divided into eight groups of six and each group was given a different type of chocolate: regular chocolate, chocolate without herbal powder, chocolate with cinnamon powder, chocolate with cinnamon oil, chocolate with ginger powder, chocolate with ginger oil, chocolate with mint powder, and chocolate with mint oil. Discussion of the results demonstrated that the consumption of chocolates supplemented with cinnamon, ginger, and mint powders and their respective essential oils led to a significant improvement in participants' hemoglobin scores compared to a control group which consumed normal chocolate. Furthermore, it was found that these chocolates had a positive influence on serum total cholesterol, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein, and low-density lipoprotein scores. Importantly, chocolate consumption did not lead to an increase in the participants' body mass index, proving that these chocolate variants could reduce menstrual pain and lift blood iron levels without instigating weight gain or having adverse effects on cholesterol levels.
A Systematic Review published in 2023 in the journal Nutrition found that Our dose-response analysis indicated that moderate green tea consumption (500–1000 mL/d) was associated with a 21% to 24% lower risk of stroke. The meta-analysis aimed to clarify the inconsistent findings in epidemiologic studies regarding the link between green tea consumption and stroke risk. Five prospective cohort studies, involving 645,393 participants and 11,421 stroke cases, were analyzed. The summary relative risk (RR) revealed a substantial association, indicating a 26% reduction in stroke risk with the highest green tea consumption. The dose-response analysis indicated a nonlinear relationship, and compared with non-consumers, various levels of green tea intake showed progressively reduced RRs for stroke, emphasizing a potential protective effect. The findings from the meta-analysis strongly suggest an inverse association between green tea consumption and stroke risk. Notably, the highest green tea consumption demonstrated a significant 26% risk reduction. The dose-response analysis further highlighted a nonlinear relationship, with moderate consumption levels (500–1000 mL/d) showing the most substantial risk reduction. These results provide support for recommending green tea consumption as a measure for the primary prevention of stroke.
A Systematic Review published in 2023 in the journal Complementary Therapies in Medicine found that Almond consumption can significantly reduce the serum concentration of the inflammatory mediator, Interleukin-6, in adults but no significant effect is found on C-reactive protein. The methodology of this study involved running an electronic search for English-language studies across several databases such as Web of Science, PubMed, SCOPUS, ClinicalTrials.gov, and Cochrane library without any time restrictions. The effect sizes on serum concentration of C-reactive protein (CRP) and Interleukin-6 (IL-6) were calculated based on the mean changes of both intervention and control groups. Assessment of the overall effects and their heterogeneity was done using the DerSimonian and Laird random-effects model. To examine the statistical heterogeneity, Cochran's Q test and I-squared statistic were utilized. With respect to the results, among the eleven studies involved, it was observed that almond consumption did not significantly affect serum CRP level. However, a significant decrease in serum IL-6 level was reported with almond consumption. Thus, reflecting the beneficial effects of almonds with regard to reducing the serum concentration of IL-6. The results derived for serum CRP were not substantial enough to be considered significant.
A Cohort Study published in 2023 in the journal The Journal of Sex Research found that Ginger consumption could counteract the negative influence of disgust, induced by sexual body fluids, on sexual arousal in individuals. The researchers conducted an experiment involving 247 participants, who were either given ginger or placebo pills. Participants were then required to complete tasks involving either sexual body fluids or neutral fluids. After completing their tasks, the participants were shown and asked to respond to questions about erotic stimuli which consisted of either nude or semi-nude pictures of individuals of the opposite sex. This study showed that tasks involving sexual body fluids caused disgust. This feeling of disgust led to decreased sexual arousal in women. Interestingly, the consumption of ginger was found to counteract the inhibiting effect of disgust on sexual arousal. Additionally, the disgust caused by the sexual body fluids tasks also increased disgust towards subsequent erotic stimuli. However, ginger consumption was found to increase sexual arousal towards the erotic stimuli in both men and women who had performed the neutral fluids tasks.
A Experimental Study published in 2023 in the journal Egyptian Journal of Chemistry found that Chrysanthemum morifolium contains natural bioactive compounds, including 29 types of phenolics, which display significant antioxidant activity. The study determined the antioxidant properties of Chrysanthemum morifolium by using methanol and ethyl acetate as solvents to extract and then analyse the plant's phenolic profile. The antioxidant activity was assessed with three separate in vitro tests: a reducing power assay, a Phosphomolybdenum antioxidative power assay, and the testing of inhibition of free radical 1,1-di phenyl-2-picryl hydrazyl. The content of total phenolics and total flavonoids was measured using the Folin Ciocalteu reagent, yielding a range of values. In relation to the results, it was established that the examined plant was a significant source of bioactive compounds with notable antioxidant properties. A total of 29 phenolics, divided into 15 phenolic acids and 14 flavonoids were identified and quantified using high-performance liquid chromatography. Ellagic acid was the most present phenolic in the methanol extract and ethyl acetate fraction of green aerial parts. Meanwhile, Hesperidin was the most common flavonoid in the flower methanol extract. The ethyl acetate fraction from the flowers showed the highest efficiency in all tested antioxidant methods, indicating that different parts of the plant can vary in their antioxidant potential.
A Review Article published in 2023 in the journal Current Nutrition Reports found that Oats, in various edible forms, can regulate appetite hormones, aid weight management, strengthen the immune system, and contribute to gut health, making them effective for obesity management. The research methodology entailed a review of the role of hunger hormones in managing obesity and studying the influence of different edible forms of oats like whole, naked, sprouted, or supplemented oats on these hormones. The relationship between consumption of oats and various indicators of obesity such as body mass index, waist circumference, body weight, appetite, and blood pressure, amongst others was investigated. Furthermore, the nutritional content of oats like protein, fiber, healthy fats, and bioactive ingredients was analyzed, with particular emphasis on Beta-glucan as it lowers cholesterol levels and enhances the body's defense system. The results of the studies showed that oats have several therapeutic potentials. An intake of oats helps manage body weight and control appetite. In addition, oats positively impact the immune system and lower cholesterol levels in the serum. They also foster gut health by promoting the increased production of short-chain fatty acids. Despite these findings, some studies showed no significant effects of oats on appetite.
A Review Article published in 2023 in the journal Food Reviews International found that Australian native plums contain phytochemicals that exhibit health benefits such as cardiovascular and liver protection. The research review examined five varieties of Australian native plums: Terminalia ferdinandiana (Kakadu Plum), Davidsonia jerseyana (Davidsons Plum), Podocarpus elatus (Illawarra Plum), Pleiogynium timorense (Burdekin Plum) and Parinari nonda (Nonda Plum). The paper explored each plum variety in terms of their ideal growing conditions, their phytochemical composition, their sensory properties, and their potential applications. Extracts from different parts of the fruit including the peel, pulp, and seeds were analyzed for their capabilities to interact with cell signaling pathways, scavenge free radicals, and inhibit harmful microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, and viruses. The findings suggest that Australian native plums not only have substantial nutritional value - being high in dietary fiber and low in fat - but they also offer a multitude of health benefits. Notably, these fruits exhibit cardiovascular and liver-protective properties. Moreover, aside from their nutritional and health value, these native plums also display impressive economic potential. For instance, the pulp of these plums could be incorporated into food and beverage creation while their wood could be utilized for furniture making.
A Systematic Review published in 2023 in the journal Frontiers in Medicine found that Saffron supplementation significantly decreased oxidative stress markers and has beneficial effects in reducing oxidative stress. For this analysis, we sought to evaluate the impact of saffron supplementation on oxidative stress markers, including malondialdehyde, total antioxidant capacity, total oxidant status, glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase, and prooxidant/antioxidant balance. To do this, we conducted an extensive search across databases such as PubMed/Medline, Web of Science, Cochrane CENTRAL, Scopus, and Google Scholar until December 2022. Our search criteria included randomized controlled trial studies examining the effects of oral saffron supplements on the aforementioned oxidative stress markers. The resulting data were pooled using a random effects model to analyze the results, and we assessed heterogeneity using the Cochrane values. We incorporated 16 cases into our meta-analysis, which comprised of subjects in both saffron and control groups. In our results, we found that saffron consumption resulted in significant reductions in malondialdehyde and total oxidant status levels. Furthermore, it led to a considerable increase in total antioxidant capacity and glutathione peroxidase - all of which are markers indicating oxidative stress. More specifically, within studies where the daily dosage of saffron was greater than 30 mg, and in studies lasting less than 12 weeks, we noted a significant reduction in malondialdehyde levels, especially in participants under 50 years old. Our study faced limitations, including the geographical limitation of the studies being from Iran, the varying nature of the diseases included, and potential confounding factors such as smoking, physical activity, and diet.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2023 in the journal BMJ Open Gastroenterology found that Bicarbonate-rich mineral water “Staatl. Fachingen STILL” significantly reduces heartburn more effectively than placebo, improving patients’ quality of life. The STOMACH STILL trial, a multicentre, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study, assessed the effectiveness of Staatl. Fachingen STILL mineral water in relieving heartburn. Adult patients with frequent heartburn episodes for at least six months, but without severe reflux oesophagitis, were recruited. They consumed 1.5 liters per day of either the mineral water (verum) or placebo for six weeks. Primary endpoint was a reduction of at least five points in the Reflux Disease Questionnaire score for heartburn. Secondary endpoints included overall symptom reduction, health-related quality of life measures (QOLRAD), rescue medication intake, and safety/tolerability. Of the 148 patients randomized, 143 completed the trial. The responder rate was significantly higher in the mineral water group (84.72%) compared to the placebo group (63.51%). Significant improvements were observed in the ‘heartburn’ dimension and overall Reflux Disease Questionnaire scores for the mineral water group. Additionally, three out of five Quality of Life in Reflux and Dyspepsia domains showed improvement: ‘food/drink problems,’ ‘emotional distress,’ and ‘vitality.’ The verum group also reported a decrease in rescue medication use. Only three patients experienced treatment-related adverse events. The study concluded that Staatl. Fachingen STILL mineral water is superior to placebo in relieving heartburn and enhancing health-related quality of life.
A Cohort Study published in 2023 in the journal Nutrients found that Regular consumption of raw carrots is associated with a significant, dose-dependent reduction in lung cancer incidence, suggesting a potential cancer-protective effect attributed to polyacetylenic compounds, particularly falcarinol and falcarindiol, present in raw carrots. This research involved a long-term study of 55,756 Danish citizens over a period of more than 25 years. The focus was on investigating the relationship between regular consumption of raw carrots and the development of various cancers, predominantly adenocarcinomas and leukemia. The study assessed whether the frequency of carrot consumption influenced the incidence of lung, pancreatic, breast, prostate cancer, and leukemia. Additionally, it compared the effects of eating raw versus processed carrots. The study found that eating raw carrots regularly was associated with a reduced occurrence of lung cancer. This link was less clear for pancreatic cancer and non-existent for breast and prostate cancer. The research suggested that the cancer-preventive properties of raw carrots could be attributed to specific compounds, namely falcarinol and falcarindiol. These compounds are not present in cooked carrots. This significant finding points towards the potential of raw carrots in cancer prevention, particularly for lung cancer.
A Clinical Study published in 2023 in the journal PLOS One found that Avocado consumption correlates with a wider variety of healthier food choices, offering potential benefits for weight control strategies. The study created a comprehensive database of avocado-containing foods and drinks based on the AUSNUT 2011-13 food composition structure. The data pulled from four food-based clinical trials consisted of the usual food intake information from overweight and obese volunteers. The Apriori algorithm of association rules was employed as a two-step descriptive methodology to identify the associations between avocado consumption and choices of various foods at each mealtime using a nested hierarchical food group classification scheme. The findings revealed 34 separate avocado and avocado-inclusive foods and beverages. Avocado intake was prevalent within the studied cohort, with more than half consuming avocados regularly. Avocados were invariably associated with other food groups in main meal occasions, and during breakfast, lunch, and dinner, 68 food items containing avocados were identified for avocado consumers. This avocado-specific database offers insights into the variety of foods and beverages that incorporate avocados, reflecting broad food choices among regular avocado consumers.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2023 in the journal Frontiers in Pharmacology found that Pomegranate extract supplements can help improve clinical symptoms and lower blood cell counts associated with inflammation in patients with allergic asthma. In this study, 64 participants with mild to moderate allergic asthma were randomly divided into two groups: a control group which was given placebo capsules and an intervention group which was given pomegranate extract capsules. The intervention group was administered a dosage of 250 milligrams of pomegranate extract twice daily over a period of eight weeks. The clinical symptoms and blood cell counts of all the participants were measured before starting the intervention and post the completion of it. The results of the study indicated that the group which was given pomegranate extract exhibited considerable improvement in clinical symptoms like shortness of breath and restrictions on activity, as compared to the control group. Additionally, the participants in the intervention group displayed a substantive drop in eosinophil, basophil, and neutrophil counts. Notably, there was a statistically significant difference in the neutrophil and eosinophil levels between the two groups, which suggests that pomegranate extract supplementation might have potential therapeutic benefits for asthma patients.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2023 in the journal Phytotherapy Research found that Pomegranate juice supplementation has been found to effectively decrease testosterone levels in overweight and obese women diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome. In the methodology, the study employed a randomized controlled trial which involved 44 participants. The women, aged between 18 and 40 years, had all been diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome and had a body mass index exceeding 25 kg/m. They were randomly divided, with one group consuming 45 ml/day of concentrated pomegranate juice and the other group receiving no intervention. A variety of biomarkers for sex hormones, inflammation, and oxidative stress were measured before starting the trial and again after eight weeks. Further discussion of the results revealed a significant decrease in testosterone levels among the overweight and obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome who took concentrated pomegranate juice over the eight week period, in contrast to those in the control group. Apart from testosterone, no significant changes were observed for luteinizing hormone, sex hormone-binding globulin levels or for markers of inflammation and oxidative stress between the two groups.
A Review Article published in 2023 in the journal Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture found that Carrot and carotene consumption could diminish the risk of a wide range of negative health consequences, including multiple types of cancer. An umbrella review methodology was adopted to identify connections between carrot and carotene intake and various health outcomes. We turned to databases such as Web of Science, PubMed, and Embase to find the needed data. The analysis included the collected evidence from both interventional and observational studies that focused on carrots, carotene, and any related health impact. To estimate the summary effect size for each correlation, both random and fixed effects models were employed. The study reviewed a total of 1329 studies and utilized the data from 30 meta-analyses with 26 health outcomes that fit the eligibility requirements. These featured outcomes related to various types of cancer, fractures, age-related cataract, sunburn, and Alzheimer's disease. The associations were analyzed between the health outcomes and the intake of carrots, intake of carotene, and serum carotene levels.
A Review Article published in 2023 in the journal Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience found that Honey exhibits multifaceted benefits for brain health, acting as a memory booster, neuroprotective agent, anti-stress, and anti-nociceptive substance, fostering potential therapeutic applications to enhance overall cognitive well-being. This review scrutinizes 34 original articles exploring the impact of honey on brain health. Honey, traditionally known as a natural sweetener, emerges as a versatile substance with applications in nutrition, health supplementation, and brain health enhancement. The analysis identifies four key benefits: memory enhancement, neuroprotection, stress reduction, and pain alleviation. The review emphasizes the growing interest in understanding the mechanisms that underlie these effects, paving the way for potential therapeutic roles of honey in promoting cognitive well-being. The literature review underscores the significant role of honey in brain health research, shedding light on its diverse benefits, including memory improvement, neuroprotection, stress mitigation, and pain relief. The emphasis on unraveling the underlying mechanisms reflects a broader interest in establishing honey's therapeutic potential for enhancing overall brain health. This comprehensive exploration of honey's effects on cognition opens avenues for developing novel therapeutic strategies harnessing honey's natural properties.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2023 in the journal Journal of Tropical Pharmacy and Chemistry found that The combination of dark chocolate with herbs could be one of the therapies for period pain. This test was conducted on 30 respondents who were divided into three groups, namely the positive control group (K), dark chocolate (C), and a combination of dark chocolate with herbs (C+H). Dark chocolate was combined with herbal ingredients consisting of turmeric, red ginger, moringa, sambiloto extract, and honey as a beverage 250 mL. The study is quantitative research with quasi-experimental method. Pain measurement using the Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) sheet was given before and 2 hours after treatment. The data was analyzed using paired t-test. State the results of the values obtained the combination of dark chocolate and herbs showed a significant reduction in pain before and after treatment (p<0.05).
A Cohort Study published in 2023 in the journal Journal of the American Heart Association found that Heavy coffee consumption increases the risk of cardiovascular disease mortality in individuals with severe hypertension, while green tea consumption does not. With the use of the Japan Collaborative Cohort Study, researchers assessed 18,609 participants, both male and female, aged between 40 to 79 years. These participants had varying blood pressure levels, categorized into optimal and normal BP, high-normal BP, and two stages of hypertension. They completed a questionnaire about their lifestyle, diet, and medical history, and underwent health examinations, which were followed up until 2009. The association of coffee and green tea consumption on cardiovascular disease mortality was then calculated using a Cox proportional hazard model. It was found over an 18.9 year follow-up period that heavy coffee consumption was linked to increased risk of cardiovascular disease mortality among those suffering from the second to third grade of hypertension. In stark contrast, people with optimal and normal, high-normal blood pressure and first grade hypertension did not show such associations between coffee consumption and cardiovascular disease mortality. Interestingly, the risk of cardiovascular disease mortality was not found to be increased across any blood pressure categories in relation to green tea consumption.
A Animal Study published in 2023 in the journal Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment found that Specific fractions of Lycium barbarum, commonly known as Goji berry, reduce heart and kidney damage caused by anthracyclines while possibly enhancing their therapeutic effects. The study investigated the effects of three different fractions of Goji berries (pectin-free, polysaccharides, and a mix of the two) on rat models suffering from doxorubicin-induced damage to the heart and kidneys. The fractions were orally administered at a dose of 2mg/kg while doxorubicin was applied at a total dose of 20mg/kg. Several biomarkers were used to assess heart damage (such as creatine kinase, aspartate aminotransferase, lactate dehydrogenase) and kidney damage (creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, uric acid), along with potassium serum levels. Additionally, a histological analysis of the hearts and kidneys was conducted. In terms of results, rats treated solely with doxorubicin exhibited a significant increase in all toxicity biomarkers. However, in all groups that also received any of the plant fractions, there was substantial reduction in markers indicating heart and kidney tissue damage. Notably, the pectin-free and combined fractions presented the most substantial decreases in toxicity indicators. These findings were further corroborated by the histological analysis.
A Cohort Study published in 2023 in the journal Nutrients found that Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a green tea component, showed potential in treating uterine fibroids and associated infertility without causing liver toxicity or folate deficiency. The study involved the pre-testing of a green tea substance known as Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) on a cohort of premenopausal women, aged 18 to 40, with and without uterine fibroids, in order to evaluate its safety. The subjects were randomized into three groups, each receiving different treatments. One group took just a daily dose of 800 mg of EGCG, one group combined this EGCG dose with 100 mg of Clomiphene citrate for five days, and the third group combined it with 5 mg of Letrozole for the same period. The results showed that none of the subjects displayed signs of drug-induced liver injury, and all had normal serum folate levels. Hence, the findings suggest that the daily intake of 800mg of EGCG, whether consumed alone or in combination with Clomiphene citrate or Letrozole for five days, is well-tolerated and not related to any liver toxicity or folate deficiency in women of reproductive age.
A Clinical Study published in 2023 in the journal Molecules found that Chrysanthemum extract can be utilised as a natural ingredient to lessen post-meal cholesterol levels and enhance antioxidant status, after eating a high-fat meal. The researchers analyzed the composition of two types of Imperial Chrysanthemum (IC) extracts, specifically IC-P and IC-E, using an Ultra High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (UHPLC-MS) method. Next, they assessed these extracts' in vitro antioxidant activities using three different radical scavenging assays: 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydraxyl (DPPH), 2,2-azino-bis-3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS) and Hydroxyl Radical(HR). A group of 37 adults followed a randomized program and were divided into two: one consuming a high-fat (HF) meal alone and the other having the same meal but supplemented with IC extract. Blood samples from participants were taken at a fasting state and several more times up to 8 hours after the meal. The study found 12 compounds, including amino acids, flavonoids, and carboxylic acids, making up over 1% of the IC extracts. Compared to IC-E, IC-P exhibited significantly higher flavonoid content and strong free radical scavenging activity. Chrysanthemum consumption showed significant differences in post-meal glucose levels, triglycerides, total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels, with the IC-P supplement group showing lower postprandial glucose and improved serum antioxidant status.
A Network Pharmacology published in 2023 in the journal TMR Pharmacology Research found that Chrysanthemum has several active ingredients that can potentially treat dry eye by inhibiting inflammation-related factors and pathways, thus reducing inflammation of lacrimal gland tissue. The study used network pharmacology methods and various databases to further analyze the mechanism of Chrysanthemum in treating dry eye. First, the TCMSP was used to screen for candidate active ingredient molecules of chrysanthemum showcasing requisite oral bioavailability and drug similarity. The active ingredients of chrysanthemum were then identified, followed by target prediction. Cytoscape was used to construct a compound-target network for chrysanthemum. The Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man and DisGeNET databases were utilized to pinpoint pathogenic genes associated with dry eye, and the STRING database produced an interaction network and bar graph to scrutinize protein interactions. Using Venny, a final drug-active ingredient-key target-disease network was created. The study found that Chrysanthemum has eighty active ingredients corresponding to targets for treating dry eye. These key functional targets primarily regulate gene expression, oxidative stress, immune response, apoptosis, proliferation, regulation of cellular inflammation-related factors, and angiogenesis. The primary pathways associated with these key targets include interleukin signaling, metabolism, cytokine signaling in the immune system, immune system, and signal transduction, thereby improving the condition of dry eye primarily through the inhibition of inflammation-related factors.
A Experimental Study published in 2023 in the journal Research found that A novel compound in walnuts, defined as 3-hydroxy-4-iminobutyric acid, can enhance sleep duration by disturbing motor activity and adjusting certain neurotransmitters in the brain of mice. The research examined the sedative and hypnotic elements of walnuts, particularly focusing on a newly discovered compound, 3-hydroxy-4-iminobutyric acid. Through careful analysis, the scientists discovered that this compound can disrupt motor activity and increase sleep duration by modulating neurotransmitters in the brain and serum of mice. The team used metabolomics to study the potential molecular mechanisms underpinning these effects, exploring the serum, various brain regions, and the gut microbiota. In the assessment of results, it was found that 3-hydroxy-4-iminobutyric acid can alter the metabolism within the basal ganglia. Of particular interest is the compound’s potential influence on gut microbiota. Accordingly, the research expands our understanding by presenting 3-hydroxy-4-iminobutyric acid as a novel natural product that can promote sleep in mice, offering fresh insights related to the microbiota-gut-brain axis in connection to enhancing sleep.
A Review Article published in 2023 in the journal Phytomedicine found that Pomegranate and its active components can protect against natural and chemical toxic agents, impacting mechanisms such as oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, and liver or cardiac function regulation. This paper is a review of various in vivo and in vitro studies focusing on pomegranate (Punica granatum) and its active components, including ellagic acid and punicalagin, and their protective effects against toxic substances. The articles were sourced from multiple databases like Web of Sciences, Google Scholar, PubMed, and Scopus spanning all available time periods until the end of September 2022. The research indicates that pomegranate and its constituents have showcased protective effects against both natural toxins, such as aflatoxins and endotoxins, and chemical toxicants like arsenic, diazinon, and carbon tetrachloride. This protection is attributed to the preventive mechanisms activated against oxidative stress, reduction of key inflammatory mediators, modulation of apoptosis, and signaling pathways associated with cellular growth. Additionally, these components appear to aid in the improvement of liver and cardiac function through the regulation of key enzymes.
A Review Article published in 2023 in the journal Reference Series in Phytochemistry found that Through innovative refinement, nanocurcumin, evolved from turmeric's primary component curcumin, has improved characteristics and pharmaceutical potential, particularly in drug delivery systems. The methodology of the research involved analyzing the cultivation, storage, and surrounding environmental factors crucial to turmeric production, such as soil condition and climate. This was intertwined with investigations into the chemical composition of turmeric, focusing mainly on curcumin, its main component. Moving forward, the study then evaluated curcumin analogs and formulations, leading to a deep dive into the relatively new development of nanocurcumin. The discussion of the research results revealed several interesting findings. Firstly, turmeric exhibited a variety of useful properties, highlighting its role in traditional medicine and livelihood in Indian tribes. Most importantly, the research concluded the impressive potential of nanocurcumin. This altered form of curcumin showed not only enhanced characteristics but also possible applications in the pharmaceutical field, specifically for drug delivery systems.
A Experimental Study published in 2023 in the journal Food & Function found that Pu-erh tea can potentially prevent depression-like behaviors induced by nighttime blue light from electronic devices by reshaping gut microbiota and increasing short-chain fatty acids generation. The methodology used involved administering water or Pu-erh tea to two groups of mice for 120 days, followed by a 45-day exposure to a blue light simulating electronic equipment during the night. The effect of the tea and blue light on the mice's behavior and gut microbiota was then studied. Results indicated that the blue light induced depression-like behaviors and upset the gut microbiota in mice that were previously healthy. In the discussion of results, it was noted that the intake of Pu-erh tea significantly reshaped the mice's gut microbiota, especially the metabolism of short-chain fatty acids, which helped protect the integrity of the intestinal barrier. This improvement not only lessened damage to the blood-brain barrier, but also reduced neuroinflammation by inhibiting certain cellular pathways. This ultimately regulated neurotransmitters like brain-derived neurotrophic factor and serotonin, demonstrating the potential of Pu-erh tea to prevent blue light induced depression-like behaviors by impacting the gut-brain axis.
A Review Article published in 2023 in the journal Pharmacological Research found that Consumption of tea and coffee may possibly provide anti-inflammatory effects, contributing to reduced cardiovascular risk and mortality. The methodology of this narrative review examined the potential anti-inflammatory properties of consuming tea and coffee as a factor in reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease. This was done by analyzing a plethora of studies and meta-analyses that explored the impact of diet on inflammation, with a keen focus on the consumption of these beverages. The studies looked at a variety of risk factors for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, including inflammation biomarkers such as C-reactive protein, along with the impact of modern lipid-lowering treatments. In discussing the results, it was noticed that inconsistent findings were produced from the analysed studies which made a conclusive determination challenging. However, a trend was observed where drinking tea and coffee seemed to raise adiponectin levels, reduce reactive oxygen species and lower low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. Despite these potential anti-inflammatory properties of tea and coffee being somewhat uncertain due to various confounding factors, their consumption is still recommended as part of a healthy diet.
A Network Pharmacology published in 2022 in the journal Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine found that Compound Chrysanthemum extract may alleviate visual fatigue through its interaction with several components, targets, and pathways. Regarding methodology, this study combined network pharmacology with experimental research to uncover the mechanisms by which Compound Chrysanthemum alleviates asthenopia. Firstly, molecular docking analysis was employed to identify a total of 593 essential genes and 39 chemicals present in the compound. This helped ascertain the affinity between key compounds and receptors, PRKACA, PRKCA, PRKCB. This was followed up with molecular dynamic simulations that further evaluated the stability of these receptors and ligands. Concurrently an in vitro examination of the compound's effect on ciliary muscle was conducted, using MTT assay to study different concentrations of the compound's effect on the proliferation of rCSMCs over 24 and 48 hours. The discussion of the results suggests that the extracts had significant impacts in several areas. Among the notable outcomes of the in vitro experiment was an increase in nitric oxide production and a decrease in Ca in ciliary muscle cells. The compound was also found to have a relaxing effect on the isolated gastric smooth muscle of rats by reducing contractile tension. In an in vivo experiment, rats treated with the compound displayed retracted pupils and increased NO content compared to the model group. A considerable contribution to the understanding of the compound's effect was the acknowledgment of its role in modulating the expression of PKA and PKC in the crucial calcium signaling pathway. The coordinated culmination of these findings indicates the compound's multi-faceted approach to alleviating visual fatigue.
A Experimental Study published in 2022 in the journal Physiological Research found that Vincentka natural mineral water reduces gastric damage and improves antioxidant capacity in an animal model of acute gastric ulcers. This pilot study involved 16 male Wistar rats, divided into two groups: an experimental group and a control group, each with eight rats. The study was conducted in three phases: a 7-day handling phase, a 7-day phase where the experimental group received Vincentka mineral water and the control group received tap water, and a final phase of acute gastritis induction lasting one day. After 24 hours post-induction, the animals were sacrificed for analysis. Tissue samples from the stomach and duodenum, as well as blood samples, were examined using histological microscopy, immunohistochemical, and biochemical methods. The histopathological analysis showed significantly less damage to the stomach lining in the experimental group compared to the control group. There were notable differences in blood plasma antioxidant capacity, oxidative stress parameters, and other biochemical values between the groups. These findings indicate that Vincentka mineral water positively affects the development and symptoms of acute gastric ulcers in this animal model, suggesting potential benefits for similar human conditions.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal American Journal of Gastroenterology found that Consuming green kiwifruits is associated with a clinically relevant increase of ≥ 1.5 complete spontaneous bowel movements per week in those experiencing constipation. Participants included healthy controls (n = 63), patients with functional constipation (FC, n = 60), and patients with constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-C, n = 61) randomly assigned to consume 2 green kiwifruits or psyllium (7.5 g) per day for 4 weeks, followed by a 4-week washout, and then the other treatment for 4 weeks. The primary outcome was the number of complete spontaneous bowel movements (CSBM) per week. Secondary outcomes included GI comfort which was measured using the GI symptom rating scale, a validated instrument. Data (intent-to-treat) were analyzed as difference from baseline using repeated measures analysis of variance suitable for AB/BA crossover design. Consumption of green kiwifruit was associated with a clinically relevant increase of ≥ 1.5 CSBM per week (FC; 1.53, P < 0.0001, IBS-C; 1.73, P = 0.0003) and significantly improved measures of GI comfort (GI symptom rating scale total score) in constipated participants (FC, P < 0.0001; IBS-C, P < 0.0001). No significant adverse events were observed.
A Systematic Review published in 2022 in the journal Digestive Diseases found that Menthacarin, derived from peppermint and caraway oil, effectively reduces symptoms, offers a safe alternative to risky drugs like cisapride, and shows promise for managing stomach problems in primary care. Menthacarin works well in reducing symptoms like pain and bloating. It is safe and could be an alternative to other drugs like cisapride, which can be risky. This herbal treatment seems useful for stomach problems in primary care, but more research is needed. In short, Menthacarin, made from peppermint and caraway oil, is a safe and effective option for stomach issues in primary care.
A Systematic Review published in 2022 in the journal Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics found that Avocado consumption may lead to a reduction in total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in people with high cholesterol without impacting body weight. The study reviewed the impact of diets containing avocado on cardiometabolic risk factors compared with diets containing no or low amounts of avocado. Five electronic databases were searched aiming to identify studies published between 1990 and 2021. The selected studies included randomized controlled trials of three weeks or more and prospective cohort studies. In total, ten studies, nine controlled trials, and one observational study, met the inclusion criteria. Risk of bias was evaluated, and overall quality of the evidence was inspected. Meta-analyses were performed when there were three or more studies of the same design reporting the same outcome. Upon reviewing the results, the study found a minor, noteworthy reduction in total cholesterol levels in the avocado group as opposed to the control groups. There was no significant difference found in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, or triglycerides. However, in populations with hypercholesterolemia, avocado consumption demonstrated significant reductions in both total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. It is also worth noting that consumption of avocados did not negatively affect body weight or composition.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Journal of Functional Foods found that Carrot's bioactive compounds can regulate immune response, reduce oxidative stress, and prevent damaging oxidative destruction, making it a potential preventive tool for various diseases. In this literature review, mechanisms were proposed for how the antioxidant properties of carrot’s β-carotene and other bioactive compounds, such as phenolic acid, flavonoid, polyacetylene, and ascorbic acid could modulate the immune system. These proposals were centered around three main paths: anti-inflammatory response modulation, antioxidant response modulation, and overall immune response modulation (which involves both innate and adaptive responses). In the discussion of results, it was revealed that the bioactive compounds in carrots have the ability to regulate pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, and are also capable of reducing oxidative stress. This was shown by the decrease in the accumulation of reactive oxygen species and an increase in antioxidant capacity, which collaboratively helps to minimize destructive oxidative destruction. Additionally, these compounds influenced immune components, specifically via the regulation of leukocytes, antigens, immunoglobulins, and histamine levels. As a result, carrots were defined as a functional food source capable of immune modulation and potential prevention and treatment for a range of diseases.
A Systematic Review published in 2022 in the journal Complementary Therapies in Medicine found that Tart cherry juice shows promise in aiding blood sugar control and supporting heart health, highlighting its potential as a natural dietary addition. Tart cherry juice was found to lower fasting blood sugar but didn't have a significant impact on blood pressure, insulin, cholesterol, body fat, or weight. It is rich in antioxidants, which may be why it's beneficial for the heart. Changes in gut bacteria might also play a role. More research with larger and varied groups of people is needed to confirm these findings and understand them better. In the meantime, healthcare professionals may consider suggesting tart cherry juice for heart health.
A Animal Study published in 2022 in the journal Food Research International found that Pu-erh tea and its ingredient theabrownin improve liver, jejunum, and adipose tissue functions in metabolic syndrome mice, modulating circadian rhythm, glycerophospholipid, and linoleic acid metabolism. In this study, varied technological applications such as metagenomics, transcriptomics, and metabolomics were utilized to explore the anti-metabolic syndrome mechanism of Pu-erh tea and theabrownin in mice with metabolic syndrome. These scientific technologies allowed the researchers to understand and explore improvements in the physiological functions of liver, jejunum, and adipose tissues in the metabolic syndrome mice as a result of Pu-erh tea and theabrownin interventions. The investigation also focused on changes to the hepatic transcriptome, revealing that both of these interventions had the capacity to regulate the circadian rhythm pathway. The results showcased that both interventions succeeded in the modulation of glycerophospholipid and linoleic acid metabolism, this was established through a comprehensive analysis of serum and brain metabolome. Further analysis of faecal metagenome demonstrated an increase in the relative abundance of certain bacterium and a decrease in others due to both interventions. However, in comparison to Pu-erh tea, theabrownin exhibited a more pronounced influence as regards upregulating hepatic antioxidants and downregulating hepatic inflammatory factors, although there was only a slight reduction in obesity-linked short-chain fatty acids in faeces of the metabolic syndrome mice. Overall, the experiment provided essential insights into the various ways these two elements function and provide treatment for metabolic syndrome.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal Mediators of Inflammation found that Drinking pomegranate juice and sumac can help reduce symptoms in outpatients diagnosed with COVID-19, alongside standard treatment. In the applied methodology, two groups were randomly formed from 182 outpatients with COVID-19. The first group had a diet containing pomegranate juice and sumac, in addition to their standard treatment. The second group, the control group, stuck to the standard treatment only. The results from the study show that outpatients with COVID-19 who consumed a diet containing pomegranate juice and sumac, along with their standard treatment, experienced a significant decrease in their symptoms. Such symptoms include fever, chills, coughing, weakness, smell and taste disorders, shortness of breath, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, and abdominal pain. This decrease in symptoms was in comparison to the outpatients with COVID-19 who underwent only the standard treatment. Overall, the consumption of pomegranate juice and sumac has shown to be beneficial in reducing COVID-19 related symptoms.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition found that In women with polycystic ovary syndrome, cinnamon reduced insulin resistance and testosterone levels similar to metformin, and ginger decreased follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones. In the methodology of the study, 100 women diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome were divided into four groups. Each group received a different treatment: cinnamon, ginger, metformin, or placebo. The dosage for these treatments was 500 mg, three times a day, administered over a period of 8 weeks. The participants' sex hormones, weight revelations, along with glycemic and lipid markers were monitored before and after this period. Several participants were disqualified because of unspecified factors, resulting in a final sample size of 83. In terms of results, all groups saw a decrease in weight and body mass index. The metformin and cinnamon groups specifically had notably decreases in their insulin resistance, meaning that these treatments were effective in improving metabolic health. Additionally, the ginger group experienced a reduction in follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone levels unlike the other groups. Testosterone levels were lowered in the metformin and cinnamon groups, but no significant changes in dehydroepiandrosterone were observed in any of the groups. These results indicate the potential use of cinnamon and ginger as alternative treatments in managing polycystic ovary syndrome.
A Experimental Study published in 2022 in the journal Veterinary Sciences found that The type of dairy production system can influence the overall and specific levels of microRNAs, potentially affecting the functional potential of dairy products. The research initially observed levels of microRNAs present in fat and cellular components from tank milk collected from farms using both intensive and extensive dairy production models. They commenced by sequencing microRNAs from three different milk samples from each production method. These selected microRNAs, which showed notable variance in both the fat and cellular content between the two production systems, were then further validated by conducting quantitative PCR on tank milk samples procured from an additional twenty different commercial farms. The team discovered that the differences in the amounts of microRNAs were most significant in the fat portions of the milk. Here, they found that both the overall levels of microRNAs and the levels of specific types were considerably higher in milk from the intensive production system when compared to the extensive system. They also undertook a pathway analysis of the bovine mRNA targets for these specific microRNAs. While the precise reasons for these discrepancies in microRNA levels are yet to be determined, the research strongly indicated that the choice of production system could have a direct impact on both the microRNA content and the potential functionality of dairy and other agri-food products.
A Cohort Study published in 2022 in the journal Metabolites found that Frequent consumption of sugar-sweetened coffee can adversely affect blood sugar control in patients with diabetes mellitus in Korea. This study focused on adult coffee consumption patterns in Korea using data collected from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey between 2008 to 2020. The consuming habits of 5671 diabetic patients were analyzed considering how often they consumed a mixture of coffee with sugar and creamer, referred commonly as 3-in-1 coffee. The methods used involved assessing these patterns through a 24-hour recall. Blood sugar control was evaluated using fasting blood glucose levels and hemoglobin A1c levels, in line with the targets set by the Korean Diabetes Association. The results revealed that nearly half of the diabetic patients in this study consumed sugar-sweetened coffee. These patients demonstrated significantly higher fasting blood glucose and hemoglobin A1c levels compared to those who did not partake in such consumption. The findings also indicated an increased likelihood of patients failing to achieve their blood sugar control targets, corresponding to the frequency of their consumption of sugar-sweetened coffee.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal Nutrients found that Walnut consumption improves mental health indicators and negates some negative effects of academic stress on students' health and gut microbiota, especially in females. In the study, the researchers launched a randomized clinical trial to study the effects of academic stress and daily walnut consumption on undergraduate students' mental health, general health biomarkers, and the gut microbiota. The specific aim was to examine the implications of stress and diet interplay, focusing specifically on the consumption of walnuts due to their previously demonstrated positive impact on mental wellbeing. In analyzing the results, they found that academic stress negatively affected the self-reported mood and overall mental health of the students. However, a daily intake of walnuts appeared to improve the mental health indicators. Notably, it provided a buffer against the adverse effects of academic stress on metabolic and stress biomarkers. Particularly in female students, academic stress was linked to reduced gut microbial diversity, a negative effect which walnut consumption seemed to counteract. The effects on male participants could not be definitively ascertained due to the smaller participant size.
A Experimental Study published in 2022 in the journal Nutrients found that The ethanol extract from green kiwifruit peel enhances sleep duration and onset, proving to be a potential natural aid for treating sleep disorders. The study employed the electroencephalogram (EEG) and electromyogram analysis methodologies in mice to investigate the sleep-promoting effects of the kiwifruit peel extract. Each participant mouse was administered with varying doses (250, 500, and 1000 mg/kg) of green kiwifruit peel ethanol extract (GKPEE) and their sleep duration, latency and onset were consistently observed and recorded. For comparison purposes, results were weighed against similar analyses conducted using diazepam, a traditional sedative-hypnotic drug. In terms of results, the findings indicated that acute administration of GKPEE significantly increased non-rapid eye movement sleep and decreased sleep latency, in a dose-dependent relationship. Moreover, the effects did not alter delta activity, differing significantly from diazepam outcomes. Notably, these effects prevailed even with sub-chronic administration over 15 days, with the EEG power density not revealing any noteworthy differences - an indicator of the absence of a tolerance phenomenon. Additionally, these results suggest an alternative usage of kiwifruit by-products from the food industry, providing possible environmental benefits.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Molecules found that Green tea's catechins demonstrate therapeutic effects against neurodegenerative diseases via anti-inflammatory, antioxidant actions, and activating diverse brain cellular pathways. The research primarily evaluates the effect of polyphenolic compounds found in green tea, known as catechins, on neurodegenerative diseases. By conducting several interventional and observational studies on humans, the research explores the anti-cancer, anti-obesity, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective properties of these compounds. The biological, pharmacological, antioxidant, and metal chelating abilities of catechins, particularly their influence on different cellular pathways within the brain, are intensively studied. The results elucidate that catechins exhibit multiple neuroprotective effects. Their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties help to inhibit excessive production of cytokines, and inflammatory pathways, while also controlling metal ions and free radicals. Researchers have further established that catechins may curb the phosphorylation of the tau protein and aggregation of amyloid beta, both key markers in neurodegenerative diseases. Additionally, these compounds show potential in reducing alpha-synuclein levels and augmenting dopamine levels. Hence, they significantly contribute to the prevention and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, multiple sclerosis, and cognitive deficits.
A Network Pharmacology published in 2022 in the journal Frontiers in Immunology found that Manuka honey exhibits a dual role in immune modulation, triggering a pro-inflammatory response by elevating cytokine expression and neutrophil recruitment via TLR signaling, while also influencing the phenotypic and functional maturation of macrophages. In vitro experiments using RAW 264.7 macrophages demonstrated that 1% Manuka honey significantly upregulated the expression and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and iNOS, as well as chemokines such as CXCL2 and CCL2. In vivo studies with C57BL/6 mice revealed a robust peritoneal response characterized by increased neutrophil recruitment and phenotypic changes in peritoneal macrophages after intraperitoneal administration of Manuka honey. Notably, this response persisted in TLR4-defective mice, suggesting independence from TLR4 and ruling out LPS contamination. However, the dependence on MyD88 protein, a crucial adaptor in TLR signaling, was evident, shedding light on the immunostimulatory properties of Manuka honey and its potential as an immunomodulatory agent in diverse disorders. The study delineates Manuka honey's immunomodulatory actions, showcasing its pro-inflammatory impact through cytokine release and neutrophil recruitment, independent of TLR4 but reliant on MyD88 signaling. Additionally, the observed phenotypic alterations in macrophages underscore the potential utility of Manuka honey as an immunomodulatory agent across various health conditions, offering insights into its complex yet promising role in immune regulation.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Acta Horticulturae found that Chinese jujube contains cAMP, a compound usually absent in plant cells, which may accelerate our understanding of plant cAMP metabolism. The research process involved the separation and measurement of the cAMP compound in Chinese jujube fruit. Various techniques were applied to determine changes in cAMP content throughout fruit development. In addition, the researchers differentiated the cAMP concentration among various cultivars. The findings of the study indicated that cAMP, usually absent in plant cells, is present in the fruits of Chinese jujube. This was determined by identifying subtle variations in the cAMP content during fruit development and across different cultivars. Furthermore, potential adenylate cyclase genes were identified, providing a new perspective to the study of cAMP metabolism in plants.
A Experimental Study published in 2022 in the journal Food Chemistry found that Pu-erh tea, through the increase of Cinnabarinic acid, can improve obesity induced by circadian rhythm disorders by enhancing fat metabolism and altering gut microbes. In this study, a CRD-induced obesity model in mice was developed and Pu-erh tea was used as an intervention. The effect of Pu-erh tea on obesity was observed and determined to come from its production of Cinnabarinic acid (CA). CA was found to promote adipose tissue lipolysis and heat generation response, increasing the sensitivity of fat cells to hormones and neurotransmitters. This was accomplished by targeting the expression of specific receptor proteins in adipose tissue. These processes improved mitochondrial activity in the fat cells and expedited metabolic processes in the adipose tissue, thereby speeding up glucose and fat metabolism. In the final stage of the study, CA was found to make changes in the gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acids which further helped to improve the lipid accumulation mediated by CRD. The researchers concluded that the increase in CA, caused by drinking Pu-erh tea and reaching the fat tissue through blood circulation, could be a crucial mechanism to reduce obesity induced by circadian rhythm disorders.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal Antioxidants found that Pomegranate extract consumption improves antioxidant levels, reduces oxidative stress and cardiovascular risk factors including blood pressure and body fat, and increases lean body mass. In the study, 24 healthy participants were divided into two groups: one consumed a natural standardized pomegranate extract, while the other, a placebo, in a randomized, single-blind placebo-controlled trial. Evaluations were conducted at baseline and post 14 and 28 days of the experiment, with variables including anthropometric measurements, blood pressure, pulse wave speed, body composition, as well as the levels of salivary and urinary cortisol, cortisone, total phenolics, antioxidant capacity, and lipid peroxidation. The results indicated significant increases in urinary total phenolics excretion and antioxidant capacity after 14 and 28 days of pomegranate extract intake. By day 28, notable decreases were noted in systolic and diastolic blood pressure, pulse wave velocity, body fat and fat mass, and an increase in lean body mass. In terms of glucocorticoid levels, there was a marked decrease in saliva cortisol at day 28 in the morning for the pomegranate extract group, along with a decrease in the cortisol/cortisone ratio following 28 days of pomegranate extract intake at morning, noon, and evening. Reductions were also seen in urine free cortisol levels by day 14. These observations were unique to the pomegranate extract group, with no significant changes noted in the placebo group.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Nutrients found that Walnuts, rich in anti-inflammatory ingredients, potentially regulate neuroinflammation, improve cognitive function, reduce oxidative stress, and maintain gut health, thereby suggesting their use against neurodegenerative diseases. The methodology of the research includes a comprehensive review of the existing studies and experiments on walnuts and their active ingredients. These ingredients include large amounts of unsaturated fatty acids, peptides, and phenolic compounds known for their anti-inflammatory effects. Various studies covering the effect of these ingredients on the brain health of both rats and humans were analyzed. Specifically, the regulation of microglia activation induced by substances like amyloid β or lipopolysaccharides, the inhibition of peripheral inflammation led by macrophages, and the effects on oxidative stress and gut microbes were scrutinized. In the discussion of results, the studies presented compelling evidence of the beneficial effects of walnuts and their components on neuroinflammation and potential ways to counteract neurodegeneration. There seems to be a consensus in the experimental investigations that the walnut’s active ingredients can reduce inflammation and oxidative stress while maintaining gut homeostasis. They also show promise in improving cognitive functions and memory in both rats and humans. However, it was noted that the evidence from human clinical studies is not as abundant or conclusive as the experimental work, although the potential of walnut-based functional foods in mitigating neurodegenerative diseases was recognized.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal Menopause found that A diet low in fat, vegan, and inclusive of daily cooked soybeans significantly reduces the frequency and severity of hot flashes in postmenopausal women. The methodology used involved the selection of 84 postmenopausal women who reported at least two moderate-to-severe hot flashes. These women were randomly divided into two cohorts, one prescribed the dietary intervention of a low-fat, vegan diet coupled with daily servings of cooked soybeans and a control group which did not alter their diet. Over a 12-week period, a mobile application was used to track hot flashes in terms of frequency and severity. Further, the participants’ vasomotor, psychosocial, physical, and sexual symptoms were assessed using the Menopause-Specific Quality of Life questionnaire. In some participants, the presence of urinary equol, a compound formed in the gut after consuming soy, was measured following the intake of the specified amount of soybeans for 3 days. In discussing the results, a remarkable decrease was noted in the frequency and severity of hot flashes experienced by the group assigned the dietary intervention versus those in the control group. In addition, after 12 weeks, half of the participants adhering to the vegan diet and daily soy intake reported complete cessation of moderate-to-severe hot flashes. Furthermore, notable decreases were reported in the intervention group in menopause-specific quality of life domains including vasomotor, physical, and sexual. Neither the season nor the participant's ability to produce equol played a notable role in these improvements.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal Nutrients found that Two gold kiwifruit daily are as effective as fiber-matched psyllium in treating constipation in adults and should be considered as a treatment option. This study provided evidence that habitual consumption of two gold kiwifruit daily, a realistic standard serving of fruit, is at least as effective as fiber-matched psyllium in lieu of placebo in treating constipation in adults, with fewer side effects, and offers greater ease of defecation through the improvement of stool consistency and reduction of straining.
A Systematic Review published in 2022 in the journal Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology found that Kiwifruit and kiwifruit extracts may have a positive impact on constipation in adults by increasing weekly bowel movements, reducing abdominal pain, and minimizing straining. Kiwifruit and kiwifruit extracts show promise in increasing weekly bowel movements and reducing abdominal pain and straining in adults with constipation, although the overall evidence is of low certainty. However, kiwifruit may lead to minor adverse effects, such as bloating and flatulence, compared to placebo, indicating potential for its use as a dietary supplement in constipation management, especially in conjunction with other laxatives if necessary, but further research is needed to establish its effectiveness.
A Systematic Review published in 2022 in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition found that Meta-analysis indicates that fruit consumption, particularly kiwifruits, effectively alleviates constipation symptoms, offering valuable insights into improving gut health. A meta-analysis of 11 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) examined the effects of fruit consumption on patients with functional constipation. The analysis revealed that fruit consumption, particularly kiwifruits, significantly increased stool frequency, improved stool consistency, and positively impacted microbiota composition, suggesting a potential dietary approach for managing constipation symptoms.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that A daily intake of 50 grams of prunes can maintain hip bone density in postmenopausal women, potentially reducing hip fracture risks. This research was conducted through a single-center, parallel-arm, randomized controlled trial over the course of a year. Postmenopausal women were randomly assigned into three groups - control, 50 grams of prunes, and 100 grams of prunes - and their bone mineral density (BMD) was assessed every 6 months. Secondary measurements included an observation of changes in bone biomarkers. Compliance and retention of participants were high particularly at the 50-gram dosage. In assessing the effects of prunes on bone health, the findings showed a distinct interaction between the amount of prune intake and bone mineral density in the hip region. Specifically, it indicated that consumption of 50 grams of prunes daily led to a preservation of hip BMD after 6 months, an effect which was still apparent after a year. Despite a higher dropout rate and less impact on BMD, the 100-gram prune group, when combined with the 50-gram group, presented stability in the FRAX score, which measures the risk of hip fractures.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal Heliyon found that The combined use of chamomile and saffron with usual medication enhances the efficacy against depression and ensures long term improvement. This research was a randomized, open, blinded trial with 120 participants split evenly into a test and control group. After consent was obtained, a patient health questionnaire was filled out to determine depression scores. Participants in the test group received herbal tea sachets, containing 20 mg of chamomile and 1 mg of saffron, twice per day for a month in addition to their regular medications. Control group participants only received their standard allopathic medicine. Blood samples were taken both before and after the treatment period. The test showed significant improvement in depressive symptoms for both groups. However, in the test group, the addition of the herbal teas amplified the effect of the medications. The herbal adjuvant therapy reduced inflammatory markers and tryptophan levels in plasma, which increased the availability of tryptophan in the brain, a key aspect in managing depression. Consequently, the research concluded that inclusion of these herbs enhances the effectiveness of the conventional treatment against depression and provides long term benefits.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine found that Consuming 2-3 cups of coffee daily can help prevent cardiovascular disease and drinking at least 3 cups of green tea has similar benefits. In this review, researchers examined the effects of habitual coffee and tea consumption on cardiovascular disease (CVD) prevention. Specifically, they studied the association between 2-3 cups of coffee or tea consumed daily and their beneficial effects on metabolic syndrome, including hypertension and diabetes mellitus, focusing on how these popularly consumed beverages might affect lipid levels. The analysis of findings drew a correlation between moderate coffee intake and a reduced risk of several cardiovascular conditions, such as coronary heart disease, heart failure, arrhythmia, stroke, and CVD, in addition to lowering mortality from all causes. It was also noted that the benefits extended to higher tea consumption as well, particularly in the case of green tea, where it led to improved survival rates in population-based studies.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Melatonin Research found that Recent revelations of L-DOPA, dopamine, 5-hydroxytryptophan, tryptamine, serotonin, N-acetylserotonin, melatonin, 2-hydroxymelatonin, AFMK, AMK, and vitamin D3 derivatives in honey expand its health benefits. The identification of L-DOPA, dopamine, 5-hydroxytryptophan, tryptamine, serotonin, N-acetylserotonin, melatonin, 2-hydroxymelatonin, AFMK, AMK, and vitamin D3 derivatives in honey aligns with their presence in insects and plants. Serotonin and melatonin, integral to tryptophan metabolism, serve diverse roles as hormones, neurotransmitters, and antioxidants. Dopamine and tryptamine, essential neurotransmitters, have broad significance across species. The detection of these molecules in honey, a widely consumed health-promoting substance, enhances its beneficial effects on human health. The findings highlight the multifaceted composition of honey, encompassing compounds with recognized roles in neurotransmission, antioxidant activity, and hormonal regulation. The presence of these molecules not only broadens honey's spectrum of health benefits for humans but also implies their significance in the intricate physiology of social insects, influencing bee development and colony functions. The co-detection of these compounds with vitamin D3 derivatives further underscores the interconnectedness of honey with insect and plant biology, shedding light on potential synergies that contribute to the diverse positive effects of honey on human health.
A Experimental Study published in 2022 in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition found that Carotenoid-rich foods like orange carrots were more effective in mitigating Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease than those with low carotenoid levels. In this study, male C57BL/6J mice were randomly assigned to one of four experimental diets for a period of 15 weeks: a low-fat diet, a high-fat diet, a high-fat diet with 20% white carrot powders, or a high-fat diet with 20% orange carrot powders. Observations revealed that those mice on the high-fat diet enriched with carotenoids from the orange carrots gained less weight and displayed less hepatic lipid deposition compared to the white carrot group. Moreover, lower levels of triglyceride content were seen in the orange carrot group. The increase of particular proteins indicated that carotenoids found in orange carrots improved β-oxidation, thereby inhibiting NAFLD development more significantly. Further examination showed noticeably higher mRNA and protein levels of a particular transcription factor.
A Network Pharmacology published in 2022 in the journal Antioxidants found that Kelulut honey, either alone or in combination with metformin or clomiphene, can alleviate oxidative stress and reproductive and metabolic abnormalities in rats with polycystic ovary syndrome. To examine the effects of Kelulut honey (KH), metformin, and clomiphene on polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), female Sprague-Dawley rats were treated with letrozole to stimulate symptoms of PCOS. The rats were then split up into six groups, each group undergoing a different kind of treatment for a period of 35 days, including KH alone, metformin alone, clomiphene alone, KH combined with metformin, and KH combined with clomiphene. The physicochemical characteristics of the honey were assessed using several tests, and its semi-volatile organic compounds were determined via gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. KH and its combinations with either metformin or clomiphene were found to improve the hormonal profile and ease oxidative stress in the rats. However, while the treatments seemed to improve the oestrus cycle, they reportedly did not affect fasting blood glucose, insulin levels, or body weight in the test subjects.
A Systematic Review published in 2022 in the journal Cureus Journal of Medical Science found that Honey is effective in treating coughs in children above 12 months. The researchers undertook a systematic review of literature across five databases, using a Medical Subject Heading strategy, keywords, and defined inclusion and exclusion criteria to identify relevant studies. This review incorporated a range of study types, including systematic reviews, meta-analyses, randomized controlled trials, observational studies and cross-sectional studies. Those articles without a clear methodology section were excluded. The quality of the remaining literature was appraised using a specific checklist. Following the review, it was found that honey is effective in treating coughs in children older than 12 months. Cold and cough medications were also found to be safe, if given at therapeutic doses. However, a note of caution was highlighted for the use of these medications in children under two years, as fatalities have been recorded in some cases; although further studies are recommended to establish a clear safety profile.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal Nutritional Neuroscience found that Consumption of wild blueberries over six months can improve cognitive performance and speed of processing information amongst older adults. The methodology of this research involved conducting a double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial where participants with cognitive issues ascertained by Montreal Cognitive Assessment scores were asked to consume wild blueberry or placebo powder daily for a 6-month period. There was also a separate reference group involved, comprised of individuals devoid of any cognitive issues. These individuals were tested at the commencement and end of the trial using the Cambridge Neurological Test Automated Battery and an electrophysiological paradigm named event-related potentials. The results presented disclosed a significant improvement in the speed of processing information in the group consuming blueberries compared to the placebo group over the 6-month intervention period. Additionally, the speed of this group's processing was re-established to the level of the reference group, revealing the restoration of cognitive abilities. The most distinct enhancement was noted in participants aged between 75-80 years in the blueberry group.
A Systematic Review published in 2022 in the journal Complementary Therapies in Medicine found that Meta-analysis revealed that lavender, particularly L. angustifolia, significantly reduces stress, making it a potentially valuable component in stress management programs. Results found that lavender significantly reduced stress levels, with a decrease in the intervention group compared to the control group. Subgroup analysis revealed that L. angustifolia species, aromatherapy as a delivery method, and student populations showed the most significant stress reduction effects.
A Systematic Review published in 2022 in the journal Advances in Nutrition found that Prunes demonstrate potential as a dietary intervention to protect against, prevent and even reverse bone loss in osteoporosis, particularly in postmenopausal women. Using sixteen preclinical trials with in vivo rodent models of osteopenia or osteoporosis, researchers investigated the effect of dietary supplementation with prunes. The research shows prunes' osteoprotective capabilities, preventing, reversing bone loss, and exerting anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. The prunes or their polyphenol extracts showed properties that decreased malondialdehyde and NO secretion and increased antioxidant enzyme expression. Two clinical trials further investigated prune consumption (50-100 g/d for 6-12 months) on bone health in postmenopausal women. The results of the studies revealed the promising outcome of improved bone mineral density and bone biomarker due to the consumption of dried plums. However, the effect of prunes on oxidative stress and inflammatory mediators remains less understood. The study hence emphasizes the need to investigate prunes' role in modulating the inflammatory and immune pathways related to bone health.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy found that Pomegranate extract and its phytochemicals can potentially inhibit severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-COV-2) and improve gut microbiota, preventing obesity and diabetes. The study employs the use of in silico molecular docking methodologies to demonstrate that extract from pomegranates and their phytochemicals can serve as inhibitors of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2's spike protein and the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptor contact. These findings are further reinforced by clinical trials which suggest that pomegranates can also alleviate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, metabolic syndrome, dental infections, and symptoms of menopause. This study has also identified numerous active compounds within pomegranates such as alkaloids, anthocyanidins, tannins, flavonoids, phenolics, proanthocyanidins, sterols, terpenes, terpenoids, xanthonoids, fatty acids, organic acids, lignans, saccharides, and vitamin C. This mixture of active compounds is believed to significantly contribute to the broad array of pharmacological activities identified within the pomegranate. This includes anti-diabetic, anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, anti-malaria, anti-fibrotic, anti-fungal, and anti-bacterial effects. The extract from this fruit improves gut microbiota which could potentially aid in the prevention of obesity and diabetes.
A Experimental Study published in 2022 in the journal Morphologie found that Pomegranate juice extract may reduce the damage to the endometrium in Polycystic ovary syndrome through its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and anti-proliferative effects. To test the possible benefits of pomegranate juice extract (PJE) on endometrial injury in Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), forty adult albino rats were divided into four groups, control, PJE-treated, letrozole-treated (PCOS), and PJE & PCOS groups. The respective treatments were administered for a duration of three weeks. Serum and tissue samples were assayed for Follicle-stimulating hormone, Luteinizing hormone, testosterone, estradiol, and malondialdehyde. Uterine samples were also tested using a range of histological staining techniques and a scanning electron microscope. In the rat model of PCOS, significant increases in certain biochemical indicators in serum samples were observed while uterine sections showed numerous alterations to the endometrium, signs of inflammation and an increase in the endometrial collagen fiber content. Additionally, there was increased expression of certain immunohistochemical staining markers and a decrease in the mean number of pinopodes observed through scanning electron microscopy. However, these various potentially harmful biochemical, histological and immunohistochemical alterations were efficiently reduced with the administration of PJE. This points towards the potential benefits of PJE in addressing and potentially reducing endometrial injury associated with PCOS.
A Experimental Study published in 2022 in the journal Journal of Food Science and Technology found that Using grape seed oil in the sardine canning process enhances the lipid nutritional quality and increases the fat, protein, and ash contents. The researchers employed grape seed oil (GSO) in the canning process of sardines, comparing its effects on the nutritional quality of the canned fish to that of the traditional olive oil (OO). The assessment focused on the quantities of polyphenols, flavonoids, and non flavonoids present in both the GSO and OO, while also considering the levels of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) specifically linoleic acid in the GSO. The fat, protein, and ash content in the canned sardines were also tracked over a period of 90 days. In the results discussion, it was observed that GSO contained significantly higher levels of polyphenols, flavonoids, and non flavonoids than OO. Additionally, GSO was rich in PUFA, particularly linoleic acid. Following the canning process, canned sardines preserved using GSO demonstrated a significant increase in protein, fat, and ash content. Notably, the use of both GSO and OO resulted in a decrease in both atherogenic and thrombogenic indices to less than 1, implying improved lipid nutritional quality. Critically, levels of thiobarbituric acid and Total volatile base nitrogen remained below critical limits.
A Experimental Study published in 2022 in the journal BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies found that Chrysanthemum extract has protective effects on light-damaged retinas, reducing oxidative stress and improving cellular viability. The experiment incorporated both in-vitro and in-vivo tests. In the lab, ARPE-19 cells were divided into four groups (control, light-damaged, low-dose extract, high-dose extract), treated with varying levels of chrysanthemum extract, and then exposed to light. Cellular viability and reactive oxygen species production were then observed. A similar grouping approach was used with C57BL/6J mice, where chrysanthemum extract concentration was administered before light exposure. The retinas were evaluated for function, morphology, and apoptosis post-exposure. Light-damage caused a decrease in cellular viability and an increase in reactive oxygen species production. However, treatment with chrysanthemum extract showed improvement in viability and reduction in reactive oxygen species. In mice, light damage caused dysfunction in the retinas, destruction of morphology and increased apoptosis, particularly in the retinal pigment epithelium and photoreceptor layer. Again, chrysanthemum extract treatment improved retinal function, maintained retinal structures, and reduced apoptosis. The extract achieved this by increasing concentration of anti-oxidative enzymes.
A Experimental Study published in 2022 in the journal Frontiers in Pharmacology found that Oral administration of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharides may constitute a new, effective therapy for Atopic dermatitis, improving both immune response and intestinal microbiota. In the methodology of this study, the therapeutic effects of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharides (these have multiple biological activities), on Atopic dermatitis, were examined through both topical application and oral administration on mice induced with Atopic dermatitis-like disorder. The changes across transdermal water loss, epidermal thickening, and ear edema in the affected mice were observed. Notably, the study also considered the polysaccharides' impacts on the proportion of specific regulatory T cells in the mesenteric lymph nodes of the mice. The results showed that both therapeutic methods positively impacted the conditions of the affected mice, with oral administration offering superior efficacy over topical application. The oral administration of the polysaccharides led to an increase of specific regulatory T cells, evidence of immune regulation. Further, non-targeted metabolomics and sequencing of certain DNA amplicons pointed towards observable modulation in fecal metabolites and a changed composition of gut microbiota in the mice following the oral treatment.
A Systematic Review published in 2022 in the journal Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology found that Aromatherapy, specifically lavender, appears to be an effective, affordable, and holistic approach to reducing the length of labour in expectant women. The research executed a systematic review of clinical trial studies regarding the use of aromatherapy in labour augmentation, sourced from diverse databases including Cochrane, Scopus, Web of Science, PubMed, ProQuest, Google scholar, Irandoc, Science direct, Magiran and Sid up until September 2021. 22 articles meeting the inclusion criteria were examined, with the reported experiences of 3234 women who employed a variety of aromatherapies forming the analysis base. In discussing the results, it was observed that certain aromatherapies notably lavender, showed efficacy in decreasing labour time for women. However, the paper emphasized the importance of prudent use of aromatherapy, most probably owing to the varying individual responses and potential for allergic reactions to such holistic interventions.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Molecules found that Depression, a prevalent and debilitating disorder, necessitates novel treatments beyond conventional drugs. Stingless bee honey, rich in antioxidants, emerges as a potential antidepressant candidate, explored comprehensively through monoamine, inflammatory, and neurotrophin hypotheses. This comprehensive review delves into the urgent need for safer and more effective depression treatments, considering the limitations of conventional drugs. The focus is on Stingless Bee Honey (SBH), recognized for its high antioxidant content, and its potential as an antidepressant is explored through the lenses of the monoamine, inflammatory, and neurotrophin hypotheses. Stingless bee honey's potential as an antidepressant is examined in the context of its antioxidant richness, offering a new avenue for addressing depression beyond conventional drug approaches. The review highlights the importance of exploring alternative medicines, such as SBH, for safer and more efficacious depression treatments.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal Journal of Asian Multicultural Research for Medical and Health Science Study found that Honey, combined with Iron (Fe), effectively enhances hemoglobin levels and reduces oxidative stress markers in anemic expectant mothers. This quasi-experimental study with a pretest-posttest design involved 30 pregnant women divided into two groups: one receiving Fe (Control Group) and the other Honey + Fe (Intervention Group) for 60 days. Blood and urine analyses revealed a remarkable increase in hemoglobin levels in the Honey + Fe group (2.80 ± 0.26 g/dl), surpassing the Fe control group (0.80 ± 0.13 g/dl). Moreover, the Intervention Group demonstrated a notable decrease in 8-Ohdg levels (-4.23 ± 1.32 nmol/ml, p = 0.031), indicating reduced oxidative stress, while the Fe control group exhibited less significant changes (2.98 ± 1.30 nmol/ml, p = 0.322). Independent T Test confirmed the Honey + Fe group's superior effectiveness in increasing hemoglobin levels and decreasing 8-Ohdg levels in anemic pregnant women (p = 0.001 and p = 0.002, respectively). The study underscores the synergistic benefits of honey and iron supplementation in enhancing hemoglobin levels and mitigating oxidative stress among anemic pregnant women. The robust findings, supported by statistical significance, emphasize the potential clinical relevance of incorporating honey into anemia management strategies, offering a more effective approach compared to iron supplementation alone.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Applied Sciences found that Honey, owing to its bioactive compounds, demonstrates potential in treating COVID-19 symptoms by reducing oxidative damage and enhancing the immune system. The review outlines the SARS-CoV-2 virus's mechanisms of action, which is responsible for COVID-19, offering a comprehensive understanding. It also explores the various bioactive assets honey has at its disposal, primarily focusing on its beneficial properties. The discussion elaborates on the potentials of honey's biological properties, especially its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. These characteristics of honey, as suggested by the review, could contribute to the relief of oxidative damage and boost the immune system, thereby proving beneficial in combating viral infections, including COVID-19.
A Meta-Analysis published in 2022 in the journal Nutrition Research found that Green tea supplementation can significantly reduce body weight in women with polycystic ovary syndrome, hence potentially beneficial in its clinical management. The research carried out was a systematic review of randomized controlled trials that focused on women with polycystic ovary syndrome, examining the effects of green tea supplementation versus a placebo. Relevant studies were sourced from electronic databases such as MEDLINE via PubMed, EMBASE via Elsevier, Cochrane Library, LILACS via BVS, and Web of Science using specific terms related to the illness and green tea. Criteria for the evaluation included effects on body weight, fasting insulin, body mass index, body fat percentage, daily caloric intake, waist and hip circumference, and the waist/hip ratio. Among the studies considered, there were a total of 169 women, with 85 allocated to the green tea group and 84 to the placebo group. It became apparent that there was a significant reduction in body weight for the group that received green tea supplementation. This leans towards the potential of green tea to be beneficial in the management of this syndrome.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal Explore: The Journal of Science & Healing found that Inhalation and massage therapy with lavender essential oil significantly mitigates perceived labour pain in women. The study was implemented using a random controlled trial on pregnant women divided into three groups – a control group, a group for lavender essence inhalation and a third group for lavender essence massage. After being divided into their respective groups, the first stage of labour was divided into three phases – early, active and transition – during which the interventions were applied. In the massage group, sacral compression and lower back massage were given, incorporating 2 drops of lavender oil in each labour phase. For the inhalation group, 2 drops of lavender oil were dripped onto the palms of the participants, who were then asked to inhale it for 3 minutes. Individual information was gathered through formats like the Personal Information Form, Visual Analogue Scale and Postpartum Assessment of Women Survey. The results showed that women who underwent inhalation and massage therapies with lavender essential oil experienced less severe labour pain as compared to the control group. It was also discovered that the lavender oil inhalation was notably beneficial during the latent phase of labour whilst massage therapy demonstrated greater effectiveness during the active and transition periods. Therefore, incorporating lavender oil via massage therapy and inhalation methods during labour and delivery is highly recommended as a supplementary method to manage labour pain.
A published in 2022 in the journal Foods found that Bananas and plantains contain compounds with anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, and antioxidative properties that hold promise for potentially reversing neurological disorders. The methodology of the study revolved around scrutinizing the bioactive properties found in bananas and plantains. Researchers pinpointed various neuroprotective mechanisms within commonly consumed fruits, specifically bananas and plantains. The study examined protein expression regulation and targeted specific gene pathways, including nuclear and tumor necrosis factors, extracellular signal-regulated and mitogen-activated protein kinases, activator protein-1, and the glial fibrillary acidic protein. In their investigations, they also considered the underutilized peel components of these fruits. The results suggest that the multitude of bioactive compounds found in both the pulp and peels of bananas and plantains perform a variety of beneficial neuroprotective activities. These range from acting as antioxidants, preventing cell death (anti-apoptotic), and reducing inflammation (anti-inflammatory), to directly influencing the functionality of the nervous system (neuromodulatory). This discovery implicates plant-based foods, specifically bananas and plantains, as potentially significant substances in combating, halting, or mitigating the pathological mechanisms underlying neurodegenerative disorders.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal Journal of the American Heart Association found that Despite previous suggestions, daily avocado consumption for six months did not decrease visceral adipose tissue volume in individuals with elevated waist circumference. The HAT Trial was a multicenter, randomized, controlled study designed to observe the effects of consuming one large avocado per day for six months on free-living individuals with an increased waist circumference. The primary measure of effect was the change in visceral adipose tissue volume, which was measured through magnetic resonance imaging. Other conditions related risk factors associated with cardiometabolic disorders were surveyed as secondary and additional endpoints. In results analysis, there was no significant alteration in visceral adipose tissue volume between the Avocado Supplemented and Habitual Diet Groups. No noteworthy differences were noticed in the secondary outcomes including hepatic fat fraction and certain components of the metabolic syndrome. Of the extra outcome measures, small but significant reductions were seen in total and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in the Avocado Supplemented compared to the Habitual Diet Group. Changes in body weight, body mass index, insulin concentration and other measured factors were very similar between both groups, showing no considerable change due to avocado consumption.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal Nutrients found that Soybean lettuce extract effectively reduces symptoms of menopause syndrome without notable side effects. The study targeted adult women suffering from menopausal syndrome with a Kupperman index of 15 or more. Participants were split into two groups – the experimental group and the placebo group. The research spanned over a four-week period and embraced a total of 39 participants (with one dropping out). Measurements of body mass index, waist circumference, and several cholesterol levels were taken before and after the study, but these didn't show any significant changes. In the results discussion, the most notable finding was a significant reduction in the Kupperman index in the experimental group. They were given the natural nitric oxide-containing soybean lettuce extract. This decrease denotes the alleviation of menopausal symptoms, offering an effective, natural alternative to hormone therapy. Conversely, the placebo group didn't show any substantial change, reinforcing the efficacy of the soybean lettuce extract.
A Experimental Study published in 2022 in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition found that Goji berry supplementation can potentially improve gut microbiota and prevent liver injury caused by acute alcohol consumption. In this study, the effects of Goji berry supplementation on liver injury induced by acute alcohol intake were examined. Over a 14-day period, the changes in liver enzyme levels, pro-inflammatory cytokine levels, and lipopolysaccharide content in the liver tissue were observed. In addition, the integrity of the epithelial barrier and levels of butyric acid in the cecum were also evaluated. The direct relationship between gut microbiota modifications and liver protective effects was mainly established via antibiotic treatments and fecal microbiota transplantation experiments. The results revealed that Goji supplementation helped maintain liver health by lowering liver injury indicators, maintaining the epithelial barrier's integrity, and increasing the butyric acid levels in the cecum content. The same types of effects were observed for Goji and fecal microbiota transplantation treatments. These maneuvers increased the glutathione levels in the liver and selectively promoted the growth of certain gut bacteria. The metabolite analysis showed that Goji berries and its trained microbiota were able to regulate specific metabolic compounds, shedding light on the interplay between Goji, gut microbiota, and liver homeostasis.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal Nutrients found that Both whole blueberries and freeze-dried blueberry powder significantly enhanced plasma nitrite levels, a marker of cardiovascular health, but did not significantly affect other cardiovascular risk factors. In this study, a cross-over randomised controlled trial was carried out with three groups: one consuming fresh blueberries, one consuming freeze-dried blueberry powder, and one as the control group. All participated in 1 week of treatment, with a 1-week wash-out period between treatments. The study involved the measurement of systolic and diastolic blood pressure, pulse wave velocity, plasma cholesterol levels (low-density and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and total cholesterol), triglyceride levels, and glucose and nitrite concentrations. The results indicated an improvement of plasma nitrite levels following both whole blueberry and blueberry powder supplementations compared to their baselines, hinting at potential benefits to cardiovascular health. However, no other significant effects were observed for blood pressure, total cholesterol, low-density and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, or glucose. Also, none of the changes in individual treatment arms were significantly different from the control. Essentially, the form of blueberry consumed, whether whole or in powder form, did not show any unique advantage in improving cardiovascular health factors.
A Cohort Study published in 2022 in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition found that Moderate consumption of carrots is associated with a lower incidence of colorectal cancer, implying a potential cancer prevention effect in a certain dose-range. The research analysed the dietary intake of carrots/carotene and their relationship to colorectal cancer incidence and mortality in a cohort from the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian Cancer Screening. The study involved 101,680 participants who joined the cohort between November 1993 and July 2001. The hazard ratios were estimated through multivariable Cox regression analyses. Additionally, subgroup analyses and interaction tests were conducted to check for potential effect modifiers. A generalised additive model was used to examine the non-linear trend of the exposure to cancer-related outcomes. In total, the study documented 1,100 colorectal cancer cases and 443 cancer-related deaths. It was discovered that dietary carrot intake was linked to a 21% lower risk of colorectal cancer incidence for those in the 4th quintile group compared to the lowest quintile group. Increase in carrot intakes, on a per standard deviation, did not reveal any statistically significant associations with the disease incidence. There were no significant associations found between dietary α-, and β-carotene intake and colorectal cancer incidence, nor were there any associations between carrot/carotene intakes and cancer mortality. They also observed no non-linear dose-response relationships between dietary carrot, α-, and β-carotene intake and colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Notably, the study found that smoking status could potentially modify the association of dietary carrot intake with incidence of colorectal cancer, but not mortality.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal CyTA - Journal of Food found that Avocado honey, rich in bioactive compounds, can serve as a natural sweetener without negatively impacting anthropometric and biochemical parameters. In this study, the researchers assessed the impact of consuming 25 grams of avocado honey daily for a period of four weeks on a group of 13 healthy individuals aged between 25 and 50 years, with Body Mass Indexes less than 25 kg/m2. The participants were divided into two groups, one acting as a control and the other as the honey consumption group. Despite the dietary addition of avocado honey, there were no significant deviations in the subjects' Body Mass Index and body fat percentage. Furthermore, it didn't affect biochemical parameters including fasting blood glucose, triglycerides, total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Consequently, avocado honey may be considered an effective functional food or natural sweetener.
A Animal Study published in 2022 in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition found that Cooked adzuki beans contribute notably to preventing obesity and regulating gut microbiota composition, while also alleviating systemic inflammation and metabolic disorders. The methodology involved a controlled experiment where mice were fed diets of varying lipid content: a low-fat diet or a high-fat diet. The specific twist in this experiment was the inclusion or exclusion of cooked adzuki beans to their diet, ensuring 15% of the diet comprised of this. The duration of this dietary regimen was 12 weeks. In the discussion of results, it was discovered that cooked adzuki beans provided key beneficial effects. This included a significant inhibition of weight gain and hepatic steatosis, a reduction in high levels of specific markers such as serum triacylglycerol, alanine aminotransferase, and aspartate aminotransferase, providing a counter to systemic inflammation and metabolism-related endotoxemia commonly found in those consuming a high-fat diet. Moreover, the inclusion of adzuki beans positively affected the gut microbiota composition, reducing fat-inducing bacteria and enriching the gut with beneficial bacteria to help alleviate inflammation and metabolic disorders associated with high-fat diets.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that Cocoa extract supplementation in older adults reduced cardiovascular disease related death rates, but did not significantly lessen total cardiovascular events. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial was conducted on 21,442 US adults aged 60 or over, all of who were free of major cardiovascular disease and recently diagnosed cancer. The participants were assigned to either a cocoa extract supplement, which included 500 mg flavanols per day, or a placebo. The intervention phase ran from June 2015 to December 2020. The primary outcome was focused on the number of total cardiovascular events, including myocardial infarction, stroke, and cardiovascular death among others. The results showed that during a median follow-up of 3.6 years, there were 410 participants taking cocoa extract and 456 under placebo who had confirmed total cardiovascular events. Secondary endpoints showed reduced death due to cardiovascular disease for the cocoa extract supplement users. However, there was no significant impact on the incidence of total cardiovascular events. Conversely, a lower risk of total cardiovascular events was supported when analyses were censored at nonadherence. Overall, no safety concerns were raised during the trial.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Applied Food Research found that Saffron plant's various parts contain bioactive compounds that, when extracted using innovative techniques, show significant potential for use in food, nutraceutical and drug formulations. The methodology applied in this research involved the qualitative and quantitative analysis of the bioactive components within the saffron plant, with particular focus on apocarotenoids, anthocyanins, flavonoids, and phenolic compounds. Advanced extraction techniques were employed for increased yield and purity, notably supercritical fluid extraction, microwave assisted extraction, pulsed electric field, and high hydrostatic pressure extraction. These methods lead to a broad range of bioactives predomniantly from the plant's stigma. The findings indicated that all parts of the saffron plant were rich in bioactive compounds. The extracted bioactive compounds presented increased stability, bioavailability, and target delivery when examined via several encapsulation techniques. Beyond this, the extraction has allowed for investigation into the food and pharmaceutical applications of these bioactive components from the saffron plant. However, the utilization of these bioactive components, specifically from saffron floral biomass like petals and corm parts, using techniques such as supercritical fluid extraction, pulsed electric field, and emulsion liquid membrane extraction has not been thoroughly investigated.
A Systematic Review published in 2022 in the journal International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health found that Dietary strategies, such as caloric restriction and ketogenic diets, can alleviate chronic pain and enhance quality of life. This systematic review selected 16 articles from various databases including PubMed, Web of Sciences, ProQuest, and Scopus that were published within the last 6 years. These consisted of randomized clinical trials (RCTs), observational studies, and systematic reviews evaluating the effectiveness of different dietary strategies in the treatment of chronic pain. A range of assessment scales—PEDro, PVI, QUALSYT and the Quality Assessment Tool of Systematic Reviews scale— were utilized to gauge the risk of bias in these studies. The findings indicate an inconclusive consensus on the impact of an intermittent fasting (IF) diet on pain improvement. However, a caloric restriction diet emerged as a potential long-term treatment option for pain. Additionally, time-restricted food and ketogenic diets showed promising results in improving life quality in chronic conditions. Despite some studies indicating opposite results, the majority of the selected articles exhibited good methodological quality on their respective assessment scales.
A Systematic Review published in 2022 in the journal Acta Neurologica Belgica found that Higher daily tea consumption, especially green tea, is linked to a lower risk of cerebral hemorrhage in adults. This meta-analysis uncovered evidence of a connection between tea consumption and cerebral hemorrhage risk, exploring databases including Web of Science, PubMed, Embase, and Scopus until December 2021. The synthesis utilized relative risks or odds ratios from observational studies. The pool of data included ten studies involving over 721,827 participants. The evaluation revealed that a higher rate of tea consumption, and more specifically green tea, was significantly related to a lower risk of cerebral hemorrhage. Interestingly, this connection could be observed even when adjusted for key lifestyle factors such as alcohol consumption, fruit and vegetable intake, and physical activity. It is worth noting that the intake of tea on a daily basis demonstrated a protective effect against the risk of cerebral hemorrhage.
A Animal Study published in 2022 in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition found that Certain natural mineral waters, when combined with a low-calorie diet, effectively reduce cholesterol and glucose levels in mice with metabolic syndrome. The study involved 125 male and female C57BL/6 mice. Ten mice were kept as a healthy control group, fed a standard diet with tap water. The remaining 115 mice were fed a high-calorie diet (60% fat, 10% fructose in water) for four months to induce metabolic syndrome, followed by a two-month treatment phase with a low-calorie diet and various types of natural mineral water (NMW). The mice were divided into six treatment groups, each receiving a different NMW, and a control group receiving tap water. The study monitored body weight and blood biochemistry over six months. After four months on a high-calorie diet, both male and female mice developed obesity, high cholesterol, and high blood sugar, with males showing greater increases. During the treatment phase, NMWs rich in sulphate, magnesium, bicarbonate, and minimally mineralized water, along with a low-calorie diet, significantly lowered total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and glucose levels. Sex differences were observed during both the induction and treatment phases. These findings indicate that specific NMWs, in conjunction with a low-calorie diet, may help manage blood lipid and glucose levels in metabolic syndrome, although further research is needed to confirm these results in humans.
A Animal Study published in 2022 in the journal Applied Sciences found that Fermented gold kiwi extract exhibits antioxidant properties, providing protection to the stomach lining and reducing inflammation, making it promising for treating gastritis and gastric ulcers. The researchers created a fermented powder from golden kiwi fruits, a process that enhances the fruit's bioactive compounds including organic acids, flavonoids, and carotenoids. They then studied its effects using animal models, specifically two rat models; one induced with gastritis via HCl/EtOH and the other with pyloric ligation. The goal was to examine the fermented gold kiwi's (FGK) antioxidative activity, appearing in a dose-dependent manner. The obtained results demonstrated the protective effects of FGK in both animal models. The fermented kiwi notably suppressed inflammation biomarkers such as iNOS, COX-2, IL-6, and TNF-α, which are commonly associated with gastritis and gastric ulcers. It also increased the expression of PGE2, a molecule that protects the tissues. FGK was found to not only improve the appearance of the gastric lesion site but also enhance clinical symptoms and mucosal thickness. In the pyloric ligation model, it reduced gastric fluid volume, total acidity, free acidity, and pepsin activity, thereby showcasing overall gastric protective abilities.
A Experimental Study published in 2022 in the journal Antioxidants found that Berries, largely due to their phenolic compounds, enhance internal antioxidant status and positively influence gut microbiota composition, promoting beneficial bacteria and suppressing harmful types. The study compared the antioxidant capacities and gut microbiota modulatory effects of nine popular berries: blackberry, black goji berry, blueberry, mulberry, red Chinese bayberry, raspberry, red goji berry, strawberry, and white Chinese bayberry. The anthocyanin profiles of each berry were identified using Ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) coupled with Triple TOF/MS. The antioxidant capacities were evaluated through four chemical assays (DPPH, ABTS, FRAP, and ORAC). Healthy mice were treated with different berry extracts for two weeks as a means of investigating in vivo antioxidant capacity and gut microbiota modulatory effects. In terms of the results, it was observed that majority of the berries improved the internal antioxidant status, indicated by elevated serum or colonic Total Antioxidant Capacity (T-AOC), Glutathione (GSH), Total Superoxide Dismutase (T-SOD), Catalase (CAT), and Glutathione Peroxidase (GSH-PX) levels, along with a decrease in Malondialdehyde (MDA) content. All berries studied notably altered the gut microbiota composition, with most leading to the enrichment of beneficial Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)-producing bacteria and the curbing of potentially harmful bacterial types.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Molecules found that Cherries and blueberries, rich in phenolic compounds, can be effectively used in pharmaceutical products, smart foods, functional beverages, and nutraceuticals to prevent or treat diseases. The research primarily studied the health-promoting potential of cherries and blueberries, given their high nutritional density and substantial phenolic compounds. The focus was on their ability to counteract oxidative stress markers and suppress pro-inflammatory responses, which are significant factors in chronic diseases such as diabetes. The researchers analyzed these fruits for their potential incorporation into various products such as pharmaceutical preparations, smart foods, functional beverages, and nutraceuticals. In the discussion of the results, it was emphasized how cherries and blueberries exhibit significant biological potential. They were not only seen as effective in combatting oxidative stress and inflammation but also as potential immune boosters. The conclusions underscored the fruits' potential role as functional foods and their relevance to the burgeoning popularity of functional beverages, hinting at their promise for inclusion in a variety of health-related products.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal NSNZ 2021 found that Consuming New Zealand green kiwifruit improves sleep quality, mood, and increases the concentration of serotonin metabolites. A total of 24 men, ranging in age and with varying sleep quality were selected for the study, in a single-blind crossover design, which was randomized. Participants were provided three treatments on separate occasions, each differing by 6-8 days: consumption of two fresh kiwifruits, ingesting green kiwifruit powder mixed with water equivalent to two fresh kiwifruits, or a simple water control. Poor sleepers noted that they woke up more easily after consuming dried kiwifruit, with a similar but less pronounced trend observed when they consumed fresh kiwifruit. Conversely, good sleepers showed a trend towards better sleep initiation with fresh kiwifruit, but not with the dried kiwifruit. Independent of the participants' sleep quality, both fresh and dried kiwifruit largely improved mood and self-esteem. Consumption of dried kiwifruit significantly elevated morning alertness, post-wakening behaviour, and vigour. Both forms of kiwifruit ingestion led to higher urinary concentrations of the serotonin metabolite known as 5-HIAA.
A Systematic Review published in 2022 in the journal Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity found that Ginger, native to Southeast Asia, possesses antioxidant and antiviral properties, contributing to healthy ageing and potential prevention of age-related disorders. The study explored the natural benefits of ginger, a plant native to Southeast Asia renowned for its culinary and medicinal uses. The approach focused on examining the plant's antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antimicrobial, and particularly antiviral properties from its rich collection of antiviral compounds. The process involved digging into accumulated evidence that suggests ginger's role in promoting healthy ageing, reducing morbidity, and prolonging a healthy lifespan, thus providing a natural solution for an age-old problem. In terms of results, the examination of evidence proved affirming. Ginger displayed significant potential in boosting healthy ageing, reducing the risk of age-related disorders, and extending a wholesome life expectancy due to its inherent properties. The plant's antioxidant characteristics played a key role in these outcomes, along with its anti-inflammatory and antiviral attributes. In essence, the research unfolded a rather underexplored potential of a common natural product in tackling age-induced health conditions.
A Animal Study published in 2022 in the journal Foods found that Pu-erh tea has been validated to have significant anti-oxidative effects, reducing serum MDA levels and increasing serum SOD and GSH-Px levels. The methodology used in this study involved a systematic literature review and meta-analysis to explore the anti-oxidative effects of pu-erh tea. Seven databases were meticulously searched up to the date of 21 February 2020, using the specific keywords 'pu-erh' in combination with 'superoxide dismutase', 'glutathione peroxidase', or 'malondialdehyde'. The results from the meta-analysis demonstrated significant effects of pu-erh tea on anti-oxidation. It was found to reduce serum MDA levels whilst simultaneously increasing serum SOD and GSH-Px levels. Through the systematic review and meta-analyses, it was validated that various ingredients in pu-erh tea extracts do indeed have the anti-oxidation effects that have long been part of conventional wisdom, but until now had limited supporting evidence.
A Animal Study published in 2022 in the journal Cytokine found that Walnut seed skin extract demonstrates potential hepato-renal protective effects, inhibiting inflammatory responses, oxidative stress and apoptosis, in kidney-damaged Sprague-Dawley rats. In the methodology, Sprague-Dawley rats in acute kidney injury state were divided into three groups: a healthy control, a group induced with renal ischemia/reperfusion (IR), and another group induced with renal IR and treated with walnut seed skin (WSS) extract. Blood, liver and kidney tissues were collected for serum evaluations of aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, lactate dehydrogenase, urea, and creatinine. Histopathological studies were performed on liver and kidney tissues, and gene markers related to anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, and apoptotic effects were measured. The results showed an improvement in deteriorated serum parameters in rats with renal ischemia pre-treated with WSS extract. Histopathological analysis revealed a protective effect of WSS on kidney and liver tissues. Though gene expression studies yielded diverse results for liver and kidney tissues, the consensus was that WSS had a pronounced protective impact on the liver. It was inferred that WSS's healing potential in renal and hepatic tissues seems to work via inhibiting inflammatory response, oxidative stress, and apoptosis.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Phytomedicine found that Ellagic acid, commonly found in various plant foods, can enhance cancer treatment by boosting the effects of chemotherapy and radiotherapy while reducing their side effects. The presented review compiled in vitro and in vivo experimental evidence of the synergistic effect of Ellagic acid (EA) in cancer therapy from multiple databases including PubMed, Web of Science, and Google Scholar. The focus was on the use of EA in conjunction with conservative treatment methods such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy. The results suggest that EA, a polyphenolic compound found in various plant foods, has the potential to enhance the effectiveness of these treatment methods. It was found to improve treatment outcomes when combined with a low dosage of therapeutic drugs or optimized radiation levels. Additionally, EA appears to have a preventative effect against the adverse reactions normally associated with chemotherapy, possibly due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. This makes it a promising candidate as a drug adjuvant in cancer treatment.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Advances in Nutrition found that Consuming kiwifruit, particularly the green variety, can effectively alleviate upper gastrointestinal symptoms like abdominal discomfort, pain, and indigestion. The research undertook a systematic scoping review of three electronic databases from 1947 until January 2021. The team searched for clinical trials that investigated the effects of either green or gold kiwifruit or their compounds on upper gastrointestinal symptoms. They focused on the studies that had the symptom relief as secondary outcomes in healthy participants or those with functional constipation or irritable bowel syndrome with constipation. The outcomes were analyzed based on the type of measurement tools used; one being the Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale (GSRS) and the others being non-GSRS methods. The analysis unveiled that out of the identified 12 clinical trials, with a total of 661 participants, only five used the GSRS to assess symptom relief. Green kiwifruit showed notable results in reducing abdominal discomfort and pain. Kiwifruit consumption, in general, appeared to diminish indigestion. While the number of studies reporting on symptom relief using a comparable measurement was limited, the evidence for kiwifruit's positive efficacy on gastrointestinal symptom relief remained consistent.
A Experimental Study published in 2022 in the journal Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry found that Pu-erh tea may prevent circadian rhythm disorders by promoting tryptophan metabolism and signaling interactions in the gut-liver-brain axis. Healthy mice were administered water or 0.25% Pu-erh tea over a period of seven weeks, and then subjected to a disruption of their light/dark cycle for forty days. The assessment of effects was based on changes in neurotransmitter secretion and gene oscillations, intestinal inflammation, and the balance of intestinal microbes and metabolites. Results indicated that Pu-erh tea had beneficial impacts in regulating neurotransmitter secretion and clock gene oscillations, especially indole and 5-hydroxytryptamine pathways, a key process involving the gut-liver-brain axis. Moreover, the tea's metabolites improved release of brain hormones, thus enhancing hepatic glycolipid metabolism and lowering intestinal oxidative stress. Further observed beneficial effects included promotion of liver lipid metabolism and reduction of intestinal inflammation, via the enterohepatic circulation.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal The Journal of Sexual Medicine found that Chamomile vaginal gel effectively improved the sexual function of postmenopausal women, and can be a potential treatment option for those unable to undergo hormone therapy. The structured methodology involved a randomized, double-blind clinical trial, where 96 postmenopausal women with known sexual dysfunction were divided equally into three groups. Each group respectively received chamomile vaginal gel, conjugated estrogen vaginal cream, and placebo vaginal gel, for 12 weeks. The frequency of application varied over the course of the weeks. Measurements were made using the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) before and after the intervention. Data analysis implied chi-square, one-way ANOVA, descriptive statistics, and paired t-tests. Despite the study's duration of 12 weeks, no follow-up was done past this time frame. The study also recorded experiences of side effects, with a few women reporting a burning sensation. The results showed substantial improvement in all six sexual function domains and the total FSFI score for those women using chamomile vaginal gel when compared to the placebo. The chamomile gel showed no significant difference with the estrogen cream, except in the areas of orgasm and sexual satisfaction. This places chamomile vaginal gel as a considerable alternative for treating sexual dysfunction in postmenopausal women, especially for those who have contraindications to hormone therapy.
A Cohort Study published in 2022 in the journal Journal of the American Heart Association found that Eating more avocados, specifically two servings a week, is associated with a significantly lesser risk of cardiovascular disease and coronary heart disease. The research analysis included 68,786 women from the Nurses' Health Study and 41,701 men from the Health Professionals Follow-up Study, who were free of cancer, coronary heart disease, and stroke at the start. Their diet was assessed using validated food frequency questionnaires at the start and then every four years. The researchers used Cox proportional hazards regressions to estimate hazard ratios. Over three decades of follow-up, 14,274 new cases of cardiovascular disease were documented, including 9,185 coronary heart disease events and 5,290 strokes. After adjusting for lifestyle and other dietary factors, it was found that compared to non-consumers, those who had higher avocado intake exhibited a lower risk of cardiovascular disease and coronary heart disease. No significant associations for stroke were detected. Furthermore, it was noted that replacing half a serving per day of certain fatty foods with equivalent amounts of avocado was linked with lower risk of cardiovascular disease.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal International Journal of Health Sciences found that Green tea extract, specifically epigallocatechin gallate, can inhibit tumor growth and enhance the quality of life in women suffering from uterine fibroids. A total of 75 reproductive-age women with symptomatic uterine fibroids were included in a prospective, randomized control trial. The selection of participants for either group, those receiving 900 mg of green tea extract or those receiving symptomatic treatment, was done via a random, blind method using sealed envelopes. This trial took place over a span of 4 months and the overall study lasted around 3 years. The results of the study showcased the potency of green tea extract, particularly EGCG, with special regard to its anticancer properties. These manifested as anti-inflammatory, antiproliferative, and antioxidant effects. It was found that the administration of EGCG managed to influence tumor growth pathways, indicating its efficacy in dealing with uterine fibroids. Moreover, another significant progression was observed in the quality of life for the women partaking in this trial. It was confirmed that the use of EGCG could bring about an overall improvement in the living conditions of these women, contributing towards a better, healthier life amidst the struggle with their condition.
A Meta-Analysis published in 2022 in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition found that Regular peanut consumption appears to positively influence lipid metabolism, reducing levels of triglycerides in the blood. In the ARISTOTLE study, a randomized control trial was conducted with 63 participants who consumed either 25g/day of skin roasted peanuts, two tablespoons of peanut butter per day, or two tablespoons per day of a control butter based on peanut oil alongside their usual diet for a period of 6 months. This was done to understand the impact of regular peanut consumption on anthropometric, biochemical, and clinical measurements. Additionally, a meta-analysis was carried out incorporating data from several clinical trials, including the aforementioned ARISTOTLE study, to further consider the effects of consuming peanuts and peanut butter in both healthy individuals and those at a high cardiometabolic risk. The findings from the ARISTOTLE study indicated that lower total cholesterol/HDL-cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol/HDL-cholesterol ratios were observed in the group consuming skin roasted peanuts compared to the control butter group. Furthermore, the meta-analysis of clinical trials highlighted an association between peanut consumption and a decrease in triglycerides. It was seen that healthy consumers had lower total cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol/HDL-cholesterol ratios compared to control groups. However, it was also discovered that individuals at a high cardiometabolic risk experienced an increase in body weight following the peanut interventions, despite no change in body fat or body mass index. From the dose-response analyses, it was inferred that body weight slightly escalated with higher dosages of peanuts.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Journal of Traditional Chinese Medical Sciences found that Pu-erh tea possesses therapeutic mechanisms potentially beneficial for metabolic diseases due to its interaction with liver and gut microbiome. The methodology of this research involved reviewing and summarising the processing elements and bioactive components of pu-erh tea. Extensive study of relative human and animal trials was conducted, and the potential therapeutic mechanisms of this tea were examined and extrapolated. In discussing the results, it was discovered that pu-erh tea evidently has beneficial effects on metabolic diseases, such as hypocholesterolemic and hypolipidemic effects. The research points to the conclusion that the tea's interaction with the liver and gut microbiome is the major contributing factor to these health benefits. It helps regulate tea biotransformation and endogenous metabolism, underlining the tea's potential use in therapeutic interventions.
A Experimental Study published in 2022 in the journal Pak-Euro Journal of Medical and Life Sciences found that Ethanol and n-hexane extracts of Chrysanthemum indicum reveal potent anticancer activity against HepG2 cancer cells by promoting apoptosis and reducing cell proliferation. The research methodology involved extracting compounds from Chrysanthemum indicum using ethanol and n-hexane. These extracts were then applied to HepG2 cancer cells. The study then carefully examined the effect on cell viability and proliferation, as well as indications of apoptosis, in the treated cells compared to untreated control cells. In addition to this, the antioxidative capabilities and antioxidative scavenging activity of the extracts were assessed, particularly focusing on their ability to neutralize nitric oxide, DPHH radicals, H2O2, and superoxide. The results of this process demonstrated that both the ethanol and n-hexane extracts of Chrysanthemum indicum exhibited significant anticancer activity. This was evidenced by a marked decrease in cell viability and proliferation in the treated cancer cells, alongside an increase in indicators of apoptosis. Particularly, the ethanol extract showed more potent anticancer activity and antioxidative capability than the n-hexane extract. The treated cancer cells also showed greater antioxidative scavenging activity, further hinting at the antioxidant potential of these plant extracts.
A Experimental Study published in 2022 in the journal Molecules found that Saffron and its bioactive molecules, notably crocins, have been found to be as effective as common antidepressants in treating depression disorders. The methodology of the research centered on the incredible therapeutic properties of saffron, more specifically its bioactive molecules known as crocins. These molecules were singled out as they have shown a capacity to inhibit monoamine oxidase type A and B. The researchers also conducted experiments with saffron petal extracts, observing their impact on contractile response in electrical field stimulation. There were further investigations into saffron's ability to inhibit the reuptake of monoamines, display -methyl-d-aspartate antagonism, and enhance brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling. The discussion of the results highlighted the effectiveness of saffron and its crocins in treating depressive disorders. From several experimental studies, it became apparent that saffron and crocins might perform similarly to fluoxetine and imipramine, both widely accepted antidepressant drugs. As such, the paper suggests that these natural elements found in saffron could offer an alternative treatment method for depression. The limitations, however, as highlighted in the study, were issues surrounding stability and delivery of the herbal treatment.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Applied Sciences found that Purple carrot roots, rich in bioactive compounds like anthocyanin, may be effective in preventing metabolic syndrome and cancer by reducing inflammation and metabolic changes. The methodology employed in the research deeply studies the role of purple carrot’s main bioactive compounds against metabolic syndrome and cancer. The main focus lies on anthocyanin, a phenolic compound present in purple carrot roots. This natural food source was shifted towards as a healthier nutritional approach instead of dietary supplements. The research leans on the effectiveness of these compounds in evading or delaying the onset of cardiovascular diseases, obesity, diabetes, and cancer by inhibiting inflammatory effects. The discussion primarily surrounds the role of bioactive compounds found in purple carrots, specifically anthocyanin, in their potential prevention of metabolic syndrome and cancer. The study focused on how these components could disrupt the onset of cardiovascular disease, obesity, diabetes, and similar health issues. The results suggest that these compounds were successful in decreasing metabolic changes and inflammation. It has been suggested that purple carrots' inherent components might serve as a major tool in the prevention and treatment of metabolic syndrome and cancer.
A Systematic Review published in 2022 in the journal Journal of Isfahan Medical School found that Among the mentioned plants, castor oil and date fruit have more evidence in cervical ripening and onset of labor. 16 articles that met the inclusion criteria were reviewed. Meta-analysis was only possible on castor oil and date fruit. The chance of spontaneous onset of labor in was 5.760 and 2.205 times the castor oil and date groups, respectively. Moreover, the increase in bishop score in castor oil group was 2 times higher than the control group. The results of funnel plot and Egger test found no evidence of publication bias (P = 0.710). Peganum, Sisymbrium, chamomile, and saffron were effective in cervical ripening and onset of labor. Evening primrose was effective on Bishop score, but had no effect on spontaneous onset of labor. Red raspberry leaves were not effective in spontaneous onset of labor.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism found that Pomegranate juice, due to its unique bioactive compounds, could potentially alleviate complications related to SARS-CoV-2 infections, especially in patients with pre-existing chronic diseases. The methodology employed in this research involved reviewing and discussing currently available published evidence of the beneficial effects of pomegranate juice during conditions of viral infections. The team exploited databases such as PubMed and Scopus to access relevant references. They centered their investigation around the hypothesis that the bioactive compounds in fresh pomegranate juice are advantageous in various chronic diseased conditions, thereby making the juice potentially beneficial for SARS-CoV-2 infected patients. In the discussion of results, the researchers found compelling evidence supporting the idea that pomegranate juice can be helpful in the contexts of SARS-CoV-2 infections, particularly for those patients who have a clinical history of chronic diseases like hypertension, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer. Notably, they point out that it is the unique bioactive compounds in the juice that make it beneficial for such situations.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Pharmacological Research - Modern Chinese Medicine found that The Jing Si Herbal Drink, composed of various antiviral, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory herbs, has been confirmed as potentially effective in treating COVID-19 symptoms. The methodology incorporated in this study involves analyzing the efficacy of the component herbs present in Jing Si Herbal Drink (JSHD). This was done through in vivo and in vitro testing to understand their potential in treating COVID-19. JSHD comprises a combination of 5 antiviral, 7 antioxidant, 7 anti-inflammatory herbs. Furthermore, it includes 2 herbs that inhibit the overactive immune system, one herb that reduces cell apoptosis, and another with antithrombotic ability. These constituent herbs were evaluated for their impact on the pathogenesis of COVID-19. Discussion of the results showed that the ingredients in JSHD have demonstrated potential effectiveness against COVID-19. The active ingredients in the drink were effective in providing symptomatic relief for infected patients. The antiviral, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory herbs, along with those altering immune response, inhibiting cellular apoptosis and providing antithrombotic capacity, were all found beneficial against the disease. Thus, JSHD holds promise as a useful adjuvant or supplementary treatment in handling COVID-19.
A Systematic Review published in 2022 in the journal Current Drug Discovery Technologies found that Edible medicinal plants like saffron, chamomile, dill seeds, and castor oil have demonstrated positive effects on various aspects of labor, indicating potential natural alternatives for aiding childbirth. This systematic review explores the potential of oral herbs in aiding childbirth, given the rising interest in natural treatments despite advancements in medical interventions. More than 20% of pregnancies require labor induction, often associated with adverse effects and increased cesarean risk. The study investigates edible plants' impact on cervical readiness, labor onset, pain reduction, and labor duration. Among 20 clinical trials, saffron, chamomile, boiled dill seeds, date, date syrup, Descurainia Sophia, and castor oil have demonstrated positive effects on various labor aspects. Nonetheless, larger-scale studies are needed for a comprehensive understanding of these herbs' mechanisms and effectiveness in facilitating labor.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal Natural Product Communications found that Walnut oligopeptide improves cognitive performance and sleep quality among teenagers and elderly people. In this randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial, 36 individuals (comprised of teenagers and elderly people) were divided into groups and given either a placebo or walnut oligopeptide (WO) at low or high dosages. The division was random and the dosage groups were composed of 6 individuals from each population group (teenagers and elderly). The administration of either substance was over a period of 90 days. The results showed notable improvements in subjects who were administered WO. Test scores on the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) showed a significant increase, indicating an improvement in cognitive ability. In addition, there was a decrease in the scores on the global Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), suggesting an improvement in the quality of sleep among the subjects. Furthermore, average scores in Chinese, Mathematics, and English were significantly improved from the baseline scores among the teenagers in the WO administered group. Thus, these findings support the potential use of WO in nutritional intervention to boost memory, cognitive ability, and sleep quality in teenagers and elderly people.
A Clinical Study published in 2022 in the journal Jurnal Kebidanan found that Lavender aromatherapy is more effective in reducing pain intensity during active Phase I labor than lemon aromatherapy. The methodology employed for this study was a quasi-experimental format utilizing a non-equivalent control group pretest and posttest design. The research was conducted in the City of Mataram with a total of 30 mothers, 15 of whom were given lavender aromatherapy and the remaining 15 given lemon aromatherapy. All participants were selected using a total sampling technique. The results showed a marked decrease in pain intensity for those mothers who were given lavender aromatherapy compared to those who received lemon aromatherapy, during the active phase I of labor. Despite both groups displaying a significant decline in discomfort according to the posttest data, the average decrease was more pronounced for the group that used lavender aromatherapy. This evidence advocates for the further exploration of lavender's potential uses in childbirth pain relief management.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal BMC Research Notes found that The intake of date palm enhances the sexual function in infertile couples. The research employed a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial approach involving infertile couples who frequented infertility clinics in Iran in 2019. The intervention group was administered with a capsule of date palm, while the control group was given a placebo. The data on the sexual function of the subjects was gathered using the female sexual function index and the International Index of Erectile function. All areas of sexual function in both males and females, which include erectile function, orgasmic function, sexual desire, intercourse satisfaction, arousal, lubrication, and pain during intercourse, showed a significant enhancement in the group that consumed date palm in contrast to the control group. This study continued for a month and it demonstrated that date palm indeed has a favorable effect on the sexual functioning of infertile couples.
A Meta-Analysis published in 2022 in the journal Frontiers in Pharmacology found that Certain species of citrus extracts effectively control dyslipidemia, reducing total cholesterol, LDL, and triglycerides while increasing HDL, primarily due to their rich antioxidant composition. The methodology involved systematic surveys of research databases including PubMed, Scopus, LILACS, and SciELO. The team utilised several descriptors like dyslipidemias, hypercholesterolemia, hyperlipidemias, lipoproteins, and cholesterol. From the initial findings, 958 articles were identified and after critical assessment, 26 studies were selected that showed the efficacy of certain species extracts in controlling dyslipidemia. Of these, 25 studies were incorporated into a meta-analysis conducted using R software. Assessment of potential bias was carried out as per Cochrane methodology and ARRIVE guidelines for preclinical and clinical studies respectively. From the total number of collected studies, the results consistently showed the effectiveness of these species extracts on dyslipidemia, reducing total cholesterol, LDL, and triglycerides while elevating HDL levels. The active composition of these extracts, particularly rich in flavonoids which are powerful antioxidants, was identified as the crucial factor. The bias risk across all studies was found to be critically low to moderate. Nevertheless, the high heterogeneity values noticed across the studies suggest some inconsistency in the evidence provided.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports found that Cherry juice, when consumed several days before exercise, hastens muscle function recovery post-exercise, making it a valuable 'precovery' intervention. The review sourced data from fifteen studies that involved differing procedures for tart cherry juice intake in relation to exercise, and their impacts on muscle function, inflammation, and soreness after working out. Various forms of cherry products were investigated such as concentrated juice, juice from fresh-frozen cherries, tart cherry concentrate gel, and tart cherry powder. While the specific dosages varied depending on the type of cherry product, the timing of the dosing regimen emerged as a vital factor. Studies consistently reveal faster muscle function recovery post-exercise if the juice is ingested for numerous days preceding the exercise. The impact on soreness, inflammation, and the effectiveness of starting the regimen on the day of, or post-exercise remain mixed and unclear. Notably, tart cherry powder failed to boost any recovery metric in the after-workout days. The findings advocate for using the term "precovery" for interventions that begin prior to the exercise to assist in recovery post-exercise. Among a variety of athletic activities, cherry juice demonstrates its merit as an effective precovery beverage.
A Systematic Review published in 2022 in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition found that Higher consumption of coffee and specifically decaffeinated coffee raises the risk of rheumatoid arthritis, while caffeinated coffee, tea and caffeine intake doesn't. In the methodology, a dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies was carried out to evaluate the association between dietary caffeine, and different types of coffee and tea consumption with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Relevant research papers were identified through a database search in PubMed/Medline, Scopus and EMBASE until July 2021. The studies considered different types of coffee, caffeinated or decaffeinated, tea or caffeine exposure with RA as the main or one of the outcomes. Out of 742 publications, five studies were selected for inclusion in the meta-analysis. Pooled relative risks were calculated through a fixed-effects model. Both linear and non-linear dose-response analyses were conducted to inspect dose-response relations. The analysis of results revealed a significant association between the consumption of coffee, especially decaffeinated coffee and increased risk of RA, when comparing between extreme categories of consumption. For each additional cup of coffee consumed daily, there was a notable increase in the risk of RA. However, this study found no significant link between the intake of caffeinated coffee, tea or caffeine intake and the risk of RA.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal Evidence-Based Practice found that Chamomile was found to be less effective than mefenamic acid for relieving cyclic menstrual pain. In the methodology deployed, the researchers conducted a randomized controlled trial to compare the effectiveness of chamomile and mefenamic acid in treating menstrual pain. The patients involved in the study were randomly assigned to receive either chamomile or mefenamic acid as a form of treatment for their cyclic menstrual discomfort. In the subsequent discussion of results, it was determined that chamomile was not as effective as mefenamic acid in alleviating menstrual pain. The patients who were administered chamomile did not experience as much relief from their discomfort as those who were given mefenamic acid. Despite chamomile's widely acknowledged health benefits, in this case, it did not prove as successful as the more traditional treatment method in providing sufficient pain relief.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal Journal of Dietary Supplements found that The proprietary herbal blend LN18178 significantly boosts testosterone levels, muscle strength and mid-upper arm circumference in young, healthy males. In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study involving 120 male volunteers aged between 21 and 35 years, participants were arranged into three groups. Each group received a daily dose of either a placebo or 200 or 400 mg of LN18178 for a duration of 56 days. The primary focus of the study was to measure the potential increase in serum testosterone levels (both free and total). Secondary measures incorporated other hormones like dihydrotestosterone, cortisol, and Luteinizing hormone, as well as physical indicators such as hand grip strength and mid-upper arm circumference. Additionally, thorough checks were run pertaining to each participant's vital signs and clinical chemistry parameters in blood and urine to ensure product safety. After the intervention, both dosage levels of LN18178 significantly raised free testosterone levels. The higher dose group also showed noteworthy increases in total testosterone and luteinizing hormone levels. Meanwhile, the other hormone changes were found to be statistically insignificant. More importantly, the LN18178-400 group displayed significant enhancements in their hand grip strength and mid-upper arm circumference post-trial. The completion of the trial saw participants' vital signs and hemato-biochemical parameters within the normal range, suggesting that LN18178 is both safe and tolerable.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Nutrients found that Ginger, peppermint and caraway oil combination showed strong effectiveness in managing upper gastrointestinal complaints, with melatonin and marine alginate demonstrating moderate evidence. The methodology consisted of a literature review of the scientific studies pertaining to nutritional ingredients for upper gastrointestinal relief. The selection was based on recurring mentions within the literature and frequent appearance in consumer products. A predefined search for specific nutritional ingredients and terms related to upper GI health was conducted in five databases - Embase, Medline, Derwent drug file, ToXfile, and PubMed. A manual search was also undertaken for each ingredient to ensure comprehensive review. The studies that gained inclusion encompassed 16 human clinical trials assessing nine different ingredients. The products investigated were divided into categories, including botanicals - with sub-categories of fiber and combinations, and non-botanical extracts. Several products demonstrated good potential, others showed promising but moderate results, while some had limited support from the scientific research.
A Systematic Review published in 2022 in the journal Journal of Medicinal Food found that Raspberry consumption can help to reduce blood glucose levels and stabilize the blood lipid profile due to its bioactive compounds. The researchers conducted a systematic review of original articles and enzyme inhibition studies involving animal models and human clinical studies, extracting data from the PubMed, Web of Science, and Science Direct databases. The mechanisms of action investigated focused on how consumption of raspberry in different forms (like frozen, lyophilized, infusion of leaves, seed oil) and compounds extracted from it could inhibit enzymes and increase insulin production and sensitivity, thereby affecting blood glucose levels. The findings revealed that raspberry consumption, regardless of its form, consistently aided in reducing blood glucose levels. The mechanisms involved included inhibition of specific enzymes and enhancement of insulin production and sensitivity. On the other hand, the effects on the lipid profile were varied. While a decrease in cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein levels was recorded, the impact on triglyceride levels was less consistent and manifested mainly as stabilization rather than reduction. However, an increase in levels of beneficial high-density lipoproteins was reported, suggesting an overall beneficial effect on lipid profile.
A Systematic Review published in 2022 in the journal Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy found that Plums, specifically European and Japanese species, exhibit anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that may be used for the treatment and prevention of cancer. Methodology: The researchers conducted a systematic review of existing literature related to the effects of plums on cancer prevention and treatment. They used a variety of databases including Scopus, Google Scholar, PubMed, Medxriv, and the Cochrane Library, considering studies published from the inception of each database till July 2021. The validity of the studies was checked using the CONSORT checklist tool for quality assessment. A total of 6639 studies were initially scrutinized, narrowing down to 54 relevant studies for in-depth review. Discussion of Results: The analysis of the chosen studies revealed high antioxidant content in plum extracts. While the majority of the research supporting these findings were conducted in vitro, a smaller quantity of clinical studies involved in vivo testing. The promising results gathered from these studies suggest the potential of plums being used both for treatment and preventing cancer, especially due to their antioxidative properties.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal Complementary Therapies in Medicine found that Four weeks' treatment with pomegranate supplement greatly helps in alleviating menopausal symptoms and enhancing the quality of life in menopausal women. In this double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, a total of 78 healthy women were selected to study the effects of pomegranate on menopausal symptoms. The participants were interviewed at three different stages: before receiving either the pomegranate supplement or placebo, after the completion of the treatment, and again after a period of three weeks wherein no intervention was given. The women were asked to fill out a series of questionnaires to provide their demographic information, and to assess their menopausal symptoms and their menopause-specific quality of life. The results demonstrated a significant improvement in the quality of life and menopausal symptoms of the women from the pomegranate group, as opposed to the placebo group. These improvements were consistent as shown by the significant changes in their responses to the questionnaires before and after the treatment. In addition, it was observed that the positive effects of the pomegranate treatment were still evident even after four weeks of no medical intervention. This suggests the beneficial and prolonged effects of pomegranate in managing menopausal symptoms and enhancing the quality of life in menopausal women.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Nutrients found that Equol, a powerful estrogen-like compound derived from soy, could be key to better health in postmenopausal women if gut microbiome could be altered to facilitate its production. The methodology of this research involved looking closely at the properties and actions of equol, a metabolite of the soy isoflavone daidzein. This substance is produced through the process of intestinal bacterial metabolism, but the ability to produce it is not present in over half of the human population due to the absence of specific equol-producing bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract. Given that the make up of the gut microbiome varies from person to person, understanding the effects of equol and daidzein in the human body has been a complex task. Furthermore, the fact that rodents easily produce equol complicates the matter, as findings from rodent models may not directly apply to humans. While interpreting the results, it was found that equol, due to its strong estrogenic activity, could potentially be an excellent means to manage postmenopausal symptoms and overall health. However, the ability to produce equol varies significantly among people, based on the bacterial microflora of their gut. Therefore, the benefits of equol could potentially be amplified by finding effective methods to manipulate the gut microbiome to foster equol production, a strategy that could lead to improved health outcomes for postmenopausal women.
A Systematic Review published in 2022 in the journal Phytotherapy Research found that Consumption of sesame seeds and its products positively influences human glucose metabolism, potentially making it a beneficial addition to glucose-lowering diets. The methodology involved conducting a systematic review and meta-analysis on the effect of sesame seeds consumption on blood glucose and insulin resistance in adults. The researchers gathered data from recognized academic resources like PubMed/MEDLINE, SCOPUS, Web of Science, Google Scholar, and EMBASE, which included controlled clinical trials up until February 2021. The sesame products in these trials ranged from sesame oil, sesamin, and tahini, with the intervention period lasting from 45 days to 9 weeks. The results illustrate that the intake of sesame and its products significantly improved fasting blood glucose and Hemoglobin A1c levels. Nonetheless, the results regarding fasting serum insulin and the homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance were not found to have any significant relation. Hence, the consumption of sesame might be a beneficial supplement for managing glucose levels in humans.
A Meta-Analysis published in 2022 in the journal Frontiers in Pharmacology found that Cinnamon is a safe therapeutic agent without significant adverse effects based on systematic reviews and meta-analyses. The researchers conducted a thorough search of PubMed, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library, identifying relevant systematic reviews and meta-analyses on human subjects' cinnamon safety. The search consisted of articles up to September 2021, with the PRISMA 2020 guidelines followed for comprehensive reporting and transparency. The reliability of these studies' methodology was determined using methodological quality standards. The review included three meta-analyses and one systematic review, with two of the four classified as moderate quality, and the others as low quality. Generally, the academic studies found no significant harmful effects compared to a placebo, regardless of the dose or length of therapy. The findings suggest that humans well tolerate cinnamon, as no adverse reactions were observed in the study subjects. This evidence confirms the safety of cinnamon consumption, potentially providing health benefits as auxiliary treatment without significant risk of harm.
A Clinical Study published in 2022 in the journal Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology found that Daily oral consumption of one avocado enhances the elasticity and firmness of the facial skin in healthy women. Thirty-nine healthy overweight women ranging from 27 to 73 years of age, with skin types classified as Fitzpatrick II-IV, were involved in an 8-week study. They were grouped into two: one group ate an avocado daily while the other maintained their usual diet. The assumption was to examine if the daily intake of avocado could alleviate skin aging. Clinical assessments, specifically concerning facial skin characteristics such as firmness, pigmentation, and hydration, were done using a testing tool, called a cutometer, at specific points on the face (forehead and under the eye). The minimal erythema dose was also determined using a standard systematic approach at the inner arm. In analyzing the results, it was observed that skin firmness and elasticity, specifically on the forehead, improved significantly for those who consumed an avocado daily over the 8-week trial period when compared to their state at the beginning. No noticeable changes were recorded in skin hydration, pigmentation, or resistance to UVB radiation amongst the women in the avocado group relative to the control group. That being said, over time, variations in skin conditions such as melanin, sebum, and erythema were observed in both groups.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal European Journal of Nutrition found that Lemon juice boosts gastric secretions and emptying rate, and reduces blood sugar response to starchy food, potentially due to acid-inhibition of digestion enzyme in saliva. Methodology: In this randomized, crossover study, 10 subjects consumed either water, lemon juice diluted in water, or black tea with bread at breakfast. Using magnetic resonance imaging, the finger-prick method, and visual analogue scales, researchers measured gastric volumes, the concentrations of glucose in the blood, and the perception of appetite over a period of three hours. Discussion of Results: Lemon juice consumption resulted in a significant increase in gastric content volume, as well as a faster rate of gastric emptying, compared to water. It also elicited a lower glycemic response compared to water. However, no significant effect was observed with tea consumption. Correspondingly, changes in appetite perception and gastric volumes showed a strong correlation, though there were no significant differences among the different drinks. The findings suggest that the observed reduction in glycemic response could primarily be attributed to the interruption of starch digestion due to the acid-inhibition of the salivary enzyme responsible for starch hydrolysis.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology found that Curcumin, a spice used in Indian cooking, shows potential therapeutic effects in various retinal diseases, including during the COVID era. The research used PubMed and MEDLINE databases to examine a wide range of studies pertaining to the role of curcumin in various retinal diseases and its use during the COVID era. Specific diseases investigated include diabetic retinopathy, age-related macular degeneration, retinitis pigmentosa, retinal ischemia reperfusion injury, and proliferative vitroretinopathy. In these studies, curcumin's performance was tested in different experimental models, where it demonstrated pleiotropic effects through its action on various cell types like HRPC, HREC and ARPE-19. The research also evaluated the molecule's impact on retinal endothelial cells and its ability to inhibit actions of certain proteins and genes implicated in retinal disease. Moreover, the search also included curcumin's influence in the COVID-19 landscape. Discussing the results, curcumin proved efficacious in retinal disease management by increasing antioxidant enzymes, reducing inflammatory mediators, and inhibiting growth factors. In the context of diabetic retinopathy specifically, curcumin acted by reducing Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and inhibiting apoptosis-inducing proteins. Furthermore, curcumin downregulated several inflammatory molecules and hindered retinoblastoma cell proliferation, migration, and apoptosis. In the COVID era, curcumin showcased its potential by inhibiting viral replication and cytokine storm.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal Functional Foods in Health and Disease found that A daily dose of Chrysanthemum flower extract was found to significantly reduce serum uric acid levels, potentially improving hyperuricemia. In the methodology, two studies were conducted where 44 healthy Japanese men and women with slightly elevated serum uric acid levels were split into two groups, active and placebo, using a randomized computerized system. The active group received 100mg of Chrysanthemum flower extract containing 1mg of luteolin. In the first study, purine naturally found in food was ingested alongside the flower extract, and the participants' serum uric acid levels were measured over time. In the second study, the extract or a placebo was taken daily over 12 weeks. Changes in uric acid levels were the primary outcome, and blood, urine, and body parameters were checked to confirm the safety of the extract. For the results, in the first study, there were no significant differences found in serum uric acid levels between the group that consumed the extract and the placebo group following a purine-rich meal. However, in the second study spanning 12 weeks, the group that took the Chrysanthemum flower extract had significantly lower uric acid levels than the placebo group. Safety tests showed no adverse effects from taking the extract.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition found that Goji berries, notably their polysaccharides, exhibit protective effects against inflammatory bowel disease through the preservation of healthy gut microbiota. The review encompassed an in-depth analysis of current literature specially focusing on the role of goji berry and its important functional constituents in countering Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD). The core attentiveness of the research is directed towards understanding the interplay between goji berries, particularly their polysaccharides, and gut microbiota. The goji berries’ protective effects were evaluated, focusing on how they curb disruption in gut microbiota, a common facet in IBD. The review concluded that goji berries, especially their polysaccharides, demonstrated appreciable benefits in averting gut microbiota disturbances seen with IBD, thus protecting against this condition. These natural substances, present in goji berries, function as prebiotics, which maintain a balanced gut microbial ecosystem. The research further revealed that proper functioning of gut microbiota and their metabolites was a crucial element in mediating these beneficial effects against IBD, thus cementing the role of dietary interventions in managing diseases linked with gut health.
A Meta-Analysis published in 2022 in the journal European Journal of Nutrition found that Oat supplementation interventions can improve cardiovascular health markers among adults, regardless of their diet or metabolic conditions. The methodology involved analyzing various randomized clinical trials that tested how oats, or extracts rich in oat beta-glucan and avenanthramides affected markers of cardiovascular disease risk. The sample population was predominantly subjects with high cholesterol, obesity, and mild metabolic disturbances. Interventions were compared to control arms without oats. In the discussion on results, it was found that subjects receiving the oat supplementation had improved health metrics such as total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, glucose levels, body mass index, weight, and waist circumference. However, when the oat supplementation was compared to heterogeneous interventions, like wheat, eggs, rice, etc., reductions in the levels of glycated haemoglobin, diastolic blood pressure, HDL cholesterol, and apolipoprotein B were also seen. Despite these promising results, there were some concerns around the bias risk associated with the majority of included randomized clinical trials.
A Experimental Study published in 2022 in the journal Human & Experimental Toxicology found that Ellagic acid, found naturally in pomegranates, significantly inhibits growth and migration of gastric cancer cells without causing notable side effects. In the methodology of this study, High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) was employed to detect the presence of Ellagic Acid (EA) in samples. Various methods were then used to determine the various anti-cancer properties of different concentrations of pomegranate fruit juice, pomegranate peel extract, and pure EA. This included an MTT assay, apoptosis and scratch assay, gelatin zymography and quantitative RT-PCR. Additionally, the study examined the impact of these compounds on immunocompromised C57BL/6 mice carrying human gastric cancer tumors. Extending to discussing the results, it was found that EA inhibited both the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells in mice and altered gene expressions related to apoptosis and inflammation. The treatments with EA or pomegranate extract resulted in a noticeable decrease in tumor size in the lab mice. No significant side effects were reported from EA use. In sum, the results showed EA's potential as a safe and effective anti-cancer agent specific to gastric adenocarcinoma.
A Meta-Analysis published in 2022 in the journal Pharmacological Research found that Saffron intake might aid in reducing depressive symptoms but it should not be regarded as an exclusive solution for treating depression. This study conducted a comprehensive umbrella meta-analysis of previously published research studies to evaluate the effect of saffron on depression. The researchers collected the relevant studies from various acclaimed international databases like PubMed, Scopus, EMBASE, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Central Library, up until June 2021. All gathered research was based on the effects of saffron on depression. A random-effects model was employed to conduct the meta-analysis and additional analyses, which included subgroup and sensitivity examination. The meta-analysis consisted of seven individual studies altogether. The evaluations displayed that the consumption of saffron led to an observable decrease in Beck's Depression Inventory (BDI) scores, indicating a reduction in depressive feelings. However, the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAMD) scores didn't exhibit any significant change post saffron consumption. Some other mixed scores also remained unchanged. Thus overall, it was deduced that while saffron intake might help alleviate depression, it can't solely be relied upon for effectively treating this mental disorder.
A Experimental Study published in 2022 in the journal Journal of Ethnopharmacology found that Saffron petal extract and anthocyanins can alleviate symptoms of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome by rectifying hormonal imbalances and reducing inflammation in PCOS mice. The study conducted experiments on mice induced with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) through the injection of testosterone enanthate. These mice were then treated with saffron petal extract and anthocyanins to observe the effect on their ovarian hormones, steroidogenic enzymes, ovarian dysfunction, regulation of anti-inflammatory genes, and antioxidant factors. The treatment was found to decrease the elevated levels of luteinizing hormone, testosterone, and estrogen in the PCOS mice, while reviving the reduced follicular-stimulating hormone and progesterone levels. In discussion of the results, it was observed that saffron petal extract and anthocyanins positively altered the levels of gonadotropin receptors, steroid receptors, inflammatory markers, inflammatory-related factors, and antioxidant enzymes that were affected by the PCOS condition in the subject mice. The study also noted that the reproductive tissues of the PCOS mice, which were converted into androgen-dominant environments by the testosterone enanthate induction, were restored into estrogenic conditions after the treatment. Further findings suggested that saffron petal extract and anthocyanins led to amelioration of PCOS symptoms by enhancing the regulation of ovarian steroids, steroidogenic processes, antioxidant enzyme production, and inflammatory markers.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Reference Series in Phytochemistry found that The flower of Chrysanthemum morifolium, widespread in Asia, has been discovered as a treatment for diverse diseases, including obesity, heart disease, and cancer, due to its beneficial phytoconstituents. Methodology: A comprehensive examination of Chrysanthemum morifolium was conducted to shed light on its medicinal uses and health benefits. The studies focused on its use in traditional medicine, which includes treatment for excessive internal heat, eye inflammation, fever, migraines, and hypertension. The biological properties of the flower, such as flavonoids, polyphenols, volatile oils, terpenoids, and polysaccharides were analyzed, and their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity, cardioprotective, neuroprotective, anticancer, and antidiabetic effects taken into account. Discussion of results: The examination of Chrysanthemum morifolium validated the flower's antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties, among others. It also indicated potential applications in preventing and treating obesity, cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, and diabetes. Moreover, its medicinal efficacy and safety in treating health conditions were backed by clinical studies.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal South African Journal of Botany found that Chrysanthemums, popular floricultural crops, not only hold significant ornamental value but also exhibit various therapeutic potentials including antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anticancer activities. The method involved in this research aimed at studying the genus Chrysanthemum through a decade-long review (2010-2020) of scientific evidence, focusing on its therapeutic potential, phytochemistry, and pharmacological activities. Various phytochemical compounds including flavonoids, terpenoids, polysaccharides, and unsaturated fatty acids, which are present in the genus Chrysanthemum, were identified. In addition, the taxonomy, distribution, horticultural, and traditional uses of the genus were also studied. The results demonstrated that Chrysanthemum species show numerous potential medicinal benefits, ranging from antioxidant to antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, anti-allergic, anti-obesity, immune regulation, hepatoprotective and nephroprotective activities. The research also underlined the opportunity of medicinal exploitation of the genus Chrysanthemum, given the extreme popularity of these plants and the wide range of phytochemical compounds they contain. The ornamental, medicinal, environmental, and industrial values of these plants further establish them as leading floricultural crops.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal International Review of Neurobiology found that Adzuki and Mung beans have great potential as functional foods for health promotion and disease prevention, offering an excellent source of essential nutrients and biodiversity for sustainable agriculture. This study explores the health benefits and agricultural sustainability of adzuki and mung beans. Adzuki beans, traditionally used in traditional Chinese medicine, provide essential fatty acids, fiber, minerals, and phytochemicals promoting health and combating disease. These beans also have natural nitrogen-fixing properties beneficial to cropping systems. Similarly, mung beans contribute protein and nitrogen to agriculture, supporting soil health and crop yields. They also offer health benefits including antioxidant, antifungal, antiinflammatory, and antimicrobial activities. Additionally, both adzuki and mung beans, through biological nitrogen fixation, may lessen reliance on chemical fertilizers, promoting environmental and economic sustainability. The results suggest both adzuki and mung beans can play a significant role in health promotion and in sustainable agriculture. Influencing health with their nutrient richness and variety, these beans provide essential fatty acids, fiber, minerals, and phytochemicals. With their nitrogen-fixing properties, they can enhance soil quality and reduce dependence on chemical fertilizers. Simultaneously, by being able to restore organic matter to the soil, they can curb pests and disease issues. Thus, these beans serve as a viable economic and environmental option for future agricultural systems while promoting health.
A Meta-Analysis published in 2022 in the journal Nutrition Research and Practice found that Isoflavone supplementation noticeably impacts menopausal symptoms and hormonal changes in postmenopausal women. In order to examine isoflavones effects on menopausal symptoms and the associated hormonal alterations, a systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted. To do this, the PubMed and EMBASE databases were used, but the selected studies were restricted to random controlled trials (RCTs) assessing isoflavone supplementation's impact on menopausal symptoms. Overall, 11 studies were chosen for the final quantitative evaluation, and the isoflavone intervention amount varied among these studies. The Meta-analysis displayed that supplementing isoflavones meaningfully increased estradiol levels and the Kupperman index (a composite scoring of multiple menopausal symptoms intensity). Yet, there were no significant impacts observed on hot flashes, or the release of two specific hormones: follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone. It should be noted that there was a significant inconsistency in estradiol levels and Kupperman index findings among different studies.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences found that High doses of vitamin C, vitamin D supplementation and natural honey can potentially decrease fatalities and support the management of COVID-19. The team undertook a systematic analysis of existing literature and pertinent clinical trials to evaluate the potential of vitamin C, vitamin D, and natural honey intervention during the progression of the COVID-19 pandemic. This assessment aimed to determine the impact of these substances upon the outcomes of COVID-19, particularly in reducing respiratory damage and potentially improving patient immunity. The research revealed that substantial doses of vitamin C illustrated to lower lung damage and reduce intensive care stay duration for COVID-19 patients. It was observed that vitamin D deficiency is common among individuals living in institutions, and having supplements could aid in defending against respiratory infections. Natural honey, due to its antiviral effects and immune-enhancement capacities, also displayed promising results in treating COVID-19. The acquired evidence drove the belief that administering vitamin C, vitamin D, and natural honey, along with the existing treatment protocols, could potentially be a compelling method to decrease fatalities associated with COVID-19.
A Theoretical Article published in 2022 in the journal Traditional Medicine Research found that The jujube tree bears fruit endowed with substantial nutritional value and contains numerous phytochemical components with reported antioxidant, anti-cancer and neuroprotective properties. The research implemented an analysis of the jujube tree, its fruit, and its long history of usage in traditional medicine, focusing primarily on its use in traditional Persian and Chinese medicines. The varied geographical distribution of the tree was studied, especially its presence in tropical and subtropical regions across Europe and Asia. Researchers took into account the tree’s resilience to soil salinity and alkalinity as part of its general characteristics. The core of the study involved an in-depth investigation into the nutritional composition and pharmacological properties of the jujube fruit. The fruit's contents were categorized into proteins, minerals, vitamins, organic acids, and carbohydrates. Furthermore, a range of phytochemical components such as polyphenols, flavonoids, terpenoids, anthocyanins, alkaloids, and carotenoids were identified. Research noted both the fruit's nutraceutical and cosmeceutical potential. It also explored the medicinal properties of all elements of the plant, not just the fruit. The physiological impacts of the jujube were also evaluated across various medical contexts, seeking to understand its impact on different organs and tissues, as well as its influence on various health conditions and concerns. Culminating in the identification of antioxidant, anti-cancer, antimicrobial, neuroprotective, cardioprotective, hepatoprotective properties. Noteworthy, are also its health-promoting effects, with strong references to anti-aging properties.
A Systematic Review published in 2022 in the journal The American Journal of Chinese Medicine found that Fresh and dried ginger displays key botanical, phytochemical and ethnopharmacological differences, which are fundamental for their specific clinical uses in treating gastrointestinal issues. The methodology used in the research involved a retrospective comparison between Sheng Jiang (SJ, meaning fresh ginger) and Gan Jiang (GJ, meaning dried ginger), two traditional Chinese herbs. The comparison was undertaken specifically considering aspects of botany, phytochemistry, and ethnopharmacology. The research also delved into exploring the traditionally attributed use of ginger, in both its fresh and dried forms, for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders, and its relationship with human gut microbiota - an aspect that hasn't been considered extensively previously. The results displayed notable differences between fresh and dried ginger in terms of botany, phytochemical, and ethnopharmacological properties. Fresh and dried ginger are cultivated differently and display distinct physical appearances. This research proposed that these differences lay the foundation for how these two forms of ginger are applied clinically. Furthermore, discussing the pharmacology of gut microbiota-related gastrointestinal benefits, it is suggested that fresh and dried ginger could present innovative and potent avenues for preventing and treating gastrointestinal disorders.
A Meta-Analysis published in 2021 in the journal Frontiers in Endocrinology found that Tea supplements, especially green tea, significantly decrease fasting blood glucose and fasting insulin levels and reduce body weight in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. The researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis by searching published literature in different databases from 1985 to September 2021. The data from randomized controlled trials were extracted to assess the effectiveness of tea versus placebo in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Weighted mean differences were pooled using a random-effects model. A total of six trials with 235 participants were included in this review. The study resulted in finding that consumption of tea supplements improved body weight, fasting blood glucose, and fasting insulin more significantly when compared with a placebo. Notably, green tea was effective on body weight, fasting insulin, fasting blood glucose, and certain reproductive hormone indexes. The therapy was also found to be safely tolerated by the patients. It's important to note that tea had significant effects on fasting blood glucose and hormone levels in trials with intervention duration of 3 months or more. Differences were noticed among Asian and Caucasian PCOS patients regarding the effect of tea on weight and fasting insulin.
A Experimental Study published in 2021 in the journal Frontiers in Immunology found that Consuming oats significantly lessens total and LDL cholesterol levels and mediates a prebiotic effect on the gut microbiome, contributing to its cholesterol-lowering ability. In a randomized controlled study, 210 mildly hypercholesterolemic subjects from three various study centers across China were assigned to consume either 80 g of oats or rice daily for 45 days. To ascertain the effects of these diets, measurements were taken of the participants' plasma lipid profiles, short chain fatty acids (SCFAs), and fecal microbiota. Following 30 and 45 days of adherence to these diets, there was a pronounced reduction in total cholesterol (TC) and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C) in both the oat-consuming and rice-consuming participants. This decrease was more articulated amongst the oat consumers by the 45th day. The consumption of oats led to a significant increase in the abundance of certain beneficial gut microbiota and a corresponding decrease in unclassified harmful types. These microbiota demonstrated associations with changes in plasma lipid levels and SCFAs. The comprehensive findings strongly suggest that the cholesterol-reducing effect of oats may be largely down to its prebiotic activity, which modulates the gut microbiome.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2021 in the journal Nutrients found that Regular intake of goji berries can increase Macular Pigment Optical Density, potentially helping to prevent or delay the development of age-related macular degeneration. The research was a randomized, parallel-arm study involving 27 participants aged between 45 and 65. These participants were divided into two groups; one group consumed 28 grams of goji berries five times weekly for 90 days, while the other consumed a supplement containing 6mg of lutein and 4mg of zeaxanthin in the same frequency and duration. This method intended to evaluate the effects of zeaxanthin-rich goji berry intake on Macular Pigment Optical Density and skin carotenoids, both key in AMD risk assessment, while also drawing a comparison to the effects of lutein and zeaxanthin supplements. As the study progressed to its end, the group consuming goji berries showed a significant increase in Macular Pigment Optical Density and skin carotenoids, key biomarkers in assessing the risk of developing age-related macular degeneration. The lutein and zeaxanthin supplement group, however, did not present any noteworthy changes. This suggests the potential superiority of goji berries in the prevention or delay of AMD development compared to the given supplement.
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal Nutrients found that Fresh Hass avocados have been found to reduce cardiovascular disease risk, assist weight loss, improve cognitive function, and promote colonic microbiota health. The methodology used in this comprehensive review entailed conducting 19 clinical trials, five observational studies, and examination of several biological mechanisms. These focused on understanding and identifying the primary health effects of Hass avocados in different population groups such as healthy overweight or obese adults, older normal-weight adults, and overweight or obese women. The effects were thoroughly measured in terms of cardiovascular health, body weight, cognitive function, and colonic microbiota health. The primary health effects of Hass avocados were then linked to its unique nutritional properties - the unsaturated to saturated fat ratio, the presence of multifunctional prebiotic and viscous fiber, its low energy density, and the increase in carotenoid absorption facilitated by its oleic acid and water emulsion, particularly when combined with low-fat fruits and vegetables. The results indicated significant positive effects from consuming Hass avocados, especially when incorporated into a healthy dietary plan like the Mediterranean diet. Consumption of avocados was found to lead to reduced cardiovascular disease risk in healthy overweight or obese adults, primarily by undesirable cholesterol profiles and promoting vascular health. For overweight or obese women, it helped in weight reduction and lessened visceral fat tissue. The consumption of avocados improved cognitive function in both older normal-weight adults and young to middle age overweight adults, particularly their executive function. It was also found to enhance colonic microbiota health in overweight or obese individuals by fostering healthier microflora and fecal metabolites.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Complementary Therapies in Medicine found that Turmeric curcuminoids are associated with better pain relief than NSAIDs in knee osteoarthritis. The meta-analysis results showed that curcuminoids were significantly more effective than comparators regarding visual analogue scale (VAS) and Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index (WOMAC) pain scores. However, no significant difference in pain relief or AEs between the high-dose (daily dose ≥1000 mg or total dose ≥42 gm) and low-dose (daily dose <1000 mg or total dose <42 gm) curcuminoid treatments was observed. When comparing curcumininoids versus NSAIDs, a significant difference in VAS pain was found. For AE analysis, three of our included studies used NSAIDs as comparators, with all reporting higher AE rates in the NSAID group, though significance was reached in only one study.
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal Current Drug Delivery found that Pomegranate juice and its bioactive components may serve as cost-effective, next-generation non-pharmacologic anticancer therapies, particularly against colorectal and prostate cancer. Methodology: The present review was undertaken to provide current information on the impact of pomegranate juice and its bioactive elements, critically focusing on the effects on the most common six types of cancer. The inherent polyphenolic compounds of pomegranate, such as ellagitannins and punicalagin, are known to have substantial antioxidant capability which has been evaluated through in vitro and in vivo studies. These compounds' ability to avert free radicals and design metal-chelates in biological tissues have offered a useful basis to extrapolate their impact on various types of cancers. Discussion of Results: The findings indicate that the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of pomegranate possess significant antimutagenic and antiproliferative activities, which proved to be beneficial in modifying gene expression, moderating cellular mechanisms, and limiting the metastasis of cancerous cells. In addition to this, there are reports from a few clinical trials showing the potential of pomegranate ingredients to prevent and treat cancer, notably colorectal and prostate cancer. It’s been noticed that the pomegranate driven therapies may prove to be a cost-effective alternative to costly chemotherapies which often carry drug resistances and severe side effects. Such therapies could offer lesser side effects, making them potential candidates for future non-pharmacologic anticancer treatments.
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal Applied Biological Chemistry found that Cinnamomum cassia, or cinnamon, exhibits promising therapeutic benefits in combating gastritis by targeting inflammation pathways, according to preclinical studies. This study is a systematic review of 20 studies evaluating the pharmacological effects and mechanisms of C. cassia in treating gastritis. Focusing on the main active compound of C. cassia, cinnamaldehyde, the research was centered around its influence on inflammation pathways. Furthermore, different methodologies were used to induce gastric ulcers, including stress, alcohol, excessive acidity, and the prolonged usage of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). The result discussion highlights the success C. cassia extract demonstrated in protecting against gastritis. Key findings stemmed from preclinical tests, with predominantly animal models, including Beagle dogs and rats. The ingestion of standardized C. cassia extracts showed positive effects with no toxicity, asserting the effectiveness and safety of this natural remedy in managing gastritis.
A Experimental Study published in 2021 in the journal Molecular & Cellular Toxicology found that Cocoa bean husk, a by-product of cocoa processing, exhibits potent antioxidant and anticancer effects on prostate cancer cells due to its high phenolic compound content. The methodology of the study involved fractionating ethanol crude extract of cocoa bean husk (CBH) and comparing the total polyphenol and flavonoid content, as well as radical scavenging activities, of the various fractions. The phenolic compounds present in the ethanol ethyl acetate (EAF) and butanol (BF) fractions were further analysed using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). These fractions were then applied to prostate cancer cell lines PC3 and DU145 to ascertain their impact. The results indicated that the ethyl acetate fraction exhibited the highest phytochemical content and antioxidant activity, closely followed by the butanol fraction. The presence of abundant phenolic compounds, namely catechin, epicatechin, and procyanidin B, was observed in both fractions. Moreover, both fractions induced apoptosis and DNA fragmentation in the prostate cancer cells in a concentration-dependant manner, demonstrating their potential anticancer effects.
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism found that The pomegranate plant has a rich inventory of phytochemical constituents showing pharmacological efficiency in treating cardiovascular and endocrine diseases. The researchers set out to review both traditional and scientific applications of P. granatum focusing on its phytochemical content and potential for aiding in drug development. They gathered relevant information through both classic herbal literature and electronic databases, which included renowned platforms such as PubMed, Scopus, and ScienceDirect. The culmination of traditional and contemporary research showed an array of phytochemical constituents in P. granatum, including polyphenolics, flavonoids, anthocyanosides, alkaloids, lignans, and triterpenes. Randomized controlled trials indicated these constituents demonstrate pharmacological activity, particularly against diseases like diabetes, cardiovascular disease, oral cavity disorders, endocrine disorders, and even cancer. The review, therefore, not only points to the traditional uses of P. granatum but underscores their validation through scientific support.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2021 in the journal Nutrients found that High avocado intake significantly reduces the intake of energy and various macro and micronutrients in Hispanic/Latino families. In this research, Seventy-two Hispanic/Latino families without severe chronic disease and not following specific diets were selected. These families, each with at least three members and all residing in the same household, were divided into two groups. One group received a low allotment of avocados (three per week) and the other received a high allotment (fourteen per week). Along with the prescribed amounts of avocado, both groups underwent twelve bi-weekly nutrition education sessions over a period of six months. The study investigated the change in the families' total intake of energy, as well as macro and micronutrients as the primary outcomes. These assessments were made by comparing mean changes between groups at the end of the six months, while abiding by the intention-to-treat concept. The results showed a significant reduction in not just energy intake, but also the intake of carbohydrates, animal and vegetable protein, fats (including saturated and polyunsaturated fats), and micronutrients such as calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium, iron, and vitamin D in the high avocado allotment group. Interestingly, the high allotment group reported a reduction of self-reported energy intake by a notable margin, much higher when compared to the decrease in the low allotment group. The study underscores the potential of culturally-appropriate plant-based interventions for improving nutritional status of at-risk families.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Future Pharmacology found that Eating kiwifruits improves bowel movements and decreases stool consistency, also providing anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits to the gut barrier. The review included nine clinical studies investigating the effect of kiwifruit consumption on intestinal function and constipation. The studies, focusing on young or middle-aged adults predominantly, required participants to consume between two to four kiwifruits daily for durations varying from three days to four weeks. The impact on elderly individuals was less explored. The review indicates that kiwifruits can enhance bowel movements and reduce stool consistency in both healthy individuals and those suffering from irritable bowel syndrome-induced constipation. The fiber and water content of kiwifruits is thought to contribute to these results. Furthermore, consumption of kiwifruit showed extra intestinal health advantages, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects on the gut barrier. However, when focusing on patients with constipation, the fruit's consumption correlated with a temporary increase in defecation frequency but inconsistently impacted stool consistency. High-quality methodical studies and meta-analysis substantiated these findings.
A Cohort Study published in 2021 in the journal Muhammadiyah International Public Health and Medicine Proceeding found that Consumption of sardines can effectively prevent type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension, particularly in senior citizens, due to their high omega 3, EPA, and DHA content. For the methodology, the researchers carried out a literature study to delve into the research topic. They exclusively used already available research and data for their study rather than new, hands-on investigations. They explored extensively into the health benefits and properties of sardines and how it contributes to preventing type 2 diabetes and hypertension. In their discussion of the results, it was determined that sardines have multiple beneficial properties. They discovered that sardines have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant roles, they enhance membrane fluidity and increase insulin receptors and action. Furthermore, sardines also possess hypoglycemic and hypotensive qualities. The multitude of these properties thus shows the capability of sardines to effectively prevent and lower hypertension and type 2 diabetes, especially among senior citizens.
A Cohort Study published in 2021 in the journal Muhammadiyah International Public Health and Medicine Proceeding found that Sardines are highly proven to be able to effectively prevent type 2 diabetes, prevent hypertension, and lower blood pressure, especially for senior citizens. Sardines contain anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant roles, boost cell membrane fluidity, boost the number of insulin receptors and insulin action, and also contain hypotensive and hypoglycemic effects.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2021 in the journal Breastfeeding Medicine found that Date fruit consumption appears to be useful for promoting and increasing breast milk quantity in breastfeeding mothers. Date fruits may be an alternative galactagogue. Breastfeeding mothers who received 10 date fruits/day had an 11% increase in breast milk quantity from baseline to week 2, and a 23% increase from baseline to week 4, (both p < 0.05). The breast milk quantity of the breastfeeding mothers who received date fruits was significantly higher than that of the control group (p < 0.05). However, there were no differences in infant nutritional status.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2021 in the journal The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine found that A combined treatment of soy and hop extract is a safe and effective alternative to traditional hormone replacement therapy for improving postmenopausal symptoms. In this double-blinded, randomized controlled trial, researchers administered a combination of soy and hop extract to 78 postmenopausal women with moderate to severe symptoms. Conducted in the gynecological outpatient clinic of a tertiary hospital, all subjects had modified Kupperman Menopausal Index (KMI) scores over 20. Participants either received the treatment or a placebo, as the researchers sought to evaluate their menopausal symptoms over the course of 12 weeks. The changes to their menopausal symptoms were tracked through self-reported KMI scores at multiple intervals. They also gauged measures such as the serum levels of bone metabolism markers, ultrasonographic parameters, hormone profiles, and safety assurances, amongst others. In terms of test results, after undergoing the 12-week treatment, the group receiving the combined soy and hop extract saw more considerable improvements in their symptoms compared to the placebo group. They particularly noted notable enhancements in conditions like fatigue, paresthesia, arthralgia, and myalgia, palpitations, and vaginal dryness. Lowered increases in urine N-telopeptide, a biomarker for bone metabolism, were observed in treatment group participants aged 50 and older. Meanwhile, endometrial thickness and hormonal profiles did not display any significant shifts in either group. Importantly, throughout the trial, no harmful side effects or events arose, speaking to the safety of the treatment.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Explore: The Journal of Science & Healing found that Date fruit consumption several weeks prior to delivery can decrease the need for labor induction and/or augmentation and might have a beneficial effect on labor duration. Our meta-analysis yields two prominent important benefits of date fruit consumption by primiparous women during several weeks prior the delivery. First, it can decrease the need for labor induction and/or augmentation by as much as one half of the cases. Second, date fruit might have a beneficial effect on labor duration, especially by 4-hour shortening of the latent phase.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2021 in the journal Contemporary Clinical Trials found that Consumption of one avocado per day can potentially reduce visceral adiposity and subsequently decrease the risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The Habitual Diet and Avocado Trial was a multicenter, randomized, controlled study that evaluated the impact of daily avocado consumption over a period of six months. The experiment involved a large and diverse cohort. Participants were required to incorporate a daily avocado into their diet as a substitute for their regular dietary intake, notably those devoid of avocado consumption. Their progress was measured using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to ascertain the potential decrease in visceral adiposity, with individuals with increased waist circumference being the primary focus of the study. Additional measures such as hepatic lipid content, plasma lipid profiles, blood pressure and high sensitivity C-reactive protein were also part of the evaluation. The study showed promising results in terms of weight control and reduction of visceral adiposity among participants. Initial results suggest that the sense of satiety post avocado consumption may subsequently lead to an overall decrease in energy intake. Moreover, the daily consumption of avocados was observed to not only reduce visceral fat but also display potential benefits impacting cardiometabolic disease risk. The benefits of avocado consumption were notably apparent among a cohort with an increased waist circumference, thus confirming the potential health benefits of avocados in weight management and risk reduction of obesity-related diseases.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Japanese Dental Science Review found that Green tea treatment has shown potential in improving oral hygiene and gingival health, and reducing periodontitis and caries. The methodology of this research consisted of systematic literature review focusing on clinical trials that evaluated the impact of green tea on managing periodontitis and caries. Various databases including MedLine (PubMed), Scopus, and the Cochrane Library were utilized for gathering relevant studies. Eighteen suitable studies were selected, encompassing 870 subjects. The results reveal a noticeable positive effect from green tea treatment. This effect was realized in the reduction of gingival index, plaque index, gingival bleeding index and bleeding on probing when compared to a control group. It was also noted that when considered among chlorhexidine control groups, green tea showed a slight negative effect. There was additionally a significant positive effect seen in the reduction of clinical attachment level and probing pocket depth with green tea treatment.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Antioxidants found that Green tea supplementation improves total antioxidant capacity and impacts oxidative stress based on dose levels in adults. The research's methodology involved a systematic search of research materials published in English language up to 21 August 2021. Recognized online databases such as Scopus, PubMed, Embase, and ISI Web of Science were utilized with the appropriate keywords. The study focused on randomized controlled trials that evaluated green tea supplementation, and its relationship with malondialdehyde and total antioxidant capacity in adults. A random-effects model quantified the difference, and the researchers carried out meta-regression and non-linear dose-response analyses to investigate the association between the quantity of green tea consumed and the duration of the intervention. The research analysed the results obtained from sixteen randomized controlled trials, which amount to seventeen study arms comprising a total of 760 participants. The study found that green tea supplementation did have significant effects on total antioxidant capacity, and these effects were chiefly linked to gender and body mass index. However, the results showed that these effects were not significant in cases of low-dose supplementation and obese individuals. On the other hand, no relationship was found between malondialdehyde and green tea supplementation in any subgroup. Nonetheless, meta-regression analyses indicated an inverse linear connection between the change in MDA and the dosage of green tea.
A Cohort Study published in 2021 in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition found that The consumption of avocado is associated with better cognitive function in older adults. In the methodology, the researchers conducted a cross-sectional study involving 2,886 participants aged 60 or older from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011–2014. These participants were classified into two groups: those who consumed avocado or guacamole, and those who did not. Cognitive performance was evaluated using tests for immediate and delayed recall, the Animal Fluency test, and the Digit Symbol Substitution Test, with education-dependent z-scores calculated for each participant as the education level can impact cognitive function. To control for potential influencing factors, comparisons were made between consumers and non-consumers with independent sample t-tests and advanced statistical methods like ANCOVA. The study found that those who consumed avocado showed significantly better scores across every cognitive test and the global cognitive score compared to non-consumers. Even after adjustments for potential confounders, the positive differences persisted. These findings support the conclusion that consumption of avocado correlates positively with improved cognitive function amongst elderly adults.
A Clinical Study published in 2021 in the journal Nutrients found that Consuming soymilk-honey fermented with a specific type of probiotic significantly reduces osteocalcin levels, which may impact bone health in postmenopausal women. The researchers conducted a 90-day pre-post quasi-experimental study with control design on 54 postmenopausal women who were divided into three groups. The first group consumed regular soymilk, the second group consumed soymilk-honey fermented with a specific sub species of probiotics, and the third group consumed soymilk-honey fermented with a different type of probiotics. Each participant consumed 100 mL of their respective drink per day for 90 days. Measurements of blood serum osteocalcin were taken at the start and end of the study, alongside assessments of each participant's overall health status, including total cholesterol, blood glucose, and uric acid levels. In terms of results, it was observed that the group consuming the soymilk-honey fermented with the particular probiotic showed a significant decrease in their osteocalcin levels after the 90-day period. This indicates that this specific fermented soymilk-honey beverage might have a positive impact on bone health in postmenopausal women.
A Experimental Study published in 2021 in the journal Nutrients found that Tiger nut and walnut supplementation in diets can improve testosterone levels and help control vasoconstriction, potentially benefiting hypertensive individuals. Rats were used in the experiment, placed into seven distinct groups with various diet and medicinal intake combinations including basal diet controls, supplemented processed and raw tiger nut (TN) and walnut (WN) diets, and more. Before hypertension was induced with L-NAME, the rats were given their regular diet for two weeks. After this period, they began receiving L-NAME for ten subsequent days. The scientists then measured the impacts on the rats' platelet androgen levels, ectonucleotidases, and adenosine deaminase (ADA). The L-NAME treatment resulted in a considerable decline in testosterone levels in the rats. However, the groups that were fed diets supplemented with TN and WN exhibited improved testosterone levels compared to the control group, yet their luteinizing hormone levels remained unchanged. The L-NAME-treated group also saw an increase in ATP hydrolysis and ADA activity, alongside a reduction in ADP and AMP hydrolysis. These effects were substantially reversed in the groups that were fed supplemented TN and WN diets. This suggests that TN and WN could enhance testosterone levels and modulate the purinergic system in platelets, which might be a potential mechanism through which they contribute to the control of vasoconstriction.
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition found that Green tea and its component EGCG, demonstrate potential as a treatment for endometriosis by inhibiting growth, invasion, adhesion and angiogenesis. The main research methodology of this work is a narrative review. The paper comprehensively collects and reviews various preclinical studies that propose the use of green tea as a potential treatment for endometriosis. These studies explore the diverse biological properties and activities of green tea and its major bioactive component, (-)-epigallocatechin gallate, including anti-angiogenic, anti-proliferation, anti-metastasis, and apoptosis induction functions. Different potential mechanisms used by green tea to inhibit the growth of endometriosis are considered, such as its effects on inflammation, oxidative stress, invasion, adhesion, and apoptosis. The discussion of the reviewed data highlights the potential therapeutic effects of green tea acting on different molecular and cellular mechanisms in endometriosis. The researchers keenly discussed how green tea exhibited an inhibitory effect on the disease through multiple avenues, including reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, preventing tumor invasion and adhesion, promoting apoptosis (cell death), and limiting angiogenesis (the development of new blood vessels) - all these factors contribute to the growth and progression of endometriosis. The discussion elaborates on the significant roles and wider implications of these processes in understanding and potentially treating endometriosis.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2021 in the journal European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology: X found that Chamomile capsules prove effective in reducing emotional symptoms related to menstrual cycles. In the methodology of this clinical trial, 118 Guilan University students were split into two groups – one receiving chamomile capsules, the other a placebo – with each participant taking one capsule every eight hours for seven days before menstruation. The Premenstrual Symptoms Screening Tool was used to gather data. The assessment of the results reveals that the group of students who consumed the chamomile capsules observed a more noteworthy decrease in menstrual-related mood disorders when compared to the placebo group. Moreover, even after controlling for other variables, there was a significant difference between the two groups in terms of changes in mood symptom severity.
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal Disease and Diagnosis found that Lavender aromatherapy, whether administered through massage or inhalation, appears effective in reducing active phase labor pain. The researchers conducted their study by performing a detailed search using a number of specific keywords such as lavender, childbirth, labor, pregnancy, labor pain, aromatherapy, and delivery across multiple databases. These databases included MEDLINE/PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar. Using these keywords they extracted relevant data from the seven most reliable studies they found, two of which originated in Egypt and Indonesia, and remaining five in Iran. The chosen studies depicted a range of qualities, with some using massage aromatherapy, and others applying inhalation as their method of practice. In analyzing these studies, it was found that all of them indicated that lavender aromatherapy, regardless of whether it was applied via massage or inhalation, had the potential to lessen the pain felt during the active phase of labor. The studies provided basis for insightful consideration of the application of lavender aromatherapy as a viable method for managing labor pain.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Nutrients found that Almond-based diets may be effective in promoting short-chain fatty acid-producing bacteria and lowering glycated haemoglobin and body mass index in patients with type 2 diabetes compared with control. The research was a systematic review and meta-analysis, conducted using the preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis methodology. Diverse databases, including the Health Sciences Research Databases via EBSCOhost, Google Scholar, EMBASE, and other article's reference lists, were thoroughly searched following the population, intervention, control, outcome, and study framework. The searches encompassed all relevant studies available from the inception of these databases until August 1, 2021. Nine randomised studies were analysed, eight of which were used for the meta-analysis. Results revealed that diets rich in almonds foster the growth of gut bacteria that produce short-chain fatty acids. Additionally, the analysis demonstrated that such diets effectively reduce both glycated haemoglobin levels and body mass index in patients with type 2 diabetes. However, the effects of almonds were not significant concerning fasting blood glucose, 2-hour postprandial blood glucose, various inflammatory markers, and certain other indicators of diabetes. The biological mechanisms attributed to reductions in glycated haemoglobin and body mass index are thought to be related to the nutritional composition of almonds, namely their high fibre content and low glycaemic index.
A Clinical Study published in 2021 in the journal Scientific Reports found that Consumption of green tea enriched with a citrus polyphenol, α-glucosyl hesperidin, can prevent weight gain and reduce body mass index, especially in individuals under 50 years. The research involved a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded, and parallel-group-designed clinical trial. Sixty healthy Japanese men and women aged between 30 and 75 were included in the study. They were instructed to consume a blend of green tea and α-glucosyl hesperidin (GT-gH). Each dosage contained 178 mg α-glucosyl hesperidin and 146 mg of an active ingredient of green tea, called EGCG. This protocol was followed for 12 weeks. Participants underwent physical, hematological, blood biochemical, and urine examinations to ensure safety. Discussion of findings showed that the GT-gH mixture played a significant role in weight management. By the end of 12 weeks, participants who consumed the GT-gH mix showed prevention in weight gain and a reduction in body mass index when compared to the control group. The anti-obesity effect was particularly observable in individuals aged below 50. These participants experienced lower levels of triglyceride, body fat percentage, and visceral fat levels, alongside a decrease in body weight, BMI, and blood LDL/HDL ratios.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology found that Green tea extract could be considered a potential agent to attenuate PCOS complications mainly due to its effect on weight loss and glycemic levels. Current evidence indicates that green tea extract (GTE) supplementation has potential beneficial effects on PCOS. Of 314 articles found in the search, four human studies and four animal studies were included. All studies in humans showed the effects of GTE on weight loss. GTE's effect on decreasing testosterone levels in humans and LH levels in animals were also reported. In addition, increases in FSH and progesterone levels in animal models were observed. Although GTE improved fasting blood sugar and insulin levels, the effect of GTE on inflammatory parameters, such as TNF-alpha and IL-6 and antioxidant status, was limited to animal studies.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Complementary Medicine Research found that Soy food intake, particularly fermented soy products, appear to have a protective effect on fracture risk among Asian women, especially in early menopause. The research team carried out a systematic review of prospective cohort studies investigating the link between soy food intake and fracture risk. The databases searched were PubMed, Scopus, and Embase up to June 2021, and the team narrowed down 695 records to include 5 high-quality cohort studies. These selected studies were mostly conducted in China, Singapore and Japan and varied in their focus on different types of fractures. The dietary intake of soy food was assessed across all studies through face-to-face interviews. In the analysis of the results, a promising relationship was found between the consumption of soy foods and a reduced risk of fractures among Asian women, notably for those in the early stages of menopause or those who consumed fermented soy products. In contrast, the association was not significant among men.
A Animal Study published in 2021 in the journal Nutrients found that Adzuki beans, when added to a high-fat diet, lessen obesity, improve liver function, enhance insulin sensitivity, and balance gut microbiota. In the experiment, mice were placed on one of three diets for 12 weeks: a low-fat diet, a high-fat diet, or a high-fat diet supplemented with 15% adzuki beans. The study observed and tested for changes related to obesity, lipid accumulation, serum lipid and lipopolysaccharide levels, liver function, hepatic steatosis, glucose homeostasis, insulin sensitivity, and gut microbiota imbalances. Through a process called PICRUSt2 analysis, the researchers were then able to draw potential associations between changes in the gut microbiota and the metabolism of various substances. In the discussion of the results, the supplementation of adzuki beans to a high-fat diet had a significant impact. Obesity and lipid accumulation were visibly reduced, as were negative impacts on liver function and unhealthy levels of serum lipids and lipopolysaccharides. Notably, glucose homeostasis was improved through an increase in insulin sensitivity. The imbalances in gut microbiota, typically seen in a high-fat diet, were significantly reversed through adzuki bean supplementation. High-fat diet dependent taxa returned to a more normal status, which in turn suggested associations with the metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids, sulfur, and two types of amino acids.
A Experimental Study published in 2021 in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition found that Co-fermentation of Ganpu tea with Chachi peel alters its chemical profile, reducing certain compounds while increasing others, thus enhancing its unique flavor. In the research, the effects of Chachi peel cofermentation on the chemical profile of Ganpu tea were examined using an ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-Q Exactive Orbitrap mass spectrometry (UHPLC-QE Orbitrap MS)-based qualitative and quantitative method combined with multivariate analysis. A total of 171 compounds were identified using a three-level strategy, including seven phenolic acids, 11 flavan-3-ols, and 27 flavonoids and flavonoid glycosides identified in pu-erh tea for the first time. The principal component analysis (PCA) of untargeted metabolomics and orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) models of targeted components revealed significant differences in the chemical profiles between raw pu-erh tea and Ganpu tea. The cofermentation process significantly reduced the total contents of phenolic acids, flavan-3-ols, and flavonoid aglycone. However, most of the quercetin glycosides, myricetin glycosides, and vitexin increased significantly. Additionally, hesperidin, a flavonoid glycoside only found in Chachi, was detected in pu-erh tea for the first time after cofermentation. Hence, this process clearly impacts the chemical composition and content changes in pu-erh tea, suggesting that cofermentation accelerates the fermentation of pu-erh tea and improves its unique taste.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Medicina found that Coffee extract supplementation significantly improves parameters of metabolic syndrome, with the effects varying according to the types and doses of coffee administered. In this systematic review and meta-analysis, the researchers sourced relevant articles from PubMed and Scopus published between 2015 and 2020. The investigation focused on randomised controlled trials that studied the impact of coffee consumption on factors like body measurements, blood sugar indices, lipid profiles, and blood pressure. Effects of green coffee extract (GCE) supplementation and decaffeinated coffee were analysed in the study. Following a meticulous extraction and analysis of data from the relevant studies, the researchers found significant improvements in parameters of metabolic syndrome upon supplementation with GCE and decaffeinated coffee. The GCE supplementation, ranging from 180 to 376 mg, was found to reduce waist circumference, triglyceride levels, systolic and diastolic blood pressure while increasing high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol levels. The intake of decaffeinated coffee reduced fasting blood glucose levels. The analysis revealed improvements in metabolic syndrome outcomes for participants consuming GCE and liquid decaffeinated coffee.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2021 in the journal Phytotherapy Research found that Pomegranate extract supplement shows potential in improving glycemic indicators, serum lipids, anthropometrics, and blood pressure in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. The study involved 44 patients who had been diagnosed with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. These individuals were randomly assigned to two groups, with one group receiving two pomegranate extract tablets daily over a period of 12 weeks, and the other a placebo. The researchers measured anthropometric values, serum lipid levels, blood pressure, and glycemic indicators before and after the intervention. In their analysis of the outcomes, the researchers found that the group which received the pomegranate extract showed reductions in total cholesterol, triglyceride levels, the ratio of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, fasting blood sugar, resistance to insulin, diastolic blood pressure, weight, body mass index, and waist circumference when compared to the placebo group. Additionally, an increase in serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol was observed within the pomegranate group, indicating the potential utility of this supplement in a treatment regimen for this condition.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2021 in the journal Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology found that A new method for assessing the effects of therapies on atherosclerosis shows that pomegranate juice/extract has a significant influence on carotid vessel-wall-plus-plaque thickness. The study utilized a tracked weighted average of carotid vessel-wall-plus-plaque thickness change in patients who've been randomly assigned to consume pomegranate juice/extract or placebo. Three-dimensional ultrasound images of patients' arteries were captured initially and a year later. These images were reassembled into three-dimensional maps and then projected onto a carotid template to create two-dimensional maps. A weight was calculated at every point on the two-dimensional map to spotlight the anatomic locations where plaque progression or regression was likely. The method used accounted for misalignment within a single subject and across various subjects to deliver a more precise assessment. The results showed a remarkable difference between patients who consumed pomegranate juice/extract and those who took placebo, based on the weighted average of vascular wall thickness change, observed from the two-dimensional maps with aligned correspondence. Thus, the study concluded that pomegranate juice/extract significantly impacts atherosclerosis, underscoring its value in the context of therapy. This methodical approach also significantly heightened the cost-effectiveness of preliminary trials for new atherosclerosis therapies.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2021 in the journal United European Gastroenterology Journal found that Small-intestinal release peppermint oil is a cost-effective treatment for Irritable Bowel Syndrome, yielding modest quality of life gains and relieving abdominal pain. In the research study, a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled trial was carried out to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of small-intestinal release peppermint oil - an often used treatment - in patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). The cost-effectiveness was analyzed from a societal perspective, using two different approaches: costs per Quality of Life Years (QALY) and costs per successfully treated patient or abdominal pain responder. The later was defined according to Food and Drug Administration (FDA) definitions. Sensitivity analyses were also conducted to further substantiate the results. This comprehensive evaluation involved 126 IBS patients randomly assigned to receive either placebo or peppermint oil. The findings showcase that peppermint oil took precedence as a dominant and effective treatment compared to placebo in considerable number of cases. Not only did it prove more successful at reducing the abdominal pain experienced by IBS patients, but analysis also positioned it as a viable option with regards to the cost-effectiveness ratio based on QALY. The results displayed that peppermint oil came out as a financially savvy treatment in varying scenarios, demonstrating a high probability of cost-effectiveness when evaluated using the abdominal pain responder outcome measure.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Nutrients found that Chocolate and cocoa product consumption significantly improved lipid profiles, but had no significant effect on other heath aspects such as cognitive function and blood pressure. A systematic search was performed on academic databases such as MEDLINE, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials. The researchers utilized a precise search strategy and keywords to gather the most relevant studies and evidence. The studies focused on a variety of health effects related to the consumption of chocolate and cocoa products, like their effects on skin, cardiovascular health, anthropometry, cognitive function, blood glucose levels, and overall quality of life. The research revealed considerable improvements in lipid profiles (particularly in triglycerides) among those who consumed chocolate or cocoa products, compared to controls. However, there were no significant differences observed in other outcome parameters related to skin health, blood pressure, cognitive function, anthropometry, blood glucose levels, and quality of life between the chocolate/cocoa consumption group and the control group. The subjects generally accepted chocolate well, with gastrointestinal disturbances and unpalatability reported as their main concerns.
A Network Pharmacology published in 2021 in the journal Plants found that A combination of extracts from chrysanthemum were found to be more effective in treating hyperuricemia and potentially developing anti-hyperuricemic functional foods. The methodology used in this study involved treating human liver cancer cells, mouse renal proximal tubule cells and hyperuricemic mice with uric acid extracted from two different plants, specifically L. (Ci) and Siebold and Zucc. (Co). It was found that the extracts from these two plants, both individually and in combination, suppressed the activity of certain enzymes involved in uric acid metabolism and influenced the expression of corresponding proteins. In discussing the results, the study identified that the combined effect of these two extracts was significantly stronger in suppressing uric acid accumulation compared to using each extract on its own. This was evidenced by an increased excretion of waste products associated with uric acid metabolism when using the combination of Ci and Co. There was also a decrease in the expression of certain proteins that facilitate uric acid accumulation. Therefore, the data suggests that a mixture of Ci and Co extracts could be effective in developing functional foods to combat hyperuricemia.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal BMC Cancer found that D-Limonene, a bioactive compound found in citrus peels, shows potential anticancer activity and is better tolerated in breast cancer patients compared to its derivative perillyl alcohol. For the methodology, the researchers conducted a comprehensive scoping review. They included peer-reviewed journal articles that reported on the effects of d-limonene and its derivatives on breast cancer in human subjects. They retrieved articles from academic databases including PubMed, EMBASE, CINAHL, Web of Science, and Cochrane reviews, and also through iterative review of bibliographies of relevant manuscripts. Titles and abstracts underwent a first round of screening against the inclusion criteria, followed by consensus meetings and full article review which resulted in the selection of a final set of studies. The results were reported in accordance with the PRISMA extension for scoping reviews. In the discussion of the results, out of 367 records, five articles reporting on both phase 1 and phase 2 trials were included in the final review. Studies assessing the effect of d-limonene indicated it was well tolerated in participants and demonstrated that d-limonene concentrated in breast tissue could cause a reduction in tumor cyclin D1 expression, associated with halting tumor proliferation. Trials with perillyl alcohol, however, showed low tolerance and no effect on breast cancer. The analysis did not reveal a meaningful change in serum biomarkers linked with breast cancer, with the exception of an increase in insulin-like growth factor-1 levels, which is typically associated with higher cancer risk.
A Experimental Study published in 2021 in the journal Complementary Therapies in Medicine found that The Licorice and Jujube formula is seen as commonly used and potentially effective for treating menopausal symptoms as per classical Chinese medicine. The methodology of this study involved exploring classical Chinese medicine textbooks to find the most frequent herbal mix used for symptoms similar to menopause. The approach taken was to sort and identify the formulas from the Encyclopedia of Traditional Chinese Medicine, a comprehensive resource in this field. Following this, a thorough review of randomized controlled trials was performed in order to determine the efficacy of the most common formula. In terms of results, it was discovered that the Licorice and Jujube formula (LJF) was the most commonly found, mentioned in 36% of the analyzed references. The review of controlled trials revealed that the LJF might be effectively utilized for the improvement of sleep-related symptoms. Additionally, experimental studies hinted at potential benefits of the LJF, including sedative, antidepressant-like, estrogenic, and antiprogestogenic effects.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases found that Drinking coffee may be linked to lower mortality risk in type 2 diabetes patients. In this study, the researchers conducted an exhaustive literature search through PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Sciences up to November 2020. They were looking for prospective cohort studies that evaluated the link between coffee consumption and the risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes. Two reviewers took on the work of extracting relevant data and assessing the certainty of evidence using the GRADE approach. A random-effects model was deployed to estimate hazard ratios. Dose-response connections were modeled using a one-stage mixed-effects meta-analysis. The researchers included ten prospective cohort studies that totalled 82,270 cases. The results showed an interesting trend: compared to those who did not consume coffee, the hazard ratios were consistently lower for mortality outcomes and cardiovascular disease, especially where the consumption rate was four cups per day. Importantly, no such association was found for either cancer mortality or stroke. The evidence suggested a potential inverse monotonic association between coffee drinking and mortality across all causes and cardiovascular disease, alongside a linear association for coronary heart disease and total cardiovascular events. The degree of certainty in these results was moderate for all-cause mortality, but was low or very low for all other reported outcomes.
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal Food Chemistry found that Pu-erh tea, with its complex components, interacts greatly with gut microbiomes and holds significant potential for healthcare applications. Pu-erh tea undergoes a post-fermentation process involving various microorganisms, leading to highly complex components. This tea has its potential benefit due to its rich interactions with the gut microbiomes; the structure and the homeostasis of which are deeply connected to human wellness and progress of various diseases. This study provides a systemic review of the current findings pertaining to the bioactive components of Pu-erh tea and their interactions with gut microbiomes. For the discussion of results, the beneficial effects of Pu-erh tea on gut microbiomes may establish its role in healthcare. These benefits are due to the tea's bioactive components' impacts on the structure of the gut microbiomes, and subsequent health improvements. Additionally, the establishment of "components-function-indicators" clues can propel the standardisation of the tea's fermentation process and development of functional tea-related products.
A Experimental Study published in 2021 in the journal Journal of Neurochemistry found that Zeaxanthin dipalmitate, a wolfberry-derived carotenoid, can delay retinal degeneration in mice modelling Retinitis Pigmentosa mainly through its anti-inflammatory and oxidative stress effects. In the study's methodology, Zeaxanthin dipalmitate (ZD) was intravitreally injected into mice on postnatal day 16. Subsequent assessment of retinal function and structure were made at P25 using visual behavior tests, multi-electrode-array recordings, and immunostaining. The involved gene expressions and their regulation by ZD were delved into through transcriptome sequencing and western blotting. In the discussion of results, it was discovered that ZD treatment significantly improved the visual behavior of the mice and delayed degeneration of the retinal photoreceptors, enhancing the light responses of photoreceptors, bipolar cells, and retinal ganglion cells. The ZD treatment led to a decline of up-regulated genes connected to inflammation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress. The study found that ZD reduces the activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and chemokine ligand 2, down-regulates the expression of the inflammatory factor GFAP, and withholds extracellular signal regulated protein kinases and P38, but not JNK pathways. All these findings indicate the potential of ZD as treatment for Retinitis Pigmentosa.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Chinese Medicine found that A variety of Chinese herbal medicines have been reported to effectively prevent or treat nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by regulation of the gut microbiota and the gut-liver axis. The key roles of CHMs in the regulation of gut microbiota and the gut-liver axis along with their mechanisms (such as modulating intestinal permeability, reducing the inflammatory response, protecting liver cells, improving lipid metabolism, and modulating nuclear receptors), were well summarized. All the knowledge and information presented here will be very helpful for researchers to better understand the applications and mechanisms of CHMs for treatment of NAFLD.
A Animal Study published in 2021 in the journal Foods found that Adzuki bean extracts have shown more potential than black soybean extracts in lowering blood pressure in hypertensive rats, acting on the renin-angiotensin system. The methodology used in this research involved the administration of varying volumes of black soybean and adzuki bean ethanol extracts to seven groups of rats, which included one group of normal rats and six groups of spontaneously hypertensive rats. The purpose of the extracts was to explore their antihypertensive effects on aspects such as blood pressure, the renin-angiotensin system, and aortic lesions. The results revealed that black soybean and adzuki bean extracts significantly reduced various biomarkers such as liver weight, triglycerides, total cholesterol, and systolic blood pressure. On a comparative basis, the adzuki bean extracts (AE) demonstrated a greater antihypertensive potential than black soybean extracts (BE). Specifically, the angiotensin II level and blood pressure in the AE-treated group were lower than those in the BE-treated group, leading to the conclusion that AE exhibits higher antihypertensive potential.
A Animal Study published in 2021 in the journal Journal of Medicinal Food found that Omega-3 fatty acids found in selected fish oils, particularly smoked eel, effectively managed dyslipidemia and reduced cardiovascular disease risk factors. The study began by inducing dyslipidemia through a high fat diet in a mouse model. After 30 days of this diet, all animals displayed hyperlipidemia. Subsequently, the diet was switched to consist of 90% standard rodent chow and 10% oil derived from different fish varieties (eel, sardine, cod liver, trout). This diet was maintained for the next 60 days. Blood glucose, total blood cholesterol, triglycerides, and high-density lipoprotein were quantified at the end of the study period. Additionally, the fish oils' omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acid percentages and ratio were taken into account by using gas chromatography. The results showed that incorporating fish oils in the diet considerably improved the hyperlipidemic state triggered by the high-fat diet. Specifically, eel and cod liver oil diets led to significant decreases in triglycerides. Meanwhile, all diets, apart from the standard rodent chow and sardine, resulted in noticeable decreases in blood glucose. Interestingly, smoked eel stood out as the best source for omega-3 fatty acids due to its optimal balance of omega-6 fatty acids, excellently alleviating the mixed hyperlipidemia induced by the high-fat diet.
A Experimental Study published in 2021 in the journal Chemistry & Biodiversity found that Chrysanthemum, a traditional Chinese medicine, shows significant antioxidant activity and hepatoprotective effects, making it a potential resource for functional foods and medicinal materials. A comprehensive evaluation of 25 common chrysanthemum varieties in China was carried out for their chemical constituents, antioxidant activity, and hepatoprotective effects. Initially, the water extracts from chrysanthemums were analysed using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and 29 chemical components were identified. It was observed that chrysanthemums were rich in chemical constituents with significant differences in the contents of phenolic acids and flavonoids among the varieties. Afterwards, the antioxidant activities of different chrysanthemums were investigated through different assays. The relationships between nine main components and antioxidant activities were examined to identify the antioxidant constitutes in chrysanthemums. The study also examined the capacity for each cultivar to protect against cell damage, with certain cultivars standing out with higher efficacy. The hepatoprotective effects of eight mainstream varieties were determined using a model of acute alcoholic liver injury. The chrysanthemums were found to protect the liver from injury by impacting relevant liver function and antioxidant indexes. Selected varieties could decrease certain liver activities, while others significantly decreased harmful content in liver tissue, showing significant antioxidant capacity.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Molecules found that Green tea consumption has been found to be effective in preventing the contraction of influenza infections. To identify the potential benefits of green tea in influenza prevention, a methodical review and combined analysis of eight distinct research studies involving 5,048 participants was completed. The effect of green tea catechin treatment was tested against control conditions and assessed based on infection rates. Five of these studies were randomized controlled trials involving 884 participants and three were cohort studies with 2,223 participants. Subgroups such as those who gargled or took orally ingested forms of green tea were also analyzed separately. Further to this, the possibility of publication biases was evaluated using Begg's and Egger's tests. The results showed both the randomized trials and the cohort studies displayed significant preventative effects on influenza infection for those treated with green tea catechins. Notably, there was no evidence of non-uniformity within the data, reinforcing these findings. The pooled results of different consumption methods further supported these findings, showing no disparities among the subgroups. These results suggest the consumption of green tea has tangible prophylactic effects against influenza infection.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Veterinary Medicine and Science found that Ginger significantly improves sperm health, enhancing quality parameters like count, viability, motility, morphology and DNA integrity, thereby boosting fertility. The study investigated the impact of ginger on semen quality across different species. It focused on key sperm parameters including count, viability, motility, morphology, and DNA integrity. The research pointed to the antioxidant properties of ginger, attributed to active phenolic compounds, which disrupt the production of free radicals - these are known to cause oxidative stress and negatively impact the quality of sperm. The study also noted ginger's androgenic activity and the associated influence on the levels of gonadotropin and sex hormones, such as testosterone. In the discussion of results, it was identified that ginger minimizes DNA failures, reduces damage to the mitochondrial genome in sperm cells, and essentially moulds a sperm with apt morphological structure. The sperm, under the influence of ginger, attains progressive motility, high viability, and increased fertility. Overall, the entire fertility indicators of sperm also saw an upswing with the usage of ginger - reinforcing its effectiveness in increasing the total motility, survival rate, the normal morphological structure of sperm, and the number of sperm cells.
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal Metabolites found that The date palm enhances both male and female fertility parameters through its nutritional attributes and antioxidant functionality. The research conducted a thorough review of the role of date palm in treating infertility. The health benefits of date palm and its varied components were explored, with a focus on their effects on reproductive parameters in both sexes. The comprehensive review shed light on how the substantial nutrients and antioxidant features of date palm can be beneficial for people dealing with infertility. In men, the study found direct links between consumption of date palm and improved hormonal levels alongside notable enhancements in seminal vesicle parameters and sperm quality. For women, this natural remedy showed a positive impact on the process of oogenesis, hormone regulation, and improving pregnancy outcomes. The focus was on the potential of date fruit as a natural enhancer of fertility, downplaying the role of any synthetic or invasive medical interventions. The study thus testifies to the innovative use of a widely available natural resource in addressing a pressing health issue.
A Experimental Study published in 2021 in the journal Molecular Nutrition & Food Research found that Boron-rich mineral and medicinal waters can significantly increase boron accumulation in fruit flies and humans, largely elevating their boron status. The researchers used inductively coupled mass spectrometry to analyze boron concentrations in 381 types of German mineral and medicinal waters, with the highest concentrations found in waters from southwest Germany. They associated the boron content with the concentration of several other bulk elements, including calcium, potassium, magnesium, and sodium. After selecting mineral waters with varying boron content - low, medium, or high - exposure experiments were conducted on fruit flies and humans. Attributed to drinking boron-rich waters, there was a higher accumulation of boron observed. In fruit flies, this build-up of boron mainly occurred in the exoskeleton. Meanwhile in humans, an increase in serum boron and 24-hour urinary boron excretion was recorded. The data provided strong indications that the boron status in both fruit flies and humans could be enhanced through the intake of such boron-rich waters.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal International Journal of Biological Macromolecules found that Tremella fuciformis polysaccharides effectively reduce inflammation in ulcerative colitis, promoting healing by restoring intestinal and mucus barrier functions. In this study, two models were utilized to investigate the impacts of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharides on ulcerative colitis: a dextran sodium sulfate-induced mice model and a lipopolysaccharide-stimulated model using Caco-2 cells. First, the dextran sodium sulfate-induced mice ulcerative colitis model was administered with the Tremella fuciformis polysaccharides. Effects were observed across several indicators such as body weight, colon length, and thickness, as well as intestinal permeability. Following that, histopathological analysis and electron microscope examinations helped delve deeper into the relationship, uncovering a reduction in inflammatory cell infiltration and a restoration of the intestinal epithelial barrier integrity. The lipopolysaccharide-stimulated Caco-2 cells model was used to further understand the role of these polysaccharides in reducing expressions of pro-inflammatory cytokines and increasing expressions related to intestinal barrier and mucus barrier.
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal Food Reviews International found that Date palm tree products and by-products are exceptionally rich in bioactive compounds offering potential health benefits, therefore suitable to be used as natural ingredients in food manufacturing. This research paper undertakes a review study summarizing the sensory properties, nutritional profiles, and health-promoting biocompounds found in date fruit and its by-products. By-products include low-quality dates, pits, leaves, and pollen; all derived during the date fruit processing. The research also followed up on recent findings regarding these products' potential development for new functional foods. The discussion assesses that date fruits and their by-products are deeply rich in unique bioactive compounds like hydroxycinnamic and hydroxybenzoic acids, flavonoids, tannins, carotenoids, tocopherols, tocotrienols, phytosterols, and phytoestrogens. These compounds were noted to contain potential health-boosting properties, making them suitable for use as nutraceutical ingredients in different food formulations. These formulated foods can aid in meeting the increasing demand for products made with natural ingredients among consumers. Also, it's noted that food matrices serve as excellent vehicles to ensure the bioavailability of these biomolecules present in the date palm products.
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal Nutrients found that Almonds can support colonic microbiota health by promoting microflora richness and diversity, increasing the ratio of symbiotic to pathogenic microflora, and concentrations of health-promoting colonic bioactives. This narrative review of 64 RCTs and 14 meta-analyses and/or systematic reviews presents a more in-depth analysis of almond clinical trials and their effects on weight measures, metabolic health biomarkers and outcomes, and colonic microbiota health than typically described in systematic reviews and/or meta-analyses. Almonds have one of the largest portfolios of RCTs on weight measures, metabolic health, and colonic microbiota of any food. These RCTs consistently support an important role for almonds in reducing body and fat mass, other weight measures, and promoting metabolic health as a premier snack for precision nutrition diets
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal Nutrients found that Recent systematic reviews and meta-analyses of nut RCTs showed that almonds were the only nut that had a small but significant decrease in both mean body mass and fat mass, compared to control diets. The biological mechanisms for almond weight control include enhanced displacement of other foods, decreased macronutrient bioavailability for a lower net metabolizable energy (ME), upregulation of acute signals for reduced hunger, and elevated satiety and increased resting energy expenditure.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Phytotherapy Research found that The consumption of cocoa or dark chocolate can reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and fasting blood sugar levels in diabetic patients. A systematic search of databases identified eight randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with 433 participants for meta-analysis. The results demonstrated a substantial reduction in LDL-c levels (WMD: −15.49 mg/dl) and FBS concentrations (WMD: −6.88 mg/dl) following cocoa/dark chocolate consumption. The study emphasizes the potential positive effects of cocoa/dark chocolate on the metabolic profile of diabetic individuals. The meta-analysis included RCTs focusing on cocoa/dark chocolate interventions in diabetic patients, with a significant pooled analysis showing reduced LDL-c and FBS levels. The findings suggest that incorporating cocoa/dark chocolate in the diet of diabetic individuals could be beneficial for managing lipid profile and glycemia. Further research is necessary to solidify these insights and understand the complete impact on metabolic health.
A Animal Study published in 2021 in the journal Animals found that Goji berry supplementation in does' diet positively influences both their reproductive and productive performance, likely through adjustment of hormonal patterns and milk production. In the methodology, this study involved an experiment with 105 nulliparous does divided into three groups two months prior to artificial insemination. The groups were distinguished by their diet: the commercial diet and those supplemented with either 1% or 3% of goji berry. They focused on assessing the effects on hormonal profile and the animals' receptive, productive, and reproductive performance. The results shed light on increasing receptivity in the group that was supplemented with 1% goji berry over the commercial diet group. Departures noted between both goji-supplemented groups with regard to hormonal concentration, specifically LH, with G1 showing slight edge. There was also a significant interaction effect observed in estrogen concentrations. Additionally, the 1% goji-supplemented group showed higher litter weight than the commercial diet group at both birth and weaning stages, along with a larger litter size at weaning. This group also exhibited the highest average milk production. The study concluded that goji berry supplementation potentially has a positive impact on reproductive and productive performance, possibly through the modulation of hormonal patterns and milk production in rabbits.
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal Molecules found that In reproductive health, honey can improve infertility, protect the postmenopausal reproductive tract, prevent toxic effects, maintain sperm quality by restoring testosterone levels and treat vulvovaginal candidiasis infections. Honey has a highly complex chemical and biological composition that consists of various essential bioactive compounds, enzymes, amino and organic acids, acid phosphorylase, phytochemicals, carotenoid-like substances, vitamins and minerals. Reproductive health and fertility rates have declined in the last 30 years. Therefore, this review aimed to highlight the protective role of honey as a potential therapeutic in maintaining reproductive health. The main role of honey is to enhance fertility and treat infertility problems by acting as an alternative to hormone replacement therapy for protecting the vagina and uterus from atrophy, protecting against the toxic effects of xeno-oestrogenic agents on female reproductive functions and helping in the treatment of gynaecological disorders, such as vulvovaginal candidiasis infection, that affect women’s lives.
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal Clinical Ophthalmology found that Curcumin, with its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial and antimutagenic properties, is a potential therapeutic agent for retinal diseases. This review paper uses various pieces of research from the literature to detail the characteristics of curcumin, a molecule produced by plants. The paper particularly focuses on the beneficial and controversial aspects of curcumin. It talks about the retina's susceptibility to oxidative stress due to its cell composition and constant exposure to photons, highlighting that retinal ganglion cells and photoreceptors are particularly sensitive to oxidative damage. The paper also points to studies that link an imbalance in reactive oxygen species to a wide range of retinal diseases. In the discussion of results, it is stated that a number of studies suggest that curcumin can be well tolerated by humans when taken orally and does not tend to have negative effects, making it a promising candidate for retinal disease treatment. However, a primary limitation is curcumin's poor bioavailability; the body can only absorb a small fraction of the substance as an active compound. Despite that, efforts have been made to improve curcumin's accessibility to target tissues in sufficient quantities.
A Experimental Study published in 2021 in the journal Journal of Ethnopharmacology found that Fructus Lycii and Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge extract improve retinal morphology and function by regulating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway to curb oxidative reactions. In terms of methodology, Fructus Lycii and Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (FS) extracts were identified through Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography analysis and administered intragastrically over four weeks to Rd10 mice, known to model retinitis pigmentosa. Following the animals' sacrifice, histopathological examination and Scotopic electroretinography analysis were performed. Oxidative stress markers were determined and the expression levels of Nrf2 and HO-1 mRNA were evaluated via quantitative real-time PCR. Western blot and immunohistochemistry were employed to identify the expression and distribution of Nrf2 and HO-1 protein. In the discussion of the results, substantial morphological improvements were observed regarding the thickness and number of the Outer Nuclear Layer, along with significant functional enhancements in a-amplitude and b-wave amplitude measurements, following FS extract treatment. In addition, the treatment led to a considerable escalation in superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase levels and a reduction in malondialdehyde levels. Furthermore, FS extract was found to stimulate the up-regulation of Nrf2 and HO-1 mRNA and protein expression, possibly underlying the observed retinal enhancements.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2021 in the journal Complementary Therapies in Medicine found that Lavandula angustifolia essential oil inhalation seemed to enhance overall sleep patterns, quality, and efficiency in postmenopausal women with insomnia. Methodology: 35 postmenopausal women, clinically diagnosed with insomnia, were recruited and divided into two groups - an Aroma Group and a Placebo Group - for a double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Over 29 days, participants in the Placebo Group inhaled sunflower oil, while participants in the Aroma Group inhaled lavender oil. Both groups were given sleep hygiene guidelines before embarking on the trial and received follow-up on a weekly basis. Evaluations were performed both pre- and post-intervention. Discussion of Results: No significant differences were noted between the two groups in terms of sleep quality. However, certain tendencies were observed. Aroma Group participants showed a noteworthy reduction in the time taken to fall asleep, depression levels and postmenopausal symptoms such as hot flashes. Moreover, polysomnography data showed increased sleep efficiency in comparison to initial levels. The improvement in sleep quality over time was observed in both groups, indicating that sleep hygiene instruction and weekly follow-ups played a significant role in influencing sleep patterns and quality.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology found that Phytoestrogens, used in various forms, have shown improvement in urogenital menopause symptoms and improved women's sexual function, promoting overall quality of life. A thorough and systematic review was conducted on databases including PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, Cochrane library, Scopus and ProQuest, spanning from the years 2000-2020. The focus was solely on randomized clinical trials. An evaluation of the quality of selected papers was carried out using the CONSORT checklist. In total, 33 high-quality papers were reviewed which discussed the different forms and uses of phytoestrogens. The results of this systematic review reveal that phytoestrogens including Pueraria Mirifica, fennel, Hop plant, Glycine Max, soy, red clover, black cohosh, ginsing, cimicifugaracemosa, genistein, diadzein, glycitein and isoflavone, used as various products such as oral capsules, pills, food supplements, enriched powders, vaginal gels, creams and suppositories, improved menopausal urogenital symptoms. Particularly, the recovery rate was found to be higher when these were applied vaginally. Further implication of these findings is the enhancement of women's sexual function following treatment, validating the use of phytoestrogens as a safe, low-risk and accessible method to alleviate urogenital symptoms.
A Clinical Study published in 2021 in the journal Journal of Herbal Medicine found that Green tea therapy can significantly improve rheumatoid arthritis symptoms, correlating with changes in specific circulating serum molecules, miR-125b and miR-146a. In this study, 100 female patients suffering from rheumatoid arthritis and 50 healthy female subjects were examined. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis underwent green tea therapy, where they consumed 5 cups of green tea daily, delivering a total of 1230 mg of catechins, over a span of 24 weeks. During this time, researchers used real-time PCR analysis to measure the levels of miR-146a and miR-125 b in the patients' peripheral blood mononuclear cells. These cells were isolated from the subjects at three distinct stages: the starting point (baseline), after 12 weeks, and finally after 24 weeks of the treatment. The observations revealed a notable increase in the level of circulating miR-125 b and decrease in miR-146 expression, and these shifts were seen to correspond positively with measures of disease activity and pain intensity in the patients after 24 weeks of the green tea therapy. Also of note was that the levels of miR-146a and miR-125b could accurately predict the clinical response to green tea therapy in 65% of the rheumatoid arthritis patients. Discrepancies in miR-146a and miR-125b levels following green tea therapy suggests that they may be attributed to the joint protective, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects of green tea. It was therefore proposed that both miR-146a and miR-125b could potentially serve as diagnostic, therapeutic, and predictive biomarkers in green tea therapy and may even have valuable application in related non-drug rheumatoid arthritis therapy.
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal Applied Sciences found that There is a notable gap in scientific research on the potential health benefits and antioxidant activity of matcha tea compared to green tea. The strategy used in this study was a literature review that critically evaluated existing research publications on both green tea and matcha tea. This focused primarily on the concentration and potential benefits of their bioactive components and polyphenols. Key areas of comparison included antioxidant activity and potential health benefits in each tea variety. The comparison was made simultaneously considering the scarcity of studies specifically focused on matcha tea. The discussion of the results became apparent that there is a significant discrepancy in the volume of scientific literature available on green tea compared to that on matcha. Despite matcha tea being rich in bioactive components and polyphenols, the lack of research has left its potential health benefits and antioxidant activity largely unexplored. This discrepancy emphasizes the immediate need to address the gap between public usage and awareness of matcha tea's benefits with scientific approval and understanding.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2021 in the journal Genes & Nutrition found that Consumption of blueberry supplement did not show significant improvement in metabolic health markers, however, it induced changes in gene expression, indicating a potential longer-term effect. The methodology of the study involved a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled intervention trial conducted with adults at risk of developing Metabolic Syndrome (MetS). Participants, consisting of 49 individuals, were asked to consume 50 grams daily of either a freeze-dried highbush blueberry powder or a placebo powder for a duration of 8 weeks. Metabolic Syndrome phenotypes were evaluated at the beginning, 4 weeks in, and at the end of the trial. To assess any metabolic changes, fasting blood gene expression profiles and plasma metabolomic profiles were observed at the start and the end of the 8 weeks. In examining the results, while significant change was reported for plasma triglyceride levels, the findings did not remain significant after adjusting for age, sex, BMI, and baseline values. Furthermore, no significant difference was observed with respect to body weight, blood pressure, fasting plasma lipid, insulin and glucose levels, insulin sensitivity, or glycated hemoglobin concentrations when comparing the blueberry supplement with the placebo. The distinctive findings were in gene expressions and the presence of certain metabolites. The blueberry supplement caused significant changes in 49 gene expressions and the abundance of 35 metabolites, and these differentially regulated genes largely belonged to immune-related pathways.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition found that Cocoa-rich products consumption can improve mood and affect in the short term. The study carried out a systematic review and meta-analysis in line with PRISMA guidelines to ascertain the effects of cocoa-derived food on depressive and anxiety symptoms, as well as positive and negative affect. Potential sources were found on Web of Knowledge and PsycINFO until April 3, 2020. Out of 761 documents screened, nine studies were picked. Two trials were involved in examining the long-term impact (>1 week) of cocoa consumption, two reviewed the short-term effects (3 days), and five studies were conducted in acute conditions (single administration). The results indicate that cocoa-rich products had a significant overall effect on reducing depressive and anxiety symptoms. There was also significant improvement in both positive and negative affect. The effect size in all meta-analyses was medium, while the heterogeneity was low. Despite these promising outcomes, the conclusions must be cautiously interpreted due to the short duration of the trials and the limited number of participants and studies included in the meta-analyses.
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal Gastroenterology Insights found that Tea polyphenols can help rebalance gut microbiota, alleviating imbalances caused by obesity, diabetes, and UV damage, with effects varying by tea type. The methodology of this review involved the process of collecting and analyzing various studies dealing with the effects of tea polyphenols on gut microbiota in both humans and animals. This included studies observing the overall gut health in relation to conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and UV damage. The comparative approach was used to differentiate the effects of different types of tea on distinct bacterial taxa present in the gut. In discussing the results, it was found that tea polyphenols consistently improved and diversified gut microbiota in animal tests. In contrast, while human trials also showed improved gut health seemingly due to a prebiotic-like effect of tea polyphenols, the evidence was not as conclusive. However, the outcomes did show that different types of teas had differing effects on the bacterial taxa present in the gut.
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal Molecules found that Green tea and its chief bioactive component have the potential to improve certain female reproductive disorders such as endometriosis, polycystic ovary syndrome, and dysmenorrhea. The study reviews the beneficial effects of green tea and its major bioactive component on female reproductive disorders, focusing on endometriosis, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and dysmenorrhea. The research highlights the role of catechins, phenolic compounds found in tea, which have been known for their health benefits due to their high antioxidative properties. The green tea or its derivative works on endometriosis through anti-angiogenic, anti-fibrotic, anti-proliferative, and proapoptotic mechanisms. In the discussion of results, it was found that green tea not only enhances ovulation and reduces cyst formation in PCOS, but it also ameliorates generalised hyperalgesia, reduces plasma corticosterone levels, and mitigates uterine contractility in dysmenorrhea. Despite the promising findings, the study acknowledges the need for more comprehensive clinical trials to fully translate these findings into clinical practice.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Food and Chemical Toxicology found that Cocoa flavanols exhibit health and aging benefits and may act as powerful agents in preventing chronic diseases such as cardiovascular and metabolic disorders, and cancer. This research primarily relies on a comprehensive review of numerous human studies conducted over the past two decades. These studies provided significant data related to the health effects of cocoa intake and its impact on various chronic diseases. The studies encompassed different demographics and health conditions. Though most studies indicate beneficial effects of cocoa on health and prevention of chronic diseases, the results exhibit some inconsistency. Different studies suggest various mechanisms of action for cocoa, but these potential pathways are still not completely understood. Also, crucial issues like recommending cocoa consumption to healthy subjects or patients, determining the appropriate dosage, or the period of intake remain unresolved. Despite these unclarities, the potential of cocoa use to decrease the risk for certain chronic diseases and improve general health and quality of life is emphasized.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2021 in the journal Clinical Nutrition found that Eating sardines twice a week for a year significantly reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in prediabetic individuals aged 65 and above. In this study, 152 individuals with prediabetes and age 65 or older were chosen from three primary care centers in Barcelona. These subjects had a fasting glucose of 100-124 mg/dL. They were divided into two intervention groups: a control group (CG) and a sardine group (SG). While both groups were given the same nutritional diet to prevent type 2 diabetes for a year, the sardine group was instructed to include 200 grams of sardines in their diet every week. Data including fasting glucose levels, type of diet followed, and other demographic variables were collected before starting and after ending the diet. After a year, the sardine group, when compared to the control group, showed significant reductions in the percentage of individuals classified as very high risk for developing type 2 diabetes. The sardine group also showed improved health parameters such as increased HDL-cholesterol and adiponectin levels, decreased triglyceride levels, and slightly reduced blood pressure. Additionally, the consumption of sardine nutrients - omega-3, EPA and DHA, vitamin D, fluorine, and taurine - was significantly higher in the sardine group. Further, changes in erythrocyte membrane fatty acids were detected only in the sardine group, which included a decrease in 5 omega-6 fatty acids and an increase in 3 omega-3 fatty acid types.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2021 in the journal Clinical Nutrition found that A one-year, sardine-enriched diet in an elderly population with pre-diabetes exerts a greater protective effect against developing type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular events. Following the nutrition intervention, 29.6% of SG subjects had left the "very high" risk group (from 37.3% to 7.7%), while only 4.9% of CG subjects had managed to do so (from 27.3% to 22.4%), a finding which is significantly different.
A Experimental Study published in 2021 in the journal Free Radical Biology and Medicine found that Black pepper and its major component, piperine, can effectively regulate anemia of inflammation by reducing the overexpression of hepcidin, a hormone that controls iron levels. The study involves a two-tier investigation, first in vitro, and then in vivo. In the laboratory, different black pepper extracts were interacted with a human liver cell line known as HepG2, and the one derived from methanol (BPME) showed the most promising result because it reduced the transcription of the hepcidin gene significantly. In addition to BPME, piperine was proven to almost entirely suppress hepcidin protein expression at specific concentrations. In the subsequent in vivo experimentation, live mice were artificially induced with an elevated level of hepcidin through oil of turpentine injections. Then they were administered with BPME and piperine, the effects of which significantly reduced the enhanced hepcidin expression. The molecular interaction studies further suggest that piperine directly binds with SMAD1 and STAT3 proteins, the critical factors behind the overexpression of hepcidin. The study found a demonstrable downregulation in hepcidin expression with the use of both the methanol extract of black pepper and the bioactive alkaloid piperine. These substances also interacted with some proteins to lower the overexpression of hepcidin initiated by inflammation. Additionally, there was a noticeable increase in iron bioavailability in the liver of treated test animals, pointing to the potential of these compounds to rectify anemia of inflammation. The findings posited black pepper as a possible therapeutic option for managing this anemic condition.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal The American Journal of Medicine found that Coffee consumption, particularly boiled coffee, may increase levels of certain cardiovascular risk markers, but no strong link was found to anti-inflammatory effects. Methodically considering pre-selected databases such as PubMed, Embase, CINAHL and more, this study rigorously searched for randomized controlled trials to analyse the impacts of coffee consumption on inflammatory indicators of cardiovascular risk. Duplicate data and trials that did not meet the study's criteria were removed. The remaining 17 studies that passed scrutiny were included in the analysis, looking particularly at effects of coffee on cholesterol levels, apolipoprotein B levels and interleukin 6 levels. This comprehensive review resulted in interesting findings. Boiled coffee emerged as a potential culprit for increased levels of total and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol along with apolipoprotein B. Filtered coffee, on the other hand, did not show similar trends. In one trial, caffeinated coffee showed a noteworthy increase in blood interleukin 6 levels compared to participants who did not consume coffee. However, no robust anti-inflammatory effects connected to coffee consumption could be confidently ascertained to be a significant factor in reducing mortality rates related to cardiovascular disease.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2021 in the journal Physiology & Behavior found that Combining resistance training with saffron supplementation enhances happiness levels and increases dopamine and serotonin concentrations more than resistance training alone. In this research, untrained young males were divided into two groups, one receiving resistance training coupled with saffron supplementation (150 mg pill of pure saffron post-workout and at a similar time on rest days), while the other received resistance training with a placebo (dextrose pill). For a period of six weeks, whole-body supervised resistance training was performed four times per week with three sets using 60-70% of their single repetition maximum. Various markers implicated in depression and happiness levels were assessed before and after this period. In terms of results, substantial increases in various markers including Anandamide, Arachidonoylglycerol, dopamine, and beta-endorphin were noticed within the group combining resistance training with saffron supplementation, yet no such changes were evident within the group who took the placebo. Compared to the placebo, the saffron group also experienced more significant improvements in happiness levels. Moreover, serotonin levels increased in both groups but were greater in the saffron-supplemented group, while tryptophan concentrations remained unchanged. Notably, both groups noted significant boosts in muscular endurance; these changes were greater with saffron supplementation.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases found that Consumption of certain foods like rapeseed/canola oil, avocados, and turmeric can lead to moderate to large reductions in LDL cholesterol levels. The research was carried out by conducting a systematic evaluation of existing guidelines, systematic reviews, and Randomised Control Trials (RCTs); we have only referred to the latter for studies on coffee intake. This was done on databases such as PubMed, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, alongside a search on the Trip database for guidelines. The time frame for the study was from its inception up until June 2019 and October 2019 respectively. Studies were included if they were at least 13 days in duration and were in English. Using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) method, 37 guidelines, 108 systematic reviews, and 20 RCTs were evaluated to analyze the strength of evidence in the context of food impacts on LDL cholesterol levels. The results of the research reveal that foods high in unsaturated and low in saturated and trans fatty acids such as rapeseed or canola oil, those with added plant sterols/stanols, and those high in soluble fibre like oats, barley and psyllium cause moderate reductions in LDL cholesterol. A moderate to a large increase was observed with unfiltered coffee though. Soy protein, tomatoes, flaxseeds, and almonds cause small reductions. Meanwhile, foods like avocados and turmeric cause moderate to large reductions with a moderate level of evidence supporting this observation. Other foods like pulses, hazelnuts, walnuts, high-fiber/wholegrain foods, green tea result in small to moderate reductions, and sugar causes a small increase. Several foods identified were either neutral or had low or very low evidence regarding their effects on LDL cholesterol levels.
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal Journal of Ethnopharmacology found that Pomegranate has a variety of phytochemicals which possess wide-ranging activities including antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-oncogenic properties, and resistance to cerebrovascular disease. The paper presents an overview of the traditional medicine theories of pomegranate, its origin and spread along the Silk Road, ethnopharmacological uses, chemical compositions, pharmacological activities, toxicology, and the involved pathways. Information was collected from various published sources like ancient and modern texts, medicinal plant monographs, pharmacopoeias and diverse electronic databases. Pomegranates, being widely cultivated in Central Asia and having spread throughout China via the Silk Road, have had significant usage in many traditional medical systems over time. They are identified to contain a vast array of phytochemicals like tannins, organic acids, flavonoids, alkaloids, and volatile oils. These compounds are observed to have extensive activities such as antioxidant, antimicrobial and anti-oncogenic properties, and also provide resistance to cerebrovascular disease. The research additionally presents a summary of the promising pharmacological pathways linked with pomegranate.
A Experimental Study published in 2021 in the journal International Journal of Molecular Sciences found that Two French natural mineral waters (NMW1 and NMW2) show anti-inflammatory effects and can reduce intestinal inflammation in mice with induced colitis. The study investigated the anti-inflammatory effects of two French natural mineral waters (NMWs) - NMW1 (rich in calcium, magnesium, sodium, carbon, and iron) and NMW2 (mainly bicarbonate) - on intestinal inflammation. Intestinal epithelial cells were stimulated with heat-inactivated Escherichia coli or hydrogen peroxide and then treated with NMWs. Additionally, moderate colitis was induced in Balbc/J mice using 1% dextran sulfate sodium. These mice were then given either NMW1, NMW2, or control water. The study assessed general symptoms, histological features of colitis, fecal lipocalin-2 levels, pro-inflammatory KC cytokine levels, and the global mucosa-associated microbiota. Both NMW1 and NMW2 showed anti-inflammatory effects in treated intestinal cells. In the colitis-induced mice, NMW1 notably reduced inflammation, evidenced by lower disease activity scores, reduced fecal lipocalin-2, decreased release of pro-inflammatory KC cytokines, and smaller intestinal epithelial lesions. NMW1 also helped in maintaining the normal state of mucosa-associated microbiota. These findings suggest the potential of these NMWs in managing inflammatory bowel disease through modulating gut microbiota.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology found that Tremella polysaccharide is a safe natural active ingredient, which can be used in the prevention, treatment and rehabilitation of diseases. Tremella polysaccharide is a full-functioning active substance, and any of its activities are not independent, but complementary to other activities. For example, Tremella polysaccharides can participate in various physiological activities such as type II diabetes, cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, inflammation and aging by regulating the expression of SIRT1 protein, which is in line with the guidelines of eastern medicine to maintain the dynamic balance of the human body through conditioning. Tremella polysaccharides are non-toxic and harmless natural ingredients that can be used for long-term contact with the human body by smearing or oral administration. It means that Tremella polysaccharides are suitable for the daily health needs of sub-healthy people and can be widely used in food, medicine and daily chemical products.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2021 in the journal BMC Endocrine Disorders found that Adding oat bran to the diet of pregnant women with gestational diabetes can help significantly reduce their fasting and postprandial blood glucose levels. In the methodology of this study, a randomized clinical trial was conducted on 112 pregnant women suffering from gestational diabetes. These women were randomly split into two groups of 56. Both groups were given a diet specifically designed for managing gestational diabetes. However, the intervention group additionally received 30 grams of oat bran daily at lunch and dinner for a period of 4 weeks. The researchers performed tests on fasting blood glucose and two-hour postprandial glucose levels for both groups prior to the intervention and then at two-week intervals during the intervention. The results of the study revealed that the average blood glucose level before the intervention showed no significant differences between the two groups. However, both the mean fasting blood glucose and the two-hour postprandial glucose levels of the intervention group showed a significant decrease two and four weeks after the intervention when compared with the control group, due to the addition of oat bran in their diet.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2021 in the journal Journal of Complementary and Integrative Medicine found that Avocado/soy unsaponifiables effectively treat osteoarthritis by controlling the balance between oxidant and antioxidant molecular markers. The methodology used in this study was a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, cross-over trial. Forty osteoarthritis patients were classified into two groups: one received avocado/soy unsaponifiables (ASU) for three months followed by three months of placebo, and the other group received a placebo first for three months followed by three months of ASU. The patients' oxidant status was evaluated by measuring their serum malonldialdehyde (MDA). Other measures such as total antioxidant capacity, reduced glutathione, and antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase and catalase were also assessed. After three months of treatment, all patients who were given avocado/soy unsaponifiables exhibited a significant decrease in their serum MDA levels, indicating lower oxidative stress. In comparison, these levels were higher at baseline and after placebo treatment. Furthermore, the treatment with avocado/soy unsaponifiables resulted in positive changes in the patients' antioxidant levels. Analysis also showed that the effect of avocado/soy unsaponifiables was consistent, regardless of the sequence in which the medication was received. These findings demonstrate that avocado/soy unsaponifiables can contribute effectively to the treatment of osteoarthritis by regulating the balance between oxidant and antioxidant molecular markers.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology found that These results indicate that a certain concentration of snow fungus polysaccharides can effectively alleviate skin damage caused by UVA, and they may be used as an effective component of cosmetics. Tremella fuciformis polysaccharides (TFPS) pretreatment can reduce the oxidative stress of UVA-treated human dermal fibroblasts cells. After TFPS pretreatment, the content of ROS and MDA in the cell decreased significantly and the total antioxidant activity was increased. Among them, the active of CAT, SOD, and GSH-Px in the cells increased significantly. TFPS can also protect fibroblasts by up-regulating Nrf2 and down-regulating Keap1 expression. Finally, it was also found that TFPS pretreatment increased the content of collagen I, elastin, and hyaluronic acid (HA) in skin fibroblasts treated with UVA.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Angiology found that Epidemiological studies suggest that the consumption of spicy chilli food is associated with reduced risk of all-cause as well as heart disease–related mortality. This systematic review and meta-analysis examined the association between spicy food (chilli pepper, chilli sauce, or chilli oil) consumption with cardiovascular and all-cause mortality. Medline and EMBASE were searched from their inception until February 2020 to identify relevant prospective cohort studies. Hazard ratios (HRs)/relative risk (RRs) were pooled via random-effect meta-analysis. Of the 4387 citations identified, 4 studies (from the United States, China, Italy, and Iran) were included in the meta-analysis. The included studies involved a total of 564 748 adults (aged ≥18 years; 51.2% female) followed over a median duration of 9.7 years. The pooled data suggested that compared with people who did not regularly consume spicy food (none/<1 d/wk), regular consumers of spicy food experienced a 12% (HR/RRpooled 0.88, 95% CI, 0.86-0.90; I 2 = 0%) lower risk of all-cause mortality. Moreover, spicy food consumption was associated with significant reduction in the risk of death from cardiac diseases (HR/RRpooled 0.82, 0.73-0.91; I 2 = 0%), but not from cerebrovascular disorders (HR/RRpooled 0.79, 0.53-1.17; I 2 = 72.2%). In conclusion, available epidemiological studies suggest that the consumption of spicy chilli food is associated with reduced risk of all-cause as well as heart disease–related mortality. Further studies in different populations are needed to confirm this association.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal International Journal of Molecular Sciences found that Isoflavones found in soybeans can reduce risks of certain cancers and alleviate menopause-related symptoms among women, such as vasomotor syndromes, spinal bone loss, and hypertension. The study overviewed soybeans' chemical composition and focused mainly on isoflavones. The research examined the processes of soybean preparation that includes cleaning, drying, crushing, and dehulling, and extraction methods to derive various soy products, particularly focusing on isoflavones - daidzein, genistein, and S-equol. Various soy products such as refined soy oil, soy lecithin, free fatty acids, glycerol, and soybean meal were discussed, along with the presence of the minor biological constituents in remaining components. The study explored the relationship between isoflavone consumption and disease prevention, particularly in relation to heart disease, cancer incidence—of the breast, bladder, and endometrial and colorectal—and menopause-related symptoms. The therapeutic effects of isoflavones were studied in the context of vasomotor syndromes, spinal bone loss, hypertension regulation, depressive symptoms during pregnancy, and in vitro glycemic control. In contrast, it failed to find definitive effects of isoflavones on cognition improvement and urogenital symptoms. The inconsistencies in defining the ingredients, doses, study durations, and outcomes of isoflavone studies proved challenging for the research.
A Cohort Study published in 2021 in the journal Nutrients found that Moderate coffee consumption may potentially reduce the risk of low HDL-C and high fasting blood glucose amongst Korean male adults. The study was designed to evaluate the link between coffee intake and the onset of metabolic syndrome, utilizing participant data sourced from the Health Examinees study. Metabolic Syndrome was identified based on the criteria set by the Adult Treatment Panel III of the National Cholesterol Education Program. The researchers deployed a multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression model to examine the relationship between different levels of coffee consumption and the incidence of metabolic syndrome. In the analysis of the results, moderate coffee consumption, approximately 1-3 cups per day, in male participants was found to have an inverse correlation with low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and high fasting blood glucose. More so, this inverse correlation was further observed with the consumption of 3-in-1 coffee, which includes sugar and creamer. This suggests that male habitual coffee drinkers may be less likely to experience low HDL-C and high fasting blood glucose, key markers of metabolic syndrome.
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal Journal of Food Biochemistry found that Pomegranate demonstrates anti-proliferative, anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory properties that can effectively control the progression of various respiratory diseases. The research methodology involved both in vivo and in vitro studies to examine the potential effects of pomegranate fruit, juice, extract, peel powder, and oil on a variety of respiratory disorders such as asthma, lung cancer, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The focus was to understand the properties of pomegranates that led to its anti-proliferative, anti-oxidant, anti-microbial, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and anti-tumorigenic effects, and how these qualities could potentially attenuate these diseases through modulation of various signaling pathways. The discussion of results revealed that pomegranate was effective in controlling the progression of diverse respiratory diseases, suggesting it could be a key therapeutic target. These results not only demonstrated the potential medical benefits of pomegranate against lung-based diseases but also highlighted its possible role in influencing the lung fibrinolytic system. The findings from both preclinical and clinical studies underscored the influence of pomegranate in tackling lung diseases.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Cureus Journal of Medical Science found that A systematic analysis indicates that ginger has a higher safety profile than NSAIDs for pain relief, with a smaller number of gastric side effects and fewer kidney risks. The use of ginger is very useful and effective as NSAIDs because of the increasing trend in the use of traditional medicine and herbal medicine, particularly for people who do not want to use chemical drugs with more side effects.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Cureus Journal of Medical Science found that Based on beneficial effects and minimal side effects, ginger may be a potential adjunct treatment for primary dysmenorrhea. This review has shown that ginger can minimize pain in one or two periods. The present analysis provides compelling proof of the impact of ginger on relieving menstrual pain. The finding in this study has verified the possibility of ginger efficacy in the treatment of primary dysmenorrhea, though no/small side effects have been identified and its use is associated with health benefits. Ginger is easily accessible due to its low cost. It can also be commonly used in the treatment of primary dysmenorrhea. The use of ginger is very useful and effective as NSAIDs because of the increasing trend in the use of traditional medicine and herbal medicine, particularly for people who do not want to use chemical drugs with more side effects. We strongly recommend that further research be performed with a greater number of patients regarding the effectiveness and protection of various doses of ginger.
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine found that The fresh rhizoma of Roscoe, a traditional Chinese medicine, has proven effects on the nervous and cardiovascular systems and has antibacterial, antitumor, and antioxidant properties. The methodology for this comprehensive review encompased the exploration of the botany, ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology of Zingiberis Rhizoma Recens. This involved studying over 100 chemical compounds found in the fresh rhizoma of Roscoe, including gingerols, essential oils, and diarylheptanoids among others. Various modern scientific methods and principles were employed in order to establish a broad understanding of the medicinal properties and potential applications of the herb. The results of the review demonstrated the multitudinous health benefits of Zingiberis Rhizoma Recens. In particular, it has thoroughly documented pharmacological effects on the nervous and cardiovascular systems. Moreover, it has been shown to have antiemetic, antibacterial, antitumor, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant effects. The study reinforced the wide usage of the herb in traditional Chinese medicine and underscored the versatility of its applications. However, it also revealed disparities in the evaluation standards of the herb's quality and clinical efficacy.
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal Current Neuropharmacology found that Saffron and its components, crocin and crocetin, show potential in treating various eye disorders, including inflammation, macular edema, and glaucoma. Using key search terms like "eye disorders" and "saffron", the authors conducted a systematic review of various literature databases such as PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar. Their search included all types of studies, with no strict inclusion criteria, covering clinical studies, in vivo and in vitro studies. They extracted data from each study for qualitative analysis. The review started with 78 articles, narrowed down to 29 relevant ones. Nine articles were clinical trials, and 20 articles examined the impact of saffron on cellular and molecular aspects of eye disorders. Through their analysis, researchers found that saffron protects photoreceptor cells from light-induced damage, decreases glucose levels in diabetic mice, and mitigates the pro-inflammatory response in retinal cells. They reported improved visual function in age-related macular edema and lowered intraocular pressure in patients with glaucoma. Furthermore, crocin, one of the saffron's main ingredients, was found to enhance the best corrected visual acuity and decrease central macular thickness in patients suffering from diabetic maculopathy.
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal Molecules found that Bee honey and propolis could have potential beneficial effects as supporting treatments for COVID-19, enhancing immunity and inhibiting viral activity. The study's methodology involved a comprehensive review of the literature on the potential anti-COVID-19 effects of bee honey and propolis, products known for their strong antimicrobial and antioxidant abilities. The researchers conducted molecular simulations to see how various flavonoids found in these products might inhibit essential viral processes. Additionally, they compared the effectiveness of propolis extracts delivered by nanocarriers to ethanolic extracts, and they examined the effects of a combination of honey and propolis on hospitalized COVID-19 patients. The findings from the review and simulations suggested that certain flavonoids in honey and propolis may inhibit the fusion of the virus spike with host cells, interactions that cause a cytokine storm, and viral replication. Propolis ethanolic extract, rutin, and propolis liposomes displayed inhibitory action against non-structural proteins of the virus in vitro while naringin inhibited viral infection in specific cells. When delivered via nanocarriers, propolis extracts showed enhanced antiviral effects against the virus compared to ethanolic extracts. Observations of hospitalized patients suggested that those treated with green Brazilian propolis or a honey-propolis combination experienced quicker viral clearance, symptom recovery, and hospital discharge, along with lower mortality rates.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies found that Raspberry leaf for childbirth, highlighting the lack of robust evidence on its effects, safety, and efficacy during pregnancy, emphasizing the need for more comprehensive research. This study aims to assess the evidence regarding the effects, safety, and efficacy of raspberry leaf in pregnancy-related contexts. The systematic integrative review analyzes 13 studies, spanning animal and human research, showcasing raspberry leaf's biophysical impact on uterine muscle. While evidence is limited, human studies indicate no significant harm or benefit, though one suggests a potential reduction in second stage labor duration and labor augmentation. Further research is warranted to better understand raspberry leaf's effectiveness in pregnancy.
A Experimental Study published in 2021 in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition found that Supplementation with standardized saffron extract improves depressive symptoms and social relationships in healthy individuals experiencing subclinical low mood and stress. The study employed a double-blind, randomized, parallel groups design involving 56 healthy male and female participants aged between 18 and 54. They received either 30 mg standardized saffron extract or a placebo daily for 8 weeks. The saffron's chronic effects on subjective feelings of anxiety, stress, and depression were evaluated using a series of questionnaires. The acute effects of saffron following exposure to a lab-based psychosocial stressor were determined through assessing psychological and physiological parameters. As part of the process, the level of crocetin, a compound found in saffron, was quantified in the participants' urine. The results indicated that individuals who received the saffron extract reported lower depression scores and improved social relationships after the 8-week period. A significant increase in urinary crocetin levels was observed with saffron supplementation, and these changes were found to be correlated with a decrease in depression scores. Additionally, the usual decrease in heart rate variability, a reaction commonly seen during the exposure to stressors, was found to be diminished after acute intake of saffron. The findings suggest that saffron extract can help improve subclinical depressive symptoms in healthy individuals and may increase resilience against the development of stress-related psychiatric disorders.
A Animal Study published in 2021 in the journal Foods found that Traditional fermented products made from soybeans and rice, commonly consumed in the Japanese diet, show significant potential in preventing the progression of fatty liver disease. In the study, C57BL/6J mice were first acclimated for two weeks. Following this period, they were segregated into groups and fed on different diets for a duration of 20 weeks. These diets included a Normal Diet (ND), a High-Fat Diet (HFD), an HFD containing 5% of the fermented soybean and rice product (denoted as HFD+M), and an HFD with 5% of a pre-fermented form of the product (HFD+PFM). The focus was on assessing the impact of these diets on the development of fatty liver disease in the subjects. The mice consuming solely the high-fat diet developed the symptoms of a typical fatty liver, as anticipated. However, the mice fed with diets that included either the fermented soybean and rice product or its pre-fermented variety showed a substantial reduction in the progression of the fatty liver disease, notably in the female subjects. This was observed in terms of diminished liver weight. Moreover, a decrease was noted in the levels of leptin and resistin, hormones linked with obesity and insulin resistance, in the serum of these groups. The male subjects also showed resistance against fatty liver disease progression upon the consumption of these diets. This study therefore demonstrates the value of including such traditional fermented food products in the diet as possible deterrents against lifestyle-induced ailments like metabolic syndrome.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2021 in the journal Journal of Functional Foods found that Enriching a regular diet with oat β-glucan can improve glycemic control, augment feelings of fullness, and positively modulate gut microbiota in individuals with type-2 diabetes. The research involved 37 subjects with type-2 diabetes, who were required to consume either oat β-glucan or microcrystalline cellulose as a control dietary supplement each day for a period of 12 weeks. The parameters assessed throughout the study included fasting glucose, insulin, a variety of hormones and peptides regulating appetite (like ghrelin, leptin, GLP-1, PYY), caloric intake, and the profile of their intestinal microbiota. The results indicated a decrease in HbA1c, insulin, C-peptide levels, as well as certain bacterial populations (Lactobacillus spp, and Butyrate-producing bacteria) in subjects who consumed β-glucan. Significant differences were observed in levels of certain hormones, namely leptin, GLP-1, and PYY, between the two groups. The intake of oat β-glucan emerged as a potential strategy to manage type-2 diabetes, by improving glycemic control, enhancing feelings of satiety, and fostering a healthier gut microbiota profile.
A Experimental Study published in 2021 in the journal Antioxidants found that Pomegranate juice extract (PPJE) appears to reduce chemotherapy-induced skin side effects by inhibiting inflammation and promoting wound repair on the skin. In this study, the impact of pomegranate (L.) juice extract (PPJE) on skin cells treated with 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU), an antineoplastic agent, was evaluated. This involved assessing the extract's ability to inhibit the release of reactive oxygen species and enhance the cellular antioxidant response of the treated skin cells. Specific attention was given to observe the overexpression of cytoprotective enzymes such as heme oxygenase-1 and NAD(P)H dehydrogenase [quinone] 1 after the introduction of PPJE. The results indicated that PPJE indeed blocked the formation of nitrotyrosine and reduced the release of cytokines, therefore indicating a dampened inflammatory response. Furthermore, it was revealed that the extract could inhibit the nuclear translocation of p65-NF-κB, a key regulator of inflammation. The study also pointed out that PPJE could curb apoptosis in cells treated with 5-FU, whilst fostering wound repair. The overall findings suggest that PPJE holds potential as a supplementary agent for managing oxidative and inflammatory issues associated with chemotherapy-induced skin side effects.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Molecules found that Current evidence shows that short-term honey supplementation following surgical or physiological menopause exerts an oestrogenic, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effect on the female reproductive system. A systematic literature search using Scopus, MEDLINE via Ovid and Cochrane Library databases was conducted. Records were screened and identified for preclinical and clinical studies addressing the effects of HS on the FRS. Data on populations, interventions, outcomes and methodological quality were extracted. Studies were synthesised using tables and written summaries. Of the 198 identified records, six fulfilled the inclusion criteria. All six records were used for data extraction: two experimental studies using rats as the model organism and four human clinical studies of honey on female reproductive health. HS elevated the progesterone levels, restrained body weight increase, prevented uterine and vaginal atrophies in ovariectomised rats, attenuated symptoms of candidiasis and improved oxidative status in patients.
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal Molecules found that Green tea, coffee, wine, and curry have beneficial health effects due to the polyphenols they contain, which possess both antioxidant and pro-oxidant properties. The research leverages epidemiological studies, clinical trials, cell-based studies and animal tests to examine the effects of green tea, coffee, wine, and curry -- and their key polyphenols -- on human health. The polyphenols investigated include epigallocatechin gallate in green tea, chlorogenic acid in coffee, resveratrol in wine, and curcumin in curry. The study concentrates on the workings of these polyphenols, primarily focusing on reactive oxygen species (ROS), and how they perform both anti- and pro-oxidant functions, fundamentally influencing different enzymes and factors with health contributions. In the discussion of the results, it is mentioned that the anti-oxidative actions of these polyphenols assist in the scavenging of ROS and the downregulation of the nuclear factor-κB, yielding beneficial anti-inflammatory effects. Conversely, their pro-oxidant actions appear to elevate ROS production, encouraging the activation of 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase that regulates different enzymes and factors for health improvement. However, the exact mechanism of how these polyphenols exhibit either pro- or anti-oxidant effects remains unclear. Also, the research underscores that while many studies note their health benefits, some others show no positive effects on health conditions such as obesity, suggesting that outcomes could be influenced by various study factors.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Annals of Medicine found that The existing evidence, although with low level of confidence, suggests that walnut intake may have a beneficial effect on cognition-related outcomes, including cognitive function, mood, and stroke. The existing evidence, although with low level of confidence, suggests that walnut intake may have a beneficial effect on cognition-related outcomes, including cognitive function, mood, and stroke. Limitations in study design and comparability render the available evidence insufficient to draw a firm conclusion regarding the effects of walnut on cognition in adults. High quality studies and standardized interventions and measurement tools are necessary to determine the role of walnut intake in cognitive health.
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal Food Reviews International found that Oily fish, particularly sardines, due to their high omega-3 and taurine content, may play a protective role in slowing the progression towards type 2 diabetes. The methodology used in this research involved an integrative review of both observational studies and clinical trials to study the potential correlation between sardine consumption and preventing type 2 diabetes. The focus was specifically on oily fish that are rich in omega-3 and taurine and contain low amounts of persistent organic pollutants, with a special emphasis on sardines due to their high concentration of the beneficial compounds. The results illustrated a possible protective effect of consuming oily fish, particularly sardines, against the progression towards type 2 diabetes. Despite the controversy surrounding fish consumption and diabetes risk, it was observed that the high content of omega-3 fatty acids and taurine in these fish might be a key factor in their potential antidiabetogenic effect. However, the presence of persistent organic pollutants in these fish creates a challenge that needs careful consideration.
A Clinical Study published in 2021 in the journal Food & Function found that Consumption of blueberries can alter levels of certain beneficial compounds in the blood, potentially contributing to improved cognitive function in older adults. The research method involved a study on 38 healthy older adults between 60 to 75 years of age, over a 90-day period. Participants were randomly assigned to two groups – a blueberry group and a control group. The blueberry group received 24 grams of freeze-dried blueberries, equivalent to a cup of fresh berries, every day, while the control group received no treatment. Blood samples were taken from the subjects before breakfast and two hours post-breakfast, on the start day, the 45th day and the 90th day. Additionally, the study subjects also took cognitive tests on these days. Results showed that after 90 days, there were significant changes in the levels of circulating phenolic compounds, including such compounds as hippuric acid, phloroglucinaldehyde and syringic acid, among others, in the blood of those who had consumed blueberries. Moreover, improvements in cognitive functions were observed and these changes were linked to alterations in the concentrations of specific phenolic compounds like ferulic acid-glucuronide, syringic acid, and malvidin-3-galactoside. These results suggest a correlation between daily blueberry consumption, changes in phenolic compounds in the blood, and improvements in brain performance.
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal SSRN Electronic Journal found that Phytochemicals in carrots, particularly carotenoids, are effective at reducing eyesight degeneration and treating chronic eye defects due to their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Throughout the review process, seventy original research and review articles were examined, all published between 2000 and 2020 across four major journal databases: Elsevier, PubMed, ResearchGate and Plos One. The focus of the search was directed by six keywords, centring on both in-vivo and in-vitro study results related to the topic of interest. Among the various findings, it was consistently revealed that carrots contain a multitude of bioactive compounds, notably carotenoids, which have been proven to be effective in halting and treating eye degenerations including Nyctalopia, Myopia, Cataracts, Age-related Macular Diseases and Glaucoma. Carotenoids have been found to work as potent antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents, defending eyes against vision loss due to oxidative stress. Thus, the increased consumption of carrots can potentially serve as a natural therapeutic approach and enhancer of vision.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Food & Function found that Almond intake significantly changed the concentrations of triglycerides, total cholesterol and low-density lipoproteins To estimate the overall effect of almond intake, we employed the random-effect model. In total, 27 studies with 36 effect sizes were included in our analysis (1154 cases and 904 control subjects). The meta-analysis revealed that almond intake significantly changed the concentrations of triglycerides, total cholesterol, and low-density lipoproteins; however it did not have a significant effect on high-density lipoprotein levels. Meta-regression analysis indicated a linear relationship between the dose of almond and change in TG. This meta-analysis concludes that almond intake can significantly reduce lipid parameters.
A Experimental Study published in 2021 in the journal JBRA Assisted Reproduction found that Pomegranate seed oil, rich in conjugated linolenic acid, potentially acts as a cytotoxic agent on tissue tumor cells, reducing polycystic ovary syndrome manifestations. First, data for this study was collected from several databases including the Cochran library, Medline, PubMed, SID, and Science Direct. Keyword searches incorporating phrases such as "medicinal plants", "polycystic ovary syndrome", "plant", "pomegranate extract", and "menstrual irregularities" were used to uncover relevant articles spanning from 1985 to 2021. The focus of the research was to investigate the impact of pomegranate seed oil, particularly its conjugated linolenic acid (CLN) content, on polycystic ovary syndrome, a prevalent endocrine disorder among women. The results revealed that CLN, found abundantly in pomegranate seed oil, had been previously reported to exert a potent cytotoxic effect on tumor tissue cells within the body. This characteristic placed CLN as a potential agent in predenting cancer, lowering LDL cholesterol in the blood, reducing triacylglycerol accumulation in the liver, and importantly, mitigating the effects of polycystic ovary syndrome. Alongside this, the research also underscored the beneficial effects of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), another group of linoleic acid isomers, in cancer growth inhibition, risk reduction of atherosclerosis, and body fat decrease.
A Experimental Study published in 2021 in the journal Gaceta Sanitaria found that Ginger honey supplementation does not reduce cortisol levels, however, it significantly increases glutathione and estrogen levels in test mice. The methodology involved an in vivo pretest-posttest control group design study conducted on 2-3 month old female Balb/c mice, selected due to not having experienced conception. These mice were split into a negative control and an intervention group, the latter receiving 28mg/20g body weight of ginger honey for 14 days. Prior to the supplementation, the mice were subjected to swimming-induced stress. Cortisol, glutathione, and estrogen levels were assessed using the ELISA testing method. In the discussion of results, the findings indicated that 14 days of ginger honey supplementation did not significantly affect cortisol levels in the female mice. Contrastingly, a considerable boost was observed in both glutathione and estrogen levels. This suggests a potential role for ginger honey supplements as complementary therapies, though not for the management of cortisol-related stress.
A Meta-Analysis published in 2021 in the journal Phytomedicine found that The study reveals that pomegranate juice does not significantly affect vascular adhesion factors, but can effectively reduce the inflammatory marker, interleukin-6. In order to evaluate the role of pomegranate in endothelial dysfunction, databases including PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Cochrane, and Google Scholar were utilized up until July 2020. Relevant studies were chosen that examined pomegranate's impacts on vascular adhesion factors, namely intercellular adhesion molecule 1, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, E-selectin, and interleukin-6. Computational tools were used to analyse this large data set. The results demonstrated that human studies showed no significant effects of pomegranate juice on intercellular adhesion molecule 1, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, and E-selectin compared to the control group. However, results revealed that pomegranate juice could significantly lower interleukin-6. Despite the absence of significant impacts on vascular adhesion factors, the notable reduction of interleukin-6 suggests the potential of pomegranate juice in treating endothelial dysfunction-related conditions such as cardiovascular diseases.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases found that Higher coffee consumption, specifically 3-4 cups daily, is associated with a 21% lower risk of stroke, with no further reductions with increased intake. The research utilized a systematic review and meta-analysis approach to investigate the link between coffee consumption and stroke risk. Random-effects models were employed to compile relative risk estimates. The assessment was structured to compare the highest and lowest categories of coffee consumption and utilized a one-stage robust error meta-regression model for stroke risk assessment. The study incorporated 21 separate studies which in total included over 2.4 million participants. The findings suggest a significant inverse connection between coffee consumption and the risk of stroke. According to the pooled relative risk analysis, the highest versus the lowest categories of coffee consumption showed a decrease in stroke risk. There seems to be a nonlinear (U-shaped) relationship between stroke risk and coffee consumption, with the lowest risk (21% lower) associated with consuming 3-4 cups of coffee per day. Sensitivity analysis suggested the influence of each individual data set on the overall result wasn't significant, and while some evidence of publication bias was witnessed, additional analysis established that potential bias didn't impact the findings noticeably.
A Review Article published in 2021 in the journal Physiological Research found that Tea and coffee possess health promoting properties and can effectively prevent and treat metabolic disorders, including obesity, through the suppression of fat storage. The paper provides a detailed review of the origin, chemical composition and properties of tea and coffee, including the health benefits associated with them. It specifically focuses on their impacts on fat storage and the potential physiological mechanisms behind their effects. The potential health effects of these plants are attributed, in part, to the presence of caffeine. Additional physiological and medicinal benefits could be linked to other molecules such as theaflavins, catechins, their metabolites and polyphenols found in tea and polyphenol chlorogenic acid in coffee. In the discussion, the paper points out that both tea and coffee can be instrumental in preventing and treating a host of metabolic disorders including metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes and obesity. The mechanism these plants employ to bring about these health benefits is through the reduction of fat storage by suppressing adipocyte functions and supporting gut microbiota. Moreover, tea also exhibits an ability to prevent obesity by reducing appetite, food consumption and food absorption in the gastrointestinal system, as well as modifying the fat metabolism.
A Experimental Study published in 2021 in the journal Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology found that Ginger supplementation can prevent ethanol-induced reproductive dysfunction by improving hormone levels, reducing oxidative damage, inflammation, and regulating genes involved in testosterone synthesis. The methodology involved twenty-four adult male rats divided into four groups for a 28-day experiment. The researchers administered either ethanol or ginger extract to respective groups and then measured varying physiological factors related to reproductive health such as testosterone levels, antioxidant enzyme activity, concentrations of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and gonadotropins hormones. In addition, gene expressions related to oxidative damage, inflammation, and testosterone synthesis were also examined. Animating the discussion of results, it was observed that the administration of ethanol significantly decreased levels of hormones, oxidative markers, and lowered gene expression involved in testosterone synthesis. Conversely, ethanol caused an increase in inflammatory markers and the expression of genes related to inflammation. On the other hand, rats given a ginger supplement positively reversed these effects, showing significant improvements in all factors, thus leading to the conclusion that ginger can prevent reproductive issues induced by ethanol. The results obtained from the histological study further confirmed these findings, reaffirming that ginger could effectively counter ethanol-induced reproductive dysfunction.
A Experimental Study published in 2021 in the journal Food & Function found that The Lycium ruthenicum Murr variety of goji berry exhibits a stronger antioxidant activity and antiproliferative effect on cancer cells compared to Lycium barbarum L. For methodology, the researchers examined the phytochemical profiles of two different varieties of goji berries: Lycium ruthenicum Murr (LRM) and Lycium barbarum L. (LB). They then evaluated the antioxidant activity of these varieties using multiple assays. For the assessments of antiproliferative effect, they tested the ability of high dose LRM and LB supplementation to interfere with cell cycle progression and induce apoptosis in MDA cells, a specific type of cancer cells. In the discussion of results, it was found that LRM overpowered LB in both antioxidant activity and antiproliferative mechanism, owing to its higher total phenolics and flavonoids. LB, while it was higher in VE and carotenoids, had less remarkable effects on cell cycle interference and apoptosis induction. Both LRM and LB triggered the activation of a proliferation-related signaling pathway; however, LB did not manage to lower the levels of two specific proteins which indicates a weaker antiproliferative effect. Despite these differences, both varieties were considered potential assets for managing the growth of cancerous cells and enhancing human health.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews found that The supplementary intake of green tea does not significantly affect blood glucose, fasting insulin, hemoglobin A1c, and insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. To examine the impact of green tea consumption on type 2 diabetes mellitus patients, a comprehensive search for relevant randomized controlled trials was conducted across multiple databases, including Web of Science, PubMed, and Scopus, without any language or time restrictions until June 2019. Both random and fixed effects models were utilized in the subsequent meta-analysis, with the I2 index employed to assess heterogeneity. The initial search resulted in 780 relevant publications, from which 14 were selected for analysis. The evaluation revealed that additional intake of green tea had negligible influence on fasting plasma glucose, fasting insulin, hemoglobin A1c, and insulin resistance indicators in individuals affected by type 2 diabetes mellitus. This conclusion is drawn from a distinct pool of research without insisting further study or discussing numerical specifics and probabilities.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2021 in the journal Biology of Sport found that Walnut consumption coupled with concurrent training improves lipid profile, steroid hormone levels, and systematic inflammation in elderly men. The study created two matched groups of fit elderly men and placed one on a diet inclusive of walnuts (15g/day for six weeks) alongside their concurrent (resistance and endurance) training. The other group did the concurrent training without the walnut-supplemented diet. The study then took fasting blood samples from the participants 48 hours before and after the intervention for biochemical assessments. The group consuming walnuts saw a significant improvement in their lipid profiles with increased high-density lipoprotein levels and decreased total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein and triglyceride levels. The walnut-eating participants also saw an increase in testosterone levels after the training, which was significantly higher than the group not consuming walnuts. Additionally, the walnut-consuming group experienced lowered cortisol levels and decreased C-reactive protein compared to the group not consuming walnuts. It is plausible the results could be attributed to the presence of polyunsaturated fatty acids in walnuts.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Nutrients found that Coffee's bioactive compounds may exhibit various health benefits such as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties on the digestive tract and stimulating effects on motor function. The methodology involved a narrative review of the impact of coffee; its by-products; and its bioactive components on the gastrointestinal system and the brain-gut axis. The gastrointestinal mucosa's reactions, mainly involving permeability, secretion, and proliferation, the neural and non-neural elements of the gut wall contributing to its motor function, and the brain-gut connection were all elements of critique and consideration. The results from the in vitro, in vivo, and epidemiological studies demonstrated that coffee induces various effects on the digestive system. For instance, it might act as an antioxidant, have anti-inflammatory effects, and act against cell overgrowth in the mucosa. In addition, coffee seems to promote motor functions in the gastrointestinal tract's external muscle layers. Nonetheless, despite these affirmed possible effects, much about coffee's accurate and detailed influence remains largely unexplored.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal International Journal of Molecular Sciences found that Regular coffee consumption, due to its bioactive compounds, may have protective effects against chronic disorders and certain neurodegenerative conditions. The paper evaluates the neuroprotective potential of the main bioactive elements in coffee: caffeine, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, trigonelline, kahweol, and cafestol. The analysis is focused on the coffee beverage as a complex mixture of these bioactive compounds. The comprehensive study includes in vitro and in vivo preclinical tests to determine the specific health benefits each of these compounds can offer. The results indicate that regular coffee intake may have defensive effects against a variety of enduring disorders; including cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, obesity, and some forms of cancer. Additionally, an interesting correlation is found between coffee consumption and a lower risk of developing certain neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and dementia. The study also highlights that regular coffee intake could possibly lower the risk of stroke. However, the study mentions that the mechanisms enabling these effects are yet to be fully understood.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Nutrients found that Isoflavones, mainly found in soy-derived products, show beneficial effects on bone health, potential cancer risk reduction, and alleviation of menopausal symptoms, but not on cardiovascular risk. The study examined the potential uses of isoflavones, phenolic compounds mostly found in soy-derived foods and several vegetables. Isoflavones are seen as potential alternative therapies for hormone-dependent disorders due to their near-identical chemical structure to estradiol. These disorders include certain cancers, cardiovascular diseases, and menopausal symptoms. The investigation involved reviewing existing scientific evidence to evaluate the potential effects of isoflavones on these diseases and health concerns. In assessing the results, the review found evidence suggesting that isoflavones could have a beneficial effect on postmenopausal women's bone health, contributing to osteoporosis prevention and treatment. However, observed study results were not entirely conclusive due to discrepancies among study designs. Contrarily, there appeared to be no significant protective effect against cardiovascular risk with soy isoflavones. In terms of cancer, preliminary observations suggested that isoflavones may reduce some types of cancer risks, such as breast and endometrial cancer. Lastly, isoflavones showed a potential role in reducing hot flushes associated with menopause. Concerning safety, most common adverse effects were mild and observed at the gastrointestinal level.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Advances in Nutrition found that Regular walnut consumption is consistently linked to improved cognitive performance in adults, particularly those at higher risk of cognitive decline. The methodology of this review involved a systematic search of four different databases - Ovid MEDLINE, Scopus, CINAHL Plus, and Embase, from their inception through to April 2020. The search aimed to identify both interventional and observational studies that investigated the effect of nut intake on cognitive outcomes in adults aged 18 and above. The specific nuts studied included almonds, hazelnuts, macadamias, pistachios, walnuts, pecans, pine nuts, Brazil nuts, cashews, and peanuts. The review then selected the most relevant studies for further analysis; out of 2,374 identified articles, 22 met the criteria, with a combined participant count of 43,793. The resulting discussion of this review's findings highlighted that, despite inconsistencies due to varying study designs and types of nuts studied, regular mixed nut intake could potentially protect cognitive function in different age groups. However, more notable was the recurrent evidence found in studies focusing on groups at a higher risk of cognitive impairment, which repeatedly reported improved outcomes. Particularly, studies specifically targeting walnut consumption consistently found it positively associated with enhanced cognitive performance. The review found homogeneous results within these walnut-centred studies, with only one out of six, including two randomized controlled trials, not reporting a positive association.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2020 in the journal Nutrients found that DKB114, a mixture of Linn flower extract, effectively reduces serum uric acid level, suggesting its potential as a dietary supplement for hyperuricemia treatment. The research employed a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial conducted across a span of 12 weeks. A total of 80 asymptomatic hyperuricemic subjects (serum uric acid level between 7.0-9.0 mg/dL) were selected and equally split into two groups. One group was administered DKB114, the investigational mixture of extracts, while the other group received a placebo. After six weeks of administration, the levels of serum uric acid were evaluated, revealing no significant difference between the two groups. By the end of the 12th week, however, subjects in the DKB114 group exhibited a noticeably larger decrease in their serum uric acid levels when compared to the placebo group. Additionally, various other health indicators including C-reactive protein and apoprotein B levels showed significant trends favoring DKB114. Further evaluations during the trial included clinical pathological tests, weight measurements and vital signs, and electrocardiogram tests which confirmed the safety of DKB114. No significant harmful effects or differences were detected in comparison to the placebo group. This concludes the positive impact and safe use of DKB114 for patients with elevated serum uric acid levels.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2020 in the journal BioMedicine found that Consumption of jujube seed had a positive impact on improving the sleep quality of postmenopausal women and could be recommended as a useful herbal medication. The results show that the medicinal jujube seed capsule improved the sleep quality of postmenopausal women. Thus, it could be recommended as a safe plant with fewer complications compared to chemical and hormone drugs for the treatment of sleep disorders. Also, during the period of consuming jujube seed capsule in this study, except for a few cases of gastrointestinal disorders and in similar studies with this herbal medicine, consumers have reported no specific side effects. Therefore, considering that about one-third of adults in the world suffer from sleep disorders, the high prevalence of sleep disorders in postmenopausal women, and the lower cost of treatment by jujube seed capsule compared to other treatments, it is suggested implementing this treatment as a useful method in improving sleep quality in postmenopausal women.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2020 in the journal Journal of Medicinal Food found that Daily consumption of tart cherry juice may reduce processes involved in accelerated atherogenesis, potentially decreasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. In this randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-arm pilot clinical trial, 19 men and women aged between 20 to 60 years who have metabolic syndrome participated. They were assigned to consume either 240ml of tart cherry juice or an isocaloric placebo-control drink twice daily for a period of 12 weeks. Initial evaluations on arterial stiffness (determined through pulse wave velocity), brachial and aortic blood pressures, wave reflection or augmentation index, and blood markers for cardiovascular and metabolic health were established as their baseline values. Despite observing no significant alterations in hemodynamics, arterial stiffness, or other assessed blood biomarkers, there was a noted decrease in oxidized low-density lipoprotein and soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 levels in the tart cherry juice group compared to the control group at the end of 12 weeks. In addition, there was a trending lower total cholesterol level in the tart cherry group versus the control at the end of the trial. These results suggest that daily tart cherry juice consumption may help decrease processes involved in the rapid progression of atherogenesis.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Journal of Functional Foods found that Jujube fruits contain a high amount of various bioactive compounds exerting antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antiobesity, anti-cardiovascular disease, hepatoprotective, antidiabetic, anti-microbial, anticancer, and gastrointestinal-protective effects. The scientific evidence has shown that jujube fruits contain a high amount of various bioactive compounds, including ascorbic acid, triterpenic acids, phenolic acids, amino acids, saponins, cerebrosides, flavonoids, polysaccharides, and mineral constituents. These phytoconstituents play important roles to suppress different diseases, exerting the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antiobesity, anti-cardiovascular disease, hepatoprotective, antidiabetic, anti-microbial, anticancer, and gastrointestinal-protective effects.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal British Journal of Nutrition found that Consuming walnuts does not significantly alter blood glucose levels, indicating cardiovascular protective effects of walnuts are not due to improved glycaemic control. The study involved a systematic review and meta-analysis of previous randomized trials that investigated the effects of walnut consumption on glycaemic control markers such as fasting blood glucose, insulin, and glycated Hb. Studies were found through a comprehensive search of databases including Medline, PubMed, CINAHL, and Cochrane up to March 2nd, 2019. The included studies' risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool. In light of the results, although 16 studies were included in the review, it was found that walnut consumption did not significantly impact fasting blood glucose levels or other markers for glycaemic control. Recognizing that the studies included in the analysis were either deemed to have 'some concerns' or 'high risk' of bias, these results suggest that the beneficial effects of walnuts on cardiovascular health aren't caused by improvements in glycaemic control.
A Experimental Study published in 2020 in the journal Bioorganic Chemistry found that Green tea polyphenolic compounds, (-)-epigallocatechin (EGC) and (-)-epicatechin-3-gallate (ECG), can diminish harmful Alzheimer's disease linked Aβ aggregates and ameliorate symptoms. Green tea compounds EGC and ECG were tested for their effects on Cu/Zn-induced or self-assembled Aβ aggregation involved in Alzheimer's disease. To do so, a combination of thioflavine T fluorescent spectrometry, inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, UV-Vis spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy, silver staining, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence assays were utilized. Findings indicate that these compounds bind mildly to Cu and Zn and reduce their caused or self-assembled Aβ aggregates. Moreover, these compounds were shown to manage neurotoxicity in mouse neuroblastoma Neuro-2a cells by decreasing the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). From the findings, the EGC and ECG in green tea showed potential in reducing the toxicity of Aβ oligomers and fibrils which are heavily linked to Alzheimer's disease. Notably, ECG has the ability to traverse the blood-brain barrier and reduce Aβ plaques within the mouse brain, showcasing its potential for neuron protection. This study highlights the potential of green tea - specifically, its polyphenolic compounds - in the prevention or reduction of Alzheimer's disease symptoms.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neuroscience found that Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids supplementation during the prenatal and perinatal period could have a protective effect on neurodevelopmental disorders including ADHD, ASD, and MDD in youth. The research implemented supplementation of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids also known as Omega-3 PUFAs, in different quantities and durations to youth with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), major depressive disorder (MDD) and autism spectrum disorder (ASD). This was carried out based on suggested dosage and duration from various randomized controlled trials and systemic literature reviews. It was observed that omega-3 PUFAs were essential nutrients not just for physical health but also for mental health, more so during the prenatal and perinatal stages of development. The results demonstrated that clinical symptoms improved in youth with ADHD, MDD and ASD after they were supplemented with Omega-3 PUFAs, especially in cases where there was high inflammation or low baseline Omega-3 index present. The research showed very promising evidence that Omega-3 PUFAs had positive effects on lethargy and hyperactivity symptoms in ASD. There was also an inclination that Omega-3 PUFAs levels and inflammation could be potential markers for treatment response in ADHD and MDD.
A Experimental Study published in 2020 in the journal Journal of Water and Health found that Mineral water increases the diversity of gut microbiota by aiding the growth of Bacteroidetes taxa. The researchers carried out the study on BALB/c mice, focusing specifically on the bacterial community in their feces and how it responds to different types of drinking water. These types included commercial bottled mineral water, natural water, purified water, and tap water. After culturing the feces in a combination of brain heart infusion broth dissolved in the four water types, they conducted a 16S rRNA gene analysis to study the bacterial composition. The bacterial composition varied significantly between the four different types of drinking water. Over time, the overall number of Operational Taxonomic Units (OTUs) decreased, with the exception of cultures grown in mineral water under aerobic conditions. Under these conditions, by the fifth day, alpha diversity differences were particularly noticeable when comparing mineral water with the other types. The most unique taxa were found within the mineral water group. Notably, the Bacteroidetes taxa showed the most significant differences, dominating in the mineral water compared to the other types of water. This indicates that using mineral water as a culture medium could lead to a progressive increase in gut microbiota diversity.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Frontiers in Pharmacology found that Flavonoids from jujube have been found to stimulate the expression of erythropoietin (EPO), a hormone stimulating blood production. Jujube promotes erythropoiesis via activation of hypoxia inducible factor-induced erythropoietin, possesses potential capacity in recycling heme iron during erythrophagocytosis, exhibits bidirectional role in regulating immune response under different conditions, contains numerous minerals including iron.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Frontiers in Pharmacology found that Recent studies have indicated that jujube possesses a wide range of pharmacological activities in nervous system, cardiovascular system, as well as anti-oxidation and anti-cancer properties. Traditionally in China, jujube is considered as a medicinal fruit that is being used in treating blood deficiency. In this review, the beneficial effects of jujubes on the hematopoietic functions are summarized and discussed. As illustrated in cell and animal models, the application of jujube extract possessed beneficial effects, including regulation of erythropoiesis via activation of hypoxia inducible factor-induced erythropoietin, potential capacity in recycling heme iron during erythrophagocytosis and bi-directional regulation of immune response. Thus, the blood-nourishing function of jujube is being proposed here. Flavonoid, polysaccharide and triterpenoid within jujube could serve as the potential active ingredients accounting for the aforementioned health benefits. Taken together, these findings provide several lines of evidence for further development of jujube as supplementary products for prevention and/or treatment of anemia.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry found that Green tea supplementation raises adiponectin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. For the methodology, an exhaustive search was undertaken in multiple databases including ISI Web of Science, PubMed, Embase, and Scopus to collect research articles pertaining to the effects of green tea supplementation on adiponectin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes up to June 2019. Both random and fixed effects models were employed in the meta-analyses as appropriate. The results of the data gathered from five trials incorporating 333 type 2 diabetic patients show that the implementation of green tea supplementation leads to a notable increase in adiponectin levels when compared to control groups. It showcases the potential role of green tea in managing diabetes through the modulation of adiponectin concentrations.
A Experimental Study published in 2020 in the journal Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine found that Chrysanthemum coronarium L. extract can both stimulate bone building cells and inhibit bone breaking cells, so has potential as a natural treatment for osteoporosis. The study examined the effects of Chrysanthemum coronarium L. extracts on in vitro cell cultures and animal models with bone loss. This was done by observing the increase and decrease of bone formation markers in different cell lines, specifically the murine preosteoblastic cell line MC3T3-E1, and the murine macrophage-like cell line RAW264.7 respectively. The results showed that the extract stimulated the differentiation of osteoblasts, cells responsible for bone formation, and inhibited osteoclast differentiation, cells that break down bone. In osteoporotic animal models, the extract prevented bone loss, preserved the structure of the small bones and improved serum bone turnover markers. This implies that the extract has promising potential as a natural therapy for osteoporotic bone loss.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Complementary Medicine Research found that Green tea consumption notably reduces body weight, body mass index, and body fat, especially in long-term use, at lower dosages, and among overweight individuals with type-2 diabetes. In this systematic review and meta-analysis, a comprehensive search was undertaken on Scopus, ISI Web of Science, and PubMed, for articles related to the topic, up until June 2019. To synthesize the data, a meta-analysis was conducted using the random effects model, and an index was employed to assess the levels of inconsistency in the findings. The assessment of this research involved evaluating eleven eligible articles. Analysis showed that green tea significantly lowered body weight, body mass index, and body fat. Notably, the advantageous effects of green tea were most observable in long-term interventions beyond eight weeks, at doses of green tea equal to or less than 800 mg per day, and among overweight patients. The study underscores the positive role of green tea consumption in improving body composition indicators among type-2 diabetes patients, given these specific conditions.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Antioxidants found that Catechins in green tea potentially counteract osteoporosis by negatively affecting bone loss processes and enhancing bone formation processes. The research paper explores the role of catechins, a key compound found in green tea, in combating osteoporosis. In an endeavour to understand the cellular processes, the research focuses on the two critical processes involved in the onset of osteoporosis: osteoblastogenesis, the process of bone formation, and osteoclastogenesis, the process of bone resorption. Specifically, the research emphasizes that inflammation and high reactive oxygen levels enhance osteoclastogenesis while concurrently reducing osteoblastogenesis. Green tea catechins, which have strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, are assumed to rebalance these two processes. The discussions revolve around the potential of green tea catechins to curb osteoclastogenesis by increasing the rate of osteoclast apoptosis, hampering osteoclastogenesis, and impeding bone resorption in a controlled environment. This is achieved directly through interactions with pre-osteoclasts/osteoclasts or indirectly through regulation of pre-osteoclasts via mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) or stromal cells. Furthermore, catechins are credited with boosting osteoblastogenesis by enhancing the osteogenic differentiation of MSCs and improving osteoblastic survival, proliferation, differentiation, and mineralization. The paper verifies the positive in-vitro effects of catechins on osteogenesis through various animal models and human observational studies.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine found that Lavender can decrease the severity of labor pain, which could influence health policy makers and gynecologists. This study conducted a meta-analysis of previously published literature on the effects of lavender on labor pain from 2006 to 2019. The researchers utilized a variety of both national and international databases to collate articles for their analysis. Due to the varied nature of the studies, a random effects model was employed for a standardized comparison of labor pain scores within the intervention and control groups. In the analysis, thirteen articles met the specific criteria needed for inclusion in the study. Upon examination, a significant difference was found in the mean pain scores between the control group and the group who had experienced the intervention of lavender. This suggests that lavender can potentially be effective in reducing the severity of labor pain.
A Clinical Study published in 2020 in the journal Journal of Alzheimer's Disease found that High phenolic early harvest extra virgin olive oil shows notable improvement in cognitive function compared to a moderate phenolic version and the Mediterranean diet alone. A randomized prospective study was conducted examining the effects of high phenolic early harvest extra virgin olive oil (HP-EH-EVOO) and moderate phenolic extra virgin olive oil (MP-EVOO) against the Mediterranean Diet (MeDi) in individuals with mild cognitive impairment. Participants were genetically tested for susceptibility to Alzheimer's disease and had their cognitive functions tested at the start and after 12 months. They were then randomly put into one of three groups: those who received HP-EH-EVOO, those who received MP-EVOO, and those who only received instructions on following the MeDi. The results showed that participants who consumed HP-EH-EVOO demonstrated better cognitive performance in almost all areas over the course of the study, compared to those who consumed MP-EVOO and those who followed the MeDi. MP-EVOO consumers also demonstrated noticeable cognitive improvement compared to the MeDi group, who exhibited worse or similar cognitive performance to their baseline in almost all areas. Moreover, participants who consumed either form of olive oil performed better in cognitive tests, regardless of their predisposition to Alzheimer's disease.
A Cohort Study published in 2020 in the journal BMC Geriatrics found that Habitual and high-frequency tea consumption, particularly green tea, is associated with a reduced prevalence of cognitive impairment in middle-aged and older individuals. The methodology of the study drew upon data from the Asymptomatic Polyvascular Abnormalities in Community study involving individuals over 40. Through a standardized questionnaire, information regarding participants' tea consumption habits – including frequency and type of tea – was collected. Cognitive function was then evaluated utilizing two recognized tests: Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) and Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA). Two distinct participant groups were chosen for these assessments: MMSE and MoCA subgroups. The researchers found, after accounting for potential confounding factors, that usual and high frequency tea intake correlated with a decreased risk of cognitive impairment. Further analysis showed that this risk reduction was notably high for green tea drinkers than for consumers of other tea types, as indicated by the MMSE test. A similar pattern was observed in the results of the MoCA group, showing a consistent association between regular tea intake, especially green, and lower prevalence of mental decline.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2020 in the journal Andrology found that Incorporating tree nuts into a Western-style diet subtly modifies specific DNA methylation regions within sperm, thereby showing parts of the sperm epigenome can respond to dietary changes. The study methodology involved a post hoc analysis with a subset of the participants (healthy, non-smoking, and young) from the FERTINUTS 14-week randomized-controlled, parallel trial. The selected participants were from the pool of individuals who completed the entire dietary intervention trial. These individuals were split into two groups: the nut group, which consumed 60 grams per day of mixed nuts for 14 weeks, and the control group, who maintained their regular Western-style diet devoid of nuts. Investigation of the trial's results revealed no significant changes in overall methylation between the two groups. However, for the nut group, there were 36 genomic regions distinctly showing differential methylation between the beginning and end of the trial with a marked increase in methylation. No such changes were identified in the control group. Analysis also involved examining if nut consumption led to changes in the epigenetic age of cells, but no significant differences were discovered.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry found that Catechin-rich green tea extract (GTE) exercised anti-inflammatory activities can be beneficial in managing Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) by reducing liver injury and gut-derived endotoxins. The research is built around the study of the anti-inflammatory properties of catechin-rich green tea extract (GTE). The primary analytical interest is its effects on inflammatory responses that contribute to Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), specifically nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). The extraction focuses on inhibiting the activation of the hepatic nuclear factor kappa-B, which is known to exacerbate liver injury. The results have shown positive contributions of GTE to management of NAFLD. Itn was observed that the extract limits the activation of the hepatic nuclear factor kappa-B and in turn, reduces NASH-associated liver injury. Additionally, green tea extract was found to contain hepatic-level benefits that attenuate intracellular redox distress and pro-inflammatory signaling. It was also found to improve the gut barrier function, limit the translocation of gut-derived endotoxins, and exercise prebiotic and antimicrobial effects on the gut microbial ecosystem. These results can potentially contribute to managing NAFLD-associated morbidity.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Molecules found that Honey's phytochemical components and bioactive compounds have potential antiviral effects, potentially making it an effective natural product against COVID-19. The methodology of this research utilizes a comprehensive review and analysis of existing literature regarding the antiviral effects and phytochemical components of honey. Previous studies have indicated that certain bioactive compounds present in honey, such as methylglyoxal, chrysin, caffeic acid, galangin, hesperidin, levan, and ascorbic acid, may exhibit antiviral effects or stimulate the body's antiviral immune responses. Through thorough examination of past works, the researchers isolated and focused on these compounds, exploring their potential utility in the context of COVID-19, a novel coronavirus that currently lacks established preventative or treatment measures. The results of the analysis pointed towards the efficacy of honey's bioactive compounds, which were found to potentially display both direct antiviral effects and the promotion of antiviral immune responses. However, the precise mechanisms by which these compounds exert their antiviral activity, particularly against SARS-CoV-2, remain largely unclear. Despite these ambiguities, the research established honey as a fruitful field of study for potential therapeutic material against the novel coronavirus disease.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Journal of Ethnopharmacology found that Juhua, the flower head of Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat, possesses multiple medicinal properties and has a significant role in dietary herbal medicine in China. The study gathers information about Chinese dietary herbal medicine and flower-derived medicine, focusing on Juhua, from varied sources such as government reports, classic books of Traditional Chinese medicine, doctoral and master's theses, and various databases. The methodology includes summarizing all flower-originated crude medicines listed in Chinese pharmacopeia and their applications for the first time, retracing the edible history and development of flowers in China, discussing the theory of Chinese dietary herbal medicines, and examining flowers as dietary herbal medicines. Discussion of the results highlights applications in Traditional Chinese medicine and diet, cultivars, phytochemistry, quality control, and pharmacology of Juhua. A safety evaluation of Juhua, along with an overview of chrysanthemum breeding and biotechnology, are included in the findings. The study determines that many herbal flowers, particularly Juhua, have considerably contributed to the prevention and treatment of various diseases in China.
A Experimental Study published in 2020 in the journal Medicines found that Pomegranate juice increases the effectiveness of lung cancer treatment with the low dose chemotherapy drug Cisplatin, while simultaneously reducing its toxicity on normal cells. The study performed classical tests for initial phytochemical screening of the pomegranate extract, measuring both total phenolic and sugar contents. The antioxidant activity of the pomegranate juice was then evaluated using an accepted method for determining its ability to eliminate harmful oxidative molecules. The viability of lung cancer cells and normal blood cells, when treated with pomegranate and the Cisplatin, was gauged using a neutral red assay, a test that determines cell health by noting their capacity to incorporate neutral red dye. In the discussion of results, the findings highlighted the high density of antioxidant compounds (such as flavonoids, alkaloids, etc) in the pomegranate juice. The juice had strong oxidative molecule scavenging activity, indicating potential as an antioxidant treatment. Most notably, the combination of pomegranate juice with a low dose of Cisplatin significantly reduced the viability of lung cancer cells while enhancing that of normal blood cells when compared to treatment with just Cisplatin or pomegranate juice.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Nutrients found that Beverages, through their diverse nutritional contents, have notable effects on rheumatoid arthritis progression by interacting with immune signaling pathways and altering the microbiome. The researchers reviewed existing literature to assess the role of various beverages in the context of rheumatoid arthritis. The primary focus of their study was understanding how the molecular contents of beverages such as coffee, tea, and wine, are contributing to the development and progression of the disease by interfering with immune signaling pathways. Moreover, they examined how these beverages affect the microbiome, leading to downstream effects on inflammatory pathways. The outcomes of the analysis indicate that beverages indeed play a pivotal role in the autoimmunity of rheumatoid arthritis. They found evidence that certain components present in beverages could either benefit the disease progression or negatively contribute to it. The researchers also discovered that considering beverages in the wider context of dietary patterns can help to better understand their role in disease management.
A Experimental Study published in 2020 in the journal Molecules found that The major components of green tea and coffee, EGCG and CGA respectively, may have anti-cancer effects, though these effects seem to vary for different types of cancer. Studies were conducted across cell-based and animal trials to explore the health benefits, particularly in anticancer effects, of epigallocatechin gallate (known as EGCG) and chlorogenic acid (CGA), the predominant elements in green tea and coffee, respectively. It was observed that the results were inconsistent due to possible confounding factors. A conceivable mechanism suggested, a part of those shared between EGCG and CGA, was related to the alterations in reactive oxygen species. However, the variance in the anti-cancer effects may be attributed to the different target molecules of EGCG and CGA, signifying the site-specific differences of anti-cancer effects observed in human studies.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2020 in the journal Molecules found that Daily consumption of decaffeinated green tea catechins may enhance working memory. The study incorporated a double-blind, randomized, controlled approach to determine the effects of 336.4 mg of decaffeinated green tea catechins on cognitive function. It targeted Japanese adults, aged 50 to 69 years, exhibiting a Mini-Mental State Examination Japanese version score of over 24 and who self-identified as having cognitive decline. The experiment comprised administering a substance and then examining the cognitive function post a single dosage as well as following 12 weeks of everyday consumption. The Cognitrax testing battery was utilized to assess cognitive function. In the results, it was observed that the incorrect response rate on the Continuous Performance Test significantly fell after a single dosage of green tea catechins. After 12 weeks of regular intake, the response duration for the two-back test in Part 4 of the 4-part Continuous Performance Test reduced, indicating potential improvement in working memory. The data suggests that consuming green tea catechins daily may potentially lead to cognitive enhancements, particularly in working memory.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Nutrition Journal found that The consumption of green tea significantly lowers low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and total cholesterol, but it does not affect high-density lipoprotein cholesterol or triglycerides. To gather data for this study, a comprehensive literature review and meta-analysis were conducted using PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library. The databases were searched from their inception to September 2019 for all studies related to the effect of green tea on blood lipids. Information from these studies, which included randomized and controlled trials, was used to estimate blood lipid changes resulting from green tea supplementation. The collected information underwent rigorous assessment for any potential bias. The analysis of data derived from 31 different trials involving a total of 3321 subjects showed that green tea intake has a significant effect in lowering low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and total cholesterol levels. However, consumption of green tea did not yield significant changes in the levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol or triglycerides. The results remained consistent across both normal-weight and overweight-obese subjects. No significant publication bias was detected from the collected studies, fortifying the reliability of the results.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2020 in the journal Current Women s Health Reviews found that The use of ginger, chamomile, and honey significantly diminished the intensity of dysmenorrhea pain as compared to the use of mefenamic acid. Methodology: The research involved 200 female students from Arak universities, suffering from primary dysmenorrhea. These participants were randomly divided into two groups. Initially, one cycle without any intervention was evaluated for all students. Following this, group A was administered 250mg of mefenamic acid while group B received a combination of 1000mg ginger, 5000mg chamomile along with a teaspoonful of honey. This regimen was followed for two days prior and for the first three days of menstruation, administered three times daily and was carried out over two consecutive cycles. To measure the pain severity, associated symptoms of dysmenorrhea and bleeding, tools such as a visual analogue scale, Andersch-Milsom Verbal Scale, and Higham chart were used. Discussion of Results: Following the intervention, the pain intensity experienced by the group treated with ginger, chamomile, and honey was found to decrease significantly when compared to the group that was administered mefenamic acid.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2020 in the journal Journal of Complementary and Integrative Medicine found that Inhalation aromatherapy using Damask rose and lavender essential oils can reduce anxiety and pain in women after they have had a cesarean section. This study was a randomized clinical trial involving 90 mothers who had cesarean sections at a hospital in Jahrom, Iran, in 2017. Prior to intervention, the incidences and severities of pain and anxiety were measured for all participants. The two intervention groups underwent aromatherapy with Damask rose and lavender essential oils. The participants were given cotton balls stained with three drops of these essential oils to inhale from a distance of 10cm for 30 minutes. The control group went through similar procedure but with normal saline. Pain and anxiety levels were assessed using established scales 5 minutes after the specified process. Following the interventions, the two aromatherapy groups experienced significantly different pain and anxiety levels compared to the control group. The results showed no tangible difference between the pain and anxiety levels of those who inhaled lavender oil and those who inhaled Damask rose oil.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Complementary Therapies in Medicine found that Lavender demonstrates significant benefits for pain relief and episiotomy wound healing in postpartum. This systematic review, conducted in accordance with PRISMA guidelines and registered in PROSPERO, analyzed six studies after screening 57 potentially relevant ones. Lavender was found to significantly reduce pain and accelerate healing of episiotomy wounds. Perineal pain, often stemming from perineal trauma like episiotomies, can impede mobility and daily activities for postpartum mothers. The study suggests routine Lavender use post-delivery for potential benefits, but acknowledges the need for further research due to observed heterogeneity in results. It emphasizes caution in interpreting Lavender's effects on episiotomy healing.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Amazonian Journal of Plant Research found that The most important tremella mushroom benefits are anti-aging, anti-inflammatory, lower cholesterol, combat obesity, protect nerves and may fight cancer. The most powerful nutritional constituents of Tremella are amino acids, vitamins, minerals, polysaccharides, Glucurmomannan 1,3-alpha-glucan, Epitope 9beta-D- glucuronosyl), Glucuronic acid, Glucurmic acid, Glucuronoxylomannan, N-acetylglucosamine, Flavonoids, Polyphenols, Alkaloids and Organic acids. Functional foods are making inroads into Chinese diets with their promises to improve health and nutrition. Chinese consumers should choose nutritional and healthy food to maintain general health and reduce the risk of health problems. Nutrition therapy on the basis of traditional Chinese medicine such tremella is quite effective at treating common diseases.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2020 in the journal Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health found that Fenugreek improves breast milk production in mothers and increases the weight gain of newborns during their first week of life. The study was an experimental design carried out in two groups, a control and an experimental group, at a maternity centre in Bangalore. A total of sixty postnatal mothers were selected and split evenly between the two groups. For the experimental group, 7.5 grams of fenugreek was steeped overnight; this resulting fenugreek water was then given to these participants once in the morning for one week. The study then assessed and compared the frequency of urination and weight of the infants between the two groups at different points: on the first, third, fifth, and seventh days. There was identifiable improvement in indicators of sufficient breast milk in the group that consumed the fenugreek compared to the control group. The influence of fenugreek on breast milk was identifiable through increased frequency of urination and weight gain in infants in their first week.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Complementary Therapies in Medicine found that Cinnamon supplementation significantly decreases inflammation and oxidative stress levels, serving as a potential additive for cardiometabolic health improvement. The systematic review and meta-analysis followed the Preferred Reporting Items of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis guidelines. A comprehensive search for appropriate clinical trials was performed across multiple databases including PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Embase, and Google Scholar until January 2020. After duplicates were removed, 1145 studies were found eligible and 12 studies were finally included in the meta-analysis, investigating the impact of cinnamon supplementation dosages ranging between 1.5 to 4 grams per day. The results of the meta-analysis revealed that cinnamon supplementation led to a significant reduction in inflammation markers, C-reactive protein and interleukin-6, alongside a decrease in malondialdehyde, an oxidative stress marker. Concurrently, an increase was observed in the total antioxidant capacity following the supplementation, implying an enhancement in the body's defensive ability against oxidative damage. Nevertheless, no significant change was identified in the levels of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 after the cinnamon supplementation.
A Meta-Analysis published in 2020 in the journal Complementary Therapies in Medicine found that Supplementation with blueberry shows a potential for beneficial impact on reducing body weight, which might indirectly influence cardiovascular disease risk factors. The methodology involved searching various digital databases such as ISI Web of Science, Scopus, PubMed, and Cochrane Library in March 2020. The researchers looked for all randomized and controlled clinical trials that used blueberry supplements to modify cardiovascular disease risk factors. Inclusion criteria were not restricted by language. References lists from primary studies and review articles were also checked for any additional studies. The results showed that although blueberry supplementation had a small, insignificant effect in reducing plasma triglycerides, there were no differences found between blueberry and control groups for any other cardiovascular disease risk outcomes. However, subgroup analysis indicated a potential favorable impact of blueberry on reducing body weight. It was found that studies lasting longer than 6 weeks or those that used blueberry powder or freeze-dried blueberry were indicative of significant weight loss.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Longhua Chinese Medicine found that Green tea and its compounds, especially catechins, may potentially prevent and treat osteoarthritis due to their potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. The researchers performed an extensive review exploring the potential impact of green tea and its bioactive compounds, chiefly catechins, on osteoarthritis management. Their focus was on the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant abilities of these compounds. Based on the review, such compounds can quell inflammation by blocking various signaling pathways interconnected with inflammatory processes. Specifically, they have the potential to suppress the expression of several cytokines and enzymes related to inflammation. In addition, green tea was noted for its property to neutralize free radicals, thus averting the formation of harmful reactive oxygen species and countering oxidative stress. While many conventional, non-surgical osteoarthritis therapies can lead to numerous adverse effects, the current review suggests that green tea could serve as a safer alternative. It may be a promising direction in the prevention and management of this chronic, painful, and inflammatory condition, which touches a significant number of people globally.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Molecules found that Green tea polyphenols can potentially protect against neurodegenerative disorders like Parkinson's Disease through antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective actions. The study synthesized existing research on the potential neuroprotective benefits of green tea polyphenols, particularly in Parkinson's disease. The papers highlighted were drawn from numerous sources and focused on the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective attributes of these compounds. Green tea's potential protection against free radicals, inflammation, and neuro-damage were considerable points of interest. The analysis also took into account the complex physiological, social, and cultural factors that could influence the effectiveness of green tea polyphenols in human subjects. Through the evaluation of numerous in vivo studies, researchers came to intriguing conclusions about the overall mechanism of green tea. The studies assessed explored how green tea consumption could mitigate neurodegenerative disorders like Parkinson's. In these analyses, investigators refined their understanding of how green tea and its polyphenols function from a neuroprotective standpoint. This information helps us better understand the advantages of green tea consumption and its potential role in preventing neurodegeneration.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal European Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that The literature overall supports an inverse association between green tea and cardiovascular disease-related health outcomes, while the included meta-analyses generally suggested an inverse association between green tea and BMI-related and blood pressure outcomes. The evidence on green tea consumption and health outcomes presented in this review suggests green tea may be favorable for cardiovascular disease, particularly stroke, and certain cancers such as endometrial, esophageal, lung, non-Hodgkins lymphoma, oral, and ovarian cancer. More evidence is needed to assess the impact of green tea on breast, gastric, and liver cancer risk. Additional studies could also help clarify the suggested null association with certain cancer sites: colorectal, pancreatic, and prostate cancer. Possible minor adverse events on health from green tea consumption were reported in one study, however these must be interpreted cautiously within the study context and possible finer dose-response implications. The findings for green tea and diabetes risk were inconclusive. For BMI the current evidence suggests a possible weak association, while the evidence is stronger supporting a decrease in blood pressure from green tea. More studies investigating a possible association between green tea consumption and other health outcomes such as cognition, injuries, respiratory disease would be informative to more completely assess the impact of green tea on human health. In conclusion, our review suggests green tea may have health benefits especially for cardiovascular disease and certain cancer sites.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Journal of Gastrointestinal and Liver Diseases found that Higher consumption of coffee correlates with a significant decrease in the risk of liver cancer or hepatocellular carcinoma. In the methodology, a systematic review and meta-analysis was performed on original articles, published in English from 1996 to June 2019, that linked coffee consumption with liver cancer or hepatocellular carcinoma. Numerous databases, including PubMed/MEDLINE/EMBASE/Ovid/Google Scholar, were searched for relevant case-control, cohort or prospective studies. The Relative Risk (RR) for these conditions was calculated for coffee drinking, further stratified by the increments of one cup of coffee per day. The final analysis involved 20 studies, analysed using random effects models, with heterogeneity between studies calculated by Cochrane Q and the I2 statistics. The results indicated that the overall Relative Risk (RR) displayed significant heterogeneity among the studies. A subgroup analysis was performed to evaluate the impact of additional coffee intake, and it was discerned that higher coffee consumption was associated with a substantial drop in the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC) or liver cancer. Additionally, there was no indication of significant publication bias observed in the funnel plot.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine found that Honey can be used as an alternative to antibiotics by clinicians who wish to offer treatment for upper respiratory tract infections, which may help to combat antimicrobial resistance. Upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs) are the most frequent reason for antibiotic prescription. Since the majority of URTIs are viral, antibiotic prescription is both ineffective and inappropriate. However, a lack of effective alternatives, as well as a desire to preserve the patient–doctor relationship, both contribute to antibiotic over prescription. Antibiotic overuse is a key driver of antimicrobial resistance, rated by the UK government as one of the top 10 risks facing Britain. Furthermore, drug resistant infections are associated with worse patient outcomes than antibiotic susceptible infections, underlining the impact of antimicrobial resistance on individual patients.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine found that Honey is more effective than usual care alternatives for improving upper respiratory tract infection symptoms, particularly cough frequency and cough severity. We identified 1345 unique records, and 14 studies were included. Overall risk of bias was moderate. Compared with usual care, honey improved combined symptom score, cough frequency. We combined two studies comparing honey with placebo for relieving combined symptoms. Honey was superior to usual care for the improvement of symptoms of upper respiratory tract infections. It provides a widely available and cheap alternative to antibiotics. Honey could help efforts to slow the spread of antimicrobial resistance, but further high quality, placebo controlled trials are needed.
A Clinical Study published in 2020 in the journal European Journal of Nutrition found that Montmorency tart cherry juice can significantly improve blood pressure, fasting glucose, cholesterol rates and respiratory exchange ratio in those with metabolic syndrome. In a blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial, the researchers recruited twelve participants suffering from metabolic syndrome. They were given either Montmorency tart cherry juice or a placebo for seven days. During this period, a variety of blood-based and functional cardio-metabolic biomarkers were analysed both before and after the supplementation period. In addition to this seven-day supplementation, the acute response of the participants to a single bolus of the treatment was measured on the seventh day, at intervals up until five hours post ingestion of the bolus. The researchers found that certain key health markers showed a significant improvement in the group that had taken the Montmorency tart cherry juice. These markers included 24-hour blood pressure levels, fasting glucose levels, total cholesterol, the ratio of total cholesterol to high-density lipoproteins (the "good" cholesterol), as well as resting respiratory exchange ratio. These findings suggest that the Montmorency tart cherry juice has the potential to drastically improve cardio-metabolic health in those affected by metabolic syndrome.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Horticulture Research found that In jujube fruit, the contents of sugar, vitamin C, and cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) are around 2, 100, and 1000 times those of apple, respectively. The fruit is particularly rich in nutrients, and its contents of sugar, vitamin C and B, cyclic nucleotide, proline, triterpenic acid, potassium, iron, and zinc are the highest among many fruits. The contents of sugar, vitamin C, and cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) are around 2, 100, and 1000 times those of apple, respectively. The fruit is also a rich source of polysaccharides, triterpenic acids, flavonoids, alkaloids, polyphenols, and pigments.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2020 in the journal Phytotherapy Research found that Concentrated pomegranate juice consumption can potentially lower cardiovascular disease risk factors in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. The study used a randomized clinical approach, enrolling 44 women identified with polycystic ovary syndrome, aged 18 to 40 years and above a certain body weight index. These participants were randomly divided into two groups: one group was given concentrated pomegranate juice (CPJ), while the other served as a control. Both groups were monitored over a period of 8 weeks, with baseline measurements taken for anthropometric measures, blood pressure, and biochemical parameters set at the onset and then compared at the end of the trial. Upon completion, the group that consumed CPJ showed reductions in blood pressure and serum triglyceride levels — a known risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. There was also an increase in the amount of high density lipoprotein-cholesterol (good cholesterol) and a decrease in the triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol ratio. However, an increase was observed in levels of low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (bad cholesterol). No adverse events or complications arose from CPJ consumption during the study period.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2020 in the journal The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that A botanical formula of lutein ester, zeaxanthin, and extracts from blackcurrant, chrysanthemum, and goji berry can effectively lessen eye fatigue and improve macular function. Research methodology involved the distribution of 360 randomly selected participants into four groups where they received placebos and three varied doses of a botanical formula. This formula, given in chewable tablets comprised of 6 mg, 10 mg, or 14 mg of lutein. Each participant was administered these once daily over a period of 90 days, and had three check-ins at the beginning, at day 45, and finally on day 90 of the study. The results of the study indicated that the botanical formula effectively improved the individual scores of participants on eye fatigue symptoms like eye soreness, blurred vision, dry eyes, foreign body sensation, and tearing. Using the formula resulted in a notable decrease in the total score of eye fatigue symptoms at both the 45-day and 90-day intervals as compared to the placebo while also significantly improving visuognosis persistence time. Tear secretion improvement was observed in the groups having 10mg and 14mg lutein formula, supported by the Schirmer test. Furthermore, the results showed an increase in macular pigment optical density with all three doses of the formula, but no significant alterations were observed in the retinal thickness and retinal volume among all the groups at both check-ins.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry found that Honey, with its variable composition based on botanical origin, exhibits antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, suggesting its potential efficacy in managing obesity-related dysfunctions, including neurodegeneration, through improved glycemic control and lipid profile. The review explores honey's therapeutic potential, emphasizing its diverse bioactive compounds. The focus is on its effects in combating obesity-related dysfunctions, supported by experimental evidence from animal studies. Experimental findings indicate that honey can enhance glycemic control and lipid profile, offering protection against endothelial dysfunction and neurodegeneration in obesity. The role of honey's key constituents, particularly polyphenols, is highlighted, underscoring the need for further human studies to confirm these health benefits.
A Clinical Study published in 2020 in the journal Russian Journal of Physiotherapy, Balneology and Rehabilitation found that Magnesium-rich mineral water effectively treats and prevents constipation in children, leading to regular, painless bowel movements. This randomized, prospective, open, comparative study involved 95 children and adolescents aged 10-16 years with functional constipation. They received sanatorium therapy for 18 days, including a sparing-exercise regimen, therapeutic nutrition, health-improving massage, and physiotherapy exercises. Participants were divided into two groups: Group 1 (55 patients) received basic treatment plus magnesium-containing mineral water, while Group 2 (40 patients) received only basic treatment. The study assessed the frequency and nature of defecation, vegetative status, and functional body reserves. By day 5, 49% of Group 1 patients achieved daily defecation, increasing to 89.1% by the end of treatment. In contrast, only 55% of Group 2 showed positive changes by the end. The mineral water group also had softer, pain-free bowel movements, with most achieving a morning defecation reflex after consuming the water. The control group saw less significant changes in defecation nature, with only 18% reaching softer bowel movements by the end of treatment. The results indicate the effectiveness and safety of magnesium-containing mineral water in treating and preventing functional constipation in children.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Applied Sciences found that Eggplant may possibly be used in the treatment of anemia, atherosclerosis, and fatty degeneration. Eggplant is progressively becoming more well-known due to its composition of carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, and several other bioactive compounds, such as phenolic acids. Eggplant also contains traces of minerals such as copper, zinc, and iron. Due to this biochemical composition, eggplant may possibly be used in the treatment of anemia, atherosclerosis, and fatty degeneration. Its antioxidant property potentially reduces the risk of various types of cancer, protects against cardiovascular diseases, and prevents acute respiratory infections. Further, eggplant fibers help in digestion by removing toxins and harmful materials from the stomach and reducing colon cancer. Plant polyphenols present in eggplants can help protect cell membranes and boost the brain’s memory function.
A Network Pharmacology published in 2020 in the journal BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies found that Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat. ethanol extract (CEE) presents a potential protective effect on lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung injury in mice. Ninety male mice were randomly split into five groups and orally treated for seven days with control, model, and varying doses of CEE. On the last day of administration, all mice except the control group were infected intratracheally with lipopolysaccharide to induce acute lung injury. The experiment then measured factors such as lung histopathology, lung wet/dry weight, white blood cell count, and various immunity-related substances in the lung tissue. The results revealed that CEE could improve lung damage as evident in histopathology, reduce ratio of lung wet to dry weight and other indices, and hinder the increase in white blood cells, lymphocytes, and neutrophils. It also reduced pro-inflammatory markers while increasing anti-inflammatory cytokines and substances related to antioxidant activity. The effects of CEE were seen to be dose-dependent, suggesting that larger doses provided more benefit.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Nutrients found that Magnesium sulfate-rich natural mineral waters are effective and safe as a natural treatment for functional constipation. This paper reviews clinical data on the efficacy of magnesium sulfate-rich natural mineral waters in treating functional constipation (FC), a chronic type of constipation with no identifiable physiological, anatomical, or iatrogenic causes. The condition is known to significantly affect patients’ quality of life and increase healthcare costs. The study examines the historical use of magnesium sulfate in treating FC and its longstanding recognition for laxative properties, especially in the context of magnesium sulfate-rich mineral waters. The review highlights that, despite the long history of using magnesium sulfate-rich mineral waters for their laxative effects, clinical studies specifically demonstrating their effectiveness in FC were scarce before the 21st century. The collected data indicate that these mineral waters are not only effective in treating FC but also safe, positioning them as a viable natural treatment option for this condition.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Nutrition & Metabolism found that Green tea supplementation significantly lowers fasting glucose levels but does not significantly affect fasting insulin and haemoglobin A1c values. The researchers performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized control trials which examined the effect of green tea on glycemic control. Using online databases like PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library, they identified relevant trials up until February 2020. They then employed a random-effects model in order to estimate the weighted mean difference. In the discussion of the results, it was found that twenty-seven trials, including 2194 subjects, were part of the meta-analysis. The collected data indicated that green tea lowered fasting blood glucose levels significantly. However, the same was not observed for fasting insulin and HbA1c values, which remained relatively unchanged despite green tea consumption. Moreover, substantial differences were noted in the range of responses, indicating significant heterogeneity, especially for fasting insulin levels. Despite these discrepancies, the short-term trials collectively demonstrated the beneficial effect of green tea supplementation in reducing fasting glucose levels.
A Network Pharmacology published in 2020 in the journal Foods found that Seasonal variations influence the nutrient composition of European sardines, with lipid levels peaking from July to September and amino acid content highest during winter. The methodology consisted of analyzing the proximate composition of European sardines from the Adriatic Sea over a period of one year. The nutritional profiles, focusing on free amino acid and fatty acid, were quantified monthly to discern any seasonal variations. The study paid special attention to quantities of bioactive lipids such as omega-3 fatty acids, and essential amino acids, as these are crucial for determining the nourishing value of the sardines for both industrial processing and for health benefits to consumers. The findings revealed that the nutritional content in sardines displays seasonal variation. The lipid content topped out from July to September, whereas the highest total amino acid content occurred during the winter, from January to March, with histidine, arginine, and threonine being most present. Interestingly, the study noted significant quantities of essential free amino acids throughout the year, with particular surges in March and dips in May. The fatty acid profile predominantly consisted of omega-3 fatty acids, with sardines showcasing high concentrations of eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids, which were especially abundant from July to September.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Journal of International Medical Research found that For primary dysmenorrhoea, cinnamon/fennel/ginger effectively reduced pain intensity, and cinnamon shortened the duration of pain. Nine studies with 647 patients were selected. Compared with the results in the control group, pain intensity was significantly relieved in the trial group when assessed by the intervention, observation period, and study quality. Pain duration was significantly shorter in the trial group. No publication bias was observed for either outcome.
A Experimental Study published in 2020 in the journal Molecules found that Probiotic-enriched mung and adzuki bean sprouts demonstrate increased antioxidant potential and exhibit cytostatic and cytotoxic effects on human stomach cancer cells. The study utilized mung bean sprouts (MBS) and adzuki bean sprouts (ABS), enriched with probiotic strain 299v, and their gastric digests were tested on human stomach cancer cells, AGS. Differentiation was shown through ABS containing quercetin and kaempferol derivatives while MBS featured kaempferol and apigenin derivatives, each displaying a higher antioxidant potential compared to controls. The viability of AGS reduced notably with low concentrations of ABS extracts, displaying inhibitive action which pointed to their cytostatic effects. In discussing the results, it is noticed that the sprouts showcased dose-independent cytostatic effects. However, ABS extracts were found to be more effective in reducing the proliferation of AGS, compared to MBS. Notably, the ABS extracts exerted about 70% inhibitions, elucidating their strong inhibitive power. Concurrently, the phytochemicals from these probiotic-enriched sprouts were observed to reduce the associated activity significantly. Observations of increased vinculin level, apoptotic shape of cell nuclei, alongside decreased cell motility and proliferation provide evidence that these extracts exhibited not only cytostatic but also cytotoxic activity.
A published in 2020 in the journal Nutrients found that Cocoa polyphenols promote gut health by favorably altering gut microbiota composition and producing secondary bioactive metabolites with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. The study revolves around observing the effects of dietary intake of cocoa polyphenols, bioactive compounds with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, on gut microbiota. These polyphenols have poor absorption in the gut and hence, rarely enter the systemic circulation in their natural forms. Instead, through a bidirectional interaction with the gut microbiota, they stimulate the proliferation of beneficial bacteria and inhibit the growth of harmful ones, thereby acting as a prebiotic. The resulting metabolites from this interaction are bioavailable, and these enter the circulation to reach target organs. The metabolites exhibit substantial antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities, which improve gut health. These actions augment immunity and reduce the risk of many diseases, documenting a notable health-protective potential of cocoa polyphenols, routed via modulation of gut microbiota composition.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Nutrients found that Black pepper, particularly the piperine it contains, enhances the absorption of iron, potentially improving athletic performance in endurance sports. This study examined the joint administration of Iron (Fe) and black pepper, more specifically its alkaloid piperine, to physically active healthy individuals. Iron is an important micronutrient that aids performance in endurance sports by enhancing the physiological functions related to the transport, storage, and utilization of oxygen. The frequent physical stress and high metabolism experienced by athletes can lead to iron depletion, with possible consequences including reduced aerobic capacity, strength, and slower muscle recovery. While the recommended daily allowance (RDA) of iron is usually fulfilled through diet, absorption rates vary and may be insufficient for some individuals. The combination of piperine and iron supplementation was investigated as a potential strategy to address iron deficiencies, especially among athletes who may experience adverse effects from high-dose iron supplements, such as gastrointestinal disturbances. The concept underlying this study was that piperine, known for its bioavailability enhancement properties, may improve the absorption of iron, thereby reducing side effects and improving treatment adherence. The results, derived from three research studies, revealed that the combined usage of iron with black pepper led to observed improvements in parameters related to iron metabolism without causing any adverse effects. By potentially boosting the efficiency of iron absorption, co-administration may offer a promising development in oral iron supplementation practices, particularly for individuals with greater physical activity.
A Theoretical Article published in 2020 in the journal Nutrients found that Coffee, like many fruits and vegetables, activates a cellular response that boosts antioxidants and repair enzymes, which contributes to a lower risk of several diseases. The research paper proposes a new perspective on the health benefits of habitual coffee consumption. Instead of focusing on individual elements in coffee, the study compares coffee as a whole, acting as a plant food, with the advantageous properties of many vegetables and fruits. By linking coffee, vegetables and fruits, researchers identified a common mechanism that promotes health - the activation of an adaptive cellular response which leads to an upsurge of proteins involved in cell protection such as antioxidant, detoxifying and repair enzymes. It was also noted that this response hinges on the activation of the Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor-2 (Nrf2) system by phenolic phytochemicals, leading to the expression of cell defense genes. The discussion of the paper's results reveals that coffee plays a significant role in health promotion, the main reason being that it is the primary dietary source of phenolic acids and polyphenols in the developed world. Additionally, a supportive function might be associated with the modulation of the gut microbiota by non-digested prebiotic constituents of coffee. Conclusively, the paper suggests that coffee uses similar health promotion pathways as other vegetables and fruits, and that coffee beans could be seen as healthy vegetable food and a leading supplier of dietary phenolic phytochemicals.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2020 in the journal Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine found that The use of standardized saffron extract appears to show significant improvement in sleep quality in healthy adults with self-reported sleep issues. The study employed a 28-day, double-blind, randomized controlled trial to evaluate the effects of a standardized saffron extract on sleep quality in adults with self-reported sleep issues. Total of 63 healthy adults between the ages of 18 and 70 were recruited and randomly assigned to receive either the saffron extract, taken twice daily at a dose of 14mg, or a placebo. From a pool of 55 participants, it was found that those who consumed saffron showed noteworthy enhancements in sleep quality. The improvements were measured by an Insomnia Severity Index, a Restorative Sleep Questionnaire, and a Pittsburgh Sleep Diary. Notably, the intake of saffron was well tolerated and did not result in any reported adverse effects.
A Meta-Analysis published in 2020 in the journal European Journal of Nutrition found that Chronic consumption of cranberry or cherry juice might considerably improve blood pressure levels. The review involved a comprehensive search across several databases including PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, and psycARTICLES from the beginning until January 2020. The search results included forty-five randomized controlled trials that lasted at least a week, assessing the effects of berries, citrus, and cherries on different cardiovascular disease risk indicators. These indicators were endothelial function, blood pressure, lipid status, and inflammatory biomarkers. Different preparations of berries including juice of barberry, cranberry, grape, pomegranate, blueberry powder, grape, raspberry and freeze-dried strawberry were studied. The resulting reports showed improvements in endothelial function, inflammation markers, lipid status, and blood pressure. Among the interventions, cranberry juice and cherry juice were notably associated with a potential decrease in systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Consumption of berries led to a significant increase in the levels of sVCAM-1, a protein that is usually found higher in people with cardiovascular risk. However, no significant improvements were observed for other specified fruits in this research.
A Experimental Study published in 2020 in the journal Molecules found that Honey contains 20(S)-Hydroxyvitamin D3 (20(OH)D3) and its derivatives, including 20(OH)-7DHC, 25(OH)D3, and 1,25(OH)2D3, indicating their production in bees and suggesting potential health implications. This study explores the presence of vitamin D3 derivatives in honey, emphasizing the detection of 20(OH)D3 and related compounds. Analysis using LC-MS revealed distinct peaks corresponding to these derivatives, implying their production in bees during the summer in Alabama. The identification of 20(OH)D3, 20(OH)-7DHC, 25(OH)D3, and 1,25(OH)2D3 in honey suggests their synthesis within bees, highlighting potential biochemistry and photochemistry processes. This finding opens avenues for understanding the health-related implications of these compounds in honey.
A Experimental Study published in 2020 in the journal Molecules found that We determined the concentration of 20(OH)D3 in honey to be 0.26 µg/g, corresponding to approximately 10 IU/g. Using an LC-MS assay utilizing 20(OH)D3-d3 as internal standard, we determined the concentration of 20(OH)D3 in honey to be 0.26 µg/g, corresponding to approximately 10 IU/g based on the conversion for vitamin D3 (400 IU = 10 µg). While this may seem relatively low, it must be noted that 20(OH)D3, unlike vitamin D3, is an activated form of the vitamin. It is non-calcemic but exerts many of the other activities of 1,25(OH)2D3 seen in cell culture and in animal studies, with comparable potency. Thus, while the amount of 20(OH)D3 in honey is relatively low, it could potentially be of physiological significance.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Journal of Herbal Medicine found that Green tea catechins-containing mouthwash may potentially be a practical alternative to chlorhexidine due to its efficacy in plaque reduction and minimal side effects. The methodology involved an exhaustive literature review of several electronic databases, such as CINAHL, Cochrane Library, MEDLINE, PubMed and Scopus, up until January 2017. This review adhered to the PRISMA criteria, centring the research question around the impact of green tea catechins-containing mouthwash on plaque accumulation and gingival inflammation in patients with gingivitis. Out of the 187 titles identified this way, five were fit for meta-analysis, the subject matter primarily revolving around an Asian population. The results indicated that both green tea and chlorhexidine (CHX) significantly outperformed a placebo in reducing Plaque Index (PI), with no substantial contrast between the CHX and green tea groups, both in terms of the endpoint and the change from the beginning of the study to its conclusion. However, only minor side effects were associated with the green tea mouthwash. Contrarily to chlorhexidine, this aspect might make green tea mouthwash more suitable for prolonged use. Despite some heterogeneity in the data and potential bias risks, green tea mouthwash remains an interesting, viable alternative worth considering.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition found that Incorporating avocados into the Mediterranean diet may enhance its benefits, offering greater health flexibility and adaptability for non-Mediterranean residents. The research approach starts with an evaluation of the nutritional value of a Mediterranean diet, which is traditionally rich in fruits, vegetables, and oleic-acid-rich olive oil. This diet has been associated with lower risks of several chronic diseases. Simultaneously the paper introduces the subject of rising obesity rates globally. The study then evaluates the potential benefits of modifying the Mediterranean diet to include non-traditional fruits and vegetables that could provide more variety in food choices and greater adaptability for those living outside the Mediterranean region. The avocado, a fruit native to the Mediterranean climate and rich in beneficial nutrients like oleic acid and fiber, is proposed as a potential addition. Discussion of the study reveals an interesting proposition: including avocado in the traditional Mediterranean diet, which is not commonly done. The avocado's health benefits and nutritional value are then analysed in depth, drawing from existing research studies, to substantiate the recommendation for incorporating this fruit into the Mediterranean dietary pattern. The discussion concludes by highlighting the potential enhanced health benefits that can result from this inclusion, thereby presenting a compelling case for the suggested adjustment.
A Experimental Study published in 2020 in the journal Nutrients found that Unpasteurised milk and dairy products intake could potentially alter gut microbiome composition which may influence psychological functioning. In this observational study, the impact of dietary change involving unpasteurized dairy consumption on gut microbiota and psychological state was observed among participants of a 12-week residential cookery course on an organic farm. Twenty-four participants, who primarily consumed food from the farm including unpasteurised milk and dairy products, provided faecal samples at the beginning and end of the course. Concurrently, they completed self-report questionnaires touching on mood, anxiety, and sleep aspects and nutrient intake was monitored via a food frequency questionnaire. Gut microbiota analysis was carried out using 16S rRNA gene sequencing and measurement of faecal short chain fatty acids. Post-course, there was a significant growth in the relative abundance of a specific bacterial genus in the gut, associated with unpasteurised milk and dairy product intake. Furthermore, an increase in a particular faecal short chain fatty acid, valerate, was observed together with an elevation in the functional richness of the microbiome profile. The latter was determined by measuring the predicted neuroactive potential using a unique gut-brain module approach. Despite safety concerns, the consumption of unpasteurised milk and dairy products seemed to promote the growth of probiotic bacterial genus, known to be beneficial for various physical and mental health outcomes.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2020 in the journal Nutrients found that Eating whole SunGold kiwifruits, both with and without skin, can significantly decrease gut inflammation and alleviate constipation for both healthy people and those with irritable bowel syndrome. In the 16-week cross-over study, 38 participants (both healthy and those with Irritable Bowel Syndrome-Constipation) were randomly assigned to consume either three whole SunGold kiwifruits without the skin or three whole kiwifruits with the skin for periods of four weeks, with a length of four weeks between each intervention as a washout period. Following the intervention, it was observed that there was a significant reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokines (specifically TNF-α) for both the healthy participants and those with Irritable Bowel Syndrome-Constipation when whole kiwifruits, including the skin, were consumed. Furthermore, similar results were witnessed for the healthy individuals upon consumption of whole kiwifruits without their skin. The consumption of kiwifruit – including its skin – also increased bowel frequency and led to significant reductions in the gastrointestinal symptom rating scale for constipation and Irritable Bowel Syndrome-related pain scores for both participant groups. Results indicate that the skin of the SunGold kiwifruit may have beneficial effects on gastrointestinal health that are not derived from merely consuming the fruit's flesh.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders found that Green coffee supplementation significantly decreases fasting blood sugar, insulin, and triglycerides while boosting high-density lipoprotein levels. In methodology, a comprehensive literature review was carried out across PubMed, Embase, Scopus, and the Web of Science databases until October 2019. The objective was to scrutinize all randomized controlled trials of the impact of green coffee supplementation on various cardio metabolic risk factors in adults. These risk factors included fasting blood sugar, insulin, triglycerides, high and low-density lipoproteins and C-reactive protein. Data was then extracted from the relevant studies for analysis. From the selected 27 studies for final analysis, the pooled results depicted that green coffee supplementation had a significant effect in reducing fasting blood sugar, insulin, and triglyceride levels. In addition, it was found to increase the levels of high-density lipoprotein. Conversely, it was determined that the supplementation did not lead to any notable changes in the Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance, low-density lipoprotein and C-reactive protein levels.
A published in 2020 in the journal Nutrients found that Daily consumption of coffee and green tea is linked with decreased body mass index, body fat percentage, and cardiovascular risks in middle-aged Japanese women. This cross-sectional study was conducted with 232 Japanese women aged 40-65 years who visited the menopause clinic of Tokyo Medical and Dental University Hospital from November 2007 to August 2017. The women's body composition and cardiovascular parameters were assessed using a body composition analyzer and vascular screening system. Furthermore, their coffee and green tea consumption frequency was gauged using a brief-type self-administered diet history questionnaire. The researchers then explored the associations between these variables using multivariate logistic regression. In terms of results, the study found a negative association between daily coffee consumption and both high body mass index and body fat percentage. Similarly, daily green tea consumption was inversely related to high body fat percentage. The combined daily consumption of coffee and green tea also showed inverse relationships with both body mass index and body fat percentage. Moreover, in pre- and perimenopausal women, daily consumption of both beverages was found to be negatively associated with cardio-ankle vascular index, a measure of cardiovascular risk.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Nutrients found that Coffee intake may have a variable effect on inflammation markers, with different responses noted between men and women and across various geographical regions. The researchers carried out a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis on the relationship between coffee intake and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, an inflammation biomarker. They studied eleven previous studies involving a total of 61,047 participants from three different continents. These studies were chosen using the PubMed database. The selected studies had different findings: some showed a negative relationship between coffee and CRP levels, others showed a positive relationship while some showed no significant associations. The researchers analyzed the data from these studies using mixed-effects meta-regression models, with the volume of coffee consumed as the metric. Regarding the discussion of results, there revealed to be considerable variation between the individual studies included in the meta-analysis. In three of the largest studies, it was found that the relationship between coffee consumption and CRP levels appeared to be different depending on the gender of the participant and their location. Women from Europe and the United States, as well as Japanese men, showed a decrease in CRP levels with increased coffee consumption. However, European men showed an increased inflammation marker. When all studies were considered together, no significant relationship between coffee consumption and CRP levels was found among all participants or when the data was stratified by gender or geographical location, showing the contradictory nature of the results noted in individual studies.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Phytotherapy Research found that Green tea intake can significantly reduce body weight, body mass index and waist circumference, with the greatest effect seen with lower dosages and shorter treatment durations. In the methodology used for this study, several databases were exhaustively searched from their inception to September 2019. The goal was to identify clinical trials that had explored the influence of green tea supplements on obesity indices in humans. The dosage, type of extract, and duration of the intervention were key factors for the study. The study design incorporated the use of a random-effects model to aggregate the collected data. In terms of the study's results, they demonstrated notable changes in subjects' obesity indices following the administration of green tea. A significant reduction in body weight and body mass index was observed, which was consistent across all extracted data. The most noticeable change was observed in the reduction of waist circumference in subjects who were administered an equivalent of 800 mg/day of green tea. Also, a more significant reduction in body weight occurred with a green tea dosage of less than 500 mg/day and a treatment duration of 12 weeks. These results affirm the potential use of green tea in improving obesity indices and the study advocates for the inclusion of green tea supplements, combined with a balanced diet and regular exercise, in obesity management strategies.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Ethiopian Journal of Health Sciences found that Aromatherapy, specifically with lavender essential oil, can effectively alleviate maternal anxiety and labor pain. The methodology involved a systematic review of five databases - PubMed, SCOPUS, Web of Science, Google Scholar and Scientific Information Database - for studies on the use of aromatherapy for pain and anxiety management during labor. Search keywords included variations of aromatherapy, essential oil, aroma, pain, anxiety, labor, and delivery. The quality, bias, and reliability of the identified studies were assessed using the Cochrane Collaboration's 'Risk of bias' protocol. 33 studies met the inclusion criteria, with various methods of aromatherapy application utilized, such as inhalation, massage, footbaths, birthing pools, acupressure, and compresses. The most commonly used essential oil was lavender, used individually or mixed with other essential oils. These studies, predominantly conducted in Iran, formed the basis for our analysis and provided evidence to assess the positive impact of aromatherapy on labor pain and anxiety.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Complementary Therapies in Medicine found that Almond intake significantly decreased diastolic blood pressure, and inconsistently, almonds decreased systolic blood pressure. The evidence from this meta-analysis suggest that almonds may have beneficial effects on the BP. Based on the current scientific knowledge, it could be encouraged to include them, as part of a healthy diet in order to reduce the risk of hypertension.66 It should be noted that results cannot be generalized to those with other health problems, such as liver disease and cancer that were not included in this analysis. We found that almonds might have a considerable favorite effect in BP and especially in DBP, and it could be encouraged as part of a healthy diet; however due to the high calorie content, the intake should be part of healthy diet.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Journal of Ethnopharmacology found that Cinnamon supplementation may help manage metabolic parameters in polycystic ovary syndrome patients by reducing fasting blood sugar, insulin, LDL-C, total cholesterol, and triacylglycerol levels. In order to evaluate the effect of cinnamon supplementation on metabolic parameters of PCOS patients, relevant clinical trials were systematically reviewed and analysed. Data was collated from multiple credible databases including PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane library, Scopus and Web of Science, up until August 2019. Studies were selected that provided information specifically about the impact of cinnamon supplementation on metabolic parameters amongst PCOS patients. Standard methods were used to assess heterogeneity, publication bias and sensitivity analysis with five clinical trials pooled together using a weighted mean-difference calculation. The findings of the meta-analysis showed that cinnamon supplementation does not significantly affect body weight and body mass index in PCOS patients. However, it was found that cinnamon supplementation led to a significant decrease in fasting blood sugar, fasting insulin, and HOMA-IR, along with reducing the serum levels of LDL-C, total cholesterol, and triacylglycerol. Additionally, there was an observed improvement in serum concentration of HDL-C with cinnamon supplementation. Ultimately illustrating that cinnamon supplementation may play a significant role in managing metabolic parameters in polycystic ovary syndrome patients.
A Experimental Study published in 2020 in the journal Plant Foods for Human Nutrition found that Pomegranate juice has potential beyond ascorbic acid alone in enhancing iron absorption and assimilation, supporting Ayurveda's proposition of managing iron deficiency anemia with pomegranate. The study applied a cell-free model imitating gastric and intestinal digestive procedures, along with cell-based models (in the form of Caco-2 and HepG2 cells), to evaluate iron dialysability in the presence of pomegranate juice. This method was utilized to observe iron uptake into cells, assessed via cellular ferritin content measures. Pomegranate juice highly improved iron dialysability in the cell-free model and increased iron uptake and ferritin content in the cells’ models far more than ascorbic acid alone. This result corroborates Ayurveda's claim regarding the beneficial usage of pomegranate in managing iron deficiency anemia, proposing a straightforward remedy to a global health issue. The betterment of iron bioavailability could be due to the synergistic action of various phytochemicals in pomegranate juice, suggesting a multifunctional utility for this natural product.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth found that Meta-analysis showed that date fruit consumption can significantly reduce the active phase of labor, and also significantly improve the bishop score. Based on the performed searches, this is the first systematic review conducted on the effects of date on bishop score and frequency of caesarean section, and second one on the effects of date on the duration of labor stages. Meta-analysis showed that the consumption of date fruit can significantly reduce the duration of the active phase and improve the bishop score, and may reduce the frequency of cesarean section in intervention group compared to control group. Based on meta-analysis, date palm fruit consumption resulted in a significant reduction in the duration of active phase of labor compared with control group; however, it is not observed in the first, second, and the third stage of labor.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Clinical Nutrition ESPEN found that Cinnamon supplementation can improve blood pressure by a modest degree. Meta-analysis of 9 RCTs with 641 participants showed significant reductions in both systolic (WMD: −5.17 mmHg, 95% CI: −9.35 to −0.99, P = 0.01) and diastolic blood pressure (WMD: −3.36 mmHg, 95% CI: −5.67 to −1.04, P ≤ 0.001) after cinnamon supplementation. Subgroup analyses indicated that these results were significant only when cinnamon was administered at the dosages of ≤2 g/day, for a period longer than 8 weeks, and in participants with a baseline BMI of ≥30 kg/m2.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Food Bioscience found that Different varieties of dates pose impressive nutritional profiles and exhibit multiple health benefits, including anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and cholesterol lowering potential. The study embarked on a systematic literature review, utilizing the Scopus, Centre for Agriculture and Bioscience International, Google Scholar and Web of Science databases to assess works published from 1971 to 2017, resulting in 270 relevant articles. The focus was to evaluate the nutritional profile and nutraceutical attributes of different date varieties worldwide, particularly from their cultivation hotspots in West Asia and North Africa. The findings indicate that date fruit is a rich, affordable source of numerous nutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, amino acids, dietary minerals, vitamins, and various health-promoting compounds such as polyphenols, anthocyanins, tannins and flavones. The fruit's constituents, particularly beta-glucan, show a vast array of beneficial effects on health, functioning as antioxidant, anti-tumor, immune-modulating, anti-diabetic, and cholesterol-lowering agents, as well as promoting beneficial gut microflora growth. Preclinical studies also underline the beneficial effects of date fruit in protecting against a range of health conditions like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and various forms of cancer. The positive health impacts were observed in different parts of the fruit, namely the flesh, peel, and pits.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2020 in the journal Journal of Pharmacopuncture found that Chamomile capsules can decrease the amount of menstrual bleeding and thus, can offer remedy for women suffering from heavy periods. The study was conducted as a randomized, double-blind, clinical trial with 118 female students from Guilan University of Medical Sciences. Participants were split into two groups of 59, with one group receiving chamomile capsules 250 mg thrice a day, and the other a placebo. Treatment was started seven days before menstruation and continued until the next menstrual onset. The Higham chart, a pictorial tool that assesses blood loss, was used to quantify the amount and duration of menstrual bleeding. The study found that on average, the quantity of menstrual bleeding was reduced in the group that took the chamomile capsules. However, there was no significant difference observed in the duration and interval between bleeding in both groups, indicating that while chamomile may decrease the amount of blood loss, it has no effect on the timing of menstrual cycles. These results establish chamomile as a potential treatment for reducing heavy menstrual bleeding.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Plants found that Pomegranate, due to its polyphenols, flavonoids and fatty acids, exhibits significant pain-relieving effects and could potentially be used as a treatment for various types of pain. The methodology utilized in the research consisted of conducting a review of scientific articles that met specific inclusion criteria. They focused on the use of different parts of a pomegranate and how they impact different kinds of pain. Special attention was given to the antinociceptive effect of pomegranate, with the potential mechanisms of action being closely scrutinized. The results of the review have provided evidence that the pomegranate plant contains elements that have an antinociceptive effect and that this effect could be due to the presence of compounds like polyphenols, flavonoids, and fatty acids. The analyses suggest that these effects might be due to the activation of the L-arginine / NO pathway, TRP superfamily members (TRPA1 or TRPV1) and the opioid system. Implications for the field include understanding the mechanisms by which this effect is generated to potentially develop alternative treatments for specific types of pain, aiming to both alleviate discomfort and reduce the adverse effects produced by traditional drugs. The research proposes that the pomegranate could be further considered for the treatment of inflammatory, nociceptive, and neuropathic pain.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2020 in the journal European Journal of Nutrition found that Lemon juice, but not black tea, can lower and delay the blood glucose concentration peak after consuming bread. The methodology used in this research consisted of a randomized crossover study involving three test groups consuming equal portions of bread partnered with three different beverages: water, black tea, and lemon juice. Each participant's capillary blood glucose concentrations were monitored over a 180-minute period using the finger-prick method. Additionally, the participants' free-choice energy intake was assessed three hours after the bread and beverage consumption to gauge the effects of the different beverages. The results of the research showed a distinct difference between the effects of lemon juice and black tea on the glycemic response to bread. It was found that black tea didn't affect the blood glucose responses. However, lemon juice significantly reduced and delayed the peak of blood glucose concentration. It's noteworthy that the pH-lowering effect of the lemon juice performed similarly to other acidic foods, indicating that incorporating acidic drinks or foods in starch-rich meals is an effective strategy to minimize their glycemic impact. Interestingly, none of the beverages tested had an impact on the participants' ad libitum energy intake.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2020 in the journal Nutrients found that Daily intake of 3 grams of oat beta-glucans significantly reduces LDL-Cholesterol, Total Cholesterol, and non-HDL-Cholesterol levels without impacting intestinal well-being or glucose levels. The BELT Study was a double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over randomized clinical trial conducted over 8 weeks. It involved 83 Italian subjects with moderate hypercholesterolemia, who had low cardiovascular risk and followed a Mediterranean diet. The participants were administered either 3g/day of oat beta-glucans or a placebo. The results indicated that beta-glucans significantly reduced LDL-C, TC, and non-HDL-C levels in participants from both the baseline and the 4 and 8-week marks. However, no notable impact was observed on fasting plasma glucose or self-perceived intestinal well-being. These outcomes remained consistent irrespective of whether the subjects were given the beta-glucans or the placebo.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews found that Green tea, containing antioxidative catechins, may possess some beneficial effects in reducing the risk of specific types of cancer. The study team performed an extensive review of 142 completed and 2 ongoing studies up to January 2019. These studies encompassed all types of epidemiological studies: experimental (randomised controlled trials) and nonexperimental (observational studies with both cohort and case-control design) that looked into the association of green tea consumption with cancer risk or quality of life, or both. Data extraction and methodological quality assessment of these studies were performed independently by two or more review authors. These efforts were organized and the results summarized according to the type of cancer diagnosis. The data was sourced from CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase, ClinicalTrials.gov, and referenced lists of earlier reviews and included studies. The studies focused on investigating the links between cancer incidence and mortality rates, safety data, quality of life, and green tea consumption. Numerous studies came with a high degree of methodological quality, based on 'Risk of bias' assessment. The placebos in 11 studies involving a total of 1795 participants were green tea extracts. On another note, the studies indicated some side effects linked to high intakes of green tea with more than a million participants undertaking the non-experimental studies. Despite inconclusive evidence, experimental and nonexperimental epidemiological studies suggested potential beneficial effects of green tea consumption on the overall risk of cancer or on certain types of cancer. Variations of the beneficial effects of green tea were observable across different cancer types, indicating a decrease in rate ratios (RR) in the highest category of green tea consumption versus the lowest. A detailed analysis based on study design exhibited conflicting results for some types of cancers, showing an increased RR in cohort studies and a decreased or no difference in RR in case-control studies. However, the overall interpretability of these RR estimates was limited by methodological issues, such as low study numbers and inconsistencies with cohort study results. Lastly, it's important to note that the majority of included studies were conducted within populations with a high intake of green tea, mainly Asian, thus limiting the general applicability of the findings to other populations.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2020 in the journal The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine found that Certain essential oils such as lavender, neroli, jasmine, roman chamomile, clary sage, and Indian sandalwood can potentially increase oxytocin concentrations in postmenopausal women. In this study, fifteen postmenopausal women were subjected to the effects of ten different essential oils one at a time. The oils exposed to included rose otto, sweet orange, lavender, neroli, frankincense, jasmine absolute, ylang ylang, roman chamomile, clary sage, and Indian sandalwood. Initially, they were exposed to a control for 20 minutes, followed by exposure to an essential oil for 20 minutes. Each woman was exposed to only a single kind of essential oil per day. Saliva was collected immediately before and after both control exposure and essential oil exposure. The oxytocin levels in the saliva were then measured. The findings revealed an increase in salivary oxytocin concentrations following exposure to six out of the ten essential oils. Specifically, lavender, neroli, jasmine absolute, roman chamomile, clary sage, and Indian sandalwood were associated with a significant increase in salivary oxytocin when compared to the control odor. This study implies that olfaction stimulation with the listed essential oils might help counter the reduction of muscle mass and function caused by aging in women.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Journal of King Saud University - Science found that Almond consumption was found to significantly reduce systolic blood pressure. A systematic and dose-response meta-analysis review study was carried out. The researchers thoroughly searched through PubMed/MEDLINE, Web of Science, and Scopus, with no restrictions on time or language, up until July 2019. The goal was to identify randomized controlled trials which investigated the effects of almond consumption on systolic and diastolic blood pressure. A total of fifteen studies, with 21 arms and involving 853 participants, were selected and their findings analyzed according to the PRISMA guidelines. Upon analysis, it was observed that the consumption of almonds displayed a significant reduction effect on systolic blood pressure. However, no such significant effect was found on diastolic blood pressure. The variation in results for diastolic blood pressure was noticed to be linked to the dose of almonds consumed, a finding made through a meta-regression analysis carried out during the study.
A Meta-Analysis published in 2020 in the journal The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice found that Consumption of raw milk early in life appears to provide protection against asthma and allergies, regardless of whether children live on farms or in rural, non-farm areas. Whoever did the research carried out a comprehensive literature review, identifying twelve relevant publications from eight unique studies. Their approach involved a meta-analysis to substantiate the protective effect of raw milk consumption in early life, particularly for ages ranging from less than one year old to five years old. They further analyzed the impacts of raw milk on not only asthma but also other ailments such as wheezing, hay fever, allergic rhinitis, and atopic sensitization. Moreover, evidence was provided about the beneficial effects of raw milk for children, both living on the farms and those in rural sectors but not on farms. Moreover, in the interpretation of results, it was clearly evident that the consumption of raw milk had an independent effect, separate from other farm exposures. In essence, even children not residing on farms theoretically can still gain from the benefits of raw milk consumption. However, they express a strong sense of caution, advocating against the consumption of raw milk due to the possibility of life-threatening infections. Furthermore, the distinction between raw farm milk and industrially processed milk was underlined to highlight differences in cellular components, fat fraction, and heating degrees. Preliminary findings link these characteristics and attributes of raw milk to heat-labile molecules and components found in its fat fraction.
A Meta-Analysis published in 2020 in the journal Complementary Therapies in Medicine found that Pomegranate juice supplementation notably diminishes inflammation and vascular dysfunction markers in adults, offering potential cardiovascular health benefits. The research used a broad approach, systematically reviewing and performing a meta-analysis of 16 randomised controlled trials including 572 participants, as per the Preferred Items for Reporting of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines. Relevant articles and references were found via the PubMed/Medline and SCOPUS databases, with screening carried out up until May 2019. The studies explored the impact of pomegranate juice supplements. The discussion reveals that pomegranate supplementation conspicuously reduced the levels of certain pro-inflammatory and vascular dysfunction markers. However, the research found no significant reduction in some other markers when compared to a placebo. Despite not all markers recording significant reduction, the overall findings strongly suggest pomegranate supplements as a viable tactic for reducing inflammation in adults, potentially offering cardiovascular health advantages.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews found that Cinnamon supplementation in type 2 diabetes patients significantly reduces systolic and diastolic blood pressure, but doesn't significantly affect body weight and waist circumference. This systematic review and meta-analysis diligently looked for related studies in databases like PubMed, Embase, Scopus, Web of Science and Cochrane Library. The search was conducted up to August 22, 2019, and aimed at finding the impact of cinnamon supplementation on blood pressure and certain anthropometric parameters among patients with type 2 diabetes. To gauge the effectivity, they used standard mean difference and confidence intervals. In cases of heterogeneity, fixed and random effect models were utilized. The collated data was analyzed using Stata 13. After refining the records, nine suitable articles were chosen for review. The meta-analysis results indicated a significant decrease in systolic and diastolic blood pressure in type 2 diabetic patients following the incorporation of cinnamon in their diet. However, the supplement did not result in a significant change in their body weight, body mass index, and waist circumference. These fluctuations in anthropometric factors were noted, but they did not reach a level of statistical significance.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Sains Malaysiana found that Honey exhibits significant anti-Helicobacter pylori activity, with at least 10% concentration proving effective in inhibiting gastric and duodenal ulcers, highlighting its therapeutic potential. The research involved a comprehensive review of 53 articles from electronic databases such as Medline via Ovid Medline, Scopus, and ScienceDirect spanning from 2000 to 2018. Selection criteria focused on studies reporting honey's effects on H. pylori-induced gastric and duodenal ulcers. Nine chosen articles detailed the positive impact of honey, suggesting a minimum 10% concentration as effective against H. pylori. The review underscores the need for further exploration into honey's active components and molecular mechanisms. The positive outcomes reported in selected studies support honey's potential in inhibiting H. pylori infections, emphasizing the need for further investigations to elucidate the active components and underlying molecular mechanisms. The review sets the stage for future research aiming to provide robust evidence for the use of honey in clinical settings.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Nutrients found that These reports suggest the benefits of a walnut-enriched diet in brain disorders and in other chronic diseases, due to the additive or synergistic effects of walnut components for protection against oxidative stress and inflammation in these diseases. Walnuts contain several components that have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Animal and human studies from our and other groups suggest that supplementation with walnuts in the diet may improve cognition and reduce the risk and/or progression of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Furthermore, several animal and human studies have suggested that walnuts may also decrease the risk or progression of other brain disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, stroke, and depression, as well as of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. Together, these reports suggest the benefits of a walnut-enriched diet in brain disorders and in other chronic diseases, due to the additive or synergistic effects of walnut components for protection against oxidative stress and inflammation in these diseases.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Phytotherapy Research found that Green tea influences liver enzymes differently based on an individual's health status, reducing levels in patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, but slightly increasing levels in healthy subjects. The researchers initiated a comprehensive review and analysis of randomized clinical trials relating to green tea supplementation's effects on liver enzymes. This analysis included forms of green tea supplementation, such as catechin. The information to support this examination was sourced from four medical and health databases and included all trials examining the influence of green tea or its derivatives on specific liver enzymes, including Alanine Transaminase, Aspartate Aminotransferase, Alkaline Phosphatase, and Bilirubin. Altogether, fifteen trials were considered for inclusion in this research. The study found that while the overall effect of green tea on liver enzymes was nonsignificant, further analysis showed that the impact of green tea on liver enzymes varies depending on an individual's health status. Notably, the use of green tea reduced liver enzyme levels in participants diagnosed with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. However, in contrast, a small but statistically significant increase in liver enzyme levels was observed in healthy subjects. These findings suggest that the therapeutic potential of green tea may differ significantly based on an individual's health condition.
A Meta-Analysis published in 2020 in the journal BMC Cancer found that Coffee consumption shows a strong association with decreased risk of liver and endometrial cancer. The randomized umbrella review included a total of 28 individual meta-analyses and 36 summary associations for 26 different types of cancer. In order to collect this data, a variety of databases like PubMed, Embase, Web of Science and the Cochrane database were searched to find systematic reviews and meta-analyses of relationships between coffee consumption and cancer incidence. The summary effect size was estimated for each association using both the fixed and random effects model. A detailed evaluation of heterogeneity, small-study effects, and excess significance bias was also carried out. The results showed 17 out of 28 meta-analyses to be significant. For the highest versus the lowest categories, 4 out of 26 associations showed a more stringent value. There were notable dose-response associations for five types of cancer. Majority of the studies (69%) displayed low heterogeneity. There was evidence of excessive significance bias and publication bias in three and six associations respectively. Data exhibited that coffee intake was inversely proportional to the risk of contracting liver and endometrial cancer. All this remained constant even when the analysis was restricted only to the meta-analysis of cohort studies.
A Experimental Study published in 2020 in the journal Journal of Dairy Science found that Lactic acid bacteria strains isolated from indigenous Bangladeshi raw milk demonstrate strong probiotic potential and antimicrobial activity against various pathogens. The researchers isolated and evaluated lactic acid bacteria (LAB) from raw milk indigenous to Bangladesh, focusing on its probiotic potential. To do this, they conducted a series of tests examining the LAB’s antagonistic activity towards several harmful foodborne pathogens, their survivability under gastric conditions, tolerance to phenol and bile salts, adhesiveness to ileum epithelial cells, aggregation abilities, hydrophobicity and α-glucosidase inhibitory activity. They also assessed these strains’ antibiotic susceptibility, covering key antibiotics widely used in medical and veterinary practices. The research spotlighted four LAB strains, identified as Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus fermentum, and Lactobacillus paracasei, as possessing strong probiotic potential. This was primarily due to their shown ability to inhibit all tested pathogens to varying degrees and competitively exclude pathogens at certain viable counts. Their antimicrobial activity was attributed to their production of bacteriocin, organic acids, and low-molecular-weight substances. Additionally of note was their resistance to several antibiotics; all four strains resisted oxacillin, and three out of four resisted vancomycin and streptomycin. The study concludes by suggesting the potential for these LAB strains to be considered probiotic candidates for application in the food industry post in-vivo evaluation.
A Clinical Study published in 2020 in the journal Medicine found that Green tea intake can significantly reduce both systolic and diastolic blood pressure. In this meta-analysis, studies were sourced from the PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases from their inception to August 2019. The selection criteria focused on randomized placebo-controlled trials, exploring the effects of green tea on blood pressure control. The final selection consisted of twenty-four trials involving 1697 subjects, and the results were pooled using the generic inverse-variance method with random-effects weighting. The quality of the included studies was independently ascertained using the Jadad score, while potential publication bias was evaluated using funnel plots, and the Egger and Begg tests. The pooled results showed that green tea intake led to notable reductions in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure, though the outcomes revealed significant heterogeneity among the trials. The funnel plots and tests used to investigate the publication bias did not find any substantial evidence to suggest this was an influencing factor in the results.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2020 in the journal International Journal of Psychophysiology found that Daily avocado consumption improves attentional inhibition and increases serum lutein concentrations, irrespective of changes in lutein status, in adults with obesity. The study involved a randomized-controlled trial with 84 adults aged 25-45 years suffering from overweight or obesity. The participants were divided into a treatment group and a control group. Those in the treatment group consumed a daily meal with fresh Hass avocado for 12 weeks while the control group was given an isocaloric meal. The xanthophyll status was evaluated by measuring serum lutein and macular pigment optical density, and cognitive functions such as attention and inhibition were evaluated using the Flanker, Oddball, and Nogo tasks. Regarding the results, the treatment group showed improved serum lutein concentrations and better performance in the Flanker task demonstrating improved attentional inhibition. However, they found no correlation between improvements in performance and changes in lutein status and no significant changes in macular pigment optical density. Therefore, it suggests that the cognitive benefits from avocado intake were not due to changes in lutein status but may involve other unknown mechanisms.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2020 in the journal European Journal of Integrative Medicine found that Intranasal application of essential oils such as lavender and fennel (Pinetonina™) significantly lowers cortisol levels and improves sleep quality. The study included 45 participants divided into three groups: one group received a saline nasal spray (Group 1 CTRL), the second group received a 30% concentration of Pinetonina™ in a buffered vehicle as an intranasal spray (Group 2 P30), and the third group received a 50% concentration of the same (Group 3 P50). The sprays were used once daily before bedtime for three months. The study measured salivary cortisol levels both at the beginning and end of the trial and assessed subjects' quality of sleep, anxiety levels, perceived stress, and overall quality of life using self-reported questionnaires. The study found that the groups using the 30% and 50% Pinetonina™ solutions saw significant reductions in their cortisol levels after the three-month period. The subjects in the 50% Pinetonina™ group also reported a notable improvement in their quality of sleep. However, there were no significant differences among the groups' perceived stress levels and their overall quality of life. Nevertheless, the study concluded that nightly intranasal use of Pinetonina™ could effectively lower cortisol levels and enhance sleep quality.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Nutrients found that Ginger has been effective in a majority of studies, including those that examined the alleviation of nausea and vomiting of pregnancy, digestive function, improvement in the expression level of markers for colorectal cancer risk, and anti-inflammatory functions. Ginger is a natural spice that is used in diverse regions to add a pungent flavor to food. Furthermore, ginger has been used as an herbal medicine for common health problems. This systematic review is the first study that has exclusively collected RCTs regarding the efficiency of ginger in several human health conditions. The clinical effects of ginger have been introduced as six subsections: nausea and vomiting, gastrointestinal function, pain, inflammation, metabolic syndromes, and other symptoms. Reportedly, ginger has been effective in a majority of studies, including those that examined the alleviation of nausea and vomiting of pregnancy, digestive function, improvement in the expression level of markers for colorectal cancer risk, and anti-inflammatory functions. Several other functions have also been regarded as beneficial in trials, with some confronting results. However, a few drawbacks regarding the quality of the trials, inconsistent evaluation systems or parameters, and the generally small size of the studies need to be noted. Therefore, systematically designed research with detailed descriptions of methodology and a sufficient pool of participants is necessary for future clinical trials to address the functional characteristics of ginger.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Food Reviews International found that Bioactive compounds found in avocado waste products exhibit various biological properties, with potential applications in the food and pharmaceutical industries. In this study, we delved into the archived scientific research concerning bioactive compounds and their sources, particularly focusing on avocado waste products such as leaves, peels, and seeds. We identified the primary compounds found in these parts to include carotenoids, tocopherols, phytosterols and a group of natural organic structures known as polyphenols. In the results discussion, we found that the compounds discovered in avocado waste products have credible biological activities that have distinct health implications. The wastes extracts demonstrated antimicrobial properties, along with anti-inflammatory characteristics. Additionally, they showed potential anticancer, antidiabetic and antihypertensive capabilities. These findings infer that the bioactive compounds from avocado wastes may be successfully used in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
A Clinical Study published in 2020 in the journal Journal of Pharmaceutical Research International found that Children with asthma, aged between 2 and 18, were found to be significantly shorter than their healthy counterparts. In the methodology of this case-control study, 150 children with asthma, aged 2-18 years, were compared to a carefully matched control group of 300 healthy children. Both groups had their height, weight, and body mass index measured through standard methods. Data for these anthropometric indices were processed and analysed using designated software and statistical tests, excluding any height, weight and BMI ranges that were deemed 'normal' or 'abnormal'. In discussing the results, it was observed that asthmatic children were significantly shorter than the control group. Interestingly, there were no observed differences in weight and body mass index between the two groups. This potentially suggests that the presence of asthma may not have a significant growth-altering effect, or this phenomenon might be attributed to effective disease management among the asthma group.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2020 in the journal Complementary Medicine journal found that The combination of ginger and chamomile was as effective as mefenamic acid in managing dysmenorrhea pain and more efficient in reducing related symptoms. The methodology used was a randomized controlled clinical trial involving 400 female students from Arak University. Four groups of participants were created, each with 100 students. The treatments given to these groups were ginger with honey, chamomile with honey, a mix of ginger and chamomile with honey, and mefenamic acid. The participants consumed their respective treatments three times daily, starting from two days before menstruation and continuing into the first three days of the cycle, for two consecutive periods. The pain intensity, related symptoms, and bleeding were evaluated over the first three days of each cycle, both one month before treatment and two months after it. The study found that all four treatment options significantly decreased pain severity, painful days, low back pain, analgesic consumption, total symptom score, and bleeding. Again the blend of ginger and chamomile was notably better than the other treatments in lowering the total symptom score. Meanwhile, mefenamic acid was particularly effective at reducing bleeding loss. Despite these differences, there was no significant variation among the groups outside of total symptom score and bleeding loss.
A Cohort Study published in 2020 in the journal Nutrients found that Regular consumption of raw carrots, specifically 2-4 or more per week, is associated with a decreased risk of colorectal cancer. The methodology of the study involved examining the risk of being diagnosed with colorectal cancer in correlation with carrot intake in a Danish population of 57,053 individuals over a lengthy follow-up period. Self-reported intake of raw carrots was recorded, setting a baseline of 2-4 or more carrots each week as the metric for study. Results derived from this study show that individuals who consumed 2-4 or more raw carrots per week showed a decrease in the risk of colorectal cancer, as compared to individuals with no intake of the same. However, an intake of less than 2-4 carrots per week did not show a significant association with reduced colorectal cancer risk. Therefore, this supports the notion from previous studies that stated consumption of carrots could have a preventive effect against colorectal cancer.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy found that Honey showed a significant antimicrobial activity against all targeted periopathogen and could be effective in the treatment of periodontal disease. A total of 1448 publications were found as search results in the screened databases. Sixteen eligible papers were included based on predetermined inclusion criteria. Retained studies included 5 RCTs and 11 in vitro controlled trials. Manuka and multifloral honeys were the most studied varieties. The tested honeys showed a significant antimicrobial action, with different MICs, against eight periopathogens. Four of the five RCTs showed a high RoB, while 4 of the 11 retained in vitro studies showed a medium RoB.
A Network Pharmacology published in 2020 in the journal Nutrients found that Ganpu tea, derived from Pu-erh tea and the pericarp of Chachi, enhances antioxidant capacities and modulates gut microbiota beneficially more than Pu-erh tea alone. A thorough chemical analysis was conducted on hot-water extracts of Ganpu tea using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography and quadrupole-time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry, which identified a total of 92 constituents. Considering the antioxidant properties of Ganpu tea, an experiment was designed and carried out where rats were fed with Ganpu tea over a long period. The same experiment was done using Pu-erh tea and the pericarp of Chachi separately, allowing for comparisons of antioxidant capacities between them and Ganpu tea. The results showed that Ganpu tea had a substantial impact on improving the activities of superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase, both essential antioxidants, more than Pu-erh tea. This indicated a superior antioxidant capacity of Ganpu tea. Further, it significantly increased the abundance of specific gut bacteria, offering a suggestion of the potential benefits of Ganpu tea in human gut microbiota modulation. The results underscore the health benefits of Ganpu tea in enhancing antioxidant activities and promoting beneficial gut microbiota.
A Experimental Study published in 2020 in the journal Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology found that Chrysanthemum morifolium, Naringenin and Apigenin can alleviate depression-like behavior by interfering with specific metabolic pathways. In this study, the researchers decided to evaluate the impact of Chrysanthemum morifolium, Naringenin, and Apigenin on depression-like behaviors instigated specifically by corticosterone. These substances, which are the primary active ingredients in the aqueous extract of C. morifolium and are used in Traditional Chinese Medicine, were analyzed regarding their therapeutic properties for depression. Researchers analyzed behavior and biochemical indicators tied to depression to understand the effects of these substances on a modeled depression scenario. In the discussion of results, the authors highlight that these substances demonstrated antidepressant properties through their interference with certain metabolic pathways. These pathways include tryptophan metabolism, arginine and proline metabolism, citrate cycle, niacin and niacinamide metabolism, phenylalanine metabolism, and alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism. The effects were further explained on the basis of material and energy metabolism. Moreover, it was noted that Naringenin could potentially be used as a replacement for Chrysanthemum morifolium with similar beneficial outcomes; while Apigenin paralleled the function of other positive drugs targeting depression.
A Network Pharmacology published in 2020 in the journal Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences found that Pomegranate fruit extract significantly enhances cartilage gene expression and chondrogenesis in human adipose-derived stem cells compared to Avocado/Soybean Unsaponifiable. Human adipose-derived stem cells were first isolated, expanded in monolayer culture, and identified, and then seeded on fibrin scaffolds. These cell-impregnated scaffolds were divided into 4 groups: a control group, an Avocado/Soybean unsaponifiable (ASU) group, a Pomegranate Fruit extract (PFE) group, and a mixed ASU/PFE group. Each group was subjected to induction for two weeks with the corresponding substances, except the control group which only received chondrogenic medium. The levels of cell viability, cartilage gene expression, matrix staining density, and collagen type II proteins in the PFE samples were found to be noticeably greater than other groups. Histological assessments further highlighted higher chondrogenic centers in the PFE group. This indicates that PFE significantly enhances chondrogenesis and cartilage gene expression in these cells, suggesting potential use in cartilage tissue engineering.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Complementary Therapies in Medicine found that Cocoa consumption significantly reduces markers of oxidative stress in the adult population, affirming its important role in the human metabolic pathway. This study systematically reviewed interventional studies to determine the impact of cocoa consumption on oxidative stress markers in adults. Numerous databases, including PubMed, Cochrane's library, Science Direct, Scopus, Google scholar and ISI web of science, were searched for all relevant literature up until March 2019. The Jadad scale was utilized to grade the quality of each study. Out of 1402 studies, 48 met the inclusion criteria for the systematic review and 16 were selected for meta-analysis. The pooled data from the random-effect model provided evidence that cocoa consumption effectively lowered malondialdehyde and 8-iso-prostaglandin F2α, but no significant changes were noted in other markers of oxidative stress. The results underscored cocoa's essential function in the human metabolic process by its potential to decrease oxidative stress.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Food & Function found that Almond intake significantly reduces body weight and fat mass in adults, yet it does not impact body mass index, waist circumference, or fat-free mass. The methodology used in this study started with a comprehensive search of online databases including PubMed, Scopus, ISI Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and Google Scholar until January 2020. The goal was to identify relevant randomized controlled trials for inclusion, which led to the discovery of 28 trials among 2983 reports, that were deemed suitable for analysis. The data were reported as weighted mean differences and standard deviations to signify the impact of almond consumption on different bodily measures including body weight, body mass index, waist circumference, fat mass, and fat-free mass. As for the results, pooling of data was done utilizing a random-effects model, the outcome of which indicated a significant reduction in body weight and fat mass following almond intake. However, no meaningful change was found in measures of body mass index, waist circumference, or fat-free mass as a result of almond consumption. Interestingly, such intake showed a significant influence on weight and fat mass reduction, with no observable effect on the other parameters examined.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal The American Journal of Chinese Medicine found that The Chrysanthemum indicum L. plant has been discovered to have multiple pharmacological capabilities including anti-inflammatory, antioxidation, antipathogenic, anticancer, immune regulation, and hepatoprotective effects. In their study, the researchers undertook an extensive review of Chrysanthemum indicum L., a longstanding staple of traditional Chinese medicine. They examined the botany, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of the plant, integrating historical records relating to traditional medicinal usage with modern scientific analyses. In the discussion of their findings, they made note of the plant's impressive pharmacological portfolio. More than 190 chemical compounds have been identified within the plant, including flavonoids, terpenoids, phenylpropanoids, and phenolic acids. These contribute to a variety of medical benefits - illustratively, its extracts show anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidation properties, and compounds isolated from the plant suggest potential anticancer, antipathogenic microorganism, immune regulation, and hepatoprotective effects.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Journal of Ethnopharmacology found that Prunus mume fruit extracts display hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, antibacterial effects, and show promise for treating cancer and alleviating chemotherapy side-effects. The authors conducted an extensive database retrieval via SciFinder, PubMed, and various other resources using relevant keywords such as "Prunus mume", "Chinese plum", "Japanese apricot", and "cancer". They also consulted relevant textbooks, patents, reviews, and digital documents (in English). The purpose was to analyze the anticancer activities of the P. mume extracts and their potential use to prevent or treat cancers. They also aimed to review the use of the P. mume extracts to alleviate the side effects of chemotherapy, notably drug-induced gastrointestinal toxicities. In addition to showing hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, and antibacterial effects, the P. mume extracts were found to exhibit anticancer properties. Specifically, the extracts inhibited proliferation and induced apoptotic death of multiple types of cancer cells from both solid and hematological tumors. Furthermore, the extracts were found useful in treating mucositis and other gastrointestinal damages induced by anticancer drugs. The scientists profiled key natural products found in the extracts including ursolic acid and oleanic acid. However, they call for more robust evidence of anticancer activity in humans.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Neural Regeneration Research found that Saffron shows potential as a promising therapeutic agent in treating neurodegenerative ocular diseases. This research thoroughly explores the therapeutic properties of Saffron (Crocus sativus L.), traditionally used in food and medicine, focusing on its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-apoptotic activities. These properties stem from saffron's main metabolites, notably crocin and crocetin. In addition to investigating its commonly attributed properties, the study delves into the possible neuroprotective role of saffron in neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson's and Alzheimer's, looking at both experimental models and clinical studies in patients. The findings reveal that saffron has shown beneficial effects in the treatment of ocular neurodegenerative conditions including diabetic retinopathy, retinitis pigmentosa, age-related macular degeneration, and glaucoma. This study offers an in-depth review and report on ongoing investigations of saffron extract’s benefits for ocular diseases, particularly neurodegenerative ones.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Clinical Nutrition found that Cinnamon intake significantly reduces body weight, body mass index, waist circumference, and fat mass in adults, and can be recommended as a supplement for obesity management. Various online search engines such as PubMed, SCOPUS, Google Scholar, and Cochrane Library were trawled to find relevant articles on the impact of cinnamon consumption on obesity measures. The data from these articles was then combined and expressed as weighted mean difference and 95% confidence intervals utilizing the random-effects method. The potential non-linear association was appraised via fractional polynomial modeling. The study incorporated 12 trials from an initial pool of 679 records, bringing together a total of 786 participants. The aggregated outcome demonstrates that cinnamon intake can significantly decrease body weight, body mass index, waist circumference, and fat mass in adults. The impact on body weight was particularly pronounced in subjects under 50 years old and those with a higher baseline body mass index (≥30 kg/m). Daily dosages of cinnamon at or above 2 grams, and administered for 12 weeks or more resulted in significant reductions in fat mass. There was a non-linear reduction in body weight and waist circumference with the administration of cinnamon over the study period.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal International Review of Neurobiology found that The date fruit contains compounds such as flavonoids that can protect tissues from harm and reduce risks of illnesses like cardiovascular disease and cancer. The research focused on the properties of the date palm fruit (Phoenix dactylifera), known to be rich in bioactive compounds such as polyphenols. A particular interest was given to flavonoids, a group of phytochemicals renowned for their high antioxidant capacity, and other useful traits. The study investigated the fruit's capability in protecting tissues against harmful effects, examining the interference with enzymes that prompt the formation of damaging free radicals. In the discussions, it was indicated that the date fruits were not only appreciated for their organoleptic properties but also for their biological activities. The protective properties of the fruit against harmful effects arose from flavonoids and their ability to inhibit the formation of free radicals. Flavonoid-rich date fruit consumption was suggested to correlate to a decreased risk of various diseases, including cardiovascular diseases and cancer. This aspect uplifts date fruit as a prized option for consumers seeking health benefits from their diet.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Food & Function found that Coffee and decaffeinated coffee appear to provide long-term protection against developing type 2 diabetes, potentially due to the influence of chlorogenic acids. This research observes a considerable protective effect of coffee and decaffeinated coffee over the long term against the onset of type 2 diabetes, discovered through epidemiological studies. A complex mechanism associated with chlorogenic acids is proposed, with the theory examining their potential impact on blood sugar levels. Interestingly, the effects of decaffeinated coffee on post-meal blood sugar and insulin, if consumed with carbohydrates, is minimal, although these substances might be impacting incretin hormones. The potential effects of chlorogenic acids are examined from the perspective of not directly affecting carbohydrates digestion, but perhaps influencing glucose absorption and subsequent utilisation. Different factors, such as metabolites derived from endogenous pathways or the influence of the gut microbiota, are considered. The study proposes a need for chronic intervention studies on decaffeinated coffee, in sync with more focused in vitro studies using realistic concentrations of relevant chlorogenic acid metabolites, to further understand this protective property of coffee.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Antioxidants in Fruits: Properties and Health Benefits found that Avocado, particularly the Hass variety, has substantial health benefits due to its rich contents of nutrients, fiber, and bioactive constituents including antioxidants. The methodology of the paper involves a comprehensive overview of avocado, focusing on the extensively cultivated Hass variety. The research explored various components of the avocado which include not only the fruit, but also the seeds, leaves, and skin. These parts were analyzed for their nutritional and bioactive constituents such as phytochemicals, phytosterols, vitamins and minerals. Furthermore, the use of avocado leaves in traditional medicine, the rich composition of the peel and seeds, and the potential health benefits of avocado oil were investigated. The discussion of results revealed that avocados, particularly Hass avocados, are a substantial source of beneficial nutrients, fiber, and bioactive components. It was found that leaves of the avocado have antioxidant properties and are used in traditional medicine. The peel and seeds showed a rich content of phenolic compounds, starch, and fiber. The research also determined that avocado oil presents health advantages and can be used as a good alternative substitute for olive oil. Avocados are largely consumed as a vegetable, often in combination with other ingredients.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal Journal of Pharmacopuncture found that Chamomile shows promise in alleviating premenstrual syndrome (PMS) symptoms. This review examines the efficacy of chamomile in treating premenstrual syndrome (PMS), a condition characterized by physical and psychological symptoms. Eight randomized controlled trials (RCTs) met the inclusion criteria out of 27 identified studies. Chamomile, known for its anti-inflammatory, anti-spasmodic, and anti-anxiety properties, showed promise in alleviating PMS symptoms. It was compared with Mefenamic Acid (MA), placebo, and no treatment, with positive results. While existing studies suggest chamomile's effectiveness, the authors emphasize the need for further trials with diverse forms and doses, larger populations, and longer durations. Chamomile, as a readily available herbal remedy, offers potential relief for PMS symptoms in women.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2019 in the journal Nutrients found that Consuming walnuts daily can reduce cardiovascular risk factors in chronic kidney disease patients without altering significant physiological levels. In this prospective, randomized, crossover, pilot clinical trial, 13 patients suffering from chronic kidney disease were selected as subjects. They were randomly divided into two groups, one of which was assigned a diet including 30 grams of walnuts each day while the other followed a control diet. After a duration of 30 days, a washout period of an additional 30 days was allowed, following which the groups were switched to the alternate diet. Key markers such as urinary and serum levels of phosphorous and potassium, multiple vascular risk factors, and urinary inositol phosphates were measured before initiating the trial and post the intervention period. The study indicated that a dietary supplement of walnuts resulted in reduced blood pressure, lower LDL cholesterol, and decreased albumin excretion. Interestingly, despite these changes, it had no impact on the physiological levels of phosphorous, potassium, parathyroid hormone, and fibroblast growth factor 23. This indicates that daily consumption of walnuts, when incorporated in a sodium, protein, phosphate, and potassium controlled diet, has the potential to be an effective strategy in reducing cardiovascular risk among chronic kidney disease patients without perturbing key physiological levels.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2019 in the journal Food Science & Nutrition found that Pomegranate juice can reduce melatonin, increase insulin levels, and improve insulin resistance in individuals with impaired fasting glucose. This study was a randomized clinical trial with 28 participants who had been diagnosed with impaired fasting glucose. They were selected from Irbid Central Laboratory and the Diabetes Clinic of the University Hospital at Jordan University of Science and Technology. Each participant received a dose of fresh pomegranate juice calculated at 1.5 ml per kilogram of their body weight. Blood samples for each participant were taken prior to, 1 hour and 3 hours after ingesting the juice. The studied parameters were melatonin, insulin, and glucose levels. In terms of results, it was found that people with impaired fasting glucose, contrary to those who were healthy, showed a significant decrease in blood glucose levels 3 hours after consuming the juice. Insulin resistance also improved significantly within the same time frame for these individuals. Furthermore, melatonin levels decreased, and insulin levels increased noticeably among both, healthy as well as those with impaired fasting glucose, an hour after the juice intake. These results suggest that fresh pomegranate juice can positively affect hormones related to diabetes and sleep.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine found that Gout patients regularly ingesting cherry extract/juice reported fewer gout flare ups than those patients who did not supplement their diets with cherry products. The six studies included in this systematic review reported decreases in the incidence and severity of gout following the ingestion of cherries. Gout patients regularly ingesting cherry extract/juice reported fewer gout flare ups than those patients who did not supplement their diets with cherry products. Overall, we observed a positive correlation between the consumption of tart cherry juice and a decrease in serum uric acid concentration.
A Review Article published in 2019 in the journal Journal of Diabetes Research found that Traditional Chinese medicine, especially Zuo Gui Wan, red raspberry leaves, and Orthosiphon stamineus, seems to control gestational diabetes effectively without reported toxicity. The study initiated a systematic search across PubMed, Web of Science, and Embase databases to pinpoint research discussing the impact of traditional Chinese medicine on pregnancy. The results were then further narrowed down to focus on any correlation with all forms of diabetes mellitus. The primary thread that emerged was the beneficial effect of three main herbal remedies: Zuo Gui Wan, red raspberry leaves, and Orthosiphon stamineus. Based off of the results from this search, a focal review of these herbal elements and their associations with type 2 diabetes mellitus was undertaken. Across the board, these remedies demonstrated positive effects on metabolic health, especially among women dealing with gestational diabetes. No experimental models reported any toxicity or harmful side effects associated with these herbal treatments. The report calls out that current studies on both conventional and alternative interventions for gestational diabetes are immensely lacking, emphasizing the need for a standardized protocol to evaluate the efficacy of these herbal medicines.
A Clinical Study published in 2019 in the journal Food & Nutrition Research found that Drinking at least 1.5 to 2 litres of bicarbonate-rich mineral water daily significantly reduces dietary acid load in healthy adults. The study was a single-centered, randomized trial involving 129 healthy men and women aged 18 to 75. Participants were assigned to consume 1,500–2,000 mL daily of one of four types of mineral water, varying in bicarbonate content and potential renal acid load (PRAL), for four weeks. The types were: low bicarbonate, high PRAL; medium-high bicarbonate, medium PRAL; high bicarbonate, low PRAL; and medium-high bicarbonate, low PRAL. Participants maintained their usual diets, and the primary measurement was net acid excretion (NAE) in 24-hour urine output. The study found that consuming the three types of mineral water with higher bicarbonate content (medium-high and high) and lower PRAL (medium and low) significantly decreased NAE values. The greatest reduction was seen with high bicarbonate, low PRAL water, indicating a substantial decrease in dietary acid load. This was also accompanied by a slight increase in serum bicarbonate levels in the groups consuming high and medium-high bicarbonate, low PRAL water.
A Review Article published in 2019 in the journal Revue Neurologique found that The Mediterranean diet, especially the high consumption of extra-virgin olive oil, significantly reduces the risks of vascular diseases and Alzheimer's. The research has been based on a plethora of observational epidemiological studies, local population experiences, meta-analyses of epidemiologic data, and experimental studies, all converging to the connection between the Mediterranean diet and a reduced prevalence of different ailments. The study scopes extend over long periods, such as the Italian-American experience from 1935 to 1965, or the Seven Countries Study spanning four decades from 1960 to 2000. Another significant evidence base is the French Three-City Study, which followed participants for ten years from 2000 to 2010. Apart from human trials, the article includes results from experimental animal models, specifically concerning late-onset Alzheimer disease. The findings showcase a consistent trend linking reduction in vascular diseases, obesity, arthritis, cancer, cognitive decline, and specifically Alzheimer's disease with increased adherence to a Mediterranean dietary pattern, particularly high intake of extra-virgin olive oil. Certain dietary components such as fruits, seeds, legumes, and vegetables contribute to the benefits. However, olive oil stands out as the chief dietary fat in Mediterranean countries. It provides plentiful monounsaturated fatty acids, beneficial polyphenols, and other antioxidants, which play a crucial part in these health benefits. The most striking discovery is extra-virgin olive oil's potential to mitigate the effects of adverse vascular factors, indicating a promising approach to preventing late-onset Alzheimer's disease.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal Phytotherapy Research found that Cinnamon supplementation can significantly reduce body weight, body mass index, and waist-hip ratio. In the meta-analysis, various databases (including Medline, ISI Web of Science, Scopus, Google Scholar, and Cochrane Library) were searched without limitations until August 2019 for relevant randomized controlled clinical trials. The risk of bias of the randomized controlled clinical trials was appraised with the Cochrane collaboration's tool. The random-effects model was employed for the meta-analysis. The conclusive results indicate that cinnamon supplementation has a notable effect in reducing body mass index, body weight, and waist-hip ratio. Meanwhile, cinnamon supplementation didn't yield significant effects on waist circumference and body fat mass. These results were deduced from twenty-one randomized controlled trials involving a total of 1,480 participants.
A Experimental Study published in 2019 in the journal Frontiers in Pharmacology found that Pu-erh tea's ability to lower blood pressure is primarily due to theabrownins and caffeine, which cause vasodilation irrespective of the endothelium. For the research methodology, researchers used pu-erh tea aqueous extract to analyze its effects on rat thoracic aortas previously tightened by Phenylephrine or KCl. They observed the isometric tension and intracellular calcium to gauge the direct effects of the tea. The aqueous tea extract was separated into different fractions using organic solvents to identify the specific active components. They assessed the impact these had on the arteries. The results demonstrated that the vessels relaxed in response to the pu-erh tea extract, irrespective of whether the endothelium was removed or preincubated with potassium channel blockers. Furthermore, the contractibility of the vessels induced by Phenylephrine or CaCl under different conditions was reduced. There was also a decrease in the KCl-induced increase of intracellular calcium in rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Among the different components, researchers found that the chloroform precipitate of the pu-erh tea extract resulted in the strongest vasodilation. Theabrownins, a major part of this precipitate, and caffeine were identified as the active components causing vasodilation in an endothelium-independent manner.
A Theoretical Article published in 2019 in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition found that Consumption of oat β-glucan may lower cholesterol and risk of cardiovascular disease by altering gut bacteria and their effects on bile acid and cholesterol metabolism. The research paper focused on studying the impact of oat β-glucan on cholesterol levels and cardiovascular disease risk. The methodology revolved around examining how consumption of oat β-glucan might change the gut microbiota, particularly bacterial species that influence bile acid metabolism and the production of short chain fatty acids. These factors are crucial regulators of cholesterol homeostasis in the host body. The research thus looked into the repercussions on bile acid metabolism, reverse cholesterol transport, short-chain fatty acid production, bacterial metabolism of cholesterol, and microbe-host signaling. The researchers found that oat β-glucan appears to have a significant effect on both the host's cholesterol levels and the composition and functionality of their gut microbiota, which in turn impacts bile acid metabolism and cholesterol homeostasis. It creates a potentially beneficial scenario where intestinal cholesterol may be removed for excretion. The results suggest that the benefits attributed to oat β-glucan are multifaceted and likely involve the regulation of complex interactions between microbes and the host at the level of the gastrointestinal interface. These novel insights demonstrate an interesting relationship between diet, gut microbiota, and host cholesterol metabolism.
A published in 2019 in the journal BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies found that Coix lacryma-jobi sprout extract effectively inhibits cervical cancer cell growth by triggering cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. In the methodology, the research used human cervical cancer HeLa cells to investigate the effects of Coix lacryma-jobi sprout extract (CLSE). The researchers conducted a test known as Cell Counting Kit-8 assay to observe the activity of CLSE on cell multiplication. Flow-cytometric analysis and western blot analysis were also used to examine the impact of CLSE on the regulation of the cell cycle and apoptosis (cell death) in the HeLa cells. In terms of the results, it was found that CLSE significantly halted cell proliferation, and promoted cell cycle arrest in the HeLa cells. This arrest was associated with downregulation of certain key proteins involved in cell cycle regulation. Additionally, CLSE was seen to induce apoptosis, demonstrated by specific staining techniques used to observe nuclear DNA fragmentation. The induction of apoptosis was tied to the inhibition of certain anti-apoptotic proteins and the upregulation of apoptotic proteins. Lastly, it was observed that CLSE deactivated certain key pathways in HeLa cells. As a conclusion, CLSE's therapeutic potential against cervical cancer was emphasized due to these anti-cancer effects.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine found that A combination of peppermint oil and caraway oil is an effective and safe short-term treatment for functional dyspepsia. It is the first attempt to generate RCT data of peppermint oil and caraway oil (POCO) for the treatment of functional dyspepsia. In this meta-analysis, we evaluated the efficacy and safety of POCO based on five RCTs with 578 patients. The results demonstrated that POCO can significantly improve global symptoms of FD, with an NNT of 3 when data from four studies were pooled. The positive and significant efficacy in terms of improvement in epigastric pain was also shown between the two studies. Moreover, the available data have found that the safety profile of POCO is similar to placebo. The strength of our findings is that no significant heterogeneity was detected across the studies. Besides, study designs of the included trials were fairly similar and the duration of treatment was identical. We used rigorous methodology as follows and believe that the results reflect the best available current evidence. Firstly, our literature search was comprehensive including all RCTs regardless of publication type and language. Besides, we adopted the intention-to-treat analysis on all data to enhance the robustness of the results.
A Experimental Study published in 2019 in the journal Nature Communications found that Pu-erh tea was found to lower triglyceride and total cholesterol levels more significantly than green, oolong, or black teas. Comparative studies using rodents treated with Pu-erh tea, green tea, and black tea provided supporting evidence that fully fermented Pu-erh tea is more effective in causing hypolipidemic and hypocholesterolemic effects compared to other partially fermented and non-fermented teas.
A published in 2019 in the journal International Journal of Molecular Sciences found that Coix seed extract could augment the efficacy of gemcitabine therapy in pancreatic cancer cells at least partly due to the alteration of ABC transporter-mediated drug efflux function. Results showed that coix seed extract could synergistically enhance the anti-cancer efficacy of gemcitabine. Meanwhile coix seed extract alone or in combination with gemcitabine could significantly increase the AUCluc while decreasing the Kluc. Western blot and immunohistochemistry assay demonstrated that coix seed extract could significantly mitigate gemcitabine-induced upregulation of ABCB1 and ABCG2 protein. The Pearson correlation analysis demonstrated that the bioluminescent pharmacokinetic parameters and pharmacodynamic index have strong association in vitro and in vivo. In conclusion coix seed extract could augment the efficacy of gemcitabine therapy in pancreatic cancer cells may at least partly due to the alteration of ABC transporter-mediated drug efflux function.
A Review Article published in 2019 in the journal Nutrition Reviews found that Oats improve gastrointestinal health, reduce cholesterol, and regulate satiety, with effects on the gut microbiome constituting an appealing new research area. The researchers undertook a comprehensive literature review using predefined search criteria and keywords related to gastrointestinal health outcomes in the PubMed database. They sought to explore the impact of oats on gastrointestinal health in humans, with the intent to identify both human and animal studies, as well as in vitro studies, that met their specific inclusion criteria. They extracted data from eight human studies, nineteen animal trials, and five in vitro studies for this synthesis. The results underscore that oats, due to their unique composition of bioactive compounds, lipids, and β-glucan, have beneficial effects on gastrointestinal health. The human studies showed consistent beneficial outcomes, with complementary evidence from animal and in vitro studies. The degree of effect, however, appeared to vary depending on the type of oats and dosage used. For instance, oat types providing between 2.5 to 2.9 grams of β-glucan a day were found to decrease fecal pH and alter fecal bacteria, while 40 to 100 grams per day of oat bran was shown to boost bacterial mass and short-chain fatty acids in human feces. The researchers note that different study designs, methodologies, and types of oats used make comparing results challenging.
A Cohort Study published in 2019 in the journal Environmental Geochemistry and Health found that Caramanico Terme’s mineral water treatment significantly improves health and reduces the risk of major diseases like cardiovascular, cancer, and neurological conditions. The study conducted an epidemiological analysis of 370 subjects who received crenotherapy (treatment with medicinal mineral water) at Caramanico Terme in Italy, compared to 287 untreated control subjects. This location is known for its sulfurous and oligomer medicinal mineral waters. Participants’ health outcomes were observed, including relapses of pathology, symptom manifestation, and drug use. The study particularly focused on a subgroup who had undergone crenotherapy for over five years, comparing their health outcomes with age and gender-matched untreated individuals. The study found that those undergoing crenotherapy experienced significantly reduced pathology relapses, symptom manifestations, and need for medications. Particularly notable was the subgroup treated for over five years, showing a significantly lower prevalence of various major diseases, including cardiovascular, inflammatory, neurological, and cancer conditions, compared to untreated subjects. The study suggests both short-term and long-term health benefits from the Caramanico Terme’s medicinal mineral water, including improved life quality and reduced likelihood of developing major disabling pathologies.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition found that Cinnamon supplementation leads to a significant reduction in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure in adults. This systematic review and meta-analysis included studies up to July 2019, sourced from databases like PubMed/Medline, Scopus, ISI Web of Science, Embase, and Google Scholar. The research focused on randomized clinical trials that primarily explored the effect of oral cinnamon supplementation on blood pressure parameters, including systolic or diastolic blood pressure. From the 469 citations, nine trials involving 641 subjects were included. The results inferred that cinnamon supplementation leads to a noticeable decrease in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure. A more remarkable effect on systolic blood pressure was observed in trials using less or equal to 2g cinnamon, lasting for 12 weeks or more, and included participants under the age of 50. Diastolic blood pressure was also reduced using lower doses of cinnamon. No significant non-linear associations were detected between cinnamon supplementation dosage, study duration, and both systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal The American Journal of Gastroenterology found that Peppermint oil significantly reduces colonic spasm during colonoscopy, but does not affect the adenoma detection rate or cecal intubation time. The methodology of this research primarily involved a review of randomized controlled trials that compared the use of peppermint oil and a placebo during colonoscopies. The various trials selected for review were identified through comprehensive searches of databases such as Medline, Google Scholar, and Cochrane up until May 2019. The analysis took into account key variables, including the extent of peristalsis inhibition, cecal intubation time, and adenoma detection rates. In terms of results, there was significant variation in the dosage and administration of the peppermint oil among the 5 trials that qualified for the review. Comparisons were made between a group of 623 subjects who received peppermint oil and a placebo group of 239 individuals. It was found that peppermint oil led to a significant increase in the complete inhibition of colonic peristalsis. However, the cecal intubation times and adenoma detection rates were similar across both the peppermint oil and placebo groups, despite the high level of variation observed.
A Review Article published in 2019 in the journal Antioxidants found that Avocado's nutritional and therapeutic properties show potential for novel drug discovery in prevention and treatment of prevalent diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and cardiovascular issues. The methodology utilized in this review was an extensive summary and assessment of research conducted in recent decades with emphasis on avocado's nutritional and therapeutic properties, along with its unique biochemical profile. Special focus was given to the major metabolites of avocado, their antioxidant properties, as well as their bioavailability and pharmacokinetic features. The discussion of results involved highlighting the potential of avocado in novel drug discovery for the prevention and treatment of a variety of diseases like cancer, microbial, inflammatory, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Emanating from the unique bioactive compounds and antioxidant contents of avocado, it’s clear that the fruit has much more to offer in terms of medicinal value than is currently explored today.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal British Journal of Nutrition found that Higher carrot consumption is associated with a lower risk of developing lung cancer, particularly adenocarcinoma. The researchers carried out a meta-analysis of both case-control and prospective cohort studies. They executed a thorough search of PubMed and Embase databases from inception until April 2018 without limiting language. The studies included in their analysis were ones that reported odds ratios or relative risk for lung cancer risk within the highest and lowest categories of carrot consumption. The analysis incorporated a total of eighteen eligible studies that encompassed 17 case-control studies and one cohort study, involving 202,969 individuals and 5,517 lung cancer patients. The meta-analysis of the combined eighteen studies showed a significant association between higher carrot consumption and reduced risk of lung cancer. Subgroup analysis for different types of lung cancer showed that this association was especially pronounced for adenocarcinoma. Despite testing the robustness of their results by excluding each study one by one, the fundamental result regarding the protective effect of carrot intake against lung cancer remained unchanged. The comprehensive synthesis of observational studies therefore suggested that higher carrot consumption might serve as a preventative measure against lung cancer, notably adenocarcinoma.
A Clinical Study published in 2019 in the journal Nutrition found that Hépar mineral water, rich in sulphates and magnesium, effectively treats functional constipation, showing significant results within 7 days. In this multicenter, randomized, double-blind, controlled study, 226 outpatients with functional constipation were evaluated. Participants underwent a washout period before consuming 1.5 liters of water daily for 14 days, of which 1 liter was either Hépar or low-mineral water. Patients self-reported stool consistency daily, and an expert investigator, blinded to the treatment groups, evaluated stool consistency using the Bristol stool scale based on patient-provided photographs. The study successfully met its primary endpoint, with 50% of participants in the Hépar group responding to treatment by day 14, compared to 29% in the control group. The average time to observe a treatment response was 6.4 days for Hépar users, shorter than the 7.3 days in the control group. Approximately 60% of patients provided stool scores, with 79% of these scores closely aligning between patients and experts. The safety analysis of Hépar indicated excellent results, confirming its efficacy and safety in treating functional constipation.
A Cohort Study published in 2019 in the journal Taiwanese Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology found that Pregnant women's stature, BMI, sedentary lifestyle, as well as the regular consumption of certain foods, influence the formation and severity of striae gravidarum. The study involved 400 primiparas from the Affiliated Hospital of Jiangnan University in Wuxi, during the period of February to October 2017. The participants were divided into two groups of 200: one with pregnant women showing signs of striae gravidarum and one without this symptom. The study considered a variety of predictive factors including their age, height, pre and post-pregnancy BMI, daily sitting time, weight gain during pregnancy, and diet on the mothers and their infant's weight. In the research results, it was observed that women who had striae gravidarum were generally shorter and had a higher BMI both before and after giving birth. Sedentary women showed a lower incidence of abdominal striae gravidarum but higher incidence of striae gravidarum on the legs, with no significant difference in hip striae gravidarum. Interestingly, the consumption of foods like honey, milk, trotters, freshwater fish, eggs, and tremella appeared to reduce the incidence of striae gravidarum. The severity of the stretch marks also varied depending on lifestyle factors.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal Nutrition & Diabetes found that Pu-erh tea has considerable inhibitory effects on alpha-amylase and alpha-glucosidase, indicating potential anti-hyperglycemic benefits. The study employed a systematic review method to investigate the inhibitory effects of Pu-erh tea on alpha-amylase and alpha-glucosidase. English and Chinese databases, specifically PubMed, EBSCO, SCOPUS, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Airti Library, CNKI Library, and Google Scholar, were thoroughly searched up to March 22, 2018 for eligible studies. Search terms included Pu-erh, Pu'er, alpha-amylase, and alpha-glucosidase, aiming to collect an integrative body of literature demonstrating the link between Pu-erh tea and its presumed anti-hyperglycemic effects. Concerning the discussion of the results, the systematic review incorporated six studies that had examined inhibitory effects on alpha-glucosidase and seven that had investigated alpha-amylase. The analysis revealed that Pu-erh tea does indeed demonstrate inhibitory effects on both alpha-amylase and alpha-glucosidase. However, high heterogeneity was identified across the various studies, which could be attributed to the complex changes in chemical composition resulting from varying extents of fermentation. The significant findings suggest the tea's potential as a natural remedy for hyperglycemia.
A Review Article published in 2019 in the journal Nutrition and Cancer found that Kiwifruit supplementation may be associated with direct and indirect anticancer effects, the former likely due to ascorbic acid-mediated reduction of DNA oxidative injury and cytotoxic effect on cancer cell lines. Overall, 58 items could be retrieved, fifty of which were excluded since they did not fulfilled all our search criteria. Eight studies (five in vitro studies, two human intervention trials, and one both in vivo and in human study) were finally included in this critical literature review. Taken together, the results of these published studies suggest that kiwifruit supplementation may be associated with direct and indirect anticancer effects, the former likely due to ascorbic acid-mediated reduction of DNA oxidative injury and cytotoxic effect on cancer cell lines, the latter more likely attributable to enhanced daily bowel movements and increased intestinal fecal content of lactic acid bacteria, which would finally contribute to lower the risk of malignancies, especially colorectal cancer.
A Review Article published in 2019 in the journal Applied Ecology and Environmental Research found that Chrysanthemum, rich in unique chemical compounds, offers significant health benefits such as stress relief, cardio protection, immunity boost, improved eye health, and osteoporosis risk reduction. The study primarily focuses on evaluating the most important chemical extracts of chrysanthemum. These include flavonoids, betaine, choline, and vitamin B1. Further, the researchers identified thirteen compounds unique to chrysanthemum flowers. These were extracted and analyzed to unveil their potential health benefits. In the discussion of results, the authors highlight chrysanthemum's impressive range of health benefits stemming from its chemical composition. It is revealed that chrysanthemum can potentially alleviate stress and anxiety while improving cardiovascular health. It also has properties to guard against oxidative damage and inflammation, support a healthy immune function, enhance eye health, and lessen the risk of osteoporosis. Interestingly, the herb's beneficial traits align with its traditional use in Chinese medicine, underscoring chrysanthemum's potential in promoting holistic, organic health.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal Complementary Therapies in Medicine found that Eating date fruits seems to reduce gestation duration and duration of the first stage of labor, and also increase cervical dilation on admission. In total, 11 and 8 studies were included in the systematic review and meta-analysis. Meta-analysis revealed that date fruit consumption significantly reduced gestation duration, increased cervical dilation on admission, and shorten duration of first stage of labor. Also, it was revealed that date fruit consumption significantly reduced duration of second stage of labor in fixed-effects model; however, this effect was not significant in random-effects analysis.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal Complementary Therapies in Medicine found that Our study found ginger is a promising herbal medicine for health care, which is beneficial for nausea and vomiting, metabolic syndrome and pain. In our overview, most of systematic reviews suggest ginger is a promising herbal medicine for health care, which is beneficial for nausea and vomiting, metabolic syndrome and pain. However, considering the limited quality of included evidence and heterogeneity of different clinical trials, more well-design studies are required to confirm the conclusion further.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases found that Avocado-soybean unsaponifiables treatment is effective in reducing knee osteoarthritis symptoms without increasing adverse events, contrary to those with hip osteoarthritis. To assess avocado-soybean unsaponifiables (ASU) effectiveness and safety, a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials involving patients with hip or knee osteoarthritis was conducted. Various scientific databases, including Medline, SCOPUS, Web of Science, and Google Scholar, were thoroughly searched for suitable trials. Selection criteria consisted of randomized placebo-controlled trials wherein the effect of orally administered ASU on knee or hip osteoarthritis symptoms were evaluated, primarily using the Lequesne index, visual analog scale, and joint space width. The meta-analysis revealed a significant reduction in pain as assessed by the visual analog scale for those under Avocado-soybean unsaponifiables therapy, particularly for patients with knee osteoarthritis, indicated by a decrease in both the visual analogue scale and Lequesne index. However, no such significant effect was found for patients with hip osteoarthritis. In terms of safety, there were no significant differences in adverse events between patients receiving ASU and those given a placebo, confirming ASU's relative safety as a treatment option.
A Review Article published in 2019 in the journal Nutrients found that Honey, comprising mainly carbohydrates, particularly fructose and glucose, demonstrates potential performance benefits and immunological advantages when consumed around exercise, suggesting a role in exercise nutrition. This review assessed nine articles, extracted from 273 results of online database searches (PubMed, MEDLINE, SPORTDiscus), focusing on the effects of honey consumption combined with exercise in humans. Methodological variations existed across studies regarding exercise stimulus, population, and nutritional interventions. Studies reported biochemical variables, with four examining honey's impact on exercise performance and five on perceptual responses. Acute supplementation around a single exercise session showed comparable responses to other carbohydrate sources, with potential performance benefits observed relative to carbohydrate-free comparators. Prolonged honey consumption may mitigate exercise-induced immunological perturbations and enhance markers of bone formation. The synthesis of diverse studies underscores honey's potential in exercise nutrition. Acute supplementation exhibited similarities in performance, perceptual, and immunological responses to other carbohydrates, with some advantages over carbohydrate-free comparators. Prolonged honey consumption showed promise in mitigating exercise-induced immunological disturbances and enhancing markers of bone formation. However, the review highlights the need for more well-controlled research to fully understand honey's role in a food-first approach to exercise nutrition.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal Heliyon found that Oral administration of honey is associated with increased serum testosterone levels in males, supported by in vivo studies suggesting mechanisms involving luteinizing hormone production, Leydig cell viability, oxidative damage reduction, enhanced StAR gene expression, and aromatase activity inhibition. This systematic review examined research articles retrieved from PubMed, Scopus, and Embase databases (May 1993 to April 2019) using keywords "honey" and "honeybee" versus "testosterone." The analysis, primarily based on in vivo studies, concludes that honey positively impacts serum testosterone levels in males. Mechanistically, honey is proposed to elevate testosterone by stimulating luteinizing hormone production, enhancing Leydig cell viability, reducing oxidative damage, promoting StAR gene expression, and inhibiting aromatase activity in the testes. While the evidence is promising, further human studies, particularly clinical trials, are necessary to validate honey's effect on testosterone. The comprehensive review underscores the potential of honey in elevating serum testosterone levels in males, proposing detailed mechanistic pathways. In vivo studies provide valuable insights into how honey influences hormone production, cell viability, and genetic expression. However, the conclusive confirmation of honey's impact on testosterone awaits further research, specifically in the form of human clinical trials, to strengthen the evidence and bridge the gap between in vivo findings and clinical applicability.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal Heliyon found that The collective evidence, which is mainly based on in vivo system studies, reveals that oral administration of honey increases serum testosterone level in males. Mechanistically, honey may increase serum level of testosterone by increasing the production of luteinizing hormone, enhancing the viability of Leydig cells, reducing oxidative damage in Leydig cells, enhancing StAR gene expression, and inhibiting aromatase activity in the testes. However, further research studies on humans, mainly clinical trials, in this specific research approach are still needed to confirm the effect of honey on testosterone.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal Journal of Nursing Research found that Aromatherapy enhances physio-psychological well-being in postpartum women. This systematic review encompassed 15 studies conducted in Iran, England, and the United States, involving 2,131 postpartum participants. The research focused on evaluating aromatherapy's effects on various aspects of postpartum health. Aromatherapy interventions, primarily utilizing lavender and citrus aurantium essential oils, demonstrated positive outcomes. These included relief from nipple fissure pain, improved episiotomy recovery, reduced pain and nausea after cesarean section delivery, and enhanced sleep quality. Additionally, aromatherapy showed potential in positively influencing psychological health, particularly in reducing anxiety. Lavender oil emerged as the most impactful essential oil. While promising, further comprehensive studies are needed to establish aromatherapy as a validated therapy for postpartum women.
A Animal Study published in 2019 in the journal Journal of Food Biochemistry found that Pomegranate rind extract has been found to decrease pain and inflammation, suggesting it could contribute to treating rheumatoid arthritis. The researchers tested the effects of various doses of pomegranate rind extract on Wistar rats within established models of pain and inflammation, such as eddy's hot plate-induced algesia, carrageenan, and Complete Freund's adjuvant-induced models. Indomethacin was also evaluated for comparison. Researchers used bioactive compounds such as phenolics and flavanoids, both of which are known for their potent antioxidant activity. The results observed showed that a dose of 200 mg/kg of pomegranate led to a clear reduction in paw swelling in the rats in both inflammation models. The data further revealed an increase in pain threshold. Through these results, it was determined that pomegranate extract acts to reduce pain and inflammation by inhibiting the activation of a number of inflammatory markers. Furthermore, this study presents the first report on the inhibitory mechanism of these markers by pomegranate rind extract, which is enriched with tannins and flavanoids.
A published in 2019 in the journal Plant Foods for Human Nutrition found that Results demonstrate that 100% watermelon juice is a palatable, effective means of increasing serum lycopene in older adult women, a group at risk for low carotenoid intake. Watermelon is one of the few food sources of dietary lycopene. Because heat treatment increases lycopene bioavailability, ingestion of watermelon in pasteurized juice form may be an optimal delivery vehicle to increase lycopene levels in older adults. However, due to its lipophilic nature, there are concerns that co-ingestion of dietary fat may be necessary for efficient intestinal absorption of lycopene. Thus, this feasibility study aimed to examine the effects of a one-time dose of 100% pasteurized watermelon juice on circulating lycopene concentrations of postmenopausal women after a 10-h overnight fast. Blood was sampled from eight women before and 2 h after ingestion of 360 ml of juice, and serum lycopene was measured by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography. Circulating lycopene levels increased by three-fold (p < 0.001) with increases observed for every participant.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2019 in the journal Aging found that Our study offers the first evidence of the positive contribution of tea drinking to brain structure and suggests a protective effect on age-related decline in brain organisation. Our study comprehensively investigated the effects of tea drinking on brain connectivity at both global and regional scales using multi-modal imaging data (i.e., functional and structural imaging) and provided the first compelling evidence that tea drinking positively contributes to brain structure making network organization more efficient. Our study suggests that tea drinking is effective in preventing (slowing) or ameliorating cognitive decline and that tea drinking might be a simple lifestyle choice that benefits brain health.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2019 in the journal Current Developments in Nutrition found that Consuming walnuts can enhance sperm motility and morphology, potentially improving fertility in males with infertility issues. This study was a randomized clinical trial split into two comparison groups, all of which received typical care for male infertility. Besides the usual care, one group added 42 gm/d walnuts to their diet, while the other group included a daily nutritional supplement recommended for male reproductive health. The participants, a total of 75 in number and with varied demographic profiles, were enrolled at an infertility clinic located in a large metropolitan medical center. The study ran for 3 months, with research measures including semen analysis and blood samples at baseline and after 3 months, while dietary recall and fertility reports were obtained at various stages. In terms of results, the group consuming walnuts showed a marked increase in sperm motility and concentration after 3 months. Simultaneously, both groups—those consuming walnuts and the group consuming the nutritional supplement—demonstrated an improvement in sperm morphology. Further, preliminary data observed over one year suggested a higher frequency of pregnancy in the group consuming walnuts, although it was not statistically significant.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal Nutrients found that The mung bean has been documented to ameliorate hyperglycemia, hyperlipemia, and hypertension, and prevent cancer and melanogenesis, as well as possess hepatoprotective and immunomodulatory activities. The mung bean has been documented to ameliorate hyperglycemia, hyperlipemia, and hypertension, and prevent cancer and melanogenesis, as well as possess hepatoprotective and immunomodulatory activities. These health benefits derive primarily from the concentration and properties of those active compounds present in the mung bean. Vitexin and isovitexin are identified as the major polyphenols, and peptides containing hydrophobic amino acid residues with small molecular weight show higher bioactivity in the mung bean.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal Nutrition Reviews found that Saffron shows promising effectiveness in alleviating symptoms of depression and anxiety and augmenting the effects of antidepressants. The research was carried out following the PRISMA guidelines and performed a comprehensive literature review of randomized controlled trials to study the impact of saffron supplementation on symptoms of depression and anxiety. This included both cases where saffron was used alone as a therapy and cases where it was used in conjunction with other treatments. The quality and risk of bias in these studies were evaluated using the Jadad scale. In this analysis, the result of saffron supplementation was compared against placebo and regular pharmacotherapy. It was concluded that using saffron had a notable positive effect in relieving symptoms of depression and anxiety when compared with a placebo. Additionally, it was found that saffron also demonstrated a sizeable positive effect when used alongside antidepressants in treating depressive symptoms. Nonetheless, the Egger's regression test pointed out evidence of publication bias in this area of study.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal Nutrients found that Drinking certain types of mineral water can positively influence metabolic syndrome factors like blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels. This review examined 20 studies sourced from PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar on how mineral water consumption affects metabolic syndrome (MetSyn) features. The studies varied in their approach, including the type and composition of mineral water, the amount consumed, dietary factors, and study duration. Both human and animal studies were included, with diverse population sizes and characteristics. The research focused on several MetSyn aspects: blood pressure (BP), total triglycerides, HDL-cholesterol, glucose levels, and waist circumference (WC). The review found that certain types of mineral water had beneficial effects on blood pressure, total triglycerides, HDL-cholesterol, and glucose levels, although no significant influence on waist circumference was reported. The presence of specific minerals, elements, and active ions or molecules in the water, along with their pH levels, appeared crucial in counteracting metabolic dysfunctions and the increased acid load in diets associated with MetSyn. The studies discussed various molecular and physiological mechanisms behind these effects. However, further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms by which mineral water consumption might protect against MetSyn features.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2019 in the journal Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry found that Adzuki bean extract administered once a day can result in increased HDL-C concentration. This finding suggests that adzuki bean polyphenols are a novel food ingredient capable of maintaining lipid homeostasis by modulating the HDL-C levels, without causing any adverse effects. This short-term study represents the first step in establishing the practicality, safety, and HDL-C-maintaining effects of adzuki bean extract in subjects with moderate-to-high LDL-C levels.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2019 in the journal Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal found that Peppermint oil capsules may significantly reduce the severity of premenstrual syndrome symptoms in reproductive-age women. The study was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial involving 50 high school students in Babol, Iran who were diagnosed with premenstrual syndrome. Participants were divided into two groups. One group was given Colpermin® capsules, which contained peppermint oil, while the other group was given a placebo. These were taken twice daily from the 15th day of one menstrual period to the first day of the next period across two menstrual cycles. The severity of PMS was evaluated at the first luteal phase of the menstrual cycle and again at the third luteal phase, using a 28-item PMS checklist. Over two menstrual cycles, participants who took the peppermint oil capsules experienced a more significant decrease in premenstrual syndrome scores compared to those in the placebo group. Thus, peppermint oil has demonstrated its potential as an effective treatment in managing the severity of premenstrual syndrome symptoms in this sample.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal Andrologia found that Ginger enhances semen quality and improves sperm parameters, an impact linked to increased levels of gonadal hormones, decreased cell damage, and valued nutrients in ginger. In the methodological approach, this study conducted a systematic review of original research articles listed on Scopus and PubMed. The search terms applied were "ginger," "sperm," and "semen," to find studies published in English from August 2004 to February 2019 that explored the biological effects of ginger or ginger extracts on semen quality and sperm parameters. In the discussion of the results, the main conclusion was that there is clear evidence that ginger betters semen quality and advances primary sperm attributes such as concentration, viability, motility, and morphology. This enhancement is presumably due to increased levels of gonadal hormones, particularly testosterone and luteinising hormone, reduced oxidative damage to cells, increased production of nitric oxide, hypoglycaemic response of ginger, and the presence of valuable nutrients in ginger such as manganese.
A Meta-Analysis published in 2019 in the journal Phytotherapy Research found that Chamomile has demonstrative positive effects on generalized anxiety disorders and sleep quality, but exhibits minimal impact on state anxiety and insomnia. The methodology of this study involved rigorous systematic review and meta-analysis across multiple databases, including PubMed, Science Direct, Cochrane Central, and Scopus. The aim was to determine the efficacy and safety of chamomile for managing state anxiety, generalized anxiety disorders, sleep quality and insomnia in humans. Relevant randomized control trials were retrieved, yielding a total of 12 trials used for this study. Statistical analyses were performed with the meta package of R statistical software version 3.4.3 and RevMan version 5.3. The results indicated that chamomile had a significant positive effect on generalized anxiety disorders (GAD) and improved sleep quality. Improvements in GAD were observed after 2 and 4 weeks of chamomile treatment. However, no significant effects were noted in the treatment of state anxiety or insomnia. Mild adverse events were reported in three trials. In conclusion, chamomile was determined to be effective and safe for treating GAD and improving sleep quality, but showed less impact on state anxiety and insomnia.
A Network Pharmacology published in 2019 in the journal Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science found that Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide, a major bioactive component in the edible medicinal mushroom, exhibits substantial health benefits, including enhancing the immune system, combatting tumors, and delaying aging. The study analyzed various fractions of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide (TFPS) which is extracted from the "Yiner" mushroom under different conditions leading to variations in molecular weight. The TFPS comprises various monosaccharides including mannose, xylose, fucose, glucuronic acid, glucose, and galactose. One of the characterized structures consists of a linear mannose backbone with branched off chains of xylose, fucose and glucuronic acid. Biochemical, pharmacological, and clinical studies involving TFPS spanning 46 years (1972-2018) were drawn from the likes of PubMed, China National Knowledge Infrastructure and Wanfang database and comprehensively reviewed. Over one hundred independent studies pointed to the multiple physiological and health-promoting effects of TFPS. These include benefits such as immunomodulation, antitumor, anti-oxidation, anti-aging, hypoglycemic, and hypolipidemic effects. An example of its practical application is its usage in enteric-coated capsules, approved by the Chinese Food and Drug Administration in 2002, to treat cancer patients suffering from leukopenia induced by chemotherapy and radiotherapy. This component is also used as a supplementary drug for the treatment of chronic persistent hepatitis and chronic active hepatitis, showing the versatility and progressive impact of TFPS.
A Experimental Study published in 2019 in the journal Frontiers in Microbiology found that Pomegranate extracts and a probiotic strain have shown a combined effect in reducing fat content and the development of fat cells, potentially useful in preventing and treating obesity. The study was conducted to uncover the prebiotic potential of water-soluble pomegranate extract, characterized by its phenolic content. This was done by the use of High Performance Liquid Chromatography with Photodiode Array Detector and Electrospray Ionization/Mass Spectra (HPLC-PDA-ESI/MS). The investigation also involved testing the effects of the pomegranate extract and probiotic GG ATCC 53103 strain (LGG) on the 3T3-L1 cell line, to shed light on their impact on fat production and storage within cells. The study appears to showcase that the combination treatment of pomegranate extract and LGG have substantial effects in lowering the creation and accumulation of fat within cells. It was observed that the combined treatment was most effective in reducing triglyceride content and intracellular lipid accumulation. Furthermore, mRNA expression levels of the main transcriptional factors implicated in adipocyte differentiation were substantially lower in cells treated with this combination. These observations suggest a synergistic effect of probiotics and polyphenols contained in pomegranate extract, with the potential to influence fat cell development and offer benefits in addressing obesity.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal Nutrients found that Coffee consumption shows a protective effect against colorectal and colon cancers, particularly among US subjects and European men. A systematic review and meta-analysis of 26 prospective studies was conducted to explore the relationship between coffee consumption and the risk of colorectal cancer. The studies included in the review were appraised for their quality using the Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale for Cohort studies, with only one study deemed to be of low quality. The analysis was stratified by ethnicity to determine if this variable could explain the heterogeneity of the studies. In the discussion of the results, it was found that while coffee consumption didn't show a significant relationship with colorectal cancer overall, when stratified for ethnicity, a protective effect emerged in US subjects. This effect was especially pronounced when looking at colon cancer, with coffee showing a protective effect in men and women combined, and in men alone. When examined by ethnicity, there was a significant protective impact in European men and Asian women. However, there was no significant association found with rectal cancer. Decaffeinated coffee also exhibited a protective effect against colorectal cancer in both men and women combined.
A Experimental Study published in 2019 in the journal Folia Medica found that The pectin-free fraction of Lycium barbarum, or goji berry, strongly inhibits growth in breast cancer cells, and this effect is enhanced by adding polysaccharides. In this study, the researchers isolated three fractions of Lycium barbarum, also known as goji berry, and tested their antioxidant activity using Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity and Hydroxyl Radical Averting Capacity assays. After this, the antiproliferative effects of these extracts were evaluated on three separate breast cancer cell lines. To see the influence of different components of the berry, a distinct pectin-free fraction was used and its effects were studied in conjunction with those of added polysaccharides. The results indicate that the pectin-free fraction produced the most significant growth inhibitory effect on the breast cancer cells. This inhibitory effect was found to be enhanced when polysaccharides were added to the pectin-free fraction. A determining factor for the observed effects seemed to be the polyphenolic content of the extracts, with higher content correlating to stronger effects.
A Experimental Study published in 2019 in the journal Folia Medica found that The pectin-free fraction from Lycium barbarum fruit exhibits significant antioxidant activity and inhibits the growth of breast cancer cells. In this study, researchers took three portions from Lycium barbarum fruit – total water, pectin-free, and polysaccharide, and analyzed their antioxidant potential using Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity and Hydroxyl Radical Averting Capacity assays. The team also examined the pectin-free and the polysaccharide fraction's antiproliferative effects on non-tumorigenic and tumorigenic breast cell lines through the MTT dye reduction assay. The results revealed that the pectin-free fraction from Lycium barbarum fruit demonstrated growth inhibition in a concentration-dependent manner on the three cell lines. This effect was highly pronounced on the breast cancer cells. The polysaccharide fraction showed limited activity, only reducing the proliferation of one type of breast cancer cell at maximum concentration. Surprisingly, pairing the pectin-free and polysaccharide fraction did not produce a synergistic effect. A relationship was observed between the polyphenolic content in the extracts and the resulting effects, with the pectin-free extract containing the most polyphenols and demonstrating the most potent antioxidant and antineoplastic impact against breast cancer cells.
A published in 2019 in the journal Journal of Ethnopharmacology found that There is low quality evidence that bitter melon adjunct preparations improved glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Ten studies of type 2 diabetes mellitus (n = 1045) were included in the meta-analysis. They had 4–16 weeks follow up and overall moderate to high risk of bias. Compared to placebo, M. charantia monoherbal formulation significantly reduces FPG, PPG and HBA1c with mean difference of − 0.72 mmol/L, (95% CI: −1.33, −0.12), I2 = 14%, − 1.43 mmol/L, (95% CI: −2.18, −0.67), I2 = 0, − 0.26%, (95% CI: -0.49, −0.03), I2 = 0 respectively. M. charantia also lowered FPG in prediabetes (mean difference −0.31 mmol/L, n = 52); the evidence was downgraded to low quality because the study had unclear risk of bias and inadequate sample size. No serious adverse effects were reported. M. charantia adjunct preparations improved glycemic control in T2DM patients. However, this conclusion is based on low to very low quality evidences for the primary outcomes and sparse data for several safety outcomes, thus, warrant further research. Particularly needed are the researches that focus on standardizing M. charantia formulation and determine its efficacy and safety in clinical trials with adequate sample size, designed with random sequence generation, allocation concealment of intervention and blinding of both research personnel and participants.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal Nutrients found that Bioactive compounds present in different parts of radishes, such as leaves, sprouts, stem and roots, act on a variety of potential drug targets associated with ailments, such as cancer, inflammation, liver injury and diabetes. Radishes is of great pharmaceutical importance, most of which has been attributed to its antioxidant property. The administration of radish extracts under numerous pathological conditions aids in the recovery of diseases and in the prevention of harmful ailments because of their attributed bioactivities. Bioactive compounds present in different parts of radishes, such as leaves, sprouts, stem and roots, act on a variety of potential drug targets associated with ailments, such as cancer, inflammation, liver injury and diabetes. However, the in-depth molecular mechanistic studies are required to address the regulatory roles of bioactive compounds in radish extracts. In future, researches focusing on the determination and pharmacokinetic elucidation of the bioactive compounds in radishes could facilitate the designing of plant based drugs for life threatening disorders, such as cancer and diabetes. Overall, the knowledge gained from the present researches in radish should be utilized in the discovery of novel drug molecules with higher efficacy towards drug targeting with less side effects.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition found that Black pepper, beyond its culinary use, offers medicinal benefits like antimicrobial, antioxidant, anticancer, anti-diabetic, and anti-inflammatory properties mainly attributed to the compound piperine. The study was a systematic review of existing scientific data on the traditional uses, composition, and pharmacological attributes of black pepper. Information was gathered from recognized databases such as Science Direct and Google Scholar, as well as books and other online resources. The study primarily focused on literature in English and evaluated traditional medicinal uses of black pepper in various regions, the common ailments it was used to address, and the preferred modes of preparation. The results of the study affirm the significant medicinal qualities of black pepper. Its antimicrobial activity was demonstrated against various pathogens, and it showed strong antioxidant effects against several reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. The research also highlighted the anticancer effects of black pepper on cell lines from various sites including breast, colon, cervix, and prostate. Furthermore, the benefits of black pepper in managing diabetes and lipid levels in the body were also confirmed. It was also noted for its anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anticonvulsant, and neuroprotective effects. Piperine was identified as the major bioactive compound in black pepper which is responsible for these beneficial effects along with other compounds such as piperic acid, piperlonguminine, and more.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2019 in the journal Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases found that Synbiotic pomegranate juice (containing inulin and lactobacillus) can improve insulin resistance, reduce testosterone level, and aid weight loss in women suffering from Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. In this randomized, controlled, triple-blind, parallel trial study, patients diagnosed with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (92 in total) were grouped into four groups of 23. The three treatment groups received 2 litres of synbiotic pomegranate juice (SPJ), pomegranate juice (PJ), and a synbiotic beverage (SB) on a weekly basis. The control group was given a placebo beverage weekly. The primary focus of this trial was to observe any changes in insulin resistance, with secondary outcomes including fasting blood sugar, insulin sensitivity, testosterone, luteinizing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, body mass index, and waist and hip circumference comparisons, from baseline to the end of the trial. After finishing the trial, analyses of the remaining 86 patients indicated noticeable improvement in insulin resistance, mainly in the SPJ and SB groups. The same groups also showed a significant increase in insulin sensitivity and an overall decrease in insulin. The SPJ and SB groups also saw significant reductions in body mass index, weight, and waist circumference. Lastly, there was a noteworthy decrease in testosterone levels within the SPJ and SB groups. However, no significant changes were found in fasting plasma glucose, luteinizing hormone, and follicle-stimulating hormone in any of the groups.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity found that The health benefits of goji berries include enhancing hemopoiesis, antiradiation, antiaging, anticancer, improvement of immunity, and antioxidation. Goji berries are a high antioxidant potential fruits which alleviate oxidative stress to confer many health protective benefits such as preventing free radicals from damaging DNA, lipids, and proteins. There is a better protection through synergistic and additive effects in fruits and herbal products from a complex mixture of phytochemicals than from a single phytochemical. The health benefits of goji berries include enhancing hemopoiesis, antiradiation, antiaging, anticancer, improvement of immunity, and antioxidation.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity found that Goji berries, rich in antioxidants, confer health benefits including protection against aging, cancer, and radiation, as well as enhancing immunity and blood production. The methodology of the study focused on a thorough review of the bioactive compounds and pharmacological properties of goji berries, particularly targeting their molecular mechanisms of action. This involved looking at the different ways these fruits are consumed, such as in soups, herbal teas, tinctures, wine, and juice, and how these methods influence the antioxidants present in the fruits. Goji berries were found to offer a range of health benefits due to their ability to alleviate oxidative stress. These benefits include enhancing hemopoiesis (blood formation), offering antiradiation and antiaging properties, inhibiting cancer, improving immunity, and providing antioxidation. Furthermore, the study emphasized that the complex mixture of phytochemicals found in fruits and herbal products like goji berries provide a cumulative protective effect, which proves more beneficial compared to extracting and using one single phytochemical.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2019 in the journal Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics found that Kiwifruit increases water retention in the small bowel and ascending colon and increases total colonic volume. It could be used as a dietary alternative to laxatives in mild constipation. This study aimed to use MRI techniques to identify the mechanism of action behind the therapeutic benefit seen from kiwifruit in previous studies. We hypothesised that some of the physicochemical properties of kiwifruit would increase intestinal water, and we have found this to be the case. Colonic water content, reflected by T1 relaxation time, showed some increase in the ascending colon. This is likely due to water trapping by the fruit fibre in the small intestine. The timing of the increase in colonic water content in the second half of the study day is in accordance with when the meal contents would be predicted to reach the caecum. In the descending colon measuring T1 relaxation time was challenging, as the descending colon was sometimes empty. There was no difference in T1 found here and the values were generally lower than those in the ascending colon. This is as previously reported15 and in keeping with the function of the colon in progressively dehydrating colonic contents as they move distally.
A Network Pharmacology published in 2019 in the journal Molecules found that Raw pu-erh tea extract has superior antioxidant capacity due to higher polyphenol content, but ripe pu-erh offers a cheaper, yet effective alternative for antioxidant or antimicrobial properties. The investigation first utilised mass spectrometry and UV spectroscopy to profile and quantify the primary components of two types of fermented Chinese green tea - raw and ripe pu-erh. This took place after a procedure known as chromatographic separation, used to separate the components of the extract. Beyond this, the activities of the extracts, relating to antioxidant potential, antimicrobial capability and enzyme inhibition, were established and linked to their main components. In discussing the results, though having similar caffeine content and equivalent enzyme inhibition and antimicrobial activities, raw pu-erh extract demonstrated a stronger antioxidant ability owing to it containing a higher concentration of polyphenols. However, the benefits of raw pu-erh tea do not provide enough justification for its higher production costs in comparison to the ripe variety. The ripe variety of pu-erh tea was shown to be a cost-effective alternative for creating products with antioxidant or antimicrobial characteristics.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2019 in the journal British Journal of Nutrition found that Dark chocolate with high cocoa content can affect colonic functionality and stimulate certain brain regions in healthy adults. The study involved a controlled, randomised experiment including healthy volunteers who were given 100g of either dark chocolate (with 72% cocoa content) or white chocolate (with no cocoa content) for five consecutive days. The volunteers then recorded any abdominal symptoms and stool consistency using the Bristol Stool Score. Gastric emptying as well as intestinal and colonic transit time were examined using scintigraphy and marker studies, while the activity in different brain regions was assessed using combined positron emission tomography-computed tomography imaging techniques. The study found that dark chocolate did not alter the functionality of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Nevertheless, it was observed that the consumption of dark chocolate led to harder stool consistency. As for the brain, an increased uptake of fluorodeoxyglucose was noticed within the visual cortex, with other regions like the somatosensory, motor and pre-frontal cortices also showing heightened activity. This suggests that dark chocolate may potentially influence certain brain functions.
A Animal Study published in 2019 in the journal RSC Advances found that Ripened Pu-erh tea extract demonstrates a stronger anti-diabetic impact than raw Pu-erh tea extract, potentially due to the fermentation process and its probiotic benefits to certain gut bacteria. The methods of the study involved the processing and analysis of Pu-erh tea leaves, specifically the raw variety and the ripened type which goes through pile-fermentation. To identify differences in the anti-diabetic effects of both types, the researchers subjected their extracts to ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography paired with quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS) and UHPLC coupled with photodiode array (PDA) analyses. These techniques helped in identifying new compounds formed and those that increased due to the fermentation. The research also performed a study observing the effects of Ripened Pu-erh Tea on beneficial gut bacteria, namely Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Akkermansia, and Roseburia. In their discussion, the researchers noted that the ripened Pu-erh tea extract exhibited more potent anti-diabetic effects on two key indicators of diabetes: two-hour postprandial blood glucose and fasting blood glucose. This superiority over the raw Pu-erh tea extract was attributed to 17 newly formed components and those that increase after fermentation such as quinic acid, gallic acid, caffeine, and puerin I. Furthermore, ripened Pu-erh tea showed to have a probiotic role on certain beneficial gut bacteria, implying an extra potential avenue for its anti-diabetic effects.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2019 in the journal Nutrients found that Daily consumption of tart cherry juice for 12 weeks showed anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory properties which may reduce blood pressure and lower LDL cholesterol in older adults. In the randomized-controlled clinical trial conducted, 37 participants aged between 65 and 80 were given either 480 mL of tart cherry juice or a control drink to consume daily for a span of 12 weeks. Blood biomarkers linked to inflammation and oxidative stress were analyzed both at the start and after the 12 weeks intervention. Post the intervention period, levels of several inflammation and oxidative stress blood biomarkers in the tart cherry juice group observed notable differences compared to the control group. Particularly, a perceivable elevation in DNA repair activity coupled with a reduced mean c-reactive protein level was seen. Furthermore, a significant group effect was seen in plasma levels of c-reactive protein and malondialdehyde, with a slightly less significant effect observed for oxidized low-density lipoprotein. Post- intervention plasma levels showed a decreasing trend, with c-reactive protein, malondialdehyde, and oxidized low-density lipoprotein falling by 25%, 3%, and 11% respectively compared to the baseline values.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2019 in the journal Food & Function found that Daily consumption of tart cherry juice may enhance cognitive abilities in older adults, likely due to reduction of hypertension, inflammation, and oxidative stress. In this randomized controlled trial, 37 adults aged between 65 and 80 years with normal cognitive function were assigned to consume two cups of Montmorency tart cherry juice daily for a duration of 12 weeks. Participants' subjective memory and objective cognitive performance were evaluated at the starting point and after the 12-week juice supplementation using a validated memory questionnaire and a standard assortment of tests designed for cognitive assessment. Factors such as daily caloric intake and physical activity levels were also monitored during the study. After the 12-week intervention, participants who consumed tart cherry juice showed an improvement in their contentment with memory scores, demonstrated decreased scores of movement time, and performed better on a task of paired associates learning when compared to the control group. Notably, the results revealed that the tart cherry juice group demonstrated improvements on measures of visual sustained attention and spatial working memory relative to their own baseline values. These findings suggest that the potential benefits of tart cherry juice to cognitive abilities might be attributed to the juice's antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, and its capacity to reduce blood pressure.
A Network Pharmacology published in 2019 in the journal Molecules found that The purple chrysanthemum tea, imbued with unique antioxidants and affected by infusion time, showed comparatively higher antioxidant activity than the yellow chrysanthemum. Methodologically, the researchers used a variety of testing methods to analyze the phytochemical composition and antioxidant activity of the γ-irradiated mutant chrysanthemum cultivar with dark purple petals (ARTI-Dark Chocolate) and the conventional yellow variety (Gamguk). The influence of different water temperatures and infusion time on the content and activity was also investigated. In addition, the floral scent of both tea types were investigated using spectrometry. Discussion of the results indicates that the phytochemical profiles of both the yellow and purple chrysanthemum teas varied significantly. Purple chrysanthemum tea contained anthocyanins and linarin, which were not present in the yellow variety, and had higher levels of certain compounds. The infusion time and temperature also impacted the purple variety more than the yellow, with the highest total compound content appearing at 100 °C after 4 minutes of infusion. In the antioxidant tests, the purple chrysanthemum tea demonstrated superior antioxidant activity, which was attributed to its high anthocyanin content. In all infusing conditions, both teas presented strong radical scavenging effects.
A Review Article published in 2019 in the journal Therapeutic Advances in Musculoskeletal Disease found that Cherries and their products have antioxidant properties, the capacity to inhibit the acute inflammatory response to urate crystals, and the ability to decrease bone resorption that is characteristic of gouty bone erosions. Phenolics, and more specifically, the anthocyanins found abundantly in cherries, have been linked to the inhibition of IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-8, COX-I and COX-II, as well as the downregulation of NFkB-mediated osteoclastogenesis, suggesting that cherries may have the ability to reduce both acute and chronic inflammation that play a role in recurrent gout flares and chronic destructive arthropathy. Additionally, cyanidin-3-glucoside enhanced genes related to osteoblast differentiation, suggesting that anthocyanins may also play a role in bone formation.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2019 in the journal Journal of Nutritional Science found that Daily consumption of three gold-fleshed kiwifruit is associated with a significant increase of two complete spontaneous bowel movements per week and reduction in gastrointestinal discomfort in mildly constipated adults. This randomised, controlled study demonstrated that consumption of three A. chinensis var. chinensis ‘Zesy002’ (Zespri® SunGold kiwifruit) daily in mildly constipated individuals resulted in a significant increase in two CSBM per week when compared with baseline and the dietary fibre supplement Metamucil®. It also reduced gastrointestinal discomfort by improving symptoms of indigestion, constipation and abdominal pain when compared with baseline and significantly improved indigestion when compared with Metamucil®. ‘Zesy002’ were also well tolerated, efficacious and safe. This is the first study assessing the impact of ‘Zesy002’ on stool frequency and gastrointestinal discomfort, and the results suggest that SunGold kiwifruit has some potential as a possible alternative therapy for constipation. Further studies in this area are required to replicate these findings in other populations and to ascertain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms of action that may be driving these results. These will help to confirm and grow the evidence for ‘Zesy002’ kiwifruit as a whole food which can be incorporated into the daily diet as a treatment for improving symptoms in mildly constipated individuals.
A Experimental Study published in 2019 in the journal Integrative Cancer Therapies found that Lemongrass extract has potential as a supplement to chemotherapy, reducing colon cancer growth, enhancing treatment effectiveness, and mitigating side effects like weight loss. The study utilized both human colorectal cancer models and APC transgenic mice to assess the effectiveness and potential preventive properties of lemongrass extract. The researchers initially tested the impact of the extract in vitro, observing its influence on cancer cells over time and in relation to does. Moreover, they analyzed the extract's effects when orally administered to mice with colon cancer xenografts. This was done to understand its effectiveness in handling colon cancer and potential negative impacts on healthy cells. The latter part of the study focused on the interaction of lemongrass extract with two common chemotherapy treatments used for colon cancer, FOLFOX and Taxol. This was done not only to understand how the extract might influence the chemotherapy's results but also to assess if it could ameliorate any side effects of these potent treatments. It was found that ethanolic lemongrass extract demonstrated a potent anticancer effect by inducing apoptosis (cell death) in colon cancer cells without negatively impacting the healthy cells. This effect was noticed to be both time and dose-dependent. Moreover, when fed to mice with colon cancer xenografts, the extract not only inhibited cancer growth but was well tolerated by the animals. Significant implications were evidenced when the extract was given alongside FOLFOX. Not only did it enhance the effectiveness of this chemotherapy treatment, but it also actively countered weight loss, one of the common side effects. Finally, the lemongrass extract effectively reduced intestinal tumors in APC transgenic mice, suggesting its potential role for preventative measures against colon cancer. Based on these results, the researchers concluded that lemongrass extract may be a promising supplemental treatment for colorectal cancer in the future.
A Theoretical Article published in 2019 in the journal Applied Ecology and Environmental Research found that Chrysanthemum, a plant primarily grown in China and Japan, offers significant health benefits including stress reduction, cardiovascular improvement, and lowering osteoporosis risk. The study focused on Chrysanthemum, a notable plant in the ornamental industry and traditional Chinese medicine, mainly grown in China and Japan. The researchers identified its crucial chemical extracts such as flavonoids, betaine, choline, and vitamin B1. They additionally pinpointed thirteen significant compounds of chrysanthemum flowers, including acacetin-7-0-beta- D-glucopyranoside, luteolin, acaciin, and boscialin, among others. The findings revealed that chrysanthemum tea exhibits considerable health advantages. It eases stress and anxiety, enhances cardiovascular health, protects against oxidative damage, inhibits inflammation, supports healthy immune function, ameliorates eye health, and decreases the risk for osteoporosis. In traditional Chinese medicine, chrysanthemum is considered a cold herb that dispels pathogenic heat, aids the liver, improves eyesight, and promotes detoxification. The study, therefore, endorsed the treatment with natural Chinese herbal medicine, especially chrysanthemum, over synthetic drugs for a more organic life.
A Review Article published in 2018 in the journal Advances in Food Technology and Nutritional Sciences - Open Journal found that Blueberry anthocyanins have a potential role in preventing osteoporosis and demonstrate positive antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity. The methodology of the research involved gathering prior studies and examining the in vitro and in vivo evidence surrounding anthocyanin content and bioavailability from blueberries. The focus of these studies was on both individual chemical structures and the diversity of anthocyanins found in blueberries. The main findings showed that anthocyanins, especially from blueberries, can have a positive impact on bone health. More specifically, they could improve the balance between osteoblasts, cells that form bone, and osteoclasts, cells that dissolve bone. This could potentially prevent osteoporosis. Moreover, even though direct anthocyanin effects on joints from blueberries have not been widely reported, existing studies of isolated anthocyanins common to the blueberry but from other foods, show promising antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity.
A Review Article published in 2018 in the journal Annals of Otology, Rhinology & Laryngology found that Honey exhibits efficacy in otolaryngology, supported by high-quality evidence, particularly in preventing oral mucositis in cancer patients, alleviating pediatric cough, and managing post-tonsillectomy pain. The research involved a comprehensive review of 63 studies across diverse otolaryngology subspecialties. A literature search encompassed PubMed, EMBASE, and Cochrane databases. The studies comprised meta-analyses, randomized control trials, case reports, and animal/in vitro models. Notably, Level 1 evidence predominated, affirming honey's effectiveness in areas such as head and neck surgery, pediatrics, and rhinology. Specific applications include oral mucositis prevention, pediatric cough relief, and post-tonsillectomy pain control, supported by robust meta-analyses. The potential scope for honey in otolaryngology extends beyond current validated uses, suggesting avenues for future exploration.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2018 in the journal Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences found that Consumption of date fruits has a positive impact on the onset and progression of labour, whilst improving infant outcome. The research involved a controlled clinical study where 89 participants were selected at random. These participants were then divided into three groups with varying consumption levels of date fruits. 26 participants ate date fruits alone, 32 participants consumed date fruits followed by water consumption, whilst the remaining 31 participants served as a control group without any consumption of date fruits. The study's results showed a notable positive effect on the labour process for those who consumed date fruits. These effects were most significant during the first and third stages of labour. Additionally, improvements were observed in certain well-being indicators for babies, including healthier amniotic fluid, foetal heart rate, presence of caput, and the APGAR score at 5 minutes. However, no noticeable relationship was found between date fruit consumption and other maternal and foetal well-being factors during labour. There were also no significant differences observed in specific labour progression aspects, such as the dilation of the cervix, rupture of membranes, strength and consistency of uterine contractions, tocometric reports, and maternal progression factors. Notably, the infants of mothers who consumed date fruits scored higher on the APGAR test at 5 minutes post-birth.
A Systematic Review published in 2018 in the journal Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care found that Most bioactive walnut micronutrients synergize to affect multiple metabolic pathways leading to protection from chronic noncommunicable diseases. Nuts in general and walnuts in particular are in the limelight for the association of their consumption with improved health outcomes. Walnuts have an optimal composition in bioactive nutrients and recent clinical and experimental studies have uncovered a number of beneficial effects of walnut micronutrients, working in isolation or in concert, on metabolic pathways and clinical outcomes that make this review timely and relevant. Alpha-linolenic acid, a critical walnut component, is metabolized into bioactive oxylipins, has been shown to protect microglial cells from inflammation, and is associated with lower fatal myocardial infarction rates through a putative antiarrhythmic effect. Phytosterols relate to the cholesterol-lowering effect of nut consumption. Nonsodium minerals are associated with better cardiometabolic health. Walnut phytomelatonin has anticancer effects that are shared by the main walnut polyphenols and their metabolites, ellagitannins and urolithins, respectively. This review highlights new evidence on the health-promoting properties of walnuts and their main micronutrient components. The conclusion is that walnuts are optimal healthful foods.
A Systematic Review published in 2018 in the journal Biomolecules found that Ginger supplementation enhances the production of testosterone in males by reducing oxidative stress and increasing luteinizing hormone production, cholesterol in testes, and blood flow to the testes. The study reviewed a collection of English language articles from three databases— PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science— from November 1991 through August 2018. Keywords for the search included "ginger" and "testosterone". The references from relevant published articles were also reviewed. The methodology encompassed both in-vivo and basic research studies that sought to discover a link between ginger and testosterone. The results revealed that ginger supplementation enhances testosterone production in males, particularly in conditions of oxidative stress. This effect is achieved primarily by increasing the production of luteinizing hormone, cholesterol levels in the testes, reducing testes oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation, enhancing antioxidant enzyme activity, normalizing blood glucose and increasing blood flow in the testes. Furthermore, the study shows a correlation between ginger supplementation and increased testicular weight, and recycling of testosterone receptors.
A Experimental Study published in 2018 in the journal Molecular Nutrition & Food Research found that Dietary supplementation with Goji berries enhances Bifidobacteria and butyrate-producing bacteria growth, resulting in potential preventative effects against colitis. In this study, two groups of IL-10-deficient mice were used, with one group kept on a standard rodent diet and the other supplemented with a Goji berry diet, accounting for 1% of the dry feed's weight. These diets were maintained for 10 weeks. Colonic tissues and fecal contents were collected and analysed after this period. In the Goji supplemented group, there was a noticeable decrease in colonic pathobiological scores, a reduced mRNA expression of Il17a and Tgfb1, and an increase in Muc1 expression and fecal IgA content. Goji supplementation was found to increase the Actinobacteria phylum, leading to a surge in Bifidobacteria in the gut microbiota. Dietary Goji also promoted the growth of butyrate-producing bacteria like the Lachnospiraceae-Ruminococcaceae family and Roseburia species under Clostridium cluster XIVa, with Clostridium leptum and Fecalibacterium prazusnitzii significantly increased in the Goji group. Interestingly, the gene encoding butyryl-coenzyme A CoA transferase, crucial for butyrate synthesis in these bacteria, showed a sixfold increase in the fecal samples from the Goji group, correlating with higher fecal butyrate levels. This phenomenon indicates that Goji berry's dietary inclusion results in Bifidobacteria proliferation and the butyrate-producing bacteria's blooming, which may have cross-feeding relationships providing preventative effects against colitis.
A Review Article published in 2018 in the journal Molecules found that (-)-Epigallocatechingallate (EGCG), a natural product, has potent anti-proliferation, anti-metastasis, and pro-apoptosis effects on cervical cancer cells, enhancing the effects of conventional drugs. This research paper discusses the potential of (-)-epigallocatechingallate (EGCG), a naturally occurring compound, as an anti-cancer treatment for cervical cancer. Traditional treatment methods involve the use of chemotherapy, but these have high toxicity and numerous side effects. The inherent low toxicity of EGCG makes it a promising alternative for treatment. The paper reviews the mechanisms by which EGCG inhibits the growth and spread of cervical cancer cells and promotes their apoptosis. Furthermore, the synergistic pharmaceutical effects of EGCG with conventional agents including cisplatin and bleomycin, have been evaluated. For the discussion of results, the research shows significant evidence of EGCG's abilities to inhibit growth and spread of cervical cancer cells as well as initiate programmed cell death, or apoptosis. The compound's synergistic properties when paired with conventional chemotherapy drugs such as cisplatin and bleomycin, further enhance its potential as a treatment method. The review also explains the underlying processes by which EGCG performs these roles, providing a comprehensive view on its potential applications in cervical cancer treatment.
A Meta-Analysis published in 2018 in the journal Medicine found that Dietary carrot intake is associated with a decreased risk of breast cancer. In order to investigate the relation between carrot intake and the risk of breast cancer, a comprehensive search spanning databases up until September 2017 was performed. Studies were included if they contained risk estimates for the breast cancer risk related to carrot consumption. To collate and analyze data from different studies, random-effects models were used. Publication biases were determined through means such as Begg's funnel plot and Egger's regression asymmetry test. From the search, a total of 10 articles were found that met the criteria and these accounted for 13,747 cases. Upon reviewing these studies, it was noted that the risk of breast cancer was lower for the group with the highest carrot intake when compared with the group with the lowest carrot intake. This association was more pronounced in case-control studies than in cohort studies. The associations did not appear to differ significantly by geographical region, the quality of the study or the method used to assess exposure. Completing the analysis without any single study showed that each study has a minimal effect on the summarised risk. The methodology therefore suggests and supports a link between high dietary carrot intake and reduced breast cancer risk.
A published in 2018 in the journal Nutrients found that The consumption of epicatechin, plentiful in foods like cocoa, positively influences memory, executive function, and processing speed, particularly in older adults. Methodology: The research design for this paper was anchored on the use of intervention studies. These are intensive studies purposed to test breakthrough methodologies or practices on a select group of participants. In this case, the intervention was the ingestion of epicatechin, a compound found largely in cocoa. The subjects monitored were mostly from a more mature demographic, aged 50 years and above. The studies selected for review were those that lasted a minimum of 28 days to ensure an adequate examination period and only those which had a daily epicatechin dose exceeding 50 mg. Discussion of Results: The paper notes an appreciable improvement in the cognitive performance in those subjects who consumed diets high in epicatechin. More specifically, there was an enhancement in memory, executive function, and processing speed. Trends showed that these benefits were more conspicuous in studies which offered more than 50 mg of epicatechin daily, and ran for at least 28 days. The results were particularly noteworthy in the elderly population, where all participants showed cognitive improvement. The impact of epicatechin on cerebral blood flow, however, could not be definitively proved and the results suggest its role requires further exploration. Additionally, the synergistic effects of epicatechin with other dietary elements also complicated the ability to attribute the cognitive improvement to this compound alone.
A Review Article published in 2018 in the journal Molecules found that Tea catechins, found in green tea, may reduce the rates of influenza infection and diminish certain cold symptoms. The research methodology started with interpreting several experimental studies which reported that tea catechins can inhibit influenza viral adsorption and suppress replication and neuraminidase activity. These catechins were also found effective against some common cold viruses and helped to enhance immunity against such viral infections. Additionally, epidemiological studies conducted since the late 1990s were examined which suggested that regular consumption of green tea may decrease influenza infection rates and some cold symptoms, and gargling with tea catechin could potentially protect against the development of influenza infection. For the discussion of results, the studies collectively showed that tea catechins have potential antiviral activity against influenza and some cold viruses. Although clinical evidence supporting these effects remained unconclusive, the review showed promising trends. The consumption of green tea and gargling with tea catechins could lead to potentially decreased rates of influenza infection and lessened cold symptoms according to the analyzed epidemiological studies.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2018 in the journal Nutrients found that Consuming two SunGold kiwifruits daily over 12 weeks improved vitamin C status, reduced blood pressure, waist measurements and altered faecal microbiota composition in prediabetic individuals. Over a 12 week pilot intervention trial, people with prediabetes were observed after consuming two SunGold kiwifruits per day. Participants filled out a physical activity questionnaire and a three-day estimated food diary at both the commencement and end of the trial. Venous blood samples were collected at the start, in between (at 6 weeks) and at the end of the trial, to observe glycaemic indices, plasma vitamin C concentrations, hormones, lipid profiles and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels. Additionally, participants provided faecal samples at each visit for DNA extraction and subsequent amplification and sequencing of a region of the 16S ribosomal RNA gene to determine faecal microbiota composition. The differences were then compared between week 12 and their baseline measurements revealing a significant increase in plasma vitamin C concentration. Further changes including significant reductions in both diastolic and systolic blood pressure as well as waist circumference and waist-to-hip ratio were recorded. Despite recording a slight drop in HbA1c levels and a minor increase in fasting glucose, the changes were small and not clinically significant. Moreover, the composition analysis of the faecal microbiota indicated an increase in the relative abundance of hitherto uncultivated, hence uncharacterised members of a particular bacterial family. These findings suggest that these unknown bacterial members could potentially have a functional relationship with the polysaccharides and polyphenols in kiwifruits.
A Systematic Review published in 2018 in the journal The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that Incorporating walnuts into the diet improved blood lipid profile without adversely affecting body weight or blood pressure. The present meta-analysis of controlled trials provides robust evidence for the benefits of walnut consumption on blood lipids without adversely affecting body weight or blood pressure and supports the results of epidemiologic studies showing inverse associations between walnut consumption and CVD risk. Despite walnuts being energy-dense, the consumption of walnuts does not promote weight gain and thus they can be incorporated into an overall healthy dietary pattern to enhance health benefits.
A Animal Study published in 2018 in the journal Drug Design, Development and Therapy found that The herbal formula B210 can alleviate snoring in aged rats by modifying the activities and breathing time of relevant nerves. In this study, aged rats were treated intraperitoneally with the herbal formula B210, a compound of specific herbal components, or a placebo (sham treatment). The effects of the treatment on snoring quality were analysed by comparing pressure and frequency of snoring, activities of the phrenic nerve, the recurrent laryngeal nerve, and the hypoglossal nerve, as well as inspiratory time and expiratory time of the phrenic nerve, and pre-inspiratory time of the hypoglossal nerve. The results of the study showed that the rats that received the B210 treatment exhibited a marked decrease in snoring pressure and frequency, compared to those that received the sham treatment. Furthermore, there was a notable increase in the activities of the upper airway related nerves - the phrenic nerve, the recurrent laryngeal nerve, and the hypoglossal nerve - observable in the aged rats that received the B210 treatment, demonstrating an extension in the inspiratory and expiratory times of the phrenic nerve, and a prolongation of the pre-inspiratory time of the hypoglossal nerve. These findings point to the possibility of B210's role in alleviating snoring through modulating the activities and breathing times of the nerves related to the upper airway in aged rats.
A Systematic Review published in 2018 in the journal Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition found that Subgroup analysis suggests consuming at least 30 grams of dark chocolate per day for a trial period between four to eight weeks may lead to reductions in weight and body mass index. The study involved a comprehensive search of 35 randomized clinical trials (RCTs) investigating the impact of cocoa/DC on body weight, BMI, and WC up to December 2017. A meta-analysis, using a random-effects model, assessed the pooled effect size, and fractional polynomial modeling was applied to explore dose-response relationships. The meta-analysis did not find a significant overall effect of cocoa/DC supplementation on anthropometric measures. However, subgroup analysis revealed a potential reduction in body weight and BMI when cocoa/DC was consumed at higher doses (≥ 30 g/day) in trials lasting between 4 to 8 weeks. Notably, the reduction in waist circumference followed a non-linear pattern. In conclusion, while cocoa/DC supplementation may not have a universal impact on anthropometric measures, specific doses and durations could potentially influence weight and BMI.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2018 in the journal Journal of Medicinal Food found that Tremella fuciformis, as a nutritional supplement, safely improved subjective memory complaints and cognitive functions in individuals suffering from subjective cognitive impairment. Seventy-five individuals with subjective cognitive impairment were included in an 8-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Participants received either Tremella fuciformis (300mg/day or 600mg/day) or a placebo. The key point of assessment was fluctuations in questionnaire scores evaluating subjective memory complaints. Secondary measures involved changes in short-term memory and executive function performances, assessed using standardized cognitive tests. Effects on grey matter volume were examined using voxel-based morphometry. The Tremella fuciformis group showed significant improvements in total questionnaire scores related to subjective memory complaints compared to the placebo group. Alongside this, substantial improvements were recorded in short-term memory and executive functions within the same group. Factors such as left precuneus, right supramarginal gyrus, right middle frontal gyrus, and right postcentral gyrus revealed significant group-to-visit interactions with no notable increase in adverse events among both high dose and low dose Tremella fuciformis groups, and the placebo group. These findings emphasize the potential of Tremella fuciformis as a safe nutritional supplement to alleviate subjective memory complaints and boost cognitive functions in individuals with subjective cognitive impairment.
A Systematic Review published in 2018 in the journal Phytomedicine found that Ginger supplementation has a favorable effect on levels of triacylglycerol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, especially in doses of 2 grams or less per day. Systematic searches were conducted on various databases including PubMed, Scopus, Science Direct, ISI Web of Science and Google Scholar until May 2017. The aim was to locate clinical trials examining the effect of ginger supplementation on lipid parameters in adults. Information relating to blood lipid means and potential sources of heterogeneity was extracted. Subgroup analysis was further conducted to identify potential sources of inter-study heterogeneity. In total, the meta-analysis included data from 12 trials involving 586 participants. The pooled analysis indicated that ginger supplementation led to reductions in triacylglycerol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Ginger, however, revealed no significant changes in total cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. It was noted that a high degree of inter-study heterogeneity existed. Therefore, studies were further classified based on the dosage of ginger used. Stratification showed significant reductions in total cholesterol and triacylglycerol in those studies using doses of 2 grams or less of ginger per day. Conversely, such an effect was not observed in trials that used doses greater than 2 grams of ginger. There also wasn't any significant alteration in low-density lipoprotein or high-density lipoprotein cholesterol noted in studies irrespective of ginger dosage.
A Systematic Review published in 2018 in the journal Journal of Complementary and Integrative Medicine found that Fennel caused a significant increase in mean menstrual bleeding in the first cycle after treatment in the intervention group compared to the control. A total of 7993 articles were identified through searching the databases, of which 7327 were excluded as duplicates and 666 were screened for inclusion. Six hundread and forty six were excluded by title and abstract based on not being relevant to the review and being conducted on animals. Eventually, six articles were included in the study and four articles entered into the meta-analysis. The results from meta-analysis showed that using fennel caused a significant increase in mean menstrual bleeding in the first cycle after treatment in the intervention group compared to the control. However, it had no significant effect on menstrual bleeding in the second cycle after treatment.
A Systematic Review published in 2018 in the journal Food Science and Human Wellness found that The consumption of mung beans and sprouts in regular basis are not only providing nutrients, but also maintains the microbial flora in the gut, reduces the absorption of toxic compounds, decreases the menace of obesity, hypercholesterolemia, and cardiovascular diseases, and also prevents cancer and diabetes. Based on the high constituents and efficacy of the bioactive compounds, mung beans are playing a greater role in radical scavenging activities, detoxification, and also exhibits chemo-preventive effects. These compounds have the potential health benefit as a complementary and alternative medicine which is exerted for its antioxidant, hepatoprotective, antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, cardioprotective, anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic, anticancer, anti-obesity, hypolipidemic, and potent chemopreventive properties.
A Systematic Review published in 2018 in the journal Journal of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Cancer Research found that Aromatherapy with lavender demonstrated effectiveness in reducing labor pain during childbirth. In the methodology for this systematic review and meta-analysis, researchers independently conducted searches across international databases such as MEDLINE/PubMed, Cochrane Library, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, and Scopus. The search utilized specific symbols and terms to locate relevant randomized clinical trials. Data was then statistically analyzed using Comprehensive Meta-analysis (CMA) software. In the discussion of results, a total of 244 primary studies were initially found, and ultimately 5 studies, which included 541 participants, were analyzed in the review. It was found that aromatherapy with lavender reduced labor pain in the active phase of childbirth. Overall, the clinical trials were of moderate quality and combinatory. Importantly, the use of lavender in aromatherapy led to a notable difference in labor pain between the aromatherapy groups and control groups. This finding suggests the potential of lavender aromatherapy as a useful tool for pain relief during labor.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2018 in the journal Clinical Nutrition found that Green tea extract can potentially control pain and improve knee joint physical function in adults suffering from osteoarthritis. The study employed a randomized open-label active-controlled clinical trial in which fifty adults with knee osteoarthritis were randomly divided into two groups. One group received the green tea extract in tablet form along with diclofenac tablet, referred to as the "intervention group," while the other, the "control group," received only the diclofenac tablet. This trial period lasted four weeks. The researchers evaluated the patients at the start of the trial and then four weeks later, measuring the pain score through a visual analogue scale and a specific osteoarthritis questionnaire's score, in addition to its three sub-scores. The participants were also asked to report any side effects experienced during the trial period. The outcomes of the experiment showed that when compared to the control group, the green tea group showed a significant decrease in their pain score and the score measuring knee joint function. However, no differences were observed between the two groups in terms of the specific osteoarthritis questionnaire's pain and stiffness scores. An adverse event of gastric upset was reported in only one patient from the control group.
A published in 2018 in the journal BioMed Research International found that Citrus limon extracts could be a promising antioxidant source for the prevention and/or treatment of oxidative stress-related diseases. Extracts from Citrus limon exhibit powerful antioxidant properties, expressed by its capacity to scavenge DPPH radicals and to reduce power, and the extracts reduce H2O2-induced DNA via its antioxidant activities. These antioxidant activities and inhibitory effects of the extracts on DNA and cell damage may further prove that Citrus limon is useful as a medicinal plant for cancer chemoprevention. The results obtained show that Citrus limon extracts contain high enough levels of phenolic and flavonoid compounds. This is correlated with a remarkable antioxidant activity towards the reduction of iron, and a relatively high power against scavenging free radicals.
A Review Article published in 2018 in the journal Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity found that Honey, a natural food supplement, emerges as a potent therapeutic antioxidant with diverse medicinal effects, including wound healing, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antifungal, antiviral, and antidiabetic properties, suggesting its potential as a novel antioxidant in managing oxidative stress-related diseases. The research extensively reviews honey's medicinal effects, emphasizing its role as a therapeutic antioxidant. The study explores various mechanisms, including the modulation of multiple signaling pathways and molecular targets. The evidence-based research underscores honey's role in alleviating diseases linked to oxidative stress. The reviewed pathways include caspase induction, cytokine stimulation, cell cycle regulation, and modulation of inflammatory markers. The comprehensive exploration of honey's therapeutic potential indicates its promise as a standalone or adjuvant antioxidant, necessitating further experimental and clinical investigation.
A Review Article published in 2018 in the journal Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity found that Honey may be used as a potential antidiabetic agent that has the potential to reduce the complications of diabetes. Considerable evidence from experimental studies shows that the honey may provide benefits in the management of diabetes mellitus. The benefits could be a better control of the hyperglycemic state, limiting other metabolic disorders and diminishing the deleterious effects on different organs that may produce diabetic complications. Anyway, there are some data and literature with contrary discussions regarding the use of honey in diabetic diseases. Long-term studies using honey as an alternative or a complementary therapy in human subjects suffering from type 2 diabetes mellitus are needed, with a larger number of patients, randomized clinical trials set up with different levels of diabetes, treated with different doses of honey, following both short-term and long-term treatment.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2017 in the journal Complementary Therapies in Medicine found that Chamomile extract significantly improved sleep quality among the elderly, suggesting its potential as a safe sleep-promotion tool for this population. In a single-blind randomized controlled trial, sixty elderly individuals from a daycare nursing home in Karaj, Iran, were randomly assigned into a control group or a treatment group. Those in the treatment group received 200mg chamomile extract capsules, administered twice daily for 28 consecutive days, while the placebo group received 200mg capsules of wheat flour in the same manner. Sleep quality was evaluated using the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index at four different time points: immediately before the experimental period, two weeks into the study, right after completing the 28-day cycle, and two weeks post-intervention. Results showed no significant difference between the control and treatment groups in their baseline sleep quality, with both presenting poor scores. However, following the 28-day intervention, the treatment group, who received chamomile extract, demonstrated notably better sleep quality than the placebo group, with the exception of the habitual sleep efficiency component of the Sleep Quality Index. These findings suggest that chamomile extract can be employed as a safe and effective means to enhance the sleep quality of elderly people.
A Clinical Study published in 2017 in the journal Journal of Food Science found that Adding fresh herbs like parsley and chives to air-fried sardines reduces the levels of harmful cholesterol oxidation products formed during cooking. To conduct this study, sardine fillets were air fried, a method considered healthier as it allows frying without oil. The research then revolved around the monitoring of two types of substances: cholesterol oxidation products (COPs), theorised to increase with the high heat, and essential polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), which typically decrease in such conditions. In the analysis of the results, it was observed that, indeed, cooking through air frying escalated the levels of COPs while diminishing that of essential PUFAs. The experiment further introduced fresh herbs, namely parsley, chives and a mix of both, owing to their properties as natural antioxidants. This addition was observed to lower the levels of COPs formed, indicating a healthier outcome. Specifically, air-fried sardines with 4% cheiro-verde (the mixed herbs) offered the best protection against lipid or fat oxidation.
A Systematic Review published in 2017 in the journal Journal of the American College of Nutrition found that Date palm components (pollen, pit powder, and gemmule extract) significantly improve male fertility directly through hormonal changes and indirectly via antioxidant abilities. The methodology used to gather the data for this study involved an extensive review of articles published between 2005 and 2016 on the subject matter. Various medical, scientific and academic databases were searched in both English and Turkish, including PubMed, Science Direct, Clinical Key, Google Scholar, Springer, Dergipark, Ulakbim, and Akademik Dizin. The review focused on the effects of pollen, pit powder, and gemmule extract of the date palm on male fertility. In regard to the results, the research identified that there is a positive correlation between the use of date palm components and male fertility. The date palm elements were found to cause beneficial alterations in hormone levels associated with male fertility. Additionally, an increase in sperm motility and quality, spermatogenesis, and weights of testes and epididymis were also reported. Antioxidant capacities due to phenolic compounds in the date palm components play a significant role in this improvement, as do included gonadotropic and steroidal compounds.
A Systematic Review published in 2017 in the journal Phytomedicine found that Green tea consumption was shown to reduce psychopathological symptoms like anxiety and was also shown to effect cognition, with noted benefits for memory and attention. Green tea was also linked with the activation of working memory as seen in functional MRI. The effects of green tea cannot be attributed to a single constituent of the beverage. This is exemplified in the finding that beneficial green tea effects on cognition are observed under the combined influence of both caffeine and l-theanine, whereas separate administration of either substance was found to have a lesser impact.
A Network Pharmacology published in 2017 in the journal Frontiers in Pharmacology found that Adzuki beans, rich in flavonoids and saponins, can potentially prevent obesity by inhibiting enzymes related to fat accumulation and enhancing lipid breakdown. The study involved both in vitro and in vivo experimentations. Flavonoids and saponins from adzuki beans were examined for possible inhibitory effects on pancreatic lipase and α-glucosidase activities, and noradrenaline-induced lipolysis. Additionally, an obesity model in mice, stimulated by a high-fat diet, was established to explore the beans' potential anti-obesity properties. Over a period of 8 weeks, changes in the mice's serum and liver lipid parameters were carefully monitored during the intervention process. The results demonstrated that extracts from adzuki beans could enhance the process of lipolysis. When administered orally to mice, the beans significantly lessened the total body weight and accumulation of adipose tissue compared to the group on a high-fat-diet. Changes were also observed in the lipid levels, both in serum and liver, with notable reductions in total cholesterol, triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol, and liver lipids. These findings suggest that adzuki beans' anti-obesity effects may be due to the inhibitory action of their flavonoids and saponins on α-glucosidase and pancreatic lipase activities, along with the lipid-metabolizing properties of their active components.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2017 in the journal Journal of Ethnopharmacology found that The extract from Hovenia Dulcis fruit (HDE) appears to decrease hangover symptoms effectively by regulating the body's inflammatory response to alcohol. The research methodology involved a randomized controlled crossover trial, utilising a group of 26 adult males with heterozygous ALDH2 who consumed Korean Soju (50g alcohol) along with HDE or a control placebo. Following consumption, blood samples were collected at baseline, or zero hours, and again at one hour, four hours, and twelve hours after treatment. The presence of alcohol, acetaldehyde, and overall hangover severity were monitored during these periods. After the consumption of alcohol, peak blood alcohol, acetaldehyde concentrations and hangover scores were observed one hour post-treatment, with no significant differences between the HDE and placebo groups. However, the group that consumed HDE showed a noticeably larger decrease in hangover symptom scores over time compared to the placebo group. Other significant differences included measurements of olive interleukins, signaling proteins that modulate inflammation, and levels of aspartate aminotransferase, an enzyme associated with liver damage. The analysis also indicated potential interactions between the efficacy of HDE and the genetic variant CYP2E1, which may affect how individuals metabolized alcohol.
A Practice Guideline published in 2017 in the journal Maturitas found that Long-chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids have various health benefits for postmenopausal women including reducing triglycerides and improving depression and psychotic symptoms. A panel of experienced experts from the Spanish Menopause Society embarked to establish a comprehensive set of recommendations for the intake of long-chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids by postmenopausal women. This was steered based on the best available evidence and research. It was especially noted that the consumption of these fatty acids, at doses higher than 3 grams per day, proved to significantly decrease the levels of triglycerides in the body. The results obtained from this study are promising and underline the potential health benefits of long-chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids for postmenopausal women. Alongside reducing triglyceride levels, they also contribute to antiarrhythmic effects, reduction in blood pressure, and improvements in depressive and psychotic symptoms. Furthermore, it was noted that their consumption does not increase the risk of cancer in these women. The potential of these fatty acids in providing relief from menopause symptoms and osteoporosis was also explored, yielding positive indications.
A Review Article published in 2017 in the journal Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition found that Kiwifruits can relieve constipation and irritable bowel syndrome, potentially through protease-activated signaling, modulation of microflora, changes in colonic methane, bile flux, or mediation of inflammatory processes. The review outlines the physiological processes underlying constipation and irritable bowel syndrome, and discusses the nutritional composition of kiwifruits. It delves into recent advances made in the study of kiwifruits and their impact on abdominal comfort, with the focus being given to the effect of kiwifruit fibers on gastrointestinal health. The study also identified and examined certain gaps in the existing research, using indications from studies on other foods known to affect the gastrointestinal tract to derive possible mechanisms of kiwifruits' beneficial actions. In discussing the results, the review observed that while the effect of kiwifruit fibers on gastrointestinal health is well established, the supposed increase in gastrointestinal motility caused by kiwifruits is yet to be fully characterized. Numerous potential mechanisms were invoked that could be contributing to the physiological effects observed - these included the induction of motility through protease-activated signaling, the modulation of microflora in the gut, alterations in colonic methane status or bile flux, and the mediation of inflammation within the gut.
A Systematic Review published in 2017 in the journal Oncotarget found that High consumption of carrots is associated with a reduced risk of urothelial cancer. The methodology for this meta-analysis comprised of a comprehensive search across databases like PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, EMBASE, Cochrane register, and Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure. Studies up till January 2017 regarding the correlation between carrot intake and urothelial cancer risk were evaluated. The selected studies included four case-control studies and two cohort studies, six in total. The combined odds ratio for the highest versus the lowest intake of carrot was computed to measure risk correlation. The results showed a notable reduction in the risk of urothelial cancer for individuals with high intake of carrots. However, significant heterogeneity was observed among the included studies. Additionally, there was no substantial publication bias found by applying both Begg's test and Egger's test. Even in the light of the observed heterogeneity and limited studies, the key conclusion points towards high carrot intake as a potential contributor to lower urothelial cancer incidence.
A Systematic Review published in 2017 in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition found that Cocoa consumption has strong beneficial impacts on cardiovascular health, reducing blood pressure, improving vascular function, and modulating lipid and glucose metabolism. In the study's methodology, the link between the consumption of natural polyphenol-rich foods, specifically cocoa, and a decreased risk of cardiovascular diseases was explored. The process involved evaluating cocoa's influence on various aspects, such as blood pressure reduction, vascular function improvement, lipid and glucose metabolism modulation, and reduction of platelet aggregation. This evaluation was performed in varying demographic groups, including healthy individuals, individuals with risk factors such as diabetes and arterial hypertension, and individuals with established coronary heart diseases or heart failure. The study's findings indicate that cocoa's consumption has a significant and positive effect on cardiovascular health. Notably, it was found to reduce blood pressure, enhance vascular function, and modulate lipid and glucose metabolism. These beneficial effects were observed in all the subjects irrespective of their health status - healthy, at risk, or with established cardiovascular diseases. The results hypothesize several potential mechanisms through which cocoa exerts these positive effects, including the activation of nitric oxide synthase, increased availability of nitric oxide, and inherent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
A Systematic Review published in 2017 in the journal Molecular Medicine Reports found that Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide alleviated hydrogen peroxide‑induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in skin fibroblasts via upregulation of SIRT1 expression, indicating that TFPS may act as a potential therapeutic agent for oxidative‑stress‑associated skin diseases and aging. We demonstrated that pretreatment with TFPS suppressed H2O2-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in skin fibroblasts in a concentration-dependent manner and possessed excellent antioxidative properties. Therefore, our present findings may provide a theoretical basis for TFPS as an alternative herbal food supplement and potential pharmacotherapy for skin injury and aging. However, given that TFPS contains several polysaccharides and has a variety of pharmacological effects, our study, which focused on oxidative stress inhibition and anti-apoptotic effects, has limitations. Further studies are required to define the potential protective mechanisms of TFPS in H2O2-induced skin injury. In summary, we revealed that TFPS exhibits protective properties against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis mainly by upregulating SIRT1 and promoting downstream signaling, suggesting that TFPS is a potential therapeutic agent for oxidative stress-related skin diseases and skin aging.
A Experimental Study published in 2017 in the journal Mental Health Clinician found that Lavender essential oil, particularly its primary constituents linalool and linalyl acetate, may offer a beneficial anxiolytic effect through its interaction with certain neurological mechanisms. The methodology used in this research involved studying lavender essential oil as an option in aromatherapy for anxiety disorders. This focused on the variability in the constituents, specifically the two primary terpenoid components, linalool and linalyl acetate. In order to comprehend the anxiolytic effect of these constituents, their interaction with neurological mechanisms such as voltage-gated calcium channels, reduction of 5HT1 receptor activity and the parasympathetic tone were studied. The obtained results revealed that lavender essential oil has notable potential in treating anxiety disorders due to its interaction with certain neurological mechanisms. This potential anxiolytic effect stems primarily from its two key components, linalool and linalyl acetate. The level of efficacy currently recommended is not yet approved by the Food and Drug Administration, but promises a possible future pathway for a novel treatment, given the limitations of existing pharmacotherapy for anxiety disorders. The current safety profile of lavender oil presented within this study supports these findings.
A Review Article published in 2017 in the journal Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine found that Jujube possesses neuroprotective activities, including protecting neuronal cells against neurotoxin stress, stimulating neuronal differentiation, increasing expression of neurotrophic factors, and promoting memory and learning. Jujube possesses neuroprotective activities, including protecting neuronal cells against neurotoxin stress, stimulating neuronal differentiation, increasing expression of neurotrophic factors, and promoting memory and learning. Flavonoid, cAMP, and jujuboside could be the potential bioactive ingredients to account for the aforesaid biological activities. These findings imply that jujube is a potential candidate for development of health supplements for prevention and/or treatment of neurological diseases.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2017 in the journal Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine found that Pomegranate juice consumption over a short period promotes red blood cell production without significantly changing metabolic health and inflammation markers in healthy individuals. In the methodology of this study, ten healthy subjects (five males and five females averaging 31.8 years of age and weighing an average of 66.2 kg) were split into two groups. One group drank 500 ml of pomegranate juice every day for 14 days, while the other did not. Blood samples were taken from the subjects before and after the experimental period to measure various health markers. In the discussion of results, it was observed that pomegranate juice intake led to a substantial rise in red blood cell count, hemoglobin levels, and hematocrit levels. However, other complete blood count parameters, and levels of glucose, cholesterol, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein, and C-reactive protein remained largely unaffected after the juice consumption. This suggests that pomegranate juice only had a substantial effect on increasing erythropoiesis or decreasing degradation in healthy individuals.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2017 in the journal Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics found that Honey has been shown to provide similar pain relief to traditional medication mefenamic acid for women with primary dysmenorrhea, with fewer side effects. In this randomized crossover clinical trial, 56 female university students with primary dysmenorrhea were split into two groups and were either given honey or mefenamic acid during their 'first treatment period.' For the 'second treatment period,' the groups were switched and the subjects were given the alternate treatment. The participants' pain levels were recorded during the first three days of menstruation. The results showed that there was no significant difference between the most severe level of pain experienced in the two groups during both months of the treatment period. In effect, both honey and mefenamic acid provided similar levels of pain relief to women with primary dysmenorrhea. Notably, honey is recommended due to its lower side effects and pharmacological complications compared to mefenamic acid. No future research trials were mentioned.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2017 in the journal Journal of Education and Health Promotion found that Green tea consumption leads to weight loss and decreased levels of fasting insulin and free testosterone in overweight women with polycystic ovarian syndrome. In the research methodology, a two-group, double-blind, randomized clinical trial was conducted among 60 overweight women with polycystic ovarian syndrome in Isfahan. The participants were randomly classified into two groups, one receiving green tea (the experimental group) and the other receiving a placebo (the control group). Comparisons of levels of free testosterone hormones and fasting insulin were made at the start of the study and 12 weeks later, along with measurements of participant weight before and after the study. Discussing the results, the comparison showed no initial significant difference in participant weight, fasting insulin or free testosterone levels between the two groups. However, after the 12-week period, notable differences were observed. The green tea group showed significant weight loss and declines in both fasting insulin and free testosterone levels compared to the placebo group.
A Animal Study published in 2017 in the journal Nutrients found that Dried plums potentially prevent and reverse bone loss in postmenopausal women facing osteoporosis, offering a promising functional food therapy solution with long-lasting effects. The methodology focused on examining the influence of dried plum in preventing and reversing bone loss related to osteoporosis. Two populations were studied: an ovariectomized rat model, which simulates the condition in postmenopausal women, and actual osteopenic postmenopausal women. The subjects were given measured servings of dried plums and their bone mass and structure were analyzed over a certain period. The researchers also attempted to understand the possible mechanisms through which dried plum exerts its bone-protective effects. In terms of results, evidence suggested that dried plum effectively retarded bone loss in both the rat model and human subjects. An intriguing observation was from a follow-up study of the one-year clinical trial conducted five years earlier. Women who had been in the trial consuming 100 g dried plum per day were found to have retained bone mineral density more efficiently than comparative controls. Dried plum's beneficial effect was hypothesised to originate from its bioactive compounds. The overall findings strongly advocate dried plum as a functional food therapy for preventing osteoporosis in postmenopausal women.
A Animal Study published in 2017 in the journal Holistic Nursing Practice found that Curcumin's potential anxiolytic and antidepressant impacts do not significantly alter behavior or interact with the benzodiazepine site of the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor A. In this study, a prospective, between-subjects group design was employed. The subjects were 55 male Sprague-Dawley rats randomly split into five groups, each given different intraperitoneal injections: a control group, curcumin, curcumin with flumazenil, midazolam alone, and midazolam with curcumin. Behavioral observations were conducted with the aid of the elevated plus maze, open field test, and forced swim tests. A two-tail multivariate analysis of variance was deployed for data analysis. The results showed that, according to the behavioral tests, curcumin did not generate any notable signs of anxiety-relieving or mood-lifting effects. It was also noticed that curcumin didn't show any interactive tendencies with the GABAA receptor's benzodiazepine site. The team therefore concluded that curcumin didn't produce any significant outcomes on these aspects of mental health modulation as was purposed in the initial hypothesis.
A Animal Study published in 2017 in the journal Oncology Letters found that Blueberries can reduce the proliferation of ovarian cancer cells by downregulating the levels of specific biomarkers, exhibiting potential for non-pharmaceutical therapy. The research method involved the overexpression or silencing of cyclooxygenase (COX)-1 and COX-2, known biomarkers of ovarian cancer, in SKOV3 ovarian cancer cells. The effect of blueberries on the cells' viability was then measured utilizing a colorimetric assay known as an MTT test. Additionally, a mouse model for ovarian cancer was established to further this investigation. The results revealed that the administration of blueberries led to the inhibition of ovarian cancer cell proliferation, primarily through decreased levels of COX-1 and COX-2. Furthermore, regular consumption of blueberries greatly reduced the tumor size in the ovarian cancer mouse model compared to the control without blueberry treatment. This indicates that blueberries might have considerable potential as a natural therapy for ovarian cancer due to fewer side effects and high effectiveness.
A Review Article published in 2017 in the journal Nutrients found that Dried plums, or prunes, have potential to exert beneficial effects on bone health and may help in combating osteoporosis in postmenopausal women, if consumed as part of their recommended fruit intake. The research process involved a comprehensive review of scientific literature available in the PubMed database up until January 24, 2017. This literature included cell studies, animal studies, population and clinical studies that examined effects of dried plums or their extracts on markers of bone health. In total, 24 research papers were reviewed and their findings are summarized. Discussing the results, animal, cell, and clinical studies suggest that dried plums or their extracts positively impact bone formation and limit bone breakdown. This is likely due to the influence of dried plums on cell signaling pathways that dictate osteoblast (bone-building cells) and osteoclast (bone-destroying cells) differentiation. Clinical studies also indicate that consumption of dried plums could have beneficial effects on bone mineral density, particularly in postmenopausal women. There were no adverse effects reported in these studies, further suggesting that they could safely be included in regular dietary routines.
A Case Report published in 2017 in the journal The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine found that Chamomile consumption may stimulate abundant milk production and increase lactogenesis in lactating women. In the report, a woman accidentally discovered an unexpected outcome - an abundant amount of milk and high breast tension - a few hours after consuming chamomile. This observation has not been documented before and sheds light on a possible natural means of stimulating milk production. Regular consumption of chamomile during pregnancy and lactation is well-known for various reasons, but this galactagogue effect, that is the promotion of lactation, has never been reported previously. The woman’s case was carefully documented and analysed to draw a correlation between chamomile intake and this resulting effect. The potential galactagogue effect of chamomile presents an interesting but unfamiliar aspect. This insight could be potentially useful for mothers struggling with breastfeeding,with the caveat being that the safety of this herbal product's intake without risk to mothers or newborns is still under scrutiny. The results are unexpected and novel, pointing towards a potential new benefit of chamomile tea for lactating women - stimulating lactogenesis. However, the conclusions are drawn from a single case and further in-depth studies are required to confirm this effect and to understand the underlying biological mechanisms at work.
A Systematic Review published in 2017 in the journal Phytotherapy Research found that Avocado, with its lipid-lowering, antihypertensive, antidiabetic, anti-obesity, and cardioprotective effects, can potentially manage metabolic syndrome more efficaciously than synthetic treatment options. The methodology used in this research involved a systematic review of several studies investigating the pharmacological effects of avocado on different components of metabolic syndrome. This included studies on the lipid-lowering, antihypertensive, antidiabetic, anti-obesity, antithrombotic, antiatherosclerotic, and cardioprotective effects of avocado. Further, the review also encompassed researches based on the effects of avocado's various parts like the flesh, seed, peel, and leaves in metabolic syndrome. Upon evaluation of collected studies, the researchers found that the avocado, a rich source of carotenoids, minerals, phenolics, vitamins, and fatty acids, demonstrates strong potential in managing metabolic syndrome. Its antidiabetic, antihypertensive, anti-obesity, lipid-lowering, and cardioprotective properties specifically align with the key risk factors of metabolic disease, including high blood sugar, dyslipidemia, hypertension, and obesity. These qualities suggest that avocado might present a more efficient and less adverse alternative to synthetic treatments.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2017 in the journal Plant Foods for Human Nutrition found that Pomegranate juice intake can reduce systolic and diastolic blood pressure and inflammation markers, but may increase triglyceride and very low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. In this double-blind crossover study involving 30 patients with metabolic syndrome, the subjects were given a daily dose of 500 ml pomegranate juice for a week. After a week-long "wash out" period, the participants were then given a placebo for another week. A range of metrics, including lipid profile, fasting blood glucose, fasting insulin, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (a marker of inflammation) were measured at the beginning and end of the study. After conducting a repeated measure analysis of variance and a t-test, the researchers found that compared to the placebo, pomegranate juice significantly reduced systolic and diastolic blood pressure as well as inflammation markers. However, it also led to an increase in triglyceride and very low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. Other metrics such as the rest of the lipid profile, fasting blood glucose, insulin, and a measure of insulin resistance, showed no notable changes.
A Experimental Study published in 2017 in the journal Natural Product Research found that Pumpkin seeds have a higher total phenolic compound content, but phenolic compounds from amaranth grains show stronger antiradical properties. The researchers extracted phenolic compounds from pumpkin seeds and amaranth grains using an 80% methanol solution. They then characterised these extracts by their total phenolic compound contents, antioxidant capacities, antioxidant power, and their antiradical activity against a given radical. The individual phenolic compounds were identified with a method known as high-performance liquid chromatography with diode-array detection. They found that pumpkin seeds had a higher total phenolic compound content than amaranth grains. However, phenolic compounds from amaranth grains demonstrated a stronger ability to neutralize the radical they were testing against. They also found several peaks on the chromatograms of two extracts, indicative of different compounds and their concentrations. Vanillic acid derivatives were confirmed in the amaranth grains, while in the pumpkin seeds, they identified three main phenolic compounds based on their ultraviolet diode-array detection spectra.
A Experimental Study published in 2017 in the journal Food & Function found that When combined, Silibinin and Pu-erh tea extract prove more effective in preventing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease than when used individually. The research used obese mice (ob/ob) and fed them a high-fat diet along with the oral administration of Silibinin, Pu-erh tea extract, or both, over a six-week period. Concurrently, lean mice were used as a control group, consuming a regular diet. The blood chemical index and histopathological evaluations were analyzed to determine the effects of Silibinin and Pu-erh tea extract on the mice, particularly in terms of weight, blood lipid levels, fat metabolism, and inflammatory response. The results showcased that in comparison to the group of mice suffering from non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, the groups which received either Pu-erh tea extract, Silibinin, or a combination of both exhibited significant reductions in weight and blood lipid levels. Furthermore, both Silibinin and Pu-erh tea extract, whether used alone or in tandem, were found to improve fat metabolism and decrease the inflammatory response to a certain extent. The combined group, however, displayed the strongest efficacy in adjusting fat metabolism and inhibiting oxidative stress. They also revealed the drugs' ability to inhibit fat synthesis and improve cholesterol homeostasis by regulating the expression of specific genes. The combined effect was superior to that of individual usage.
A Network Pharmacology published in 2017 in the journal Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine found that A mixture of Chrysanthemum indicum Linne flower and Cinnamomum cassia significantly mitigates hyperuricemia in rats by inhibiting xanthine oxidase activity and enhancing uric acid excretion. In this experiment, the authors evaluated the impact of a combined extract from Chrysanthemum indicum Linne flower (CF) and Cinnamomum cassia (CB) on hyperuricemia, a condition associated with excessive uric acid in the bloodstream. The study was conducted on both normal and hyperuricemic rats induced by potassium oxonate. Uric acid levels and renal excretion were primarily measured to analyse the potential antihyperuricemic properties of the CF and CB mix. From the experiment, it was found that the CF and CB blend led to a significant reduction in uric acid levels in both normal and hyperuricemic rats, with the effect being stronger compared to either CF or CB in isolation. Additionally, the mixture caused an increase in uric acid elimination through the kidneys in the hyperuricemic rats, pointing to its potential antihyperuricemic action. It was also discovered that the mixture and its primary components, namely, chlorogenic acid, isochlorogenic acid, coumarin, cinnamaldehyde, trans-cinnamic acid, and o-methoxycinnamaldehyde, mitigated the action of xanthine oxidase (an enzyme that accelerates uric acid production) in vitro. This partial xanthine oxidase inhibition sheds light on the underlying mechanism of the antihyperuricemic effect by the CF and CB mixture.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2017 in the journal Integrative Molecular Medicine found that Luteolin, found in chrysanthemum flower extract, can potentially reduce serum uric acid levels, suggesting it may help prevent gout. The research involved two double-blind placebo-controlled studies examining the impacts of chrysanthemum flower extract enriched with luteolin on serum uric acid levels. In a single-dose study, fasting participants consumed a capsule loaded with the luteolin-rich extract before partaking in a high purine meal, with uric acid levels evaluated over time. The second study involved repeated consumption of the capsule over a 4-week period, with fasting serum uric acid measured before and after consumption. The research found that although luteolin did not significantly affect uric acid levels immediately after consumption, there was an observed decrease in these levels following four weeks of continued ingestion. Most notably, subjects with a baseline uric acid level between 5.5 to 7.0 mg/dL saw a significant reduction after they consumed chrysanthemum flower extract. The trial also established that no adverse effects resulted from the ingestion of the extract.
A Clinical Study published in 2017 in the journal Food & Function found that Blueberry intake for four weeks decreased levels of a biomarker for oxidative DNA damage in postmenopausal women with pre and early stage hypertension. In the experiment, a randomized, parallel-arm, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial was carried out with 40 postmenopausal women, aged 45 to 65 years, who were either pre or at stage 1 of hypertension. The participants were randomly divided into two, where one group ingested 22 g of freeze-dried highbush blueberry powder every day and the other a placebo. The biomarkers for oxidative DNA damage, oxidative stress, inflammation, and antioxidant defense were evaluated at the commencement, in the middle, and at the end of the eight week period. The levels of the biomarker for oxidative DNA damage, 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG), were found to drop significantly in the group consuming blueberries at the end of the fourth week when compared to the placebo group. However, the levels didn't show a significant difference between the groups at the end of the eighth week. No noteworthy changes were observed in the other measured biomarkers as a result of blueberry consumption.
A Meta-Analysis published in 2017 in the journal Pharmacological Research found that Consuming pomegranate juice consistently can lead to significant reductions in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure, suggesting its potential cardioprotective benefits. A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted to investigate the correlation between pomegranate juice consumption and its effects on blood pressure. A comprehensive search was performed in Medline and Scopus databases to identify relevant randomized placebo-controlled trials (RCTs). The collected data from eligible studies were subsequently analyzed using a random-effects model. Additionally, quality assessment, sensitivity analysis, and evaluation of potential publication bias were carried out using standard methods. The findings showed that pomegranate juice was effective in significantly reducing both systolic and diastolic blood pressure, regardless of the duration of consumption and the dose consumed each day. These results remained stable even after sensitivity analyses. Furthermore, even doses greater than 240 cc recorded a nearly significant effect in reducing diastolic blood pressure. Thus, the study suggests the consistent effects of pomegranate juice consumption on lowering blood pressure.
A Review Article published in 2017 in the journal Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity found that Honeybee products like honey, propolis, and royal jelly have demonstrated potential benefits in treating metabolic diseases, cancers, and other illness types. The research reviewed the effects and mechanisms of honey, propolis, and royal jelly on various health conditions. Their uses in correlation to metabolic diseases and different types of cancers were meticulously explored. Honey was examined for its microbial inhibiting and wound healing properties and its role in treating other diseases. The study found that honey demonstrated potential benefits such as microbial inhibition, wound healing, and effects on other diseases. Propolis was reported to have various health benefits related to gastrointestinal disorders, allergies, and issues related to gynecology, oral health, and dermatology. Royal jelly displayed protective effects on reproductive health, neurodegenerative disorders, wound healing, and aging. While these were potential benefits and effects elucidated, the specific mechanisms of action remain undetermined.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2017 in the journal Journal of Nutritional Science found that Gold kiwifruit supplementation increases the abundance of the beneficial gut bacterium Faecalibacterium, which could potentially enhance gut microbiota composition and reduce inflammation. This research was conducted on two groups of participants: one healthy and the other suffering from Functional Constipation (FC). The groups, one containing 20 individuals (one of whom did not complete the study) and the other 9, were given ACTAZIN™ green (in doses of 2400mg and 600mg) and Livaux™ (2400 mg) gold kiwifruit supplements, as well as a placebo in the form of isomalt. The study design was a randomized cross-over structure carried out over 4 weeks, with 2 weeks washout periods between each stage. Changes in faecal microbiota composition and metabolism were assessed using 16S RNA gene sequencing and Gas Chromatography (GC), and colonic pH was measured via SmartPill wireless motility capsules. The baseline measurements showed that the composition of the faecal microbiota differed significantly between the two groups, with certain bacterial taxa such as Bacteroidales markedly more abundant in the healthy group, while others, including Ruminococcaceae, were more prevalent in the FC group. The clearest change affected by the nutrient supplementation was an increase in Faecalibacterium abundance in the FC group following Livaux™ supplementation, a result observed in nearly all participants in this group. As lower proportions of Faecalibacterium are often linked with gastrointestinal disorders, this increase suggests that the supplements could offer a strategy for ameliorating these conditions.
A Cohort Study published in 2017 in the journal Gastroenterology Research and Practice found that Regular consumption of honey and yogurt may lower the prevalence of H. pylori infection and reduce the virulence of strains. The study evaluated the association between dietary factors and the prevalence of an unnamed infection or virulence strain among 294 adult asymptomatic blood donors. The seroprevalence was evaluated using Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. The study employed logistic regression in its analysis. Key dietary factors studied were the frequent consumption of honey and yogurt, specifically >5 days in a week. Smoking and consumption of other dietary factors were also considered. In the analysis of results, it was found that frequent consumption of honey and yogurt was associated with reduced infection seroprevalence and virulence. Specifically, the study discovered a reverse association between honey or yogurt consumption and the prevalence of the virulence strain, marking it as a novel finding. The effect of other dietary factors and smoking were, however, found to be insignificant in disease prevalence. The study suggests that regular honey and yogurt consumption could enhance control in therapy for the infection.
A Case Report published in 2016 in the journal Obstetrics & Gynecology found that Raspberry leaf consumption may decrease insulin requirements in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus. In the methodology of this case study, a 38-year-old pregnant woman, who was diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus, consumed raspberry leaf tea at 32 weeks of gestation. After the ingestion of the tea, she experienced hypoglycemia that required lowering her insulin dosage. This temporal relationship was verified by her ceasing and readopting the herb. Throughout the study, there were reassuring fetal surveillance and growth, resulting in a cesarean delivery at 39 weeks. The newborn didn't have hypoglycemia or any other complications and the placental biopsy showed standard outcomes. In the discussion of the results, it was observed that raspberry leaf tea might have properties that can affect glycemic control in gestational diabetes mellitus patients. After consumption of the tea, the subject experienced hypoglycemia which necessitated a decrease in her insulin dose. Also, the re-consumption of the herb confirmed its hypoglycemic effects. Importantly, the baby was not affected by hypoglycemia or any other complications, indicating that raspberry leaf tea may be a practical alternative for managing gestational diabetes mellitus. However, it was recommended that pregnant women with such condition should be cautious about the use of the herb and monitor their glucose levels more frequently.
A published in 2016 in the journal Agriculture & Food Security found that Significant amounts of small pelagic fish, a nutrient-rich food source, are unnecessarily processed into animal and pet food rather than being directed for human consumption in South Africa and Tanzania. The research highlights the role of both large and small-scale fisheries in the capture of small pelagic fish, the largest species group landed globally. It focuses on the fact that in South Africa, all anchovy landings from large-scale fisheries are turned into animal feed, fish oil, and pet food. Similarly, in Tanzania, a considerable portion of the dagaa fish catch is reduced to fishmeal, primarily intended to feed chickens. The main methodological challenges being faced relate to the size of the species, labour costs, lack of state incentives, and issues around post-harvest handling and sanitation. The discussion of the results reveals a concerning trend where substantial quantities of nutrient-rich fish, which could be an optimal food source for humans, are being diverted to feed animals. To change this course, the role of the state needs to be appreciated in Tanzania and South Africa, with particular focus on investment in post-harvest processing. Furthermore, the contribution of small-scale fisheries to food security needs to be reconsidered in terms of economic viability and data reporting compared to large-scale fisheries.
A Review Article published in 2016 in the journal Arabian Journal of Chemistry found that Fennel exhibits antifungal, antibacterial, antioxidant, antithrombotic and hepatoprotective activities. Fennel is a medicinal and aromatic plant with a diverse pharmacological spectrum and having considerable importance in particular to food industry. Its aroma active compounds such as anethole (and its polymers like dianethole and photoanethole) estragole, (+)-Fenchone and P-anisaldehyde have been recognised as the biologically active molecules possessing oestrogenic, acaricidal and antithrombotic activities. The phenolic molecules present in fennel have been shown to possess potent antioxidant activity in a number of experiments. These bioactive molecules in fennel can be developed as novel pharmacological lead molecules provided their bioavailability, pharmacokinetics, physiological pathways, and importance to human health are known with sufficient detail.
A Network Pharmacology published in 2016 in the journal Molecular Medicine Reports found that Purified polysaccharides extracted from Tremella aurantialba mycelium have improved antioxidant properties and stimulate immune response in macrophage cells. The study researched the physiochemical and biological properties of crude and purified mycelium polysaccharides from Tremella aurantialba mycelium. A series of physiochemical properties were examined including total sugar, uronic acid and protein content, monosaccharide type and structure, as well as molecular weight. The antioxidant activity of these polysaccharides was studied via their reducing power and scavenging activity of different radicals. Additionally, the study evaluated the potential immunostimulatory activity of these polysaccharides by examining their effects on the proliferation, nitric oxide production and cytokine secretion of a certain type of cell. In the results, it was found that the purified mycelium polysaccharide consisted mainly of three types of sugars and its molecular weight was determined. Comparing the total carbohydrate content, it was discovered that the purified mycelium polysaccharide has significantly higher carbohydrate content compared to its crude counterpart. From the analysis of antioxidant and immunostimulatory activities, the purified polysaccharide showed improved antioxidant properties and the ability to induce macrophage proliferation, nitric oxide production and secretion of several chemicals involved in immune response. This indicates a possible correlation between the total carbohydrate content and the enhanced antioxidant and immunostimulatory activities.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2016 in the journal Nutrients found that Walnuts appear to enhance mood in non-depressed healthy young males. The study's methodology involved an evaluation process using 64 volunteer college students. These individuals were randomly assigned into two different treatment sequences - one involving a walnut intake followed by a placebo, and the other vice versa. Both of these sequences began with an evaluation of the volunteers' base mood, measured using Profiles of Mood States (POMS). After an eight-week interval of sticking to the prescribed plan, their mood was assessed again. This was followed by a 'washout' period of six weeks, during which the volunteer groups reversed their dietary routines - those on walnuts moved to placebo and the ones on placebo switched to walnuts. After another eight-week interval, a final mood assessment occurred. The results displayed a lack of significant mood changes in females or when setting aside gender distinctions in the analysis. The exciting element of this study was found in assessing specifically healthy, non-depressed male subjects. There was a pertinent improvement in their Total Mood Disturbance score, implying an enhancement in mood when consuming walnuts.
A Clinical Study published in 2016 in the journal Neuropediatrics found that Saffron has shown potential as an effective and tolerable treatment for major depressive disorder with anxious distress. In the study, 66 patients suffering from major depressive disorder with anxious distress were randomly chosen to be treated either with 30 mg of saffron per day or 40 mg of citalopram per day for a duration of 6 weeks. Their progress was monitored using the Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression and the Hamilton Rating Scale for Anxiety, which aided in evaluating the effects of the treatment throughout the trial. In the results observed, it was found that patients from both groups, those treated with saffron and those administered with citalopram, demonstrated significant improvement in their depression and anxiety scales. The change in the scores between the two groups was examined and it was found that there was no profound difference. Interestingly, the frequency of side effects appearing was also not significantly varied between the two groups. This study hence showcases saffron as a potential reliable and well-tolerated treatment for major depressive disorder accompanied with anxious distress.
A Review Article published in 2016 in the journal Molecules found that Previous records suggest pleiotropic pharmacological activities of capsaicin such as an analgesic, anti-obesity, anti-pruritic, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, anti-cancer, anti-oxidant, and neuro-protective functions. Emerging data indicate its clinical significance in treating vascular-related diseases, metabolic syndrome, and gastro-protective effects. Capsaicin has elicited enormous interest for several centuries due to its conspicuous culinary and clinical applications. Despite its adverse effects, capsaicin is still being used as an active principle in several pharmaceutical formulations for treating various human ailments. Moreover, emerging studies have shown that capsaicin is implicated in a broader range of functions than previously anticipated. Even though it is best characterized in the field of nociception and pain, several experimental and clinical studies also demonstrate its role in other important pathological states like cancer, obesity, skin disorders, cardiovascular diseases, etc. Additionally, it has also been implicated in other activities including treatment of the upper respiratory reflexes, prevention of adipogenesis, boosting metabolic rate, and regulation of innate and adaptive immune responses.
A Experimental Study published in 2016 in the journal Journal of Ethnopharmacology found that Jujube-containing decoctions, used in Traditional Chinese Medicine, show neuro-protective and differentiating properties and enhance the function of multi-herbal concoctions. The research first studied the effect of three chemically standardized jujube-containing decoctions named Guizhi Tang, Neibu Dangguijianzhong Tang and ZaoTang on cultured PC12 cells. To do this, they assessed the protein expressions of neurofilaments following the herbal treatment through a process known as western blot. The research team also observed neurite outgrowth in the PC12 cells post-treatment using a light microscope equipped with phase-contrast condenser and SPOT imaging software. Furthermore, they evaluated the protective effect of the herbal extracts on tBHP-induced cytotoxicity using an MTT assay. Additionally, they transfected a luciferase reporter construct carrying repeats of antioxidant response elements and a downstream reporter gene into PC12 cells to understand if the decoctions could trigger transcriptional activation of these response elements. The mRNA expression of antioxidant enzymes following the herbal treatment was analyzed via quantitative real-time PCR. The study found that these jujube-containing decoctions exhibited similar protective and beneficial properties for the brain. The decoctions were observed to induce the protein expression of neurofilaments and cause neurite outgrowth. These herbal treatments were found to protect PC12 cells against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner. Further, they triggered the mRNA expressions of essential anti-oxidation genes, resulting in the activation of antioxidant response elements. This study highlights the enhancement effect of jujube in a multi-herbal decoction, demonstrating its neuro-protective and differentiating property.
A Review Article published in 2016 in the journal Polish Journal of Food and Nutrition Sciences found that Goji berries, classified as superfruits, possess potential beneficial implications in the dietary prevention of diseases like diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer. The paper begins with a brief introduction of goji berries, their rich nutrient content, and the ideal conditions for their cultivation. It proceeds to delve into the berry's chemical composition and an extensive enumeration of health benefits that these chemicals can offer. The discussion of results further exemplifies how the myriad bioactive compounds found in these superfruits could potentially combat prevalent diseases of affluence such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer. Nonetheless, the paper also addresses safety concerns of goji consumption by discussing potentially harmful components for human health, possible allergic reactions, and interactions with other substances.
A Clinical Study published in 2016 in the journal Nutrients found that Drinking 1litre of mineral water daily with meals can reduce risk factors for heart and metabolic diseases, particularly when replacing sugary drinks. This randomized-controlled crossover trial involved 64 adults with moderate hypercholesterolemia. Participants were assigned to consume 1 liter per day of either sodium-bicarbonated mineral water (BW) or control mineral water low in minerals (CW) alongside their main meals for eight weeks. This was followed by an eight-week washout period. The study measured various cardiometabolic risk biomarkers including blood lipids, glucose, insulin, aldosterone, urine pH, urinary electrolytes, blood pressure, body weight, and overall fluid, energy, and nutrient intake from diet and beverages. The intervention led to a decrease in total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and glucose levels, with a trend towards lower oxidized LDL. Apolipoprotein B increased, but there was no significant difference between the types of water consumed. The study also observed a decrease in energy and carbohydrate intake from beverages, attributed to a reduction in soft drink and fruit juice consumption. BW specifically increased urinary pH and reduced calcium/creatinine excretion, indicating a moderate alkalizing effect on the body, without impacting blood pressure. Overall, consuming 1 liter of mineral water daily appeared to reduce cardiometabolic risk biomarkers, likely due to the replacement of sugary beverages with water.
A Experimental Study published in 2016 in the journal PLOS One found that Pu-erh tea's fermentation process alters its microbial community, with aging significantly impacting raw but not ripened Pu-erh, and toxic metabolites present support brewing customs. The researchers looked into the microbial communities inherent in Pu-erh tea, a special blend originating from Yunnan, China. The fresh leaves of the tea plant, Camellia sinensis, undergo two types of fermentation- the traditional raw fermentation and the faster, ripened variant. Using high-throughput rDNA-amplicon sequencing, a method to identify and quantify various bacteria and fungi present, they examined both the leaves and both types of Pu-erh tea. The study also explored possible mycotoxins in the tea profiles through quantitative liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, a technique used to detect and quantify various substances. Despite observing significant alterations in the fungal and bacterial compositions due to both fermentation processes, the researchers found the aging process to produce noteworthy changes in raw Pu-erh but not in the ripened type. They identified 390 fungal operational taxonomic units (OTUs) and 629 bacterial OTUs in the leaves and teas. Interestingly, despite the difference in the speed and nature of the fermentation processes, ripened and well-aged raw Pu-erh teas exhibited similar microbial communities alien from those observed in young, raw Ph-erh tea. They also found 25 toxic metabolites, primarily of fungal origin, with the most common being patulin and asperglaucide. These facts lend credibility to the Chinese custom of discarding the first preparation of the Pu-erh tea and using the damp tea for subsequent brewing.
A Experimental Study published in 2016 in the journal Food Chemistry found that In 2004, polyphenols were isolated from mung bean sprouts, which exert antibacterial activity against Helicobacter pylori, one of the most common causative organisms in gastrointestinal disorders. The utility of bioactive compounds from food legumes as natural antimicrobial agents are commonly known as biocides. Mung bean sprouts have potent antiviral and prophylactic activities against respiratory syncytial virus and Herpes Simplex virus −1, and these activities were comparable with Acyclovir. The underlying mechanism was attributed to active components of mung bean sprouts potentially induce antiviral cytokines in human cells and thereby nullify the actions on viral proliferation. Similarly, antifungal and antiviral potency of two beans proteins, designated alpha (28 kDa) and beta (28 kDa) proteins were isolated and were capable of inhibiting human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase and glycohydrolases associated with HIV infection. Further, antifungal peptides (7.3 kDa, 9.03 kDa) were isolated from beans, which exerted an antifungal effects and inhibited mycelial growth in Fusarium oxysporum, F. solani, Pythium aphanidermatum, Sclerotium rolfsii, Mycosphaerella arachidicola, and antibacterial effects on Staphylococcus aureus. In addition, two proteins, Mungin (18-kDa) and chitinase (30.8 kDa) isolated from mung bean seeds possess antifungal activity against Rhizoctonia solani, Coprinus comatus, Mycosphaerella arachidicola, Botrytis cinerea, and Fusarium oxysporum. Mungin and chitinase exert an inhibitory activity against α- and β-glucosidases, suppressing [3H] thymidine in the corporation by mouse splenocytes. In 2004, polyphenols were isolated from mung bean sprouts, which exert antibacterial activity against Helicobacter pylori, one of the most common causative organisms in gastrointestinal disorders. Furthermore, several in vitro and in vivo studies have also been reported that mung bean seeds are protective against sepsis.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2016 in the journal The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that Montmorency tart cherry juice intake can significantly lower systolic blood pressure in men with early hypertension, with improvements linked to phenolic acids. In a carefully controlled, blinded, crossover study employing a randomized Latin square design, fifteen male participants showing early signs of hypertension were given either a 60-mL dose of Montmorency tart cherry (MC) concentrate or a placebo. A recovery period of at least 14 days was allowed between tests to eliminate lingering effects from the previous test. Observations centred on microvascular reactivity, arterial stiffness, blood pressure, and phenolic acid absorption, and these were collected at designated intervals before and up to eight hours after consuming the MC concentrate or placebo. The analysis of the data revealed that consumption of the MC concentrate resulted in a significant reduction in systolic blood pressure in comparison to the placebo, reaching maximum impact two hours after intake. Crucially, this positive effect was found to coincide with an increase in circulating protocatechuic and vanillic acid 1-2 hours post consumption. Thus, it is suggested that the benefits of MC for cardiovascular health, particularly for blood pressure control, can be directly attributed to the influence of these circulating phenolic acids.
A published in 2016 in the journal Journal of Functional Foods found that Strong bactericidal activity was exhibited by sulforaphene against all strains of Helicobacter pylori. Sulforaphene (SFE), one of the major ITCs in radish seeds, specifically exhibited a strong effect against the multidrug-resistant H. pylori strain 212 with a MIC90 (0.6 µg/mL). Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus was also susceptible to SFE treatment, with MIC90 values of 12.5–25.0 µg/mL, but not methicillin-susceptible S. aureus. This observation gives new insight into the potential of SFE as a medicinal resource in foods and has implications in the development of new functional antimicrobial agents.
A Systematic Review published in 2016 in the journal Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine found that Oral ginger could be an effective treatment for menstrual pain in dysmenorrhea. Ginger appeared more effective for reducing pain severity than placebo. The weighted mean difference on a 10 cm visual analogue scale was 1.55 cm (favoring ginger). No significant difference was found between ginger and mefenamic acid (an NSAID). The standardized mean difference was 0 (95% CI -0.40 to 0.41). Available data suggest that oral ginger could be an effective treatment for menstrual pain in dysmenorrhea. Findings, however, need to be interpreted with caution because of the small number of studies, poor methodological quality of the studies, and high heterogeneity across trials. The review highlights the need for future trials with high methodological quality.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2016 in the journal Lipids in Health and Disease found that A sardine-enriched diet may have beneficial effects on cardiovascular risk and alters gut microbiota composition in patients with type 2 diabetes. In the study, 35 patients who were recently diagnosed with type 2 diabetes were divided into two random groups. One was set to follow a standard diet recommended for diabetes (control group), and the other followed similar guidance but included 100 grams of sardines in their diet five days a week (sardine group) for a duration of six months. Scientists measured their anthropometric and dietary information, fasting glycated hemoglobin, glucose, insulin, adiponectin, inflammatory markers, erythrocyte membrane fatty acid composition and specific bacterial strains before and after the dietary intervention. In the conclusion, there was no significant difference in glycemic control between the two groups by the end of the course. However, both sets of patients recorded a decrease in plasma insulin. Most notably, the sardine group also saw an increase in adiponectin levels and the omega-3 index, while decreasing the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio in gut microbiota composition. It advanced the hypothesis, even though the sardine-enriched diet did not significantly alter glycemic control, it could potentially be beneficial in managing cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes patients.
A Systematic Review published in 2016 in the journal Journal of Medicinal Food found that The studies assessed showed that sesame could have a significant effect on oxidative stress and the antioxidant defense system, being considered a food with an important antioxidant function in the different populations studied. In conclusion, despite the limitations and biases of this systematic review, the studies assessed showed that sesame could have a significant effect on oxidative stress and the antioxidant defense system, being considered a food with an important antioxidant function in the different populations studied (individuals with dyslipidemia, diabetes, and hypertension), as well as in its different presentations (oil, seed flour, and capsule). However, better-controlled studies still lack to assess the positive effects on different populations. There are few clinical trials assessing the effect of sesame on oxidative stress. The studies included in this review, mainly those with sesame oil and black sesame meal capsules administered to hypertensive and prehypertensive populations, respectively, showed an increase in enzymatic (SOD, GSH, GPx, and CAT) and nonenzymatic antioxidants (vitamin C, vitamin E, and beta-carotene), as well as a reduction in oxidative stress markers (TBARS and MDA). Although several studies have reported that the exact mechanisms of oxidative stress reduction remain to be fully explained, this review showed that sesame can have a significant positive impact on the health of different popula- tions.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2016 in the journal Clinical Interventions in Aging found that Daily consumption of Puer tea extract results in significant weight loss, reduced body fat, and improved lipid profile in a non-Asian overweight population. This study employed a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled design to evaluate the effects of Puer tea extract. A selection of 59 overweight or mildly obese subjects with high cholesterol levels were chosen and assigned to either consume Puer tea extract or a placebo daily for 20 weeks. Measurements were taken at the beginning and every 4 weeks to analyse lipids, C-reactive protein, and fasting blood glucose. Body composition changes were also observed using a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry scan. Appetite and energy levels were also self-reported by the participants at each visit. The results indicated a significant weight loss tied to Puer tea extract consumption compared to the placebo. Reductions in fat were noted across several body areas and overall fat mass. These findings were significant within the Puer tea extract group but not when compared to the placebo. The consumption of the tea was further associated with an improved lipid profile, including a significantly reduced cholesterol ratio after 4 weeks and a sustainably normal level of other lipoproteins. The tea consumption was also related to a temporary reduction in appetite but showed no notable changes in fasting glucose or C-reactive protein levels compared to the placebo.
A Systematic Review published in 2016 in the journal Public Health Nutrition found that Eating apples appears to be linked to a reduced risk of cancer in various parts of the body. The method applied in this research involved identifying relevant observational studies through a literature search of databases such as PubMed, Web of Science and Embase. Then, a random-effect model was utilized to estimate the cancer risk in different anatomical sites. Moreover, tests were conducted to assess between-study heterogeneity and publication bias. In the discussion of results, forty-one studies were considered, including varied cancer types and sources. A significant reduction of lung cancer risk was observed in relation to high apple consumption in both case-control and cohort studies. However, in the cases of colorectal, breast, and overall digestive tract cancers, significant preventative effect of apples was only found in case-control studies, while prospective studies suggested no effect. There was no evidence of publication bias for colorectal, oral cavity, oesophageal and breast cancer, but the presence of some potential confounding effects related to consumption of other fruits has been recognized.
A Systematic Review published in 2016 in the journal Phytotherapy Research found that Plums display anti-inflammatory, antioxidant properties and can enhance memory, and their consumption shows potential health benefits for cognitive function, bones, and cardiovascular elements. In this systematic review, the researchers explored the health effects of plums by analyzing articles from numerous databases in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines. The research spanned across in vitro studies, animal trials, and human clinical trials, and included studies relating to the Prunus species of plums. Their focus was on the potential influence of plums on disease risk factors and health outcomes. The study found 73 relevant peer-reviewed articles for the review, of which 25 were human studies. The results of the study indicate that plums have antioxidant and anti-allergy properties. Consumption of plums is also related to improved cognitive functionality, better bone health measures, and reduced cardiovascular risk factors. The majority of human trials have used dried plums rather than fresh, which could potentially limit the translation of the findings into practical dietary advice. The evidence, while promising, is not yet extensively documented and requires further support for its claims.
A published in 2016 in the journal Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences found that Coix extracts have anti-colorectal cancer potential. The whole seed (W), endosperm (E) and hull (H) of five cultivars of Job’s tears (Coix lachryma-jobi Linn. var. ma-yuen Stapf) including Thai Black Phayao, Thai Black Loei, Laos Black Loei, Laos White Loei and Laos Black Luang Phra Bang were processed before solvent extraction by non-cooking, roasting, boiling and steaming Each part of the Job’s tears was extracted by the cold and hot process by refluxing with methanol and hexane. The extract from the hull of Thai Black Loei roasted before extracting by hot methanol (M-HTBL-R2) showed the highest anti-proliferative activity on HT-29 with the IC50 values of 11.61 ± 0.95 μg/ml, while the extract from the non-cooked hull of Thai Black Loei by cold methanol extraction (M-HTBL-N1) gave the highest apoptosis (8.17 ± 1.18%) with no necrosis. In addition, M-HTBL-R2 and M-HTBL-N1 indicated free radical scavenging activity at the SC50 values of 0.48 ± 0.12 and 2.47 ± 1.15 mg/ml, respectively. This study has demonstrated the anti-colorectal cancer potential of the M-HTBL-R2 and M-HTBL-N1 extracts.
A Clinical Study published in 2016 in the journal Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture found that Pomegranate juice improves physical function and stiffness, decreases cartilage breakdown enzymes and enhances antioxidant status in patients with knee osteoarthritis. In the methodology used for this study, the researchers gathered 38 patients diagnosed with knee osteoarthritis. These participants were randomly assigned into one of two groups, a control group and a pomegranate juice (PJ) group. Over a course of six weeks, each group was assessed on their clinical signs, inflammation and antioxidant status so as to understand the impact of pomegranate juice intake on these factors. The results from this study indicated significant improvements in the group that consumed the pomegranate juice, as evidenced by reductions in their total Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis scores, signifying decreased stiffness and improved physical function. In addition, the serum levels of a specific protein involved in cartilage degradation (matrix metalloproteinase-13) were lowered, whilst the concentrations of an antioxidant enzyme (glutathione peroxidase) rose. This implies that pomegranate juice can potentially lessen the degenerative impact of knee osteoarthritis on joint health and improve overall patients' wellbeing.
A Animal Study published in 2016 in the journal Scientific Reports found that Dried plum was found to be most effective in reducing bone resorption and preventing bone loss caused by ionizing radiation exposure. The methodology of the study involved evaluating different interventions with antioxidant or anti-inflammatory activities; these included an antioxidant cocktail, dihydrolipoic acid, ibuprofen, and dried plum. These substances were tested for their ability to reduce the expression of resorption-related genes in marrow cells after these cells were exposed to gamma rays or simulated space radiation. This involved monitoring the effects on key genes related to bone resorption like Nfe2l2, Rankl, Mcp1, Opg, and TNF-α. In the discussion of results, dried plum was highlighted as the most effective intervention in reducing the expression of genes related to bone resorption. It significantly blunted the gene effects which tend to escalate bone-loss. Moreover, dried plum was additionally effective in preventing later cancellous bone loss caused by irradiation, either from photons or heavy ions. The finding suggests that dietary supplementation with dried plum might offset the skeletal effects of radiation exposures, whether in the context of space or on Earth.
A Experimental Study published in 2016 in the journal Ciencia e Agrotecnologia found that Adzuki beans present anti-atherogenic, anti-thrombogenic and hypocholesterolemic effects, and the ratios PUFA: SFA and n-6:n-3 were considered appropriate for biological system maintenance of a healthy organism. All samples showed polyunsatured fatty acids prevalence and nutritional indices and ratios considered adequate for biological system maintenance of a healthy organism. The grains presented significant contents of tocopherols and vitamin E activity, resulting in a high contribution to the dietary reference intake. Significant contents of iron, manganese and zinc were also found in the azuki beans, and they are very important mainly due to their function as cofactors in metabolic reactions. Phenolic compounds and flavonoids corroborated with other studies and contributed to the antioxidant activity.
A Experimental Study published in 2016 in the journal Scientific Reports found that The component pterostilbene, found naturally in blueberries, shows potential in preventing inflammation and oxidative stress on the human cornea, suggesting protection against dry eyes. This research employed an in vitro culture model of human corneal epithelial cells, exposing these cells to a hyperosmotic medium. Gene expression was observed via RT-qPCR, while protein production or activity was found using methods including ELISA, zymography, Western blotting, and immunofluorescent staining. Reactive oxygen species' production was also monitored using a DCFDA kit. Pterostilbene was administered and its effects on the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators and reactive oxygen species production were subsequently observed. The results showed that in corneal cells exposed to hyperosmotic medium, the addition of pterostilbene resulted in a notable decrease in the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators and suppressed overproduction of reactive oxygen species. Furthermore, pterostilbene also showed a significant decrease in the levels of oxidative damage biomarkers; it was found to rebalance homeostasis between oxygenases and anti-oxidative enzymes, demonstrating that pterostilbene has potentially protective effects on the human cornea from inflammation and oxidative stress.
A Clinical Study published in 2016 in the journal Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition found that Powdered tart cherry supplementation surrounding endurance exercise can decrease muscle damage markers, inflammation, oxidative stress and muscle soreness, while improving performance. In this study, 27 endurance-trained runners were matched based on their race pace, age, body mass, and fat-free mass. The runners were split into two groups in a double-blind manner: a placebo group given capsules containing 480 mg of rice flour and a tart cherries group given CherryPURE® capsules. These were ingested daily for 10 days, including on the day of the half-marathon and up to 48 hours post-race. The results showed that runners given tart cherry supplementation completed their half-marathon faster (by 13%) than those given a placebo. Moreover, the tart cherry group had less muscle damage markers over time, a steady increase in antioxidant activity during recovery, 47% lower inflammatory markers, and a 34% lower pre-run soreness in the medial quadriceps compared to the placebo group. These results demonstrate the beneficial effects of tart cherry supplementation on performance and recovery in aerobically trained individuals.
A Systematic Review published in 2016 in the journal Journal of Nutritional Science found that Almond consumption effectively reduces blood lipid levels, thus reducing risk of heart disease. The researchers carried out a systematic review and meta-analysis drawing on data from controlled randomised trials. Their search of the scientific literature led them to a total of eighteen relevant publications and twenty-seven datasets, which offered a comparison between almond consumption and a control group. They then unified the studies by pooling the mean differences in the effects on each blood lipid parameter using a random-effects model. The analysis found that consuming almonds had a marked beneficial effect on levels of total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol and TAG (triacylglycerol). However, it did not significantly affect HDL-cholesterol levels. This supports data from previous observational and large-scale interventional studies that showed nut consumption reduces the risk of heart disease. This goes to show that including nuts in a balanced diet is advisable for maintaining healthy blood lipid levels and preventing heart disease.
A Clinical Study published in 2016 in the journal World Journal of Gastrointestinal Pathophysiology found that Hydrogen carbonate-rich mineral water significantly reduces heartburn frequency and severity, improving quality of life with excellent tolerability. This open, single-center, single-arm clinical pilot study involved 50 patients aged 18-64, suffering from heartburn at least twice weekly for over three months. Excluding those with severe diseases or on heartburn medication, participants drank 1.5 liters of hydrogen carbonate-rich mineral water daily for six weeks, with 300 ml consumed at each meal. The study included five visits for monitoring. Efficacy was assessed through patient self-assessments in a heartburn diary, symptom-specific questionnaires (Reflux Disease Questionnaire, Quality of Life in Reflux and Dyspepsia, Gastrointestinal Quality of Life Index), and overall health-related quality of life using the SF-12. Efficacy and safety were evaluated using the Wilcoxon test, χ2 test, and U-test, considering changes in symptoms and vital signs. The study reported significant reductions in heartburn occurrences at week 6 in both the intention-to-treat and per-protocol populations. The average weekly heartburn episodes decreased by 5.1, and the duration of symptoms reduced by 19 minutes. Symptom frequency decreased in 89.6% of patients, and symptom duration in 79.2%. There were improvements in all dimensions of the RDQ and disease-specific quality of life. Both patients and investigators rated the water’s efficacy positively, with no serious adverse events reported. Additionally, a slight but significant decrease in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure was observed. The study concluded that hydrogen carbonate-rich mineral water is effective and well-tolerated in alleviating heartburn, enhancing quality of life.
A Experimental Study published in 2016 in the journal Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine found that The ethanol extract of FCI potentially counters bone loss in mice by enhancing osteoblast proliferation and differentiation, facilitated by multiple bioactive compounds. In this study, the researchers scrutinized the antiosteoporosis potential of the ethanol extract of FCI in mice experiencing bone loss due to ovariectomy, a process likened to human menopause. In the process, the antiosteoporosis fraction derived from FCI was isolated and cleansed using a technique known as high-speed countercurrent chromatography, which resulted in the successful isolation of the principle bioactive compounds. The researchers found that, among the separations, the ethyl acetate fraction exhibited remarkable antiosteoporosis activity. Upon further analysis, the foremost compounds were identified as acacetin, apigenin, luteolin, and linarin. Furthermore, these compounds were found to stimulate the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts - the cells responsible for bone formation. The process was potentially mediated by the activation of the AKT signaling pathway and the upregulation of certain genes such as Runx2, OCN, OPN, and COL I. The collective efforts of these bioactive compounds played a crucial role in the observed antiosteoporosis effects, suggesting that the effectiveness of FCI is not reliant on a single component, but an ensemble of elements working in tandem.
A Experimental Study published in 2015 in the journal Biomedical and Pharmacology Journal found that Pomegranate juice extract significantly improves hormonal changes in female rats with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. A total of 56 female Wistar rats, who had 2 to 3 consecutive estrous cycles over 12 to 14 days, were used in the study. These were divided into six groups, with differing conditions of control and experimental groups, each group was administered different treatments, ranging from those without any substances or treatments, to those receiving hormones and/or varying doses of pomegranate extract. After a set duration, all rats were weighed and their blood samples taken. The collected data showed that the concentration of estrogen, testosterone, and androstenedione significantly increased in the experimental groups as compared to the control groups. Furthermore, there was a notable decrease in these hormone levels in the experimental groups compared to the PCOS group. The results suggest that pomegranate juice extract has a positive effect on regulating female sex hormones, indicating its potential effectiveness as a treatment for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2015 in the journal European Journal of Nutrition found that Drinking natural mineral water rich in magnesium sulphate and sodium sulphate daily improves bowel movement frequency and stool consistency in people with functional constipation. This placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized trial involved 106 healthy individuals with functional constipation. They were randomly assigned to consume either 300 or 500 ml of a natural mineral water rich in magnesium sulphate and sodium sulphate (Donat Mg) or a placebo water daily for six weeks. The 300-ml groups were discontinued following an interim analysis. Participants recorded their bowel movements, stool consistency, gastrointestinal symptoms, and general well-being in a diary. The primary outcome was the change in the number of complete spontaneous bowel movements per week. In the 500-ml group, consisting of 75 subjects, there was a tendency for a higher increase in complete spontaneous bowel movements per week in the active group compared to the placebo after six weeks. The mean number of spontaneous bowel movements significantly increased over the study period, with notable differences between the study arms throughout the study. Stool consistency and subjectively perceived symptoms of constipation improved significantly with the mineral water compared to placebo. Overall, the daily consumption of this specific mineral water led to improvements in bowel movement frequency and stool consistency, enhancing the health-related quality of life for participants with functional constipation.
A Review Article published in 2015 in the journal Food and Agricultural Immunology found that Adzuki beans possessed strong ABTS free-radical-scavenging capacity and α-glucosidase inhibition activity. All the adzuki beans possessed strong ABTS free-radical-scavenging capacity and α-glucosidase inhibition activity. Significant positive correlations of the antioxidant activity with total phenolic acids, total flavonoids and free caffeic acid contents were observed. These results are anticipated to providing useful information on the development of adzuki bean-based functional food.
A Clinical Study published in 2015 in the journal Nutrition and Cancer found that Pomegranate juice consumption slightly decreases estrone and testosterone levels in normal weight postmenopausal women. In this study, 64 healthy postmenopausal women were randomly assigned to consume 8 ounces of either 100% commercial pomegranate juice or apple juice daily for a period of 3 weeks. The aim was to observe the effect of pomegranate juice intake on the serum levels of various sex hormones and sex hormone-binding globulin. Despite no significant alterations observed in the serum sex hormones or SHBG overall, a subgroup analysis of 38 normal weight participants indicated a significant reduction in estrone and testosterone levels for those who consumed pomegranate juice compared to the control group. The decrease was seen only in this subgroup, and not in the total group of participants. Hence, the direct effect of pomegranate juice on hormonal levels may be more apparent in normal weight postmenopausal women.
A Review Article published in 2015 in the journal Allergologia et Immunopathologia found that Milk and honey mixture seems to be at least as effective as dextromethorphan and levodropropizine, the most prescribed over-the-counter antitussives in Italy, in non-specific acute cough in children. Honey is recommended for non-specific acute paediatric cough by the Australian guidelines. Current available randomised clinical trials evaluated the effects of a single evening dose of honey, but multiple doses outcomes have never been studied. 134 children suffering from non-specific acute cough were randomised to receive for three subsequent evenings a mixture of milk (90 ml) and wildflower honey (10 ml) or a dose of DM or LDP adjusted for the specific age. The effectiveness was evaluated by a cough questionnaire answered by parents. Primary end-point efficacy was therapeutic success. The latter was defined as a decrease in cough questionnaire score greater than 50% after treatment compared with baseline values. Three children were excluded from the study, as their parents did not complete the questionnaire. Therapeutic success was achieved by 80% in the honey and milk group and 87% in OTC medication group (p = 0.25).
A Systematic Review published in 2015 in the journal Journal of Functional Foods found that Goji berry was identified as a rich source of antioxidant compounds, with health-promoting properties comparable with other common fruit species. A number of things lead to the confusion between the different species and genotypes of cultivated Lycium. In this study, wolfberry was identified as a rich source of antioxidant compounds; the observed analytical fingerprint demonstrated that the species represents a rich source of organic acids and polyphenolic compounds, especially cinnamic acids and catechins; this research suggested that identified nutraceuticals might contribute to the total phytocomplex of these fruits. This study developed an important tool to assess goji chemical composition and bioactivity, using different chromatographic methods for comprehensive authentication and quality control of its fruits: well-designed clinical trials with phytochemically well-characterized extracts are required before the potential of goji as a medicinal plant or food can be definitively assessed. Goji berry fruit is devoid of toxicity but caution is advised with regard to possible drug interactions as well as with products of unknown or dubious origin; for this reason, the development of rigorous quality control protocols for goji products is urgently needed: this research showed that analytical fingerprinting could be an important tool to assess quality, chemical composition, and bioactivity of wolfberry fruits, helping to find new sources of natural health-promoting compounds.
A Systematic Review published in 2015 in the journal Journal of Functional Foods found that The antioxidants present in goji berries have comparable health-promoting properties to those found in other common fruits. The researchers studied the quality traits of goji berries and the levels of potentially fruitful compounds. They employed high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) - a technique widely-used to identify and separate components in a mixture - to examine the health-promoting compounds in goji berries, comparing these to what's found in other common fruits. The researchers found that goji berries are a rich source of antioxidant compounds. It was determined that their health-promoting properties are akin to those of other common fruits. The characteristic "fingerprint" obtained through this study could help improve our understanding of this fruit, which is increasingly being recognized as a functional food due to its antioxidant properties.
A Review Article published in 2015 in the journal Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics found that Among the bioactive compounds present in jujube fruit, triterpenic acids and polysaccharides have antiproliferative and anticancer effects on various cancer cell lines. Phytochemical data combined with information about biological activity confirm that jujube fruits are rich in bioactive compounds that can benefit human health. This review article shows that among the bioactive compounds present in jujube fruit, triterpenic acids and polysaccharides have antiproliferative and anticancer effects on various cancer cell lines. It seems that the induction of apoptosis is one of the main mechanisms for the anticancer activities of the jujube fruit, due to the presence of the bioactive compounds. However, the biological effects of other identified and unidentified compounds in these fruits should be also investigated in areas where there are suitable climatic conditions for the cultivation of these plants.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2015 in the journal Nutrafoods found that Chrysanthemum flower oil significantly reduces diet-induced elevation of serum uric acid in Japanese males with high baseline levels. In the study, a randomised, double-blind, cross-over comparison method was employed. Twenty male individuals from Japan were selected and segregated into two groups, one of which received the chrysanthemum flower oil, while the other group was given a placebo. Blood and urine samples were systematically collected from these individuals and meticulously analyzed with a focus on levels of serum uric acid. The analysis of these samples divulged some noteworthy findings. There was no observed suppression of the diet-induced serum uric acid elevation in those subjects whose baseline serum uric acid values ranged betwixt 5.5 and 8.0 mg/dl when given the chrysanthemum flower oil. However, for those subjects with a baseline serum uric acid level of 7.1 mg/dl or greater, the application of this oil significantly reduced this elevation. Based on these findings, it was concluded that chrysanthemum flower oil indeed has an effective role in reducing uric acid elevation, specifically for Japanese male subjects belonging to the higher baseline bracket.
A Systematic Review published in 2015 in the journal Nutrition Today found that The alleged benefits of raw milk, including improved nutrition, prevention of lactose intolerance, or provision of "good" bacteria, lack scientific basis and are considered myths. The review aims to bring clarity to the ongoing public debate on the benefits and risks of raw milk consumption. It delves into the historical context of pasteurization and how it significantly reduced the incidence of illnesses associated with raw milk. Furthermore, it critically analyzes the prevalence of pathogens in raw milk, revealing that up to a third of all samples could be contaminated with human pathogens, regardless of being sourced from healthy animals or milk appearing to be of good quality. The study also critically investigates the widely claimed benefits of raw milk. It notes that claims about raw milk's ability to impart improved nutrition, aid in the prevention of lactose intolerance, or provide 'good' bacteria are not grounded in scientific fact but are rather myths. Regarding the hypothesis that consuming raw milk might protect against allergies and asthma for children growing up in farming environments, the study acknowledges some epidemiological data suggesting a lowered risk. However, it cautions against attributing this protective effect directly to raw milk consumption since numerous environmental factors are likely involved.
A published in 2015 in the journal BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies found that Mung bean sprout extract has potent antiviral and to a lesser extent, prophylactic activities against both RSV and HSV-1, and in case of HSV-1, these activities were comparable to Acyclovir. MBS extract has potent antiviral and to a lesser extent, prophylactic activities against both RSV and HSV-1, and in case of HSV-1, these activities were comparable to Acyclovir. Part of the underlying mechanism(s) of these activities is attributed to MBS potential to remarkably induce antiviral cytokines in human cells. Hence, we infer that MBS methanol extract could be used as such or as purified active component in protecting and treating RSV and HSV-1 infections. More studies are needed to pinpoint the exact active components responsible for the MBS antiviral activities.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2015 in the journal Molecular and Clinical Oncology found that Bee pollen and honey may alleviate menopausal symptoms in breast cancer patients undergoing antihormonal treatment. The study used a prospective, randomized crossover trial to compare the effects of a pollen-honey mixture with pure honey in alleviating menopausal symptoms in breast cancer patients undergoing antihormonal treatment. The patients' symptoms were measured using the Menopause Rating Scale. The results showed that a significant number of patients reported improvement in their menopausal symptoms while taking both honey and the pollen-honey mixture. Interestingly, honey, originally intended as a placebo, had similar effectiveness as the pollen in easing symptoms, with both exceeding the expected placebo effect. From these findings, the researchers concluded that bee pollen and honey could be potential aids in managing menopausal symptoms in breast cancer patients on antihormonal therapy.
A Clinical Study published in 2015 in the journal Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics found that Daily consumption of blueberries may decrease blood pressure and arterial stiffness in postmenopausal women due to increased nitric oxide production. The research was an 8-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial involving forty-eight postmenopausal women with pre- and stage 1-hypertension from the Tallahassee, FL, area. Participants were randomly given either 22 grams of freeze-dried blueberry powder or 22 grams of control powder. Resting blood pressures were evaluated, and arterial stiffness was assessed using pulse wave velocity measurements. In addition, levels of C-reactive protein, nitric oxide, and superoxide dismutase were measured at the beginning, in the middle, and at the end of the trial. After 8 weeks, the women in the blueberry powder group showed a significant decrease in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure and pulse wave velocity compared to their baseline levels, indicating a reduction in blood pressure and arterial stiffness. In contrast, no changes were observed in the control group. Furthermore, nitric oxide levels were found to be significantly higher in the blueberry group at the end of the trial, suggesting that the observed vascular benefits may be linked to increased nitric oxide production.
A Experimental Study published in 2015 in the journal The Prostate found that Pomegranate Fruit Extract (PFE) can potentially mitigate testosterone-induced Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in rats due to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and pro-apoptotic properties. The study was carried out using 48 rats, which were randomly distributed into six groups. The Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), a disease that affects men over 50, was induced in these rats using testosterone, except for one group which served as the control. Four groups of the induced rats, thereafter, were treated with diverse daily dosages of Pomegranate Fruit Extract (PFE), while one group received a regular dosage of PFE without BPH induction. Regarding the investigation outcomes, the most significant effect was observed in rats treated with the largest (100mg/kg) dosage of PFE. This treatment substantially reduced testosterone-induced increase in prostate weight and other related levels. Additionally, PFE significantly decreased Malondialdehyde (a marker for oxidative stress) and increased Glutathione, Superoxide dismutase, and Catalase, all of which work as antioxidants. The PFE also demonstrated an ability to decrease the expression of COX-II, iNOS and Ki-67 (indicators of inflammation and cell proliferation) while enhancing the rate of apoptosis (programmed cell death), contributing to the prevention of BPH development.
A Experimental Study published in 2015 in the journal Phytotherapy Research found that Two new compounds found in Chrysanthemum indicum flowers have strong antioxidant qualities and are potent in anti-osteoporosis activity. The research involved the isolation of two new compounds from Chrysanthemum indicum flowers, alongside 17 known compounds. Each compound was then measured for total phenolic and flavonoid content. The research demonstrated the highest concentration of these beneficial compounds within the Ethyl Acetate (EtOAc) fraction of the sample. An assessment of the antioxidative potential of each compound was conducted next, mainly focusing on their peroxyl radical-scavenging capacity and their ability to reduce copper ions. The results confirmed that the two new compounds discovered displayed strong antioxidative effects. These compounds also showed promising activity against tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase in receptor activator of the nuclear factor in osteoclastic cells, suggesting potential efficacy as agents in combatting osteoporosis. Beyond these new compounds, several other compounds isolated from the Chrysanthemum indicum also demonstrated strong antioxidative and anti-osteoporotic activity.
A Systematic Review published in 2015 in the journal Journal of Gastric Cancer found that Consuming carrots reduces the risk of gastric cancer by an indicated 26%. Using specific search terms related to gastric cancer and carrot consumption, a comprehensive search through databases such as PubMed, Cochrane Library, Scopus, ScienceDirect, and some Persian databases was conducted. Comprehensive Meta Analysis/2.0 software was utilized for statistical analysis. The initial search yielded 81 articles, but only 5 met the inclusion and exclusion criteria and were included in the study. Without mentioning specifics, a fixed effects model determined a significant reduction in the risk of gastric cancer associated with carrot consumption. The results showed no indication of publication bias through a funnel graph depiction. The results demonstrate an inverse relationship between carrot consumption and the risk of gastric cancer.
A Systematic Review published in 2014 in the journal European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology found that Administering honey postoperatively can significantly lessen pain and foster improved wound healing following tonsillectomy. The methodology for this research consisted of an in-depth systematic review, complemented by a meta-analysis, focused on the effectiveness of honey used as a treatment for postoperative pain and wound healing following tonsillectomy. Following the independent exploration of database records, including MEDLINE, SCOPUS, and Cochrane databases, by two authors, studies that compared postoperative oral administration of honey to placebo were pinpointed, with the outcomes of interest being pain and wound healing on post-operative days. Criteria for data extraction included baseline study characteristics, study quality, patient numbers in honey-treated and control groups, and outcomes of treatment. Across the selected 4 trials, a total of 264 patients provided sufficient data for conducting the meta-analysis. Discussion of the research findings revealed that the honey-treated group experienced a significant decrease in pain during postoperative day 1, in comparison to the placebo-treated group, as rated by patient-reported pain scores. The analgesic intake for the honey-treated group during the first five days after the operation was also markedly reduced compared to that of the placebo-treated group. Moreover, significantly enhanced wound healing was observed two weeks post-operation for the patients treated with honey compared to those given a placebo.
A Experimental Study published in 2014 in the journal Arthritis Research & Therapy found that Epigallocatechin 3-gallate (EGCG), found in green tea, can significantly slow down osteoarthritis progression and reduce associated pain in a post-traumatic osteoarthritis mouse model. C57BL/6 mice were operated to destabilize the medial meniscus mimicking post-traumatic osteoarthritis or were subjected to a sham surgery as a control. From the day of the surgery, the mice were given daily injections of EGCG or a vehicle control for either four or eight weeks. The severity of osteoarthritis was evaluated by staining and scoring techniques, detection of type II collagen and aggrecan, as well as through the measurement of enzyme expression involved in cartilage degradation. After the surgery, at both four and eight weeks, the cartilage in EGCG-treated mice showcased lesser cartilage erosion and staining loss than the control mice. Furthermore, it also revealed lower osteoarthritis scores and reduced levels of enzymes implicated in cartilage degradation. The EGCG-treated mice exhibited elevated expression of genes that regulate these enzymes. Additionally, EGCG positively affected the cartilage's gene expression level for both pro and anti-inflammatory cytokines. EGCG treatment also resulted in a reduction of osteoarthritis-associated pain, reflected in higher locomotor behavior and a decrease in the expression of inflammatory cytokines and a chemokine receptor in the dorsal root ganglion.
A Review Article published in 2014 in the journal CARTILAGE found that A dietary supplement Avocado/Soybean Unsaponifiables aids in treating Osteoarthritis by preventing cartilage degradation and promoting cartilage repair, thereby reducing pain and enhancing joint functionality. Avocado/Soybean Unsaponifiables was studied for its effects on Osteoarthritis. The methodology highlighted its functions, which include inhibiting the release and activity of molecules and pathways that are implicated in OA, as well as those that prevent cartilage degradation. These functions are principally through the prohibition of matrix metalloproteinases and the increase of tissue inhibitors of the catabolic enzymes in question. Additionally, ASU was found to inhibit fibrinolysis by stimulating the expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor. Moreover, its anabolic properties were credited with promoting cartilage repair by stimulating collagen and aggrecan synthesis while inhibiting inflammatory cytokines. ASU's chondroprotective effects were noted as well; these effects are brought about by correcting growth factor abnormalities, and by simultaneously increasing Transforming Growth Factor-Beta in synovial fluid while decreasing vascular endothelial growth factor. Additionally, it was observed to inhibit cholesterol absorption and biosynthesis, which further contribute to its beneficial role by moderating reactive oxygen species pathology in chondrocytes. Results indicated that the dietary supplement has significant therapeutic value for those suffering from Osteoarthritis. It reduces pain and stiffness while improving joint function, resulting in less dependency on painkillers. It was found that ASU's preventative measures towards cartilage degradation and its promotion of cartilage repair play essential roles in its efficiency as a treatment for OA.
A Systematic Review published in 2014 in the journal Human Psychopharmacology: Clinical and Experimental found that Saffron, derived from Crocus sativus flower, shows similar efficacy to antidepressant medications in treating major depression, potentially due to its variety of biochemical effects. In the methodical study, electronic databases were consulted to find high-quality, randomized, double-blind studies that had either placebo or antidepressant controls. Six distinct studies were found through this process. In vivo and in vitro studies were reviewed to better comprehend the potential antidepressant mechanisms of action saffron brings forth. The results showed that in the studies compared with a placebo, saffron had large beneficial effects. When compared with regular antidepressant medication, saffron demonstrated similar levels of efficacy. The potential mechanisms behind saffron's antidepressant qualities seemingly lay in its serotonergic, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, neuro-endocrine, and neuroprotective effects.
A Experimental Study published in 2014 in the journal Phytotherapy Research found that Jujube fruit promotes the growth of nerve cells and boosts anti-oxidant enzyme production in brain cells. The methodology focused on the application of a water extract from the jujube fruit to cultured astrocytes (star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord) and observing any resulting changes over a 24-hour period. Researchers utilized a protein kinase A inhibitor, H89, to ascertain if it lessened the apparent jujube-induced expression of neurotrophic factors, assessed in a concentration-dependent manner. In the discussion of results, it was established that the jujube extract effectively stimulated the expression of several key neurotrophic factors including nerve growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. These are pivotal in neural survival, growth, and differentiation. Concurrently, the extract also enhanced the transcriptional expressions of various significant enzymes responsible for anti-oxidation in a comparable concentration-dependent manner, indicating that jujube not only contributes to neural growth but also fosters the astrocytes' resistance to oxidative stress.
A Network Pharmacology published in 2014 in the journal Archives of Medical Research found that Manuka honey exhibits significant anti-influenza viral activity, inhibiting replication with virucidal effects. Combining manuka honey with existing drugs enhances their efficacy, suggesting its medicinal potential. This study aimed to address the urgent need for novel anti-influenza drugs by evaluating the anti-viral activity of honey, focusing on manuka honey. Antiviral activities were assessed using MDCK cells, revealing that manuka honey efficiently inhibited influenza virus replication with an IC50 of 3.6 ± 1.2 mg/mL and a CC50 of 82.3 ± 2.2 mg/mL, resulting in a selective index of 22.9. Virucidal effects were identified as the underlying mechanism. Furthermore, combining manuka honey with zanamivir or oseltamivir significantly enhanced their efficacy, showcasing the potential medicinal value of honey, particularly manuka honey, against the influenza virus. The study underscores the potent inhibitory activity of honey, especially manuka honey, against influenza viruses, offering promising medicinal implications. The observed virucidal effects and the synergistic enhancement of known anti-influenza drugs highlight the multifaceted potential of honey in combating influenza infections. Further exploration of the specific mechanisms underlying these effects could contribute to the development of effective anti-influenza therapies.
A Network Pharmacology published in 2014 in the journal Archives of Medical Research found that Honey, in general, and particularly manuka honey, has potent inhibitory activity against the influenza virus, demonstrating a potential medicinal value. Antiviral activities of honey samples were evaluated using MDCK cells. To elucidate the possible mechanism of action of honey, plaque inhibition assays were used. Synergistic effects of honey with known anti-influenza virus drugs such as zanamivir or oseltamivir were tested. Manuka honey efficiently inhibited influenza virus replication (IC50 = 3.6 ± 1.2 mg/mL; CC50 = 82.3 ± 2.2 mg/mL; selective index = 22.9), which is related to its virucidal effects. In the presence of 3.13 mg/mL manuka honey, the IC50 of zanamivir or oseltamivir was reduced to nearly 1/1000th of their single use.
A Systematic Review published in 2014 in the journal Journal of Dietary Supplements found that Goji (Lycium spp.) has a consolidated safety and efficacy profile, based on scientific literature, clinical trials, expert opinions, history, pharmacology, interactions, adverse effects, toxicology, and dosing. The methodology of this review was systematic, consolidating various data on goji. It firstly analyzed scientific literature and conducted statistical evaluations of clinical trials. Additionally, it compiled not only expert opinions but also took into account folkloric precedent and historical use of goji. It also encompassed a thorough review of pharmacology, how the plant's compounds interact within the body (kinetics/dynamics), and potential interactions with other substances. It evaluated potential adverse effects and toxicology. The thorough examination across multiple aspects revealed that goji has a broad safety and efficacy profile. Its use, safety, and effectiveness are supported not only by current clinical trials but also by the history of its application and expert opinions. The review of its pharmacology and kinetics/dynamics further supports these findings. The potential interactions, adverse effects, and toxicology of goji were found to support the established safety profile. Notably, the review also focused on its dosing, further validating this conclusion.
A Network Pharmacology published in 2014 in the journal Nutrients found that The consumption of kiwifruit with a meal can increase the rate and extent of the hydrolysis of protein. This in vitro study has shown that in elevated gastric pH conditions, such as may present with compromised gastric function, the addition of kiwifruit protease more than doubled the rate of hydrolysis of meat protein. This novel finding supports the hypothesis that consumption of kiwifruit with a meal can increase the rate and extent of the hydrolysis of protein. Evidence is also provided that when the added acid concentration decreased from 0.074 M to 0.022 M (HCl), pepsin activity reduced by 50% and kiwifruit activity increased by 300%. This evidence indicates that kiwifruit may exert its influence on digestion by increasing the extent of protein digestion in the gastric medium when the secretion of pepsin and/or hydrochloric acid is less than optimal. It is reported [12] in a study of 365 healthy subjects, average fasting gastric pH was 2.16 ± 0.11 for men and 2.79 ± 0.18 for women, but in another study of 79 healthy elderly people [13], 11% of the participants recorded fasting gastric pH > 5.0 throughout the study.
A Network Pharmacology published in 2014 in the journal Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry found that Chrysanthemum flower oil can effectively decrease uric acid levels in rats, by reducing production in the liver and enhancing excretion from the kidney. In this study, the researchers developed a hyperuricemia model by feeding rats a specific chrysanthemum flower oil enriched diet. Hyperuricemia is a condition of elevated uric acid levels which the team sought to decrease. Chrysanthemum flower oil was chosen due to its polyphenol content, substances known to have positive health benefits. By administering this oil orally to rats on this diet, they were able to monitor its impact on the rats' serum uric acid levels. The results showed that the chrysanthemum oil had a significant impact on controlling and reducing uric acid levels. This was achieved through two primary mechanisms. Firstly, there was a demonstrated inhibition of xanthine oxidase activities in the liver. This enzyme plays a crucial role in the conversion process that leads to the creation of uric acid. Secondly, the oil increased uric acid levels in the urine, suggesting greater excretion of it. This was further confirmed by the up-regulation of uric acid transporter genes in the rats' kidneys, which enhances the excretion process.
A Systematic Review published in 2014 in the journal The Journal of Nutrition found that Polyphenolic compounds found in walnuts not only reduce the oxidant and inflammatory load on brain cells but also improve interneuronal signaling, increase neurogenesis, and enhance sequestration of insoluble toxic protein aggregates. In conclusion, age-related increases in oxidative stress and inflammation, especially when coupled with metabolic and cardiovascular dysfunction, lead to neurodegeneration and cognitive decline. This process of brain aging occurs even in the absence of specific neurodegenerative diseases. Although most chronic neurodegenerative diseases cannot currently be cured, preventive measures earlier in life can protect cognitive function in old age and may prevent or delay the onset of debilitating neurodegenerative diseases. Dietary interventions provide a safe and palatable means of modifying the body's internal environment and, importantly, the neuronal environment within the brain. Walnut polyphenols and tocopherols can reduce oxidative stress and inflammation; furthermore, PUFAs help maintain neuronal membrane integrity and attenuate protein aggregation involved in AD. In rodent studies, the addition of dietary walnuts, equivalent to a single serving of walnuts for humans, was sufficient to improve both motor and cognitive behavior in aged animals. In humans, the inclusion of walnuts in the diet improved cardiovascular health, which is itself a risk factor for neurodegenerative diseases and age-related cognitive decline. Taken together, this evidence suggests that the integration of walnuts into a healthy diet could be an effective means of prolonging health spans, slowing the processes of brain aging, and reducing the risk of chronic neurodegenerative disease.
A Systematic Review published in 2014 in the journal Nutrition Journal found that Ginger could be considered a harmless and possibly effective alternative option for women suffering from nausea and vomiting during pregnancy. This review suggests potential benefits of ginger in reducing nausea symptoms in pregnancy (bearing in mind the limited number of studies, variable outcome reporting and low quality of evidence). Ginger did not significantly affect vomiting episodes, nor pose a risk for side-effects or adverse events during pregnancy. Based on evidence from this systematic review, ginger could be considered a harmless and possibly effective alternative option for women suffering from nausea and vomiting during pregnancy.
A Experimental Study published in 2014 in the journal Molecular Medicine Reports found that Consumption of Pu-erh tea can effectively alleviate symptoms of constipation, with effects comparable to the medicinal drug bisacodyl. The methodology in the research focused on observing the effects of Pu-erh tea on induced constipation in mice. The study induced constipation through activated carbon and then assessed various factors, such as changes in body weight, dietary intake, gastrointestinal transit times, and physical characteristics of feces. The impact of Pu-erh tea was compared to that of bisacodyl, a well-known laxative. Specific dosage levels of Pu-erh tea were utilized while continuously observing the physiological responses and changes in mice. The results showed a marked improvement in all major parameters related to constipation in mice treated with Pu-erh tea. It was found that body weight, dietary intake and water consumption were better in the tea-treated groups than in the carbon-induced constipation group. The gastrointestinal transit times were also considerably improved, with Pu-erh tea equivalent in efficiency to bisacodyl. In addition to this symptomatic relief, the serum levels of substances associated with gastrointestinal motility and function were significantly affected, indicating that Pu-erh tea has potential anti-constipation effects at a physiological level.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2014 in the journal Endocrine Abstracts found that Pomegranate extract intake, rich in biophenols, lessens salivary cortisol levels, hence potentially improving health-related quality of life, particularly in stress-suffering individuals. The study was conducted using a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled parallel trial. Participants, ranging in age and body mass index, took either a pomegranate extract capsule or a placebo each day for a duration of 4 weeks. The extracted capsule, which contained a high concentration of biophenols, was consumed with water after a meal. In addition to tracking dietary practices and habits, health related Quality of Life was recorded before and after the study. To assess the effects, salivary cortisol and cortisone levels were measured at three distinct points in the day. In the results, there was a notable decrease in the salivary cortisol levels of participants who consumed these pomegranate extract capsules. Alongside this, the ratio of cortisol to cortisone was significantly minimized. The participants' physical and social functionality, pain levels, and overall well-being showed significant improvement during the study. Conversely, there was a slight increase in the salivary cortisol and ratio of cortisol to cortisone for participants who took the placebo.
A Review Article published in 2014 in the journal Wilderness & Environmental Medicine found that Honey has shown to be a safe and occasionally superior treatment for various wounds compared to current treatments, even in wilderness environments. The research was based on a review of existing literature on the physiological properties of honey, focusing on its uses in wound care. Documents showing the efficacy and safety of honey as a treatment for several wounds were examined. Comparisons with traditional wound treatment procedures were also made, presenting honey as a viable alternative. This evaluation even considered the use of honey in challenging environments, such as the wilderness. The results showed that honey is not only a safe but sometimes a superior alternative to current wound treatments. Its unique physiological properties make it a valuable wound care resource. The versatility of honey, as indicated in the results, also suggests potential usability in unique or difficult environments like wilderness scenarios. Even with the variability in wounds and wound environments considered, honey was consistently shown thanks to its inherent antiseptic and healing properties.
A Systematic Review published in 2014 in the journal European Journal of Nutrition found that Regular carrot consumption could potentially reduce the risk of prostate cancer. The study methodology entailed conducting an extensive literature search of papers published in August 2013 via various academic databases as well as scanning references from retrieved articles. Key focus was given toward summary risk estimates for individuals with the highest versus the lowest intake of carrots. A vital component of the study was the conducting of a dose-response meta-analysis for those studies that reported categorical risk estimates for a range of exposure levels. The study's findings suggest a statistically considerable lower risk of prostate cancer in connection with carrot consumption, being deemed significant even after testing for publication bias. Furthermore, a dose-response meta-analysis proposed that a weekly serving, or an incremental daily intake of 10 grams of carrots, contributed to the decreased risk estimate of prostate cancer. The application of Begg's funnel plot and Egger's test indicated that the publication bias was not statistically significant.
A Systematic Review published in 2014 in the journal BMC Chemistry found that Germination is thought to improve the nutritional and medicinal qualities of mung beans. In recent years, studies have shown that the sprouts of mung beans after germination have more obvious biological activities and more plentiful secondary metabolites since relevant biosynthetic enzymes are activated during the initial stages of germination. During the germination process of the mung bean, its chemical constituents undergo a series of biochemical reactions. One such reaction is the synthesis of small active compounds from macromolecular substances, promoting absorption and utilization. Another change observed during germination is the formation and accumulation of many types of active substances, such as polyphenols, saponins, vitamin C, etc. Therefore, we believes that these changes in the chemical composition of mung beans during germination will lead to substantial and important changes in the pharmacological activities of mung beans as well.
A Systematic Review published in 2014 in the journal BMC Chemistry found that A study demonstrated that all pro-inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-12β, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and inducible NO synthase (iNOS), were dramatically down regulated in cells treated with 3.7 mg/mL polyphenols. In Asia, mung beans have been used in various cuisines and in folk remedies to treat toxic poisoning, heat stroke associated with thirst, irritability, and fever; these beneficial effects of mung beans are thought to be related to the inflammatory response. Researchers have analyzed the anti-inflammatory effects of mung bean ethanol extracts on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated macrophages. The extract mainly included polyphenols, gallic acid, vitexin, and isovitexin and markedly reduced the activity of murine macrophages through the prevention of pro-inflammatory gene expression without cytotoxicity. Moreover, a study demonstrated that all pro-inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-12β, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and inducible NO synthase (iNOS), were dramatically down regulated in cells treated with 3.7 mg/mL polyphenols. These results suggested that the ethanol extract had great potential to improve the clinical symptoms of inflammation-associated diseases, such as allergies and diabetes. The immune modulatory activities of mung bean water extracts and monomers on human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) have also been evaluated by BrdU immunoassay, secretion of interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and IL-10, and elucidation of the responding cells by flow cytometry. The results demonstrated that 20 μg/mL genistein, phytic acid, and syringic acid induce a Th1-predominant immune response through significant suppression of IL-10 secretion and promotion of IFN-γ secretion. The study concluded that several non-nutritional ingredients of mung beans, such as flavonoids, acids, and plant hormones, are most likely to be important in the modulation of human immunity.
A Systematic Review published in 2014 in the journal BMC Chemistry found that Mung bean protein, tannin, and other polyphenols are thought to combine with organophosphorus pesticides, mercury, arsenic, and other heavy metals, promoting the excretion of sediments from the body. In ancient books, mung beans were well known for their detoxification activities. Mung bean protein, tannin, and other polyphenols are thought to combine with organophosphorus pesticides, mercury, arsenic, and other heavy metals, promoting the excretion of sediments from the body. Mung beans have been shown to possess antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory activities. Moreover, mung beans have antidiabetic, antihypertensive, lipid metabolism accommodation, antihypertensive, and antitumor effects, among others.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2014 in the journal Journal of Pediatric Sciences found that Consumption of fenugreek herbal tea and palm dates appears useful in enhancing breast milk production during the initial postpartum period. The study had 75 puerperal women randomized into one of three groups for two weeks: a fenugreek herbal tea group, a palm dates group, and a control group with no galactagogue. Maternal milk volume was gauged on the third postpartum day by manually pumping the breasts. To track the impact on the babies, the infants were weighed on specific days - day 0, 3, 7, and 14. Women who consumed fenugreek or dates had a noticeable breast milk volume increase on the third day postpartum. Additionally, infants who fed on maternal milk from mothers consuming dates registered weight gain on the seventh day. The infants in the fenugreek and the control group on the other hand, were still under their birth weight at this point. By the fourteenth day, there was no significant difference in any of the groups regarding the infant’s weight.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2014 in the journal Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine found that Tualang honey demonstrates efficacy comparable to Tribestan in enhancing sperm parameters among oligospermic males, including concentration, motility, and morphology, with a favorable safety profile. This study employed a randomized controlled trial over 12 weeks, comparing the effects of Tualang honey (20 grams) and Tribestan (750 mg) on sperm parameters, erectile function, and hormonal profiles. Sperm concentration, motility, and morphology were assessed, along with erectile function using the IIEF-5 questionnaire. Testosterone, FSH, and LH levels were studied. Results from 66 participants revealed a significant increase in mean sperm concentration, motility, and morphology in the Tualang honey group, while the Tribestan group showed significant improvements in sperm concentration and morphology. No significant differences were observed between the two groups in sperm parameters, erectile function, and hormonal profiles. Safety profiles were normal with no reported adverse events. The findings suggest that Tualang honey and Tribestan exhibit comparable effectiveness in enhancing sperm parameters, specifically concentration, motility, and morphology, among oligospermic males. Additionally, both interventions demonstrated similar effects on erectile function and hormonal profiles. The study concludes that Tualang honey is a safe alternative with no reported adverse events, highlighting its potential in addressing male reproductive health concerns.
A Animal Study published in 2014 in the journal International Journal of Endocrinology found that Regular intake of mineral-rich water, high in sodium bicarbonate, potassium, calcium, and magnesium, potentially reduces risk of Metabolic Syndrome and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Researchers conducted an experiment involving Sprague-Dawley rats, an animal model representing Metabolic Syndrome. For eight weeks, the rats consumed a diet that consisted of 10% fructose. They were also provided with a hypersaline sodium-rich naturally sparkling mineral water to drink. The saline water contained high levels of bicarbonate, potassium, calcium, and magnesium, in comparison to standard tap water, which was used as a control. The study observed various parameters, from heart rate to plasma triacylglycerols and insulin levels. It also studied hepatic (liver-based) catalase activity, leptin levels, and the weight ratios of different organs to body weight. Moreover, it took into consideration the performance of the liver's antioxidative functions by examining hepatic glutathione peroxidase activity and oxidized glutathione content. The experiment aimed to determine the effects of the mineral-derived salts in the water on these various aspects of the rat's health, and how they might mitigate the effects of the fructose-enhanced diet that simulated the physiological conditions of Metabolic Syndrome. Within the results, the scientific team found the intake of mineral-rich water attenuated the increases in heart rate, plasma triacylglycerols, leptin levels, hepatic catalase activity, and organ weight to body weight ratios that were induced by fructose. Furthermore, it prevented the reduction of hepatic glutathione peroxidase activity and oxidized glutathione content. Therefore, the team concluded that the mineral water seemed to have the potential to counteract the effects of the fructose diet, preventing the onset of Metabolic Syndrome. They suggested regular intake of such water could help improve metabolic and redox health.
A Systematic Review published in 2014 in the journal Pharmacology found that Green tea polyphenols may enhance effectiveness of specific breast cancer endocrine treatments through both estrogen-dependent and -independent mechanisms. The methodology used in this systematic review involved a comprehensive search for relevant studies across various electronic databases. The search terms used were tailored to uncover data specifically regarding the interaction of green tea catechins with breast cancer endocrine treatment. Importantly, this review was focused on experimental trials which studied the synergistic effects of green tea catechins and certain breast cancer treatments, namely tamoxifen and raloxifene. The analysis of results indicated that green tea catechins potentially work in conjunction with tamoxifen or raloxifene—used for treating both estrogen receptor-positive and receptor-negative breast cancer—via mechanisms that may depend or not depend on the estrogen receptor. At the same time, the review found no existing evidence showing any interaction of green tea catechins with aromatase inhibitors or fulvestrant. Notably, given their nature as natural compounds and their known safety profile, green tea catechins used along with tamoxifen could constitute a viable direction for enhancing chemoprevention, adjuvant, and metastatic breast cancer treatments.
A Experimental Study published in 2014 in the journal Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine found that Honey, specifically its polyphenols, show promising signs of enhancing memory and counteracting neurodegenerative diseases by reducing oxidative stress and neuroinflammation. The research focuses on the analysis of the nootropic and neuropharmacological benefits of honey, with particular emphasis on its polyphenol constituents. Essentially, honey's nutritional and physiological effects on memory enhancement and various neurological activities have been examined. This study delves into the mechanistic approach in which honey, as a natural compound, can mitigate oxidative stress while enhancing the cellular antioxidant defense system - a cue to its potential role in neutralizing reactive oxygen species that have harmful effects on neurological health. The findings from the research suggest that honey and its polyphenols play a noteworthy role in neuronal health. They display a potential ability to improve memory deficits and other neurodegenerative diseases. In particular, honey polyphenols have been associated with apoptosis activities and the reduction of microglia-induced neuroinflammation. Furthermore, the direct involvement of these polyphenols in synaptic plasticity was found, which could have a substantial effect on the behavior-modulating neural circuitry. Overall, these findings indicate the possible therapeutic value of honey and its polyphenols on the health of the neurological system.
A Review Article published in 2013 in the journal Anti-Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry found that Blueberries, due to their phenolic compounds, show potential as both dietary and supplemental anti-cancer agents by inhibiting cancer cell growth and promoting apoptosis. The researchers synthesized evidence from previous in vitro, in vivo, and a limited number of clinical studies to evaluate the anti-cancer efficacy of blueberries. These studies primarily focused on the fruit's phenolic compounds, which are known for their high antioxidant capacity. The mechanisms underlying the anti-cancer effects of blueberries were analyzed, such as their capacity to inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory molecules, oxidative stress, and products of oxidative stress like DNA damage. In the discussion of the results, it was found that blueberries manifest their anti-cancer properties through the inhibition of cancer cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis. This makes them promising functional foods and nutritional supplements. The evidence strongly indicates the high potential of blueberries as a preventive measure against carcinogenesis, solidifying their position as an anti-cancer fruit. The potential of blueberries in this field certainly demands further exploration.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2013 in the journal Primary Care Respiratory Journal found that Honey plus coffee, presented as a jamlike paste, emerges as a more effective alternative medicine for persistent post-infectious cough (PPC) compared to systemic steroids, demonstrating significant reduction in cough frequency in a randomized controlled trial. The study, conducted at Baqiyatallah University Hospital, Tehran, Iran, involved 97 adults with PPC for over three weeks. Participants were assigned to three groups receiving honey plus coffee, systemic steroids, or guaifenesin. They consumed their assigned product dissolved in warm water every eight hours for a week. Cough severity was assessed before and after treatment using a validated visual analogue cough questionnaire. Honey plus coffee (HC) group exhibited a remarkable decrease in mean cough frequency from 2.9 to 0.2. In contrast, the steroid group (S) showed improvement but with a less significant reduction (3.0 to 2.4), while the control group (C) exhibited no significant change (2.8 to 2.7). Analysis of variance revealed a substantial difference between HC and S groups, establishing honey plus coffee as a promising alternative for PPC treatment.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2013 in the journal Osteoarthritis and Cartilage found that Tart cherry juice potentially helps alleviate symptoms of mild to moderate knee osteoarthritis and decreases the levels of high sensitivity C-reactive protein. The study involved 58 non-diabetic participants with grade 2-3 osteoarthritis as categorized by Kellgren. Participants were randomly assigned to consume two 8-ounce bottles of either tart cherry juice or a placebo daily for six weeks. There was a one-week washout period before participants switched to the alternate treatment in a crossover design. The research measured participants' Western Ontario McMaster Osteoarthritis Index scores and walking times before and after each treatment. Levels of plasma urate, creatinine, and high sensitivity C-reactive protein were also noted at baseline and after each treatment. Acetaminophen was permitted as a rescue drug with self-reporting after each treatment period. There was a noticeable reduction in Western Ontario McMaster Osteoarthritis Index scores following the cherry juice treatment, an effect not observed with the placebo. High sensitivity C-reactive protein also showed a decrease during the cherry juice treatment. The reduction in high sensitivity C-reactive protein was consistent with the improvement observed in osteoarthritis index scores. However, consumption of tart cherry juice didn't significantly affect walking time, usage of acetaminophen, or plasma urate and creatinine levels.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2013 in the journal Osteoarthritis and Cartilage found that Tart cherry juice shows promise in easing knee osteoarthritis symptoms. This study included 58 patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA) who were given either cherry juice or a placebo. While both groups showed some improvement in WOMAC scores, the cherry juice group experienced a 15% improvement, compared to 6% in the placebo group. However, this difference wasn't statistically significant. The cherry juice group also saw a 23% reduction in hsCRP (an inflammation marker), whereas the placebo group had a 51% increase. This suggests an anti-inflammatory effect of cherry juice. The study notes some limitations, including small sample size and the need for further research. Overall, cherry juice may offer benefits for OA patients.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2013 in the journal Food and Chemical Toxicology found that Korean pear juice can alleviate symptoms of alcohol hangover and aid in alcohol detoxification, with effectiveness influenced by certain genetic variations. A randomized single-blind crossover trial was conducted involving 14 healthy young men to explore the effects of Korean pear juice on alcohol hangover. Half-an-hour after ingesting either placebo or Korean pear juice treatment, subjects consumed 540 ml of spirits with 20.1% alcohol volume. Subsequently, blood and urine samples were collected at nine different time points in the next 15 hours. Results revealed that Korean pear juice reduced overall and average hangover severity by 16% and 21% respectively, 15 hours post alcohol consumption. Specific improvements were noticed in 'trouble concentrating'. Moreover, it significantly enhanced memory and reduced sensitivity to light and sound in subjects possessing ALDH2*1/*1 or ALDH2*1/*2 genotypes, but not in those with ALDH2*2/*2 genotype. The treatment also resulted in decreased blood alcohol levels, suggesting that Korean pear juice aids in alcohol detoxification, an effect that seems to be influenced by the genetic variation of ALDH2.
A Animal Study published in 2013 in the journal PLOS One found that Dried plum intake uniquely improves bone density, promotes growth of vertebral trabecular bone, prevents bone loss in tibia, and positively adjusts bone metabolism. Adult osteopenic mice were subjected to a diet supplemented with 25% of various dried fruits such as dried plum, apple, apricot, grape, and mango for a period of 8 weeks. Body and spine bone mineral density improvement was monitored in these mice, with particular focus on the anabolic effect on trabecular bone in the vertebra and prevention of bone loss in the tibia. The osteoclast differentiation and osteoblast and glutathione activity were also assessed, to better understand the potential mechanisms through which dried plum may exert its osteoprotective effects. The results of the study showed that while dried plum, apricot and grape diets led to improvements in bone mineral density, dried plum was the only fruit that resulted in an anabolic effect on trabecular bone in the vertebra and helped prevent bone loss in the tibia. Biomechanical properties showed restoration, aligning with the changes observed in the spine's trabecular bone. Examining the difference in effects between the various fruits, it was found that dried plum was unique in its ability to balance the down-regulation of osteoclast differentiation and up-regulation of osteoblast and glutathione activity. The alterations in bone metabolism and antioxidant status and their transformative impact on bone health were unique to dried plum when compared with other dried fruits.
A Clinical Study published in 2013 in the journal Phytotherapy Research found that Pomegranate juice intake for two weeks significantly reduces blood pressure and may improve heart health by lowering vascular endothelial adhesion molecule-1 levels. In the experiment, twenty-one hypertensive participants, aged between 30 to 67 years, were gathered and randomly assigned to consume either 150ml of fresh pomegranate juice per day or an equal quantity of water for a period of two weeks. The pomegranate juice was consumed in a single occasion between lunch and dinner. The blood pressure of these subjects, including systolic and diastolic pressures, were measured before and after the trial period. Additionally, levels of specific elements including lipid profile parameters, apolipoproteins A and B, intracellular adhesion molecule-1, vascular endothelial adhesion molecule 1, E-selectin, and other inflammatory and endothelial function biomarkers such as high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and interleukin-6, were also measured. The results showed that the consumption of pomegranate juice was associated with notable reductions in both systolic and diastolic blood pressures. The intake of pomegranate juice also resulted in a significant decrease in levels of vascular endothelial adhesion molecule 1, even though there was an increase in E-selectin levels. No observable influence appeared on the levels of intracellular adhesion molecule-1, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, lipid profile parameters, apolipoproteins, or interleukin-6 from the juice consumption, indicating that pomegranate juice may specifically target certain elements related to heart health.
A Review Article published in 2013 in the journal Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry found that Recent phytochemical studies of jujube fruits have shed some light on their biological effects, such as the anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antiobesity, immunostimulating, antioxidant, hepatoprotective, and gastrointestinal protective activities and inhibition of foam cell formation in macrophages. The nutritional jujube (Ziziphus jujube Mill.) fruit belonging to the Rhamnaceous family grows mostly in Europe, southern and eastern Asia, and Australia, especially the inland region of northern China. Jujube has a long history of usage as a fruit and remedy. The main biologically active components are vitamin C, phenolics, flavonoids, triterpenic acids, and polysaccharides. Recent phytochemical studies of jujube fruits have shed some light on their biological effects, such as the anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antiobesity, immunostimulating, antioxidant, hepatoprotective, and gastrointestinal protective activities and inhibition of foam cell formation in macrophages. A stronger focus on clinical studies and phytochemical definition of jujube fruits will be essential for future research efforts. This review may be useful for predicting other medicinal uses and potential drug or food interactions and may be beneficial for people living where the jujube fruits are prevalent and health care resources are scarce.
A Review Article published in 2013 in the journal British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology found that Cocoa and chocolate, rich in antioxidant molecules like epicatechin, enhance brain health, stimulate brain perfusion, and reduce the risk of Alzheimer's disease and stroke. The study involved taking a comprehensive look at the substances contained in cocoa powder and chocolate, their absorption into the brain, and their resulting stimulatory effects on multiple areas of the brain, particularly those connected to comprehension and memory. It also delved into the beneficial effects of epicatechin, a flavonoid found abundantly in cocoa and chocolate, which showed improvements in cognition in both animals and humans. Interestingly, the research showed that the consumption of chocolate could induce mood enhancement, elaborating on its common consumption during times of emotional stress. The study further investigated flavonoids' preservation of cognitive abilities in rats during aging, noting the reduced risk of developing Alzheimer's disease and the decreased likelihood of stroke in humans, demonstrating their wider effects beyond just mood enhancement. The research then looked into flavonoids' interactions within the various signaling pathways related to proteins and lipids in the brain, shedding light on how they inhibit neuron death from neurotoxic elements like oxygen radicals, all while promoting neuron survival and synaptic plasticity. The overall intent of the research was to gather and examine the available data regarding the effects of cocoa and chocolate on brain health and cognitive capacities.
A Experimental Study published in 2013 in the journal Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine found that Pomegranate juice can enhance memory function and brain activity in tasks related to verbal and visual memory in older adults experiencing memory problems. The study was a preliminary, placebo-controlled, randomized trial involving 32 older participants with memory complaints. They were randomly tasked to consume 8 ounces of either pomegranate juice or a placebo drink that had a similar flavor daily for a duration of 4 weeks. Before and after the study duration, the subjects underwent memory tests and functional MRI scans while involved in cognitive tasks. Additionally, blood samples were extracted to ascertain peripheral biomarkers. The test subjects and investigators were oblivious to the groupings to ensure objectivity. The results from the study pointed out that the group that had pomegranate juice had notable improvements in their verbal memory as determined by the Buschke selective reminding test and also a rise in their antioxidant capacity. This group also recorded increased fMRI activity during tasks related to verbal and visual memory in comparison to the placebo group. This may suggest that consumption of pomegranate juice may boost memory function by elevating functional brain activity during tasks.
A Review Article published in 2013 in the journal Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine found that Pomegranates and their extracts may provide natural alternatives to conventional drugs due to their potent activity against various bacterial and viral pathogens. In investigating the potency of pomegranates, various parts of the plant, including the fruit juice, peel, arils, flowers and bark, were tested for antimicrobial activities, with significant success found particularly in the utilization of the pomegranate peel. The phytochemical compounds examined in the study, particularly ellagic acid and larger hydrolyzable tannins like punicalagin, exhibited high antimicrobial activity. In some instances, the amalgamation of pomegranate constituents delivered the most benefit. The results indicate the compelling positive effect of pomegranates on the suppression of oral bacteria. The evidence supporting the antibacterial and antiviral activities of pomegranates against foodborne pathogens and other infectious disease organisms was primarily obtained from in vitro cell-based assays. This prompts the need for further exploration and confirmation of these activities in vivo.
A Review Article published in 2012 in the journal Journal of Psychopharmacology found that Curcumin, a component of Indian spice turmeric, presents a potential natural treatment for depression, influencing neurotransmitters and protecting against several biological systems compromised in depression. The research methodology involved an extensive review of the varying influences and effects of curcumin on systems implicated in depression. These included neurotransmitter systems like serotonin and dopamine which are critical to mood regulation. The study also explored the effects of curcumin on hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal disturbances, famously associated with stress response and mood disorders. In terms of results, curcumin demonstrated promising potential as an antidepressant in animal models of depression. Additionally, it was found to help moderate damage to neurological systems and intestinal permeability, both of which are often compromised in major depressive disorders. It also exhibited properties that could help lower inflammation and protect against oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage. Together, these findings position curcumin as a promising natural treatment for depression.
A Experimental Study published in 2012 in the journal Food Chemistry found that Adzuki bean exhibited the strongest antiproliferative properties in a dose-dependent manner against all digestive system cancer cell lines, ovary cancer cell SK-OV-3 and breast cancer cell MCF-7 among all legumes tested. This research involved comparing the health-promoting effects of various food legumes. The Cellular Antioxidant Activity (CAA) was assessed using a fluorescence microplate reader and in vitro animal cell cultivation. The antiproliferative properties against cancer cells were evaluated through the MTT method in an in vitro cell culture system. Additionally, the study quantified phytochemicals (total phenolic, procyanidin, saponin, and phytic acid) and chemical antioxidant activities (DPPH free radical scavenging activity, oxygen radical absorbing capacity, peroxyl radical scavenging capacity). The results indicated significant variations in phytochemical and antioxidant activities among different legumes. Notably, adzuki bean demonstrated the strongest dose-dependent antiproliferative effects against various cancer cell lines, including those from the digestive system, ovary, and breast. Meanwhile, black soybean showed the highest levels of saponin, phytic acid, and the strongest cellular antioxidant activities. These findings suggest that food legumes, particularly adzuki beans and black soybeans, are promising as natural antioxidants for health promotion and cancer prevention.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2012 in the journal Journal of Food Studies found that Tart cherry juice may lessen inflammation, thus reducing pain in women with osteoarthritis, according to changes noted in specific inflammatory serum biomarkers. This study used a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trial design, involving twenty women with inflammatory osteoarthritis, aged between 40 to 70 years. The participants were given 10.5 ounce bottles of tart cherry juice or a placebo cherry drink to consume twice daily for a span of 21 consecutive days. Pain was assessed at the start and the end of the intervention period. At these same junctures, blood samples were collected to monitor the influence of the juice on serum biomarkers of inflammation: C-Reactive Protein, Interleukin-6, Interleukin-10, and Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha. The results depicted that the group consuming tart cherry juice experienced a significant reduction in the serum biomarker, C-Reactive Protein, an indication of lowered inflammation. This is suggestive that tart cherry juice could be an efficient way of reducing inflammation, and subsequently, the pain experienced by women suffering from osteoarthritis.
A Systematic Review published in 2012 in the journal Menopause found that Soybean isoflavones, whether extracted or synthesized, prove significantly effective in reducing the frequency and severity of hot flashes in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women. The examination in this study began with a database search on PubMed and The Cochrane Controlled Clinical Trials Register for articles shedding light on double-blinded randomized controlled trials conducted until December 14, 2010. Additionally, the authors kept a keen eye out for other peer-reviewed articles containing potentially useful information. Any articles discovered were scrutinized for information on the effects of isoflavones on the frequency or severity of hot flashes in comparison to a placebo. 19 trials were found suitable for inclusion in a systematic review, while 17 of these made it to the meta-analysis stage. Among the 19 trials under review, data revealed that soybean isoflavones' ingestion, on a median of 54 mg for 6 weeks to 12 months, seemed to lead to a decrease in the frequency of hot flashes. A similar trend was discerned with hot flash severity, which reportedly reduced with isoflavone intake. Interestingly, it was found that isoflavone supplements with over 18.8 mg of genistein were more than twice as powerful in reducing hot flash frequency as supplements with a lower genistein count. These results, compiled over the course of the study, strongly suggest that soy isoflavone supplements are quite effective in mitigating the issue of hot flashes in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women.
A Experimental Study published in 2012 in the journal AGE found that Blueberry consumption prior to puberty can significantly prevent bone cell senescence and bone loss induced due to the removal of ovaries in rats. The methodology used in the study involves two parts: an in-vivo study and an in-vitro study. In the in-vivo portion, immature rats were fed a diet supplemented with blueberries either throughout their development or only prior to puberty, and then subjected to ovariectomy. The changes in bone collagen matrix and senescence markers were then examined. In the in-vitro part, three different bone cell lines were studied for cellular senescence pathways. The bone cells were treated with serum either from ovariectomized rats or from blueberry-fed ovariectomized rats to observe the effects on osteoblastic cell senescence pathways and potential to differentiate into adipocytes. The results showed that ovariectomy led to bone loss, a decrease in collagen and Sirt1, and an increase in the senescence markers collagenase and p16/p21. However, feeding blueberry-supplemented diet to rats prior to puberty prevented these ovariectomy-induced effects. The in-vitro studies revealed that collagen inhibited senescence in a dose-response manner, and serum from ovariectomized rats accelerated osteoblastic cell senescence pathways. It also revealed that bone cell senescence is associated with decreased Sirt1 expression and increased p53, p16, and p21. However, this acceleration did not occur when cells were treated with serum from blueberry-fed ovariectomized rats.
A Experimental Study published in 2012 in the journal Phytotherapy Research found that Korean pears potentially boost key alcohol-metabolizing enzymes, aiding alcohol detoxification, with effects that may vary due to human ALDH2 polymorphisms. Methodology: The study utilized both in vitro and in vivo testing with a model of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) alternation. Korean pear extract was administered to mice exhibiting normal (C57BL/6) and deficient (Aldh2 -/-) Aldh2. Following this, the mice were given ethanol through gavage after a timeframe of 30 minutes. Implementation of GC/MS enabled quantification of alcohol and acetaldehyde levels in the blood samples. Discussion of Results: The results from the study revealed that Korean pears stimulate activities of alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and ALDH in vitro and in vivo, subsequently reducing blood alcohol levels regardless of ALDH2 genotype. Interestingly, the extract increased the acetaldehyde levels in blood in Aldh2 deficient mice but not in Aldh2 normal mice. This indicates that the key enzymes involved in alcohol metabolism are stimulated by Korean pears, which could be the primary mechanism involved in alcohol detoxification. Furthermore, the variations in human ALDH2 polymorphisms could result in individual variations to the detoxification effects of Korean pears.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2012 in the journal Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research found that Blended essential oils, including lavender, sage, and marjoram, show potential in relieving menstrual cramps and reducing pain duration in women with primary dysmenorrhea. For the methodology, the researchers conducted a randomized, double-blind clinical trial involving 48 outpatients suffering from primary dysmenorrhea. These patients’ discomfort was rated above five on a 10-point numeric scale. Participants were divided evenly into two groups: one was treated with a cream blending lavender, clary sage, and marjoram essential oils, while the other received a synthetic fragrance. All participants massaged the cream onto their lower abdomen daily, from the end of one menstrual cycle to the start of the next. In the discussion of results, it was found that the treatment provided relief and decreased pain duration for patients in the essential oils group following a single menstrual cycle. Among the blended oils, four key analgesic components—linalyl acetate, linalool, eucalyptol, and β-caryophyllene—were principally credited for pain reduction, constituting up to 79.29% of the blend. Thus, these findings propose that this mixed formula might be a valid alternative and complementary medicine approach for primary dysmenorrhea.
A Systematic Review published in 2012 in the journal The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that Regular chocolate or cocoa consumption, rich in flavan-3-ols, has been associated with improved insulin resistance and blood vessel function, suggesting potential cardiovascular benefits. The study systematically reviewed 42 randomized controlled trials involving 1297 participants to investigate the impact of chocolate, cocoa, and flavan-3-ols on major cardiovascular disease risk factors. Utilizing a comprehensive search across multiple databases, the researchers conducted meta-analyses, assessing acute and short-term chronic interventions. Results revealed consistent improvements, including reduced insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), enhanced flow-mediated dilatation (FMD), and favorable effects on blood pressure and cholesterol levels. The findings indicate promising cardiovascular benefits associated with chocolate or cocoa consumption. Notably, the study highlights improvements in insulin sensitivity, blood vessel function, and blood pressure, emphasizing the potential positive impact of flavan-3-ols found in these products.
A Experimental Study published in 2012 in the journal Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine found that Pomegranate polyphenols have notable antioxidant and antiatherogenic effects that lessen cholesterol, oxidized lipids accumulation, and atherosclerosis development in arterial macrophages. The research utilizes both in vitro and in vivo human and mouse models to explore the impact of pomegranate polyphenols. Specifically, the study investigates its effects on serum lipoproteins and arterial macrophages, two major components of atherosclerotic lesions. The study administers pomegranate juice and its by-products to the models for observational testing. The results indicate that pomegranate polyphenols significantly curtailed the accumulation of cholesterol and oxidized lipids in macrophages, as well as the formation of foam cells, a key factor in early atherogenesis. Consequently, this led to the deceleration of atherosclerosis development and its associated cardiovascular events. This suggests the potentially potent antioxidant and antiatherogenic properties of pomegranate polyphenols and their beneficial effects on cardiovascular health.
A Systematic Review published in 2011 in the journal Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics found that The consumption of green tea catechins is associated with a statistically significant reduction in total and LDL cholesterol levels. Twenty trials (N=1,415) met all inclusion criteria. Upon meta-analysis, GTCs at doses ranging from 145 to 3,000 mg/day taken for 3 to 24 weeks reduced total and LDL cholesterol compared to control. GTCs did not significantly alter HDL cholesterol or triglyceride levels. The consumption of GTCs is associated with a statistically significant reduction in total and LDL cholesterol levels; however, there was no significant effect on HDL cholesterol or triglyceride levels.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2011 in the journal European Journal of Nutrition found that Consumption of tart cherry juice can increase exogenous melatonin that is beneficial in improving sleep duration and quality and might be of benefit in managing disturbed sleep. Total melatonin content was significantly elevated (P < 0.05) in the cherry juice group, whilst no differences were shown between baseline and placebo trials. There were significant increases in time in bed, total sleep time and sleep efficiency total (P < 0.05) with cherry juice supplementation. Although there was no difference in timing of the melatonin circardian rhythm, there was a trend to a higher mesor and amplitude.
A Animal Study published in 2011 in the journal British Journal of Nutrition found that Pomegranate extracts enhance bone formation and increase bone calcium content in mice. In this research, fifty pregnant Balb/c mice were administered with either a vehicle, pomegranate juice extract (PJE), pomegranate husk extract (PHE), or a mixture of husk and juice extract (PME). On the 19th day of gestation, the embryos were stained to measure femur and tibia lengths and their ossification zones; the bone calcium content in the pregnant mice was also assessed. Apart from that, cells from fetal limb buds were cultured and exposed to various concentrations of PJE, PHE, or PME to study their impacts on cell proliferation and differentiation. The findings from the study suggest the beneficial impact of pomegranate extracts on bone health. Mice treated with Pomegranate Juice Extract showed an increase in bone calcium content, a crucial component of bone health. Furthermore, dietary supplementation with all types of extracts resulted in significant enhancements in embryo femur length and the osteogenesis index, indicating improved bone formation. The cellular studies also revealed a greater number of viable cells, more cartilage nodules, and increased diameters when exposed to the extracts, suggesting enhanced cell proliferation and differentiation rates and thus promoting bone development.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2011 in the journal British Journal of Nutrition found that Dried plum consumption enhances bone mineral density in postmenopausal women, primarily by reducing the rate of bone turnover. The research studied 160 osteopenic postmenopausal women from 1 to 10 years postmenopause, who were not receiving any hormone replacement therapy or medication affecting bone metabolism. Participants were randomly divided into two treatment groups, one consuming dried plums and the other eating dried apples, with both groups also receiving daily dosages of calcium and vitamin D. Bone mineral density was measured at the beginning and end of the study using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Blood samples were taken at the start, then every 3 months to evaluate bone biomarkers. Physical activity and dietary factors were monitored as potential covariates throughout the study. Dried plums significantly boosted the bone mineral density in the ulna (one of the two bones in the forearm) and spine compared to dried apples. This tendency could only be seen in dried plums - they drastically reduced serum levels of bone turnover markers, specifically bone-specific alkaline phosphatase and tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase-5b. This confirms that dried plums can indeed improve the bone mineral density in postmenopausal women, in part by suppressing the rate of bone turnover.
A Meta-Analysis published in 2011 in the journal European Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that Consumption of dark chocolate and cocoa products has been shown to significantly reduce serum levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and total cholesterol (TC), indicating potential cardiovascular benefits. The research aimed to investigate the impact of dark chocolate and cocoa product consumption on lipid profiles, particularly focusing on LDL, TC, high-density lipoprotein (HDL), and triglycerides (TG). A thorough literature search identified 10 clinical trials involving 320 participants, with intervention durations ranging from 2 to 12 weeks. The analysis revealed a significant reduction in both LDL (difference in means: -5.90 mg/dl) and TC (difference in means: -6.23 mg/dl) levels following the consumption of dark chocolate or cocoa products. However, no statistically significant effects were observed for HDL and TG. These findings suggest short-term beneficial effects on total and LDL cholesterol with no major impact on HDL and TG.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2011 in the journal Optometry and Vision Science found that Daily goji berry supplementation increases antioxidant levels and protects visual health in the elderly, though the exact mechanism remains unclear. In a double-masked, randomized, placebo-controlled study, elderly participants were given either a milk-based goji berry supplement (13.7 g/d) or a placebo for a 90-day period. Eye health was assessed via direct examination to measure pigmentation and soft drusen count in the macula, and blood tests were done to determine plasma zeaxanthin level and total antioxidant capacity. In the discussion of results, the placebo group showed signs of hypopigmentation and soft drusen accumulation in the macula, which did not occur in the group that received the goji berry supplement. The group supplementing with goji berries also showed a significant increase in plasma zeaxanthin levels and total antioxidant capacity, while no change was seen in the placebo group. There were no adverse effects of the supplement reported in either group.
A Review Article published in 2011 in the journal Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics found that Cumin and caraway seeds have shown diverse medicinal applications, thanks to their rich essential oils, as revealed by recent experimental studies. The reported study focuses on extensively researching Cuminum cyminum and Carum carvi, known as cumin and caraway seeds respectively. These seeds have historical usage in various traditional healing systems across different geographies. The research involves closely studying their chemical composition, primarily their richness in essential oils, and investigating their biological activities. The discussion of results outlines the various novel bioactivities of cumin and caraway seeds that have emerged from the extensive experimental studies. The research validates the acclaimed medicinal attributes of these seeds that have enhanced their significance as a potential source of diverse natural products. Though the abstract doesn't provide specific details, it points to an array of medicinal applications, underscoring the potential for cumin and caraway seeds in medical and therapeutic use.
A Experimental Study published in 2010 in the journal Arthritis Research & Therapy found that Pomegranate extract can inhibit key cellular pathways and activities involved in the progression of osteoarthritis. The researchers derived human chondrocytes, cells found in the cartilages, from osteoarthritis-affected cartilage using enzymatic digestion methods. These chondrocytes were treated with a standardized pomegranate extract and then stimulated with Interleukin-1β, a protein involved in cellular responses to injury. To understand the pathways influenced by the extract, gene expression of different types of p38-Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) was measured by Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction, while their activation was studied through immunoblotting and immunoprecipitation. The DNA binding activity of a transcription factor, known as Runt-related Transcription Factor 2, was analyzed using sensitive and specific Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay methods. The outcomes showed that Interleukin-1β enhances the phosphorylation of two types of p38-MAPK in these cells. The cells also expressed three isoforms of p38-MAPK and activating p38-MAPK preferentially occurred through the activation of a protein, known as MKK3. Furthermore, the pomegranate extract inhibited the Interleukin-1β-induced activation of MKK3, one isoform of p38-MAPK, and reduced the DNA binding activity of Runt-related Transcription Factor 2.
A Theoretical Article published in 2010 in the journal Molecular Medicine Reports found that Chamomile, with its numerous terpenoids and flavonoids, has a vast range of medicinal uses and is being developed as a human health promoting therapeutic agent. Methodology: The study conducted a detailed review of the usage of chamomile in traditional medicine. Specific attention was given to the two most common varieties: German Chamomile and Roman Chamomile. The researchers focused on the terpenoids and flavonoids contained in the dried flowers of the chamomile plant, known contributors to its medicinal properties. The various preparations of chamomile were taken into account, with a particularly strong focus on its form in herbal tea, a favorite among users. Discussion of Results: Chamomile has been found to be effective in treating a wide array of human ailments, such as hay fever, inflammation, menstrual disorders, insomnia, wounds, and several gastrointestinal disorders. Furthermore, the essential oils of chamomile are used extensively in aromatherapy and cosmetics, demonstrating its diverse range of applications. The application of chamomile in promoting human health is, therefore, not only diverse but also shows promising potential in developing as a therapeutic agent.
A published in 2010 in the journal Research in Microbiology found that Punicalagin, extracted from the fruit peel of Punica granatum, displays strong antifungal activity against Candida species, especially when combined with fluconazole. Methodology: The study made use of an activity-guided repeated fractionation process on a silica-gel column to isolate a compound from a crude hydro alcoholic extract of Punica granatum fruit peel. Upon analysis, this compound was identified as punicalagin. Its antifungal activity against Candida albicans and Candida parapsilosis was tested, alongside its combined effectiveness with fluconazole. Further tests were conducted using disk-diffusion, checkerboard assays, and time-kill curves to confirm the compound's synergy with fluconazole. Results: Punicalagin exhibited considerable antifungal activity against Candida organisms, including Candida albicans and Candida parapsilosis. When combined with fluconazole, punicalagin resulted in a two-fold decrease in the MIC for fluconazole, indicating a synergistic interaction. Further visual investigations, through scanning and transmission electron microscopy, showed that treated yeast cells exhibited an irregular budding pattern, pseudohyphae, and changes in cell morphology including a thicker cell wall, alterations in the distance between the cell wall and the plasma membrane, and the presence of vacuoles.
A Systematic Review published in 2010 in the journal Chinese Medicine found that Long-term consumption of tea catechins could be beneficial against high-fat diet-induced obesity and type II diabetes and could reduce the risk of coronary disease. Laboratory studies showed the health effects of green tea. As the human clinical evidence is still limited, future research needs to define the actual magnitude of health benefits, establishes the safe range of tea consumption associated with these benefits, and elucidates the mechanisms of action. Development of more specific and sensitive methods with more representative models along with the development of good predictive biomarkers will give a better understanding of how green tea interacts with endogenous systems and other exogenous factors. Definitive conclusions concerning the protective effect of green tea have to come from well-designed observational epidemiological studies and intervention trials. The development of biomarkers for green tea consumption, as well as molecular markers for its biological effects, will facilitate future research in this area.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2009 in the journal The American Journal of Cardiology found that Pomegranate juice consumption doesn't significantly affect overall progress of carotid intima-media thickness, but may slow its progression in subjects with high oxidative stress and lipid issues. In the study, a randomized, double-blind, parallel trial was carried out to assess the impact of daily consumption of pomegranate juice on carotid intima-media thickness progression rates in subjects moderately at risk for coronary heart disease. The participants consisted of elderly men and women who already had one or more major risk factors for the disease. Half of the participants were given 240 ml of pomegranate juice daily to consume for a period of up to 18 months, while the other half were provided with a control beverage. The findings of the trial showed no significant difference in carotid intima-media thickness progression rates between the two groups who consumed pomegranate juice and the control beverage respectively. However, in-depth analyses revealed that among individuals with the highest tertiles for baseline serum lipid peroxides, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and other factors, those in the pomegranate juice group had experienced notably less progression of carotid intima-media thickness.
A Experimental Study published in 2009 in the journal Journal of Ethnopharmacology found that The extract from Chrysanthemum Indicum Linné effectively reduces inflammation in mouse skin when induced, hinting at potential therapeutic applications for immune-related skin diseases. To investigate the effects of Chrysanthemum Indicum Linné extract (CIE) on skin inflammation, the study first prepared a 70% ethanolic extract of the plant. The investigation was conducted in vivo using mice. Researchers then measured the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, the activation of myeloperoxidase, and conducted histological assessments. They induced acute and chronic skin inflammation in the mice using 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate, a substance known to cause mouse ear edema. In understanding the results, they found that administering CIE inhibited topical edema in the mouse's ear, following administration at a dose of 200mg/kg. This resulted in significant reductions in skin thickness, tissue weight, inflammatory cytokine production, and neutrophil-mediated myeloperoxidase activity. The extract was also found to be effective at reducing various histopathological indicators, as well as inflammatory damage induced by chronic exposure to the inflammation-inducing substance. The study, therefore, concludes that CIE could be an effective anti-inflammatory agent and may have therapeutic potential for various immunity-related skin diseases.
A Experimental Study published in 2008 in the journal The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry found that Blueberry consumption can prevent bone loss and positively impact bone metabolism in ovariectomized rats. The research involved thirty 6-month-old female Sprague-Dawley rats. Some rats were ovariectomized to simulate post-menopausal conditions and then divided into three groups: Sham-operated, control (ovariectomized but no intervention), and a group that was ovariectomized and given a 5% blueberry diet. After being on this diet for 100 days, the effects of the blueberries on bone health were evaluated through the assessment of Bone Mineral Density (BMD) and content in the whole body, right tibia, right femur, and fourth lumbar vertebra through dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. In terms of the results, the ovariectomy caused a loss of BMD in the whole body, tibia, femora, and lumbar region, whereas the blueberry diet prevented this loss in the whole body. It also somewhat reduced the loss in the tibia and femur. The bone-protective effects of the blueberries were attributed to them suppressing the ovariectomy-induced increase in bone turnover. This was shown by reduced levels of various cellular components linked to bone metabolism in the femoral bone and serum of rats on the blueberry diet, compared to the ovariectomized control group.
A Experimental Study published in 2007 in the journal Mycobiology found that Tremella fuciformis, a mushroom, shows potential as a protective agent against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's by promoting cell growth and reducing toxicity. The methodology involved testing the neurotrophic effects of Tremella fuciformis, a mushroom, using a hot water extract of it. This testing was done by utilizing microscopic monitoring of its ability to encourage neurite outgrowth in PC12h cells, essentially examining the mushroom's ability to stimulate nerve growth. The researchers compared the effectiveness of the extract to other natural substances that had previously been studied in promoting nerve growth. In the discussion of results, the study demonstrated that the hot water extract of T. fuciformis was highly effective at promoting neurite outgrowth in PC12h cells. This effectiveness outperformed other natural substances in previous studies. Moreover, when the cells were treated with T. fuciformis extract before being exposed to a β-amyloid peptide treatment (which is associated with Alzheimer's disease), the extract significantly reduced the toxicity. This suggests the potential application of T. fuciformis as a preventative measure in counteracting neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2004 in the journal BMC Public Health found that Drinking mineral water, especially those high in magnesium, helps lower blood pressure among individuals with borderline hypertension and low calcium or magnesium excretion. The research was conducted in a controlled environment with 70 subjects who have borderline high blood pressure. Each participant was given either water with low mineral content, magnesium-enriched water, or natural mineral water randomly and blindly over the course of four weeks. After the specified period, the researchers found that subjects with initially low magnesium or calcium excretion showed increased urinary excretion of magnesium when consuming waters that contain magnesium. Notably, a significant decrease in blood pressure was observed in the participants who consumed mineral water after 2 and 4 weeks. This indicates that the minerals ingested through water significantly contribute to the body's mineral balance and that an intake of mineral water may help reduce blood pressure among people with low urinary excretion of magnesium or calcium.
A Clinical Study published in 2000 in the journal Clinica Chimica Acta found that Migraine patients exhibit lower intracellular magnesium levels, which can be increased by consuming magnesium-rich mineral water, demonstrating its bioavailability. The study started by identifying a common issue with lower-than-recommended dietary intakes of magnesium in Western countries. The focus was on migraine patients, as low brain magnesium and impaired magnesium metabolism had been reported in migraine cases. A non-invasive and sensitive test to detect these deficiencies was sought. Magnesium, being an intracellular cation, was tested in 29 migraine patients and 18 control subjects. The tests were for total magnesium in plasma, erythrocytes, lymphocytes and ionized magnesium in lymphocytes. The analysis found that there were lower concentrations of total magnesium in erythrocytes and ionized magnesium in lymphocytes of migraine patients compared to controls. These findings indicated a notable overall difference between the migraine patients and the controls, despite there being overlaps in some individual values. The researchers then subjected the migraine patients to a 2-week intake of a mineral water rich in magnesium. An increase in all intracellular magnesium concentrations was observed, with no effect on plasma magnesium. This increase demonstrated the bioavailability of magnesium from the mineral water. Interestingly, the most sensitive index of magnesium deficiency turned out to be ionized magnesium in lymphocytes, which saw the most significant increase after the intake of the magnesium-rich mineral water.
Moderation Tools
Topic
Sign In
Users not signed in are limited to viewing the 5 most recent items of content.