LH
How to submit an article:
- Registered users can submit any published journal article that has a unique DOI (Digital Object Identifier) name or link to Research Hub.
- For example, you can paste the full DOI link:
https://doi.org/10.1109/5.771073or just the DOI name:10.1109/5.771073into the field above and click submit. - The person who is first to submit a valid article to Research Hub will forever be credited for it, and every article submission earns you +6 Research Points.
Also known as: Luteinizing Hormone
Related Topics
Published research studies are articles that present the findings of original research that has undergone a peer-review process and has been made publicly available in scholarly journals, books or other media.

Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) seeds and by-products in metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disorders: A systematic review of clinical studies
2024 Jan Phytomedicine Nunes YC, Santos GO, Machado NM, Otoboni AMMB, Laurindo LF, Bishayee A, et al.
Peanuts and their products, containing phytochemicals, can improve metabolic parameters and have the potential to be used as a sustainable and low-cost alternative for the prevention and treatment of MetS and CVD.
Systematic Review Review Article Peanut
Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Activity of Cucumis sativus and Citrus macroptera Herbal Formulation: An In-Vitro Study
2024 Jan 07 Cureus Journal of Medical Science Amani T, Surenthar M, Shanmugam R
The combination of cucumber, citrus, and glycerol extract demonstrated significant antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, comparable to standard values, as indicated by assays such as 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging, Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2), Bovine serum albumin (BSA), and Egg albumin (EA) denaturation assays. The extracts showed appreciable effects at concentrations of 30, 40, and 50 µl, with the maximum concentration of 50 µl exhibiting optimal antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity.
Experimental Study Antioxidant Anti-Inflammatory Cucumber
New approaches to the pathogenesis of peptic ulcer based on the protective action of saliva with special reference to roughage, vegetable fibre and fermented milk products
2024 Jan Psychoneuroendocrinology Malhotra SL
Review Article Stomach UlcerPeptic ulcers may be prevented and cured by well-chewed food rich in vegetable fibers and fermented milk products, which increase protective salivary mucus and decrease damaging bile flow.

The Association of Tongue Scalloping With Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Related Sleep Pathology
2023 Dec Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Weiss TM, Atanasov S, Calhoun KH
Clinical Study Obstructive Sleep Apnoea Sleep Tongue Scalloping SnoringTongue scalloping can be a useful clinical indicator of sleep disorders, including snoring history and obstructive sleep apnea.

Daily blueberry consumption for 12 weeks improves endothelial function in postmenopausal women with above-normal blood pressure through reductions in oxidative stress: a randomized controlled trial
2023 Jan Food & Function Woolf EK, Terwoord JD, Litwin NS, Vazquez AR, Lee SY, Ghanem N, et al.
Daily consumption of freeze-dried blueberry powder for 12 weeks improves endothelial function through reduced oxidative stress in postmenopausal women with above-normal blood pressure.
Randomised Controlled Trial Blueberry Oxidative StressResearch insights are moderated by the Research Hub team and offer an at-a-glance overview of interesting research findings.

2024 Psychoneuroendocrinology
Peptic ulcers may be prevented and cured by well-chewed food rich in vegetable fibers and fermented milk products, which increase protective salivary mucus and decrease damaging bile flow.
Review Article Stomach Ulcer
New approaches to the pathogenesis of peptic ulcer based on the protective action of saliva with special reference to roughage, vegetable fibre and fermented milk products
Malhotra SL

2023 Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery
Tongue scalloping can be a useful clinical indicator of sleep disorders, including snoring history and obstructive sleep apnea.
Clinical Study Obstructive Sleep Apnoea Sleep Snoring Tongue Scalloping
The Association of Tongue Scalloping With Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Related Sleep Pathology
Weiss TM, Atanasov S, Calhoun KH

2022 Frontiers in Nutrition
In women with polycystic ovary syndrome, cinnamon reduced insulin resistance and testosterone levels similar to metformin, and ginger decreased follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones.
Randomised Controlled Trial Ceylon Cinnamon Cinnamon FSH Ginger Insulin Resistance
A comparison of the effects of cinnamon, ginger, and metformin consumption on metabolic health, anthropometric indices, and sexual hormone levels in women with poly cystic ovary syndrome: A randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled clinical trial
Dastgheib M, Barati-Boldaji R, Bahrampour N, Taheri R, Borghei M, Amooee S, et al.

2022 Molecules
Green tea's catechins demonstrate therapeutic effects against neurodegenerative diseases via anti-inflammatory, antioxidant actions, and activating diverse brain cellular pathways.
Review Article Alzheimer's Disease Cognitive Function Green Tea Multiple Sclerosis Neurodegenerative Diseases
Green Tea Catechins Attenuate Neurodegenerative Diseases and Cognitive Deficits
Afzal O, Dalhat MH, Altamimi ASA, Rasool R, Alzarea SI, Almalki WH, et al.

2022 Frontiers in Pharmacology
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) demonstrates weight loss efficacy and metabolic benefits in overweight and obese individuals
Systematic Review Obesity
Efficacy and safety of traditional chinese medicine treatment for overweight and obese individuals: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Wen ZG, Zhang QQ, Zhang LL, Shen MF, Huang YS and Zhao LH
Review Articles
Review articles summarise and critically evaluate the current state of research on a specific topic or field by synthesising multiple primary research studies.

Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) seeds and by-products in metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disorders: A systematic review of clinical studies
2024 Jan Phytomedicine Nunes YC, Santos GO, Machado NM, Otoboni AMMB, Laurindo LF, Bishayee A, et al.
Peanuts and their products, containing phytochemicals, can improve metabolic parameters and have the potential to be used as a sustainable and low-cost alternative for the prevention and treatment of MetS and CVD.
Systematic Review Review Article Peanut
New approaches to the pathogenesis of peptic ulcer based on the protective action of saliva with special reference to roughage, vegetable fibre and fermented milk products
2024 Jan Psychoneuroendocrinology Malhotra SL
Review Article Stomach UlcerPeptic ulcers may be prevented and cured by well-chewed food rich in vegetable fibers and fermented milk products, which increase protective salivary mucus and decrease damaging bile flow.

Green Tea Catechins Attenuate Neurodegenerative Diseases and Cognitive Deficits
2022 Nov 06 Molecules Afzal O, Dalhat MH, Altamimi ASA, Rasool R, Alzarea SI, Almalki WH, et al.
Review Article Green Tea Cognitive Function Multiple Sclerosis Parkinson's Disease Neuroprotective Alzheimer's Disease Neurodegenerative DiseasesGreen tea's catechins demonstrate therapeutic effects against neurodegenerative diseases via anti-inflammatory, antioxidant actions, and activating diverse brain cellular pathways.

Efficacy and safety of traditional chinese medicine treatment for overweight and obese individuals: A systematic review and meta-analysis
2022 Oct 05 Frontiers in Pharmacology Wen ZG, Zhang QQ, Zhang LL, Shen MF, Huang YS and Zhao LH
Systematic Review ObesityTraditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) demonstrates weight loss efficacy and metabolic benefits in overweight and obese individuals

Honey as an Adjuvant in the Treatment of COVID-19 Infection: A Review
2022 Aug 03 Applied Sciences Soares S, Bornet M, Grosso C, Ramalhosa MJ, Gouvinhas I, Garcia J, et al.
Review Article Immunity COVID-19 Antioxidant Honey Anti-InflammatoryHoney, owing to its bioactive compounds, demonstrates potential in treating COVID-19 symptoms by reducing oxidative damage and enhancing the immune system.
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are research studies that involve people and are conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of new treatments or interventions, such as drugs, medical devices, or behavioural therapies.

Daily blueberry consumption for 12 weeks improves endothelial function in postmenopausal women with above-normal blood pressure through reductions in oxidative stress: a randomized controlled trial
2023 Jan Food & Function Woolf EK, Terwoord JD, Litwin NS, Vazquez AR, Lee SY, Ghanem N, et al.
Daily consumption of freeze-dried blueberry powder for 12 weeks improves endothelial function through reduced oxidative stress in postmenopausal women with above-normal blood pressure.
Randomised Controlled Trial Blueberry Oxidative Stress
A comparison of the effects of cinnamon, ginger, and metformin consumption on metabolic health, anthropometric indices, and sexual hormone levels in women with poly cystic ovary syndrome: A randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled clinical trial
2022 Nov 29 Frontiers in Nutrition Dastgheib M, Barati-Boldaji R, Bahrampour N, Taheri R, Borghei M, Amooee S, et al.
Randomised Controlled Trial Cinnamon Testosterone Metabolic Syndrome FSH Ginger PCOS Insulin Resistance Metformin Ceylon Cinnamon LHIn women with polycystic ovary syndrome, cinnamon reduced insulin resistance and testosterone levels similar to metformin, and ginger decreased follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones.

Effect of Incorporating 1 Avocado Per Day Versus Habitual Diet on Visceral Adiposity: A Randomized Trial
2022 Jul 19 Journal of the American Heart Association Lichtenstein AH, Kris‐Etherton PM, Petersen KS, Matthan NR, Barnes S, Vitolins MZ, et al.
Randomised Controlled Trial Visceral Fat AvocadoDespite previous suggestions, daily avocado consumption for six months did not decrease visceral adipose tissue volume in individuals with elevated waist circumference.

Efficacy and Safety of Lianhua Qingke Tablets in the Treatment of Mild and Common-Type COVID-19: A Randomized, Controlled, Multicenter Clinical Study
2022 Feb 10 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Zhang L, Wu L, Xu X, Yuan Y, Jiang R, Yan X, et al.
These preliminary findings indicate Lianhua Qingke (LH) tablets may be effective in symptomatic COVID-19, especially in relieving coughing.
Randomised Controlled Trial Lian Hua Qing Ke Li
The Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Medicine Based on Semi-Targeted Metabolomics to Improve IVF Outcomes in Senile Patients
2021 Nov 10 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Ma YJ, Yuan LH, Xiao JM, Jiang HY, Sa YH, Sun HQ, et al.
Qi-Zi-Yu-Si decoction can effectively improve the IVF outcome and clinical symptoms of senile patients. Follicular fluid metabolites were significantly changed in senile infertile women with kidney qi deficiency, and the mechanism by which kidney-invigorating herbs improve IVF treatment outcomes may be related to glycerophospholipid metabolism and steroid hormone biosynthesis.
Randomised Controlled Trial Chinese Herbal MedicineStudy Protocols
Published study protocols are detailed plans that outline the objectives, methodology, statistical analyses, and organisation of a research study that have been made publicly available for others to review and use as a reference.
Presentation Slides

Review Article
Peptic ulcers may be prevented and cured by well-chewed food rich in vegetable fibers and fermented milk products, which increase protective salivary mucus and decrease damaging bile flow.
Malhotra SL

Clinical Study
Tongue scalloping can be a useful clinical indicator of sleep disorders, including snoring history and obstructive sleep apnea.
Weiss TM, Atanasov S, Calhoun KH

Randomised Controlled Trial
In women with polycystic ovary syndrome, cinnamon reduced insulin resistance and testosterone levels similar to metformin, and ginger decreased follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones.
Dastgheib M, Barati-Boldaji R, Bahrampour N, Taheri R, Borghei M, Amooee S, Mohammadi-Sartang M, Wong A, Babajafari S, Mazloomi SM

Review Article
Green tea's catechins demonstrate therapeutic effects against neurodegenerative diseases via anti-inflammatory, antioxidant actions, and activating diverse brain cellular pathways.
Afzal O, Dalhat MH, Altamimi ASA, Rasool R, Alzarea SI, Almalki WH, Murtaza BN, Iftikhar S, Nadeem S, Nadeem MS, Kazmi I

Systematic Review
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) demonstrates weight loss efficacy and metabolic benefits in overweight and obese individuals
Wen ZG, Zhang QQ, Zhang LL, Shen MF, Huang YS and Zhao LH

Review Article
Honey, owing to its bioactive compounds, demonstrates potential in treating COVID-19 symptoms by reducing oxidative damage and enhancing the immune system.
Soares S, Bornet M, Grosso C, Ramalhosa MJ, Gouvinhas I, Garcia J, Rodrigues F, Delerue-Matos C

Randomised Controlled Trial
Despite previous suggestions, daily avocado consumption for six months did not decrease visceral adipose tissue volume in individuals with elevated waist circumference.
Lichtenstein AH, Kris‐Etherton PM, Petersen KS, Matthan NR, Barnes S, Vitolins MZ, Li Z, Sabaté J, Rajaram S, Chowdhury S, Davis KM, Galluccio J, Gilhooly CH, Legro RS, Li J, Lovato L, Perdue LH, Petty G, Rasmussen AM, Segovia‐Siapco G, Sirirat R, Su

Meta-Analysis
Certain species of citrus extracts effectively control dyslipidemia, reducing total cholesterol, LDL, and triglycerides while increasing HDL, primarily due to their rich antioxidant composition.
Carvalho BMR, Nascimento LC, Nascimento JC, Gonçalves VSS, Ziegelmann PK, Tavares DS, Guimarães AG

Experimental Study
Saffron petal extract and anthocyanins can alleviate symptoms of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome by rectifying hormonal imbalances and reducing inflammation in PCOS mice.
Moshfegh F, Balanejad SZ, Shahrokhabady K, Attaranzadeh A

Systematic Review
Acupuncture's potential in reducing menopausal hot flush frequency compared to sham acupuncture, and its similarity in impacting hormone levels to hormone therapy.
Liu C, Wang Z, Guo T, Zhuang L, Gao X

Experimental Study
Gypenosides, the main functional component from the vine Gynostemma pentaphyllum, display potential as a treatment for Retinitis Pigmentosa by protecting photoreceptor cells from degeneration.
Alhasani RH, Zhou X, Biswas L, Li X, Reilly J, Zeng Z, Shu X

Review Article
Green tea and its compounds, especially catechins, may potentially prevent and treat osteoarthritis due to their potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Barbalho SM, Goulart RA, Buglio DS, Araujo AC, Guiguer EL

Review Article
Citrulline supplementation combined to high intensity interval training is more effective in improving functional capacities and body composition in healthy older adults than high intensity interval training alone.
Buckinx F., Carvalho L.P., Marcangeli V., Dulac M., Hajj Boutros G., Gouspillou G., Gaudreau P., Noirez P., Aubertin-Leheudre M.

Systematic Review
Acupuncture could promote the recovery of menstrual cycles as well as downregulate the levels of LH and testosterone in patients with PCOS.
Wu J, Chen D, Liu N

Systematic Review
Antenatal perineal massage reduces severe perineal trauma and postpartum complications.
Abdelhakim AM, Eldesouky E, Elmagd IA, Mohammed A, Farag EA, Mohammed AE, Hamam KM, Hussein AS, Ali AS, Keshta NHA, Hamza M, Samy A, Abdel-Latif AA

Systematic Review
Acupuncture reduced more headache days and the times of using painkiller and was more effective in reducing the frequency and degree of headache than western medicine and sham acupuncture.
Li YX, Xiao XL, Zhong DL, Luo LJ, Yang H, Zhou J, He MX, Shi LH, Li J, Zheng H, Jin RJ

Systematic Review
Regular dietary intake of olive oil reduces the levels of certain inflammation markers, making it a beneficial alternative dietary fat, especially for managing IL-6.
Fernandes J, Fialho M, Santos R, Peixoto-Plácido C, Madeira T, Sousa-Santos N, Virgolino A, Santos O, Vaz Carneiro A

Systematic Review
L-citrulline supplementation significantly decreased non-resting brachial and aortic systolic blood pressure.
Yang HH, Li XL, Zhang WG, Figueroa A, Chen LH, Qin LQ

Randomised Controlled Trial
Acupuncture therapy does not impact the severity of Obstructive Sleep Apnea, blood pressure, or quality of life in hypertensive patients.
Silva MVFP, Lustosa TC, Arai VJ, Couto Patriota TLG, Lira MPF, Lins‐Filho OL, Chalegre ST, B.B.A.S. K, Secundo IV, Pedrosa RP

Systematic Review
Acupuncture and its combined therapy may be effective for treating female infertility, however, the included studies are not robust enough to draw a firm conclusion.
Yun L, Liqun W, Shuqi Y, Chunxiao W, Liming L, Wei Y
Systematic Review
Ginger supplementation enhances the production of testosterone in males by reducing oxidative stress and increasing luteinizing hormone production, cholesterol in testes, and blood flow to the testes.
Banihani SA

Meta-Analysis
Children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder are found to have lower ferritin levels and are more likely to have iron deficiency.
Tseng PT, Cheng YS, Yen CF, Chen YW, Stubbs B, Whiteley P, Carvalho AF, Li DJ, Chen TY, Yang WC, Tang CH, Chu CS, Yang WC, Liang HY, Wu CK, Lin PY

Randomised Controlled Trial
Dark chocolate reduces subsequent food intake in postmenopausal women more effectively than milk and white chocolate.
Marsh CE, Green DJ, Naylor LH, Guelfi KJ

Systematic Review
Acupuncture yielded results similar to those observed in groups treated with occlusal splints for pain in myofascial temporomandibular disorder.
Ana Carla Bezerra De Carvalho Justo Fernandes, DDS, MSc/Dayanne Monielle Duarte Moura, DDS, MSc/Laura Géssica Dantas Da Silva, DDS, MSc/Erika Oliveira De Almeida, DDS, MSc, PhD/Gustavo Augusto Seabra Barbosa, DDS, MSc, PhD

Randomised Controlled Trial
A 14-session course of needling at Fengchi is relatively safe for treating posterior circulation ischemia with vertigo.
Wen Y, Zhang C, Zhao Xf, Deng Sz, He S, Huang Lh, Tian G, Meng Zh

Systematic Review
Acupuncture may have a positive impact on recovering menstrual cycles, reducing BMI, and lowering luteinizing hormone (LH) levels in women with polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS).
Qu F, Wu Y, Hu XY, Barry JA, Zhou J, Wang FF, Ye YH, Zhang R, Han SP, Han JS, Li R, Taw MB, Hardiman PJ, Robinson N
Clinical Study
Drinking hydrogen carbonate-rich mineral water significantly reduces heartburn episodes and improves quality of life in individuals with dyspeptic symptoms.
Pohl U, Auinger A, Bothe G, Uebelhack R

Experimental Study
Pomegranate juice extract significantly improves hormonal changes in female rats with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
HOSSEIN KARGAR, LEILA KARGAR, EBRAHIM TAVAKOL, NAZANIN SHAFIEI, FARZAD POORGHOLAMI, ELHAM RAHMANIAN, MOHAMMAD POURAHMADI, ZAHRA HASANPOUR

Systematic Review
The bioactive components and biological activities were superior for green (unripe) jujube fruit (as pulp and seed) compared to the ripe fruit.
Sirithon Siriamornpuna, NatthidaWeerapreeyaku, Sahapat Barusrux

Randomised Controlled Trial
Tualang honey demonstrates efficacy comparable to Tribestan in enhancing sperm parameters among oligospermic males, including concentration, motility, and morphology, with a favorable safety profile.
Ismail SB, Bakar MB, Nik Hussain NH, Norhayati MN, Sulaiman SA, Jaafar H, Draman S, Ramli R, Wan Yusoff WZ

Animal Study
Regular intake of mineral-rich water, high in sodium bicarbonate, potassium, calcium, and magnesium, potentially reduces risk of Metabolic Syndrome and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
Pereira CD, Severo M, Araújo JR, Guimarães JT, Pestana D, Santos A, Ferreira R, Ascensão A, Magalhães J, Azevedo I, Monteiro R, Martins MJ

Randomised Controlled Trial
The daily use of avocado-soybean unsaponifiable-expanscience (ASU-E) reduces the progression of joint space narrowing in patients with hip osteoarthritis.
Maheu E, Cadet C, Marty M, Moyse D, Kerloch I, Coste P, Dougados M, Mazières B, Spector TD, Halhol H, Grouin JM, Lequesne M

Systematic Review
Regular chocolate or cocoa consumption, rich in flavan-3-ols, has been associated with improved insulin resistance and blood vessel function, suggesting potential cardiovascular benefits.
Hooper L, Kay C, Abdelhamid A, Kroon PA, Cohn JS, Rimm EB, Cassidy A

Punicalagin, extracted from the fruit peel of Punica granatum, displays strong antifungal activity against Candida species, especially when combined with fluconazole.
Endo EH, Garcia Cortez DA, Ueda-Nakamura T, Nakamura CV, Dias Filho BP
Executive Summary
Write an executive summary in the form of a blog article on the topic of "Research into Chinese medicine treatment for LH" summarising the research below and using language that can be easily understood by patients and avoiding medical jargon using a professional and caring tone of voice.
Write an executive summary in the form of a blog article on the topic of "Researched Chinese medicine treatments for LH" summarising the research below in an objective and easy to understand way, and using language that can be easily understood by patients. Group the article into Chinese medicine treatments first, followed by nutrition and other treatments. Avoid using medical jargon and use a professional and caring tone of voice.
Write me a concise but easy to understand executive summary on the topic of "Chinese medicine treatments for LH" based on the following research that I will give you. Your summary should be 2 paragraphs long in Australian English spelling and include references to the studies.
A Review Article published in 2024 in the journal Psychoneuroendocrinology found that Peptic ulcers may be prevented and cured by well-chewed food rich in vegetable fibers and fermented milk products, which increase protective salivary mucus and decrease damaging bile flow. The research conducted a review of epidemiologic studies focusing on the variations of diet and eating patterns related to the prevalence of peptic ulcer disease across various communities. The effects of dietary patterns were assessed on saliva, gastric juice, and bile. The role of bile was specifically examined in the pathogenesis of peptic ulcer, with the argument that it, rather than hydrochloric acid, played a causal role. The role of saliva in preventing peptic ulcers was emphasized, particularly the protective nature of salivary mucus which is swallowed with food. The study then suggested the types of diets that can help prevent peptic ulcers, including those rich in roughage, cellulose, vegetable fibers, and fermented milk products such as ghee and yogurt. The research posited this kind of diet can increase the amount of salivary mucus and consequently decrease the flow rate of harmful bile. The study also noted that these insights showed minor changes in diet, and a slower pace of consumption could lead to substantial health benefits. Moving from dietary composition to eating behaviors, it was suggested that food should be well-masticated to ensure these beneficial digestive processes have an opportunity to occur. At the same time, the research made the case that specific dietary components, particularly short-chain fatty acids like those found in milk products, can retard gall bladder contraction, thereby reducing the amount of bile entering the duodenal lumen. This secondary action further contributes to the potential prevention of peptic ulcers.
A Clinical Study published in 2023 in the journal Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery found that Tongue scalloping can be a useful clinical indicator of sleep disorders, including snoring history and obstructive sleep apnea. In the study, sixty-one patients from an otolaryngology clinic were evaluated with historical and physical examinations for tongue scalloping, snoring, and other symptoms linked to sleep-disordered breathing and obstructive sleep apnea. The evaluation of tongue scalloping was graded on a scale from 0 to 3. Additionally, twenty-five patients underwent overnight polysomnography to definitively diagnose sleep pathology. In the discussions of results, it was found that 44% of patients displayed some degree of tongue scalloping, and this symptom was primarily found in males. Among patients diagnosed with obstructive sleep apnea or having a snoring history, the presence of any tongue scalloping was detected. It also showed a positive correlation with increasing Mallampati and modified Mallampati airway classifications. Besides, the presence of tongue scalloping was indicative of abnormal sleep efficiency, increased apnea-hypopnea index, and nocturnal desaturation greater than 4% below the normal baseline, suggesting it could serve as a predictor of sleep pathology.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition found that In women with polycystic ovary syndrome, cinnamon reduced insulin resistance and testosterone levels similar to metformin, and ginger decreased follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones. In the methodology of the study, 100 women diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome were divided into four groups. Each group received a different treatment: cinnamon, ginger, metformin, or placebo. The dosage for these treatments was 500 mg, three times a day, administered over a period of 8 weeks. The participants' sex hormones, weight revelations, along with glycemic and lipid markers were monitored before and after this period. Several participants were disqualified because of unspecified factors, resulting in a final sample size of 83. In terms of results, all groups saw a decrease in weight and body mass index. The metformin and cinnamon groups specifically had notably decreases in their insulin resistance, meaning that these treatments were effective in improving metabolic health. Additionally, the ginger group experienced a reduction in follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone levels unlike the other groups. Testosterone levels were lowered in the metformin and cinnamon groups, but no significant changes in dehydroepiandrosterone were observed in any of the groups. These results indicate the potential use of cinnamon and ginger as alternative treatments in managing polycystic ovary syndrome.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Molecules found that Green tea's catechins demonstrate therapeutic effects against neurodegenerative diseases via anti-inflammatory, antioxidant actions, and activating diverse brain cellular pathways. The research primarily evaluates the effect of polyphenolic compounds found in green tea, known as catechins, on neurodegenerative diseases. By conducting several interventional and observational studies on humans, the research explores the anti-cancer, anti-obesity, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective properties of these compounds. The biological, pharmacological, antioxidant, and metal chelating abilities of catechins, particularly their influence on different cellular pathways within the brain, are intensively studied. The results elucidate that catechins exhibit multiple neuroprotective effects. Their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties help to inhibit excessive production of cytokines, and inflammatory pathways, while also controlling metal ions and free radicals. Researchers have further established that catechins may curb the phosphorylation of the tau protein and aggregation of amyloid beta, both key markers in neurodegenerative diseases. Additionally, these compounds show potential in reducing alpha-synuclein levels and augmenting dopamine levels. Hence, they significantly contribute to the prevention and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, multiple sclerosis, and cognitive deficits.
A Systematic Review published in 2022 in the journal Frontiers in Pharmacology found that Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) demonstrates weight loss efficacy and metabolic benefits in overweight and obese individuals TCM interventions, particularly polyherbal preparations, effectively reduced weight, BMI, waist and hip circumference in overweight and obese individuals across 25 studies with nearly 2,000 participants. TCM also improved glucose and lipid metabolism by reducing fasting blood glucose, triglycerides, and total cholesterol while increasing HDL levels. TCM treatments were generally well-tolerated and safe, with some mild adverse effects.
A Review Article published in 2022 in the journal Applied Sciences found that Honey, owing to its bioactive compounds, demonstrates potential in treating COVID-19 symptoms by reducing oxidative damage and enhancing the immune system. The review outlines the SARS-CoV-2 virus's mechanisms of action, which is responsible for COVID-19, offering a comprehensive understanding. It also explores the various bioactive assets honey has at its disposal, primarily focusing on its beneficial properties. The discussion elaborates on the potentials of honey's biological properties, especially its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. These characteristics of honey, as suggested by the review, could contribute to the relief of oxidative damage and boost the immune system, thereby proving beneficial in combating viral infections, including COVID-19.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2022 in the journal Journal of the American Heart Association found that Despite previous suggestions, daily avocado consumption for six months did not decrease visceral adipose tissue volume in individuals with elevated waist circumference. The HAT Trial was a multicenter, randomized, controlled study designed to observe the effects of consuming one large avocado per day for six months on free-living individuals with an increased waist circumference. The primary measure of effect was the change in visceral adipose tissue volume, which was measured through magnetic resonance imaging. Other conditions related risk factors associated with cardiometabolic disorders were surveyed as secondary and additional endpoints. In results analysis, there was no significant alteration in visceral adipose tissue volume between the Avocado Supplemented and Habitual Diet Groups. No noteworthy differences were noticed in the secondary outcomes including hepatic fat fraction and certain components of the metabolic syndrome. Of the extra outcome measures, small but significant reductions were seen in total and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in the Avocado Supplemented compared to the Habitual Diet Group. Changes in body weight, body mass index, insulin concentration and other measured factors were very similar between both groups, showing no considerable change due to avocado consumption.
A Meta-Analysis published in 2022 in the journal Frontiers in Pharmacology found that Certain species of citrus extracts effectively control dyslipidemia, reducing total cholesterol, LDL, and triglycerides while increasing HDL, primarily due to their rich antioxidant composition. The methodology involved systematic surveys of research databases including PubMed, Scopus, LILACS, and SciELO. The team utilised several descriptors like dyslipidemias, hypercholesterolemia, hyperlipidemias, lipoproteins, and cholesterol. From the initial findings, 958 articles were identified and after critical assessment, 26 studies were selected that showed the efficacy of certain species extracts in controlling dyslipidemia. Of these, 25 studies were incorporated into a meta-analysis conducted using R software. Assessment of potential bias was carried out as per Cochrane methodology and ARRIVE guidelines for preclinical and clinical studies respectively. From the total number of collected studies, the results consistently showed the effectiveness of these species extracts on dyslipidemia, reducing total cholesterol, LDL, and triglycerides while elevating HDL levels. The active composition of these extracts, particularly rich in flavonoids which are powerful antioxidants, was identified as the crucial factor. The bias risk across all studies was found to be critically low to moderate. Nevertheless, the high heterogeneity values noticed across the studies suggest some inconsistency in the evidence provided.
A Experimental Study published in 2022 in the journal Journal of Ethnopharmacology found that Saffron petal extract and anthocyanins can alleviate symptoms of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome by rectifying hormonal imbalances and reducing inflammation in PCOS mice. The study conducted experiments on mice induced with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) through the injection of testosterone enanthate. These mice were then treated with saffron petal extract and anthocyanins to observe the effect on their ovarian hormones, steroidogenic enzymes, ovarian dysfunction, regulation of anti-inflammatory genes, and antioxidant factors. The treatment was found to decrease the elevated levels of luteinizing hormone, testosterone, and estrogen in the PCOS mice, while reviving the reduced follicular-stimulating hormone and progesterone levels. In discussion of the results, it was observed that saffron petal extract and anthocyanins positively altered the levels of gonadotropin receptors, steroid receptors, inflammatory markers, inflammatory-related factors, and antioxidant enzymes that were affected by the PCOS condition in the subject mice. The study also noted that the reproductive tissues of the PCOS mice, which were converted into androgen-dominant environments by the testosterone enanthate induction, were restored into estrogenic conditions after the treatment. Further findings suggested that saffron petal extract and anthocyanins led to amelioration of PCOS symptoms by enhancing the regulation of ovarian steroids, steroidogenic processes, antioxidant enzyme production, and inflammatory markers.
A Systematic Review published in 2021 in the journal Acupuncture in Medicine found that Acupuncture's potential in reducing menopausal hot flush frequency compared to sham acupuncture, and its similarity in impacting hormone levels to hormone therapy. This study aimed to assess acupuncture's effectiveness and safety in treating menopausal hot flushes and its impact on hormone levels. Through meta-analyses of thirteen randomized controlled trials involving 1784 patients, it found that acupuncture reduced hot flush frequency compared to sham acupuncture, but didn't affect end scores of frequency or severity. Acupuncture demonstrated hormone level effects similar to hormone therapy. However, due to limited trial quality and quantity, further high-quality trials are necessary for definitive conclusions.
A Experimental Study published in 2020 in the journal Experimental Eye Research found that Gypenosides, the main functional component from the vine Gynostemma pentaphyllum, display potential as a treatment for Retinitis Pigmentosa by protecting photoreceptor cells from degeneration. In this study, researchers used zebrafish carrying a specific mutation that leads to early retinal degeneration like in Retinitis Pigmentosa, a group of genetic retinal disorders. The mutation, present in the retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator interacting protein 1 gene, was exposed to Gypenosides. The substance was sourced from Gynostemma pentaphyllum, a climbing vine, and previously found to combat oxidative stress and inflammation in optic neuritis cells. The results suggest significant benefits from the application of Gypenosides to retinitis pigmentosa. Treatment of the mutated zebrafish resulted in a notable decrease in the death rate of photoreceptor cells. The reaction of antioxidant genes typically associated with oxidative stress was also significantly reduced. Furthermore, there were marked reductions in reactive oxygen species and malondialdehyde production, along with diminished expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Overall, the outcome indicates that Gypenosides effectively counteracted the harmful effects of the mutation, protecting the photoreceptors from degeneration.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Longhua Chinese Medicine found that Green tea and its compounds, especially catechins, may potentially prevent and treat osteoarthritis due to their potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. The researchers performed an extensive review exploring the potential impact of green tea and its bioactive compounds, chiefly catechins, on osteoarthritis management. Their focus was on the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant abilities of these compounds. Based on the review, such compounds can quell inflammation by blocking various signaling pathways interconnected with inflammatory processes. Specifically, they have the potential to suppress the expression of several cytokines and enzymes related to inflammation. In addition, green tea was noted for its property to neutralize free radicals, thus averting the formation of harmful reactive oxygen species and countering oxidative stress. While many conventional, non-surgical osteoarthritis therapies can lead to numerous adverse effects, the current review suggests that green tea could serve as a safer alternative. It may be a promising direction in the prevention and management of this chronic, painful, and inflammatory condition, which touches a significant number of people globally.
A Review Article published in 2020 in the journal Experimental Gerontology found that Citrulline supplementation combined to high intensity interval training is more effective in improving functional capacities and body composition in healthy older adults than high intensity interval training alone. The decrease in BMI and android fat mass were significantly greater in the high intensity interval training + citrulline group than in the high intensity interval training + placebo group. Finally, a greater increase in self-paced gait speed and fast-paced gait speed were also observed in the high intensity interval training + citrulline group than in the high intensity interval training + placebo group.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Medicine found that Acupuncture could promote the recovery of menstrual cycles as well as downregulate the levels of LH and testosterone in patients with PCOS. Twenty two studies with 2315 participants were included in this systematic review and meta-analysis. A pooled analysis showed a recovery of the menstrual period in the acupuncture group. Furthermore, there were significant decreases in the luteinizing hormone (LH) and testosterone in the acupuncture group. No significant differences were observed in the rates of live birth, pregnancy, and ovulation, and no significant differences were observed in the LH/follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) ratio. There was insufficient evidence to support that acupuncture could promote live birth, pregnancy, and ovulation. However, acupuncture could promote the recovery of menstrual cycles as well as downregulate the levels of LH and testosterone in patients with PCOS.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal International Urogynecology Journal found that Antenatal perineal massage reduces severe perineal trauma and postpartum complications. This meta-analysis of 11 randomized controlled trials involving 3467 patients found that antenatal perineal massage significantly reduces the risk of perineal tears and episiotomy, especially severe tears. Additionally, it leads to shorter second-stage labor, less postpartum perineal pain, and improved wound healing. While some heterogeneity and publication bias were noted, this study supports the routine recommendation of antenatal perineal massage for labor preparation, emphasizing its benefits in reducing perineal trauma and improving obstetric outcomes. Further research with larger sample sizes is encouraged to confirm these findings and explore additional benefits, such as postpartum sexual satisfaction and incontinence reduction.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Pain Research & Management found that Acupuncture reduced more headache days and the times of using painkiller and was more effective in reducing the frequency and degree of headache than western medicine and sham acupuncture. Based on high quality of evidence, we conclude that acupuncture is more effective and safer than medication or sham acupuncture in the treatment of migraine. However, the methodological quality, risk of bias, and reporting quality of SRs in acupuncture for migraine still needs improvement in future.
A Systematic Review published in 2020 in the journal Nutrition found that Regular dietary intake of olive oil reduces the levels of certain inflammation markers, making it a beneficial alternative dietary fat, especially for managing IL-6. The methodology of this review involved summarising data from randomized controlled trials to investigate the impact of regular dietary intake of olive oil on three specific inflammatory markers: C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. These studies looked at how regular usage of olive oil as part of the diet can affect these markers and provide benefits to individuals who implement it in their dietary routine. The trials focused primarily on the Mediterranean diet, which is known for its high usage of olive oil as a main fat source. The results indicate that olive oil, when consumed on a consistent basis, can reduce the levels of inflammatory markers. It has been observed to be particularly effective in managing levels of interleukin-6. The results obtained from the review of these trials suggest that olive oil can indeed be a beneficial supplement to diet with potential impacts on managing inflammation and related diseases. They hint at potential effectiveness of olive oil as a nutritious factor in mitigating the adverse impacts of a diet high in unhealthy fats, by providing it as a healthier alternative.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal Nutrition & Metabolism found that L-citrulline supplementation significantly decreased non-resting brachial and aortic systolic blood pressure. L-citrulline supplementation significantly decreased non-resting brachial and aortic systolic blood pressure. Brachial diastolic blood pressure was significantly lowered by L-citrulline regardless of resting status. Given the relatively small number of available trials in the stratified analyses and the potential limitations of these trials, the present findings should be interpreted cautiously and need to be confirmed in future well-designed trials with a larger sample size.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2019 in the journal Journal of Sleep Research found that Acupuncture therapy does not impact the severity of Obstructive Sleep Apnea, blood pressure, or quality of life in hypertensive patients. The study examined the effects of acupuncture on blood pressure and Obstructive Sleep Apnea severity in hypertensive patients. These patients, all suffering from mild to moderate Obstructive Sleep Apnea, were randomly divided into two groups, one of which received acupuncture treatment while the other received sham-acupuncture treatment, essentially a placebo. Each patient's condition was assessed before and after ten acupuncture sessions, relying on measures such as polysomnography, around-the-clock blood pressure monitoring, and a life quality survey. A total of 44 patients completed the study, the group covering both genders, with an average age of 57 years, and a diverse range of body mass indices and apnea-hypopnea indices. It's important to note that there were no distinguishable differences observed in the apnea-hypopnea index, daytime or nighttime blood pressure, or life quality between the group that received genuine acupuncture treatment and the group that received the placebo treatment.
A Systematic Review published in 2019 in the journal Medicine found that Acupuncture and its combined therapy may be effective for treating female infertility, however, the included studies are not robust enough to draw a firm conclusion. Current evidence identified from this review suggested that acupuncture may be effective in the treatment of female infertility. The conclusion of this present review is limited by the low quality of the included studies. Future multicenter RCTs with rigorous methodological quality are needed to clarify the role of acupuncture in female infertility.
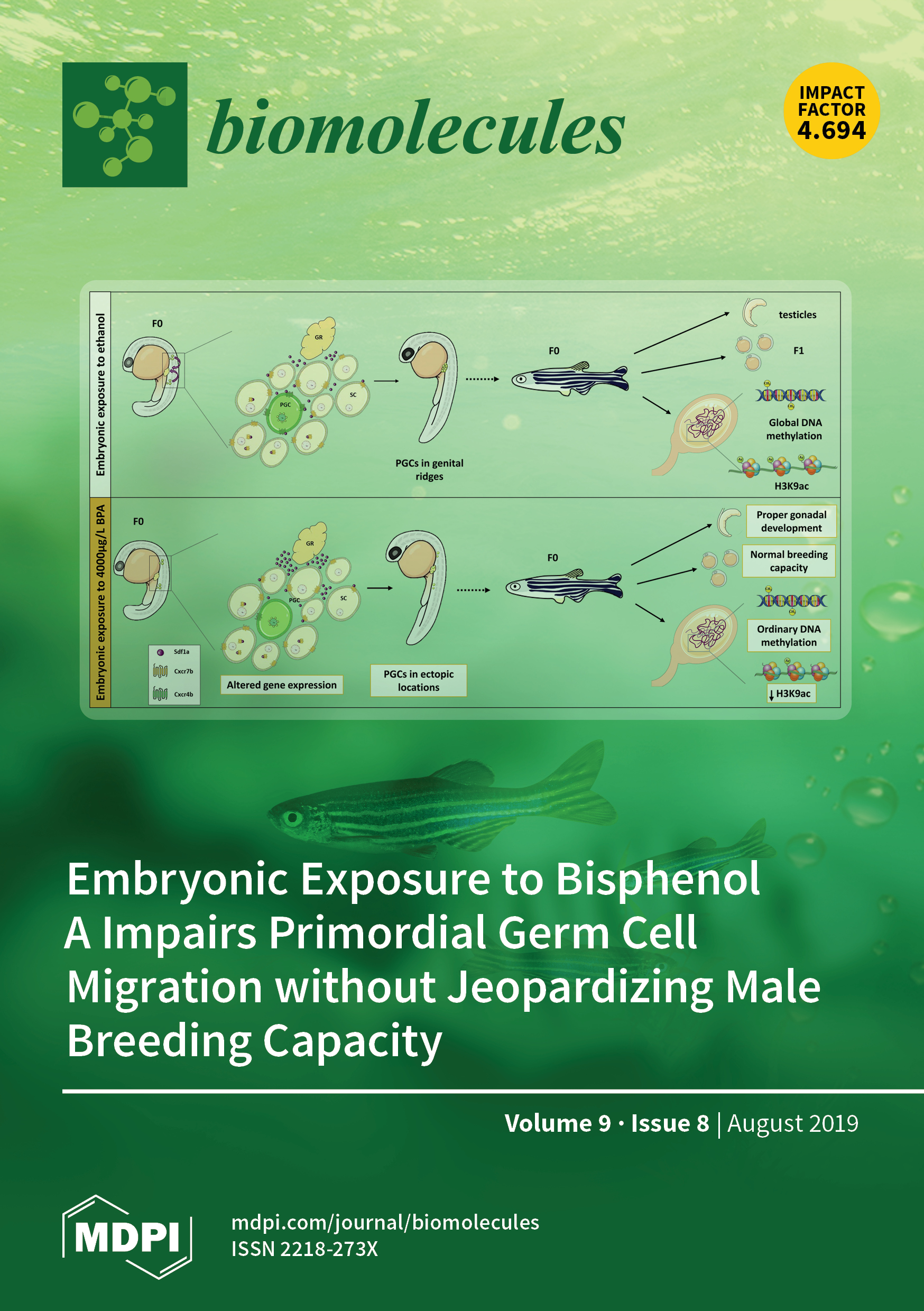
A Systematic Review published in 2018 in the journal Biomolecules found that Ginger supplementation enhances the production of testosterone in males by reducing oxidative stress and increasing luteinizing hormone production, cholesterol in testes, and blood flow to the testes. The study reviewed a collection of English language articles from three databases— PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science— from November 1991 through August 2018. Keywords for the search included "ginger" and "testosterone". The references from relevant published articles were also reviewed. The methodology encompassed both in-vivo and basic research studies that sought to discover a link between ginger and testosterone. The results revealed that ginger supplementation enhances testosterone production in males, particularly in conditions of oxidative stress. This effect is achieved primarily by increasing the production of luteinizing hormone, cholesterol levels in the testes, reducing testes oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation, enhancing antioxidant enzyme activity, normalizing blood glucose and increasing blood flow in the testes. Furthermore, the study shows a correlation between ginger supplementation and increased testicular weight, and recycling of testosterone receptors.
A Meta-Analysis published in 2018 in the journal Scientific Reports found that Children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder are found to have lower ferritin levels and are more likely to have iron deficiency. For the methodology of this meta-analysis, numerous databases such as PubMed, ScienceDirect, Cochrane CENTRAL, and ClinicalTrials.gov were searched for relevant studies up until August 9, 2017. The principal outcomes were the differences in peripheral iron levels between children diagnosed with ADHD and healthy controls, and the severity of ADHD symptoms in children with and without iron deficiency. Seventeen articles met the strict inclusion criteria and were therefore included in the meta-analysis. Discussing the results, peripheral serum ferritin levels (a measure of iron storage) were found to be significantly lower in children with ADHD. However, no notable difference was found in serum iron or transferrin levels (measures of iron transport). In addition, children with iron deficiency displayed more severe ADHD symptoms. Importantly, a significant link between ADHD and iron deficiency was also established.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2017 in the journal Appetite found that Dark chocolate reduces subsequent food intake in postmenopausal women more effectively than milk and white chocolate. In the study, 14 healthy postmenopausal women participated in three separate experimental trials done in a counterbalanced order. Each trial was conducted at a specific time and was spaced one week apart. The women's food intake, appetite perceptions, mood, and levels of certain appetite-related peptides were measured and analyzed following their consumption of an isocaloric amount of dark chocolate (80% cocoa), milk chocolate (35% cocoa), and white chocolate (cocoa butter). The results indicated a significant decrease in food intake after consuming dark chocolate compared to milk and white chocolate. Furthermore, blood glucose and insulin levels were found to temporarily increase after consuming milk and white chocolate, unlike in the case of dark chocolate. In addition, the consumption of high cocoa content chocolate, like dark and milk chocolate, elevated the pancreatic polypeptide, which differed from the response to white chocolate. The conditions had no significant effect on active ghrelin or leptin hormones, and the mood of the participants remained largely unaffected.
A Systematic Review published in 2017 in the journal Journal of Oral & Facial Pain and Headache found that Acupuncture yielded results similar to those observed in groups treated with occlusal splints for pain in myofascial temporomandibular disorder. A total of four randomized clinical trials using acupuncture (traditional, trigger point, and laser) for TMD treatment met the eligibility criteria and were included. Although the studies featured small sample sizes and short-term follow-up periods, acupuncture yielded results similar to those observed in groups treated with occlusal splints and were significantly superior than those obtained from placebo acupuncture–treated groups. Despite the weak scientific evidence supporting its efficacy, acupuncture treatment appears to relieve the signs and symptoms of pain in myofascial TMD. More controlled and randomized clinical trials with larger sample sizes are needed in this field of research to verify these initial findings.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2016 in the journal Neural Regeneration Research found that A 14-session course of needling at Fengchi is relatively safe for treating posterior circulation ischemia with vertigo. Acupuncture at Fengchi (GB20) in the posterior neck improves vertigo. However, subarachnoid hemorrhage and spinal epidural hematoma have been reported to occur after acupuncture in the posterior neck. Therefore, in the present study, we assessed the safety of acupuncture at Fengchi. Of the 136 patients, 120 completed the study. There were no significant differences between pretreatment and posttreatment test results in any of the groups. Only five patients suffered from minor adverse events (needling pain, slight hematoma and transient chest tightness). No serious adverse events were found. Our results indicate that a 14-session course of needling at Fengchi is relatively safe for treating posterior circulation ischemia with vertigo.
A Systematic Review published in 2016 in the journal European Journal of Integrative Medicine found that Acupuncture may have a positive impact on recovering menstrual cycles, reducing BMI, and lowering luteinizing hormone (LH) levels in women with polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). In this systematic review and meta-analysis, the clinical effectiveness of acupuncture in treating polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) was investigated. The review included nine randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving a total of 531 women with PCOS. The analysis revealed that acupuncture showed promise in improving the recovery of menstrual cycles, reducing body mass index (BMI), and lowering luteinizing hormone (LH) levels among women with PCOS. However, caution is advised in interpreting these findings due to the limited methodological quality of the included RCTs. Despite the positive outcomes observed in certain parameters, further high-quality research is needed to establish the full scope of acupuncture's potential as a treatment for PCOS.
A Clinical Study published in 2016 in the journal Open Journal of Gastroenterology found that Drinking hydrogen carbonate-rich mineral water significantly reduces heartburn episodes and improves quality of life in individuals with dyspeptic symptoms. This one-arm pilot study involved 56 men and women experiencing frequent heartburn. Participants were instructed to drink 1.5 liters of mineral water high in hydrogen carbonate daily for six weeks. They kept a daily diary to record the number and duration of heartburn episodes. Additionally, several questionnaires were used to assess the effects of the water on their condition and quality of life. These included the Reflux Disease Questionnaire (RDQ), Quality of Life in Reflux and Dyspepsia questionnaire (QOLRAD), Gastrointestinal Quality of Life Index (GILQI), and the Short Form Health Survey (SF-12). The study analyzed changes in symptoms and quality of life before and after the treatment using the Wilcoxon test. The study reported a significant decrease in the number of weekly heartburn episodes and the duration of each episode after the six-week intervention. Participants also experienced a notable reduction in the severity of heartburn, regurgitation, and dyspeptic complaints. There was a significant improvement in disease-specific quality of life as measured by GILQI and QOLRAD, and in general health-related quality of life as assessed by SF-12. These findings suggest that drinking hydrogen carbonate-rich mineral water can be an effective alternative treatment for dyspeptic symptoms and heartburn, leading to an enhanced quality of life.
A Experimental Study published in 2015 in the journal Biomedical and Pharmacology Journal found that Pomegranate juice extract significantly improves hormonal changes in female rats with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. A total of 56 female Wistar rats, who had 2 to 3 consecutive estrous cycles over 12 to 14 days, were used in the study. These were divided into six groups, with differing conditions of control and experimental groups, each group was administered different treatments, ranging from those without any substances or treatments, to those receiving hormones and/or varying doses of pomegranate extract. After a set duration, all rats were weighed and their blood samples taken. The collected data showed that the concentration of estrogen, testosterone, and androstenedione significantly increased in the experimental groups as compared to the control groups. Furthermore, there was a notable decrease in these hormone levels in the experimental groups compared to the PCOS group. The results suggest that pomegranate juice extract has a positive effect on regulating female sex hormones, indicating its potential effectiveness as a treatment for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
A Systematic Review published in 2014 in the journal Journal of Functional Foods found that The bioactive components and biological activities were superior for green (unripe) jujube fruit (as pulp and seed) compared to the ripe fruit. Compared to the properties of ripe pulp, the green pulp of each variety possessed higher phenolic contents, DPPH scavenging activity, and FRAP value. The anti-glycation properties of the jujube samples ranged between 52 and 72%, depending on the ripening stage and variety. Phenolic content was positively correlated with antioxidant and anti-glycation activities, but not with total flavonoid content. Green jujube pulp possessed greater anti-glycation than the ripe jujube pulp in all varieties studied. The water extracts of Bombay and Taiwan jujubes caused moderate Jurkat leukemic cell deaths but with low apoptosis induction effects. This study provides practical information about how best to take advantage of the bioactive compounds and health implications of the jujube as a potential source for functional and nutritive applications.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2014 in the journal Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine found that Tualang honey demonstrates efficacy comparable to Tribestan in enhancing sperm parameters among oligospermic males, including concentration, motility, and morphology, with a favorable safety profile. This study employed a randomized controlled trial over 12 weeks, comparing the effects of Tualang honey (20 grams) and Tribestan (750 mg) on sperm parameters, erectile function, and hormonal profiles. Sperm concentration, motility, and morphology were assessed, along with erectile function using the IIEF-5 questionnaire. Testosterone, FSH, and LH levels were studied. Results from 66 participants revealed a significant increase in mean sperm concentration, motility, and morphology in the Tualang honey group, while the Tribestan group showed significant improvements in sperm concentration and morphology. No significant differences were observed between the two groups in sperm parameters, erectile function, and hormonal profiles. Safety profiles were normal with no reported adverse events. The findings suggest that Tualang honey and Tribestan exhibit comparable effectiveness in enhancing sperm parameters, specifically concentration, motility, and morphology, among oligospermic males. Additionally, both interventions demonstrated similar effects on erectile function and hormonal profiles. The study concludes that Tualang honey is a safe alternative with no reported adverse events, highlighting its potential in addressing male reproductive health concerns.
A Animal Study published in 2014 in the journal International Journal of Endocrinology found that Regular intake of mineral-rich water, high in sodium bicarbonate, potassium, calcium, and magnesium, potentially reduces risk of Metabolic Syndrome and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Researchers conducted an experiment involving Sprague-Dawley rats, an animal model representing Metabolic Syndrome. For eight weeks, the rats consumed a diet that consisted of 10% fructose. They were also provided with a hypersaline sodium-rich naturally sparkling mineral water to drink. The saline water contained high levels of bicarbonate, potassium, calcium, and magnesium, in comparison to standard tap water, which was used as a control. The study observed various parameters, from heart rate to plasma triacylglycerols and insulin levels. It also studied hepatic (liver-based) catalase activity, leptin levels, and the weight ratios of different organs to body weight. Moreover, it took into consideration the performance of the liver's antioxidative functions by examining hepatic glutathione peroxidase activity and oxidized glutathione content. The experiment aimed to determine the effects of the mineral-derived salts in the water on these various aspects of the rat's health, and how they might mitigate the effects of the fructose-enhanced diet that simulated the physiological conditions of Metabolic Syndrome. Within the results, the scientific team found the intake of mineral-rich water attenuated the increases in heart rate, plasma triacylglycerols, leptin levels, hepatic catalase activity, and organ weight to body weight ratios that were induced by fructose. Furthermore, it prevented the reduction of hepatic glutathione peroxidase activity and oxidized glutathione content. Therefore, the team concluded that the mineral water seemed to have the potential to counteract the effects of the fructose diet, preventing the onset of Metabolic Syndrome. They suggested regular intake of such water could help improve metabolic and redox health.
A Randomised Controlled Trial published in 2013 in the journal Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases found that The daily use of avocado-soybean unsaponifiable-expanscience (ASU-E) reduces the progression of joint space narrowing in patients with hip osteoarthritis. The conducted trial was a prospective, randomised, double-blind study with parallel groups under placebo control over three years. The participants included symptomatic hip osteoarthritis patients having experienced pain for a minimum of one year and featuring a joint space width (JSW) between 1 and 4 mm in the affected hip. Participants were assigned randomly to a daily intake of 300 mg ASU-E or a placebo. Annual pelvic radiographs in standing position were performed, with the primary focus on the change in JSW at the end of year three. Despite no significant difference in mean JSW loss between the ASU-E group and placebo, fewer progressors (patients with JSW loss of 0.5mm or more) were recorded in the ASU-E group, marking a 20% decrease compared to the placebo group. This indicates a potential therapeutic effect of ASU-E on the structural integrity of hip joints in osteoarthritis patients. However, clinical outcome comparisons did not yield any significant differences between the groups. The safety profile of ASU-E was determined to be excellent.
A Systematic Review published in 2012 in the journal The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that Regular chocolate or cocoa consumption, rich in flavan-3-ols, has been associated with improved insulin resistance and blood vessel function, suggesting potential cardiovascular benefits. The study systematically reviewed 42 randomized controlled trials involving 1297 participants to investigate the impact of chocolate, cocoa, and flavan-3-ols on major cardiovascular disease risk factors. Utilizing a comprehensive search across multiple databases, the researchers conducted meta-analyses, assessing acute and short-term chronic interventions. Results revealed consistent improvements, including reduced insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), enhanced flow-mediated dilatation (FMD), and favorable effects on blood pressure and cholesterol levels. The findings indicate promising cardiovascular benefits associated with chocolate or cocoa consumption. Notably, the study highlights improvements in insulin sensitivity, blood vessel function, and blood pressure, emphasizing the potential positive impact of flavan-3-ols found in these products.
A published in 2010 in the journal Research in Microbiology found that Punicalagin, extracted from the fruit peel of Punica granatum, displays strong antifungal activity against Candida species, especially when combined with fluconazole. Methodology: The study made use of an activity-guided repeated fractionation process on a silica-gel column to isolate a compound from a crude hydro alcoholic extract of Punica granatum fruit peel. Upon analysis, this compound was identified as punicalagin. Its antifungal activity against Candida albicans and Candida parapsilosis was tested, alongside its combined effectiveness with fluconazole. Further tests were conducted using disk-diffusion, checkerboard assays, and time-kill curves to confirm the compound's synergy with fluconazole. Results: Punicalagin exhibited considerable antifungal activity against Candida organisms, including Candida albicans and Candida parapsilosis. When combined with fluconazole, punicalagin resulted in a two-fold decrease in the MIC for fluconazole, indicating a synergistic interaction. Further visual investigations, through scanning and transmission electron microscopy, showed that treated yeast cells exhibited an irregular budding pattern, pseudohyphae, and changes in cell morphology including a thicker cell wall, alterations in the distance between the cell wall and the plasma membrane, and the presence of vacuoles.
Moderation Tools
Topic
Sign In
Users not signed in are limited to viewing the 5 most recent items of content.